TNM Staging and BI-RADS Grading for Breast Cancer
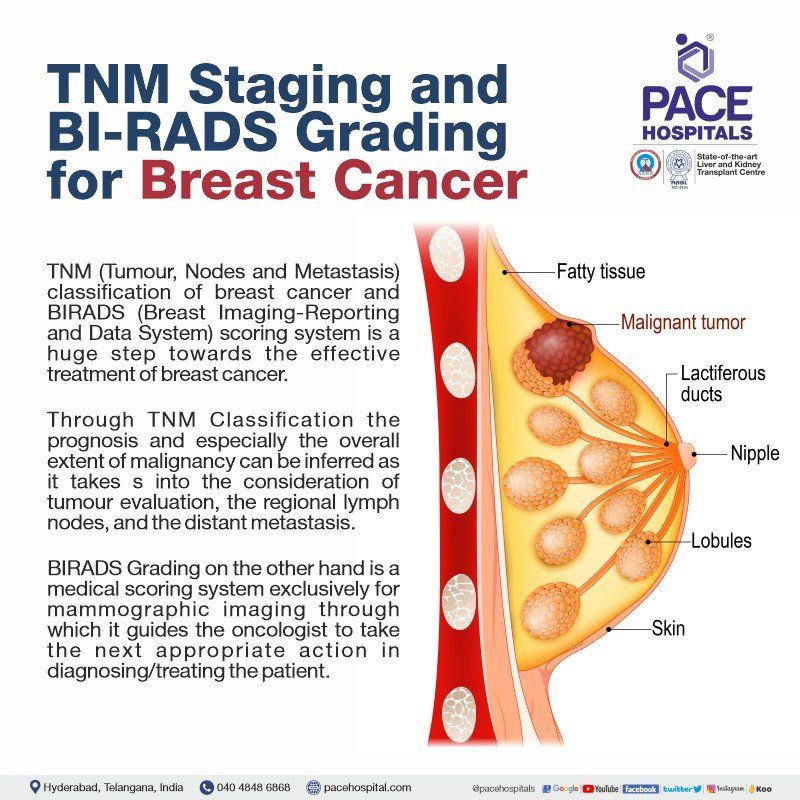
TNM staging of breast cancer conveys the extent of malignancy to the oncologist, and BI-RADS is a tool to standardize mammography findings.
There are already various diagnostic tools to identify the presence of a breast cancer and the extent of its metastasis to other organs. Nevertheless, owing to the complexity of the disease and its myriad ways of diagnostic procedures, there was still a lacuna in the understanding and treatment of breast cancer and its metastasis as a whole. A clear-cut conclusion for the status of breast cancer and the immediate steps to proceed was necessary.
TNM classification of breast cancer and BI-RADS scoring system is a huge step towards the effective treatment of breast cancer.
TNM Staging for Breast Cancer
The TNM system is considered as the gold standard for breast cancer staging. T, N, and M which stand for Tumour, Nodes and Metastasis are given in the form of numbers and letters following those prefixes. An increasing tumour stage index indicates the cancer's progression. The following classifications are based on pathologic (surgical) terms.
T categories for breast cancer
The letters T followed by a number between 0 and 4 indicate the extent to which the primary tumour has spread to the skin and the chest wall. Larger tumours or tumours that have spread to nearby tissues indicate a higher T score.
- TX: Primary tumour cannot be assessed.
- T0: No evidence of primary tumour.
- Tis: Carcinoma in situ (DCIS, or Paget disease of the breast with no associated tumour mass)
- T1 (includes T1a, T1b, and T1c): Tumour is 2 cm (3/4 of an inch) or less across.
- T2: Tumour is more than 2 cm, but not more than 5 cm (2 inches) across.
- T3: Tumour is more than 5 cm across.
- T4 (includes T4a, T4b, T4c, and T4d): Tumour of any size growing into the chest wall or skin. This includes inflammatory breast cancer.
N categories for breast cancer
The letters N and a number between 0 and 3 indicate whether or not breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes close to the breast, and, if it has, how many lymph nodes are affected.
Research indicated that a cancer cell deposit must either contain 200 cells or measure at least 0.2 mm across (less than 1/100 of an inch) in order to be classified as N stage. Cancer metastasis smaller than 0.2 mm (or fewer than 200 cells) does not affect stage but is recorded with special test abbreviations (i+ or mol+).
Micrometastases are defined as cancerous tumours that have spread to an area at least 0.2 mm (or 200 cells) in size but are smaller than 2 mm in size (one mm is about the size of the width of a grain of rice). If no other cancerous tissue has spread, only the tiniest tumours, called micrometastases, are considered. The N stage can and does progress if the cancer has spread to areas larger than 2 mm. Macrometastases is a term used to describe these larger areas, but the term "metastases" is more common.
NX: Nearby lymph nodes cannot be assessed (for example, if they were removed previously).
N0: Cancer has not spread to nearby lymph nodes
- N0(i+) Depicts that the cancer has not spread beyond a 0.2-millimeter diameter area containing fewer than 200 cells. Isolated tumour cells (i+) are detected in either standard stains or a more advanced staining method called immunohistochemistry, but only in very low numbers.
- N0 (mol+) Although cancer cells in underarm lymph nodes are not visually detectable (even with special stains), traces of cancer were detected using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Using a molecular test like RT-PCR, even a small number of cancer cells can be detected.
N1: Sentinel lymph node biopsy reveals cancer has spread to one, two, or three axillary (underarm) lymph nodes, or cancer has spread to internal mammary (near the breast bone) lymph nodes.
