Pediatric Liver Transplant Hospital in Hyderabad | Surgery & Care
At PACE Hospitals, dept. of Pediatric Hepatology and Liver Transplantation is having team of the best pediatric liver transplant surgeon and pediatric hepatologist in Hyderabad, they are having extensive experience in performing living donor paediatric liver transplant and deceased donor paediatric liver transplant with the high success rate.
Advanced Centre for Paediatric Liver Transplant in India
PACE Hospitals is one of the Advanced Centre for Paediatric Liver Transplant in Hyderabad, Telangana, India backed up with team of the best pediatric liver transplant surgeon, pediatric hepatologist, transplant anesthesiologist and other paramedical staff.
Dept. of Pediatric Hepatology and Liver Transplantation at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad evaluates the donor and recipient and thoroughly before performing the paediatric liver transplant by checking physical fitness, mental health, medical and radiological investigations including all necessary blood test, urine test, MRI or CT Scan to ensure the fitness of the recipient and the living donor.
Media and News Release - Pediatric Liver Transplant at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad
Department of Pediatric Liver Transplantation
Department of Pediatric Liver Transplant at Pace Hospitals, provides extensive and exceptional quality of living donor and deceased donor paediatric liver transplant. The department comprises with a multidisciplinary team of pediatric liver transplant and dedicated liver intensive care units (LICU), pediatric intensive care units (PICU) that help to accomplish complex surgeries with high success rates.
Our team of pediatric liver transplant surgeons, pediatric transplant hepatologists are having extensive experience in performing complex transplants and surgeries, they are highly trained and skilled to perform the surgery with precision and accuracy. Pediatric Liver Transplant Transplant team is backed with state-of-the-art technology, The World’s First Universal Surgical Robotic System, State-of-the-art facility, world-class laser treatment equipment offering comprehensive treatment.
Pace Hospitals is considered as one of the Best Pediatric Liver Transplant Hospital in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Pediatric Liver Specialist team has treated many patients with diseases and conditions related to various types of pediatric liver diseases.
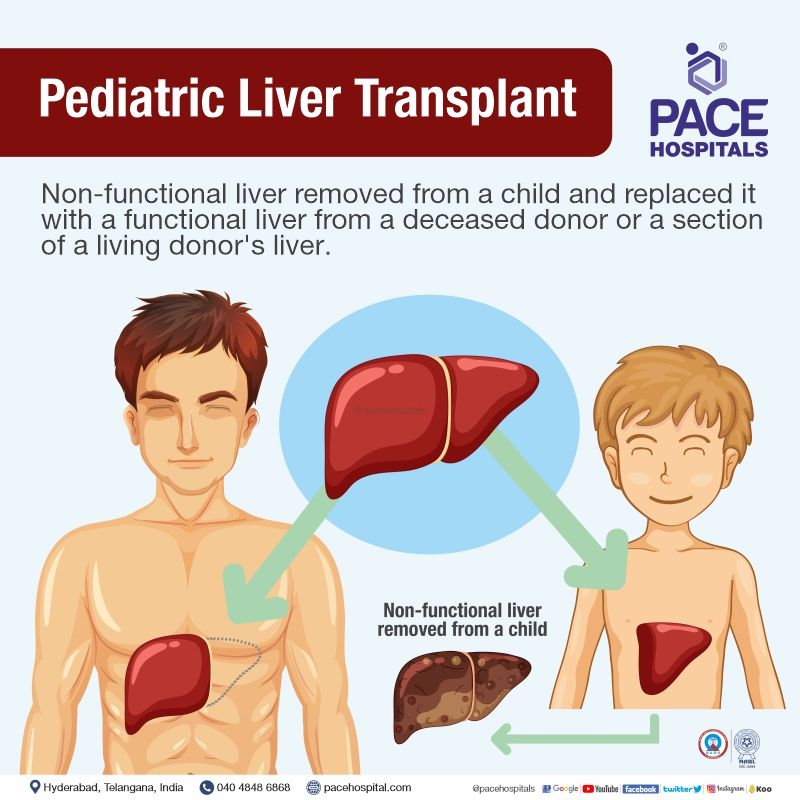
What is Pediatric Liver Transplant?