- N1mi Lymph nodes under the arm have microscopic cancer metastases. Lymph node cancer metastases are at least 0.2 mm in size, but no more than 2 mm.
- N1a One to three lymph nodes under the arm have been affected by cancer, and at least one lymph node has cancer larger than 2 millimetres in diameter.
- N1b Sentinel lymph node biopsy revealed that cancer had spread to internal mammary lymph nodes on the affected side (it did not cause the lymph nodes to become enlarged).
- N1c Auxiliary lymph nodes 1 & 3 have cancer, and the tumour in at least one of them is at least 2 millimetres in size. By performing a sentinel lymph node biopsy, cancer can also be detected in lymph nodes located in the chest wall on the same side as the primary tumour.
N2: Cancer has spread to 4-9 lymph nodes under the arm, or cancer has enlarged the internal mammary lymph nodes
- N2a Cancer affected 4-9 lymph nodes under the arm, and at least one of these lymph nodes has cancer larger than 2 millimetres in size.
- N2b One or more lymph nodes within the breast have become enlarged due to cancer spread.
N3:
- N3a: As a result of cancer spreading to 10 or more axillary lymph nodes, with at least one lymph node showing cancer growth greater than 2 mm, OR It has been determined that cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the collarbone (infraclavicular nodes), with at least one area of metastasis measuring more than 2 millimetres in size.
- N3b: Internal mammary lymph nodes are enlarged and cancer has spread to at least one axillary lymph node (with at least one area of cancer spread greater than 2 mm). OR on sentinel lymph node biopsy, cancer has spread to the internal mammary lymph nodes and four or more axillary lymph nodes (with at least one area of cancer spread greater than 2 mm).
- N3c:
There is at least one area of cancer spread greater than 2 mm in the supraclavicular nodes on the same side as the cancer.
M categories for breast cancer
If the letter M is followed by a 0 or 1, it means that the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body.
- M0: No distant spread is found on x-rays (or other imaging tests) or by physical exam.
- cM0 (i+): There are a small number of cancer cells in the blood or bone marrow (detectable only with specialised testing), or there are small clusters of cancer cells in lymph nodes elsewhere than the underarm, collarbone, or internal mammary regions (no larger than 0.2 mm).
- M1: Radiological or anatomical evidence of metastasis to distant organs (typically the bones, lungs, brain, or liver) and/or a biopsy demonstrating metastatic disease with a tumour size greater than 0.2 mm.
The combination of the above three factors results in the staging of breast cancer. The staging of breast cancer is categorised as follows.
| Stage | T (Tumour) | N (Nodes) | M (Metastasis) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tis | N0 | M0 |
| I (1) | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| II (2) | T0–T3 | N0–N1 | M0 |
| IIIA (3A) | T0–T3 | N1–N2 | M0 |
| IIIB (3B) | T4 | N0–N2 | M0 |
| IIIC (3C) | Any T | N3 | M0 |
| IV (4) | Any T | Any N | M1 |
Grading System for Breast Cancer
The progression and metastasis of a breast tumour are measured using this grading system. Tumours are classified using a grading system that takes into account both the microscopic appearance of cancer cells, tissue and the rate at which those cells are likely to divide and spread. Low-grade cancer cells resemble normal cells more closely and spread and multiply more slowly than high-grade cancer cells.
With the following three characteristics a pathologist can determine the extent to which cancer cells and tissue are abnormal.
- The extent of tumour tissue encompassing normal breast ducts.
- The size and shape of the nuclei in the tumour cells.
- The number of dividing cells present
A pathologist will look at these three characteristics to determine the extent to which cancer cells and tissue are abnormal. The 3 possible grades are:
- Total score of 3 to 5 - G1 (Low grade or well differentiated).
- Total score of 6 to 7 - G2 (Intermediate grade or moderately differentiated).
- Total score of 8 to 9 - G3 (High grade or poorly differentiated).
BI-RADS
The Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) was developed by the American College of Radiology to standardize mammographic reporting. Through the use of BI-RADS reporting, radiologists are able to provide a conclusive assessment and actionable recommendations for the oncologists in a standardised and transparent manner. It applies to mammography, ultrasound, and MRI.
There are seven assessment categories with four possible recommendations:
(a) additional imaging evaluation,
(b) routine interval screening,
(c) short-term follow-up, and
(d) biopsy
BI-RADS Category, Assessment and Direction
BI-RADS 0: Assessment incomplete - Need additional imaging evaluation (additional mammographic views or ultrasound) and/or For mammography, obtaining previous images not available at the time of reading
BI-RADS 1: Negative - Symmetrical and no masses, architectural distortion, or suspicious calcifications
BI-RADS 2: Benign - 0% probability of malignancy
BI-RADS 3: Probably benign - <2% probability of malignancy, may be a short interval follow-up could be suggested
BI-RADS 4: Suspicious for malignancy - 2-94% probability of malignancy. For mammography and ultrasound, these can be further divided:
- BI-RADS 4A: low suspicion for malignancy (2-9%)
- BI-RADS 4B: moderate suspicion for malignancy (10-49%)
- BI-RADS 4C: high suspicion for malignancy (50-94%), Biopsy to be considered
BI-RADS 5: Highly suggestive of malignancy - >95% probability of malignancy, appropriate action should be taken
BI-RADS 6: Known biopsy-proven malignancy - Appropriate action should be taken; Assure that definitive treatment is completed
The probability of a biopsy positive for malignancy increases from less than 2% for BI-RADS category 3 mammograms to 20-30% for category 4 mammograms, to greater than 95% for category 5 mammograms.




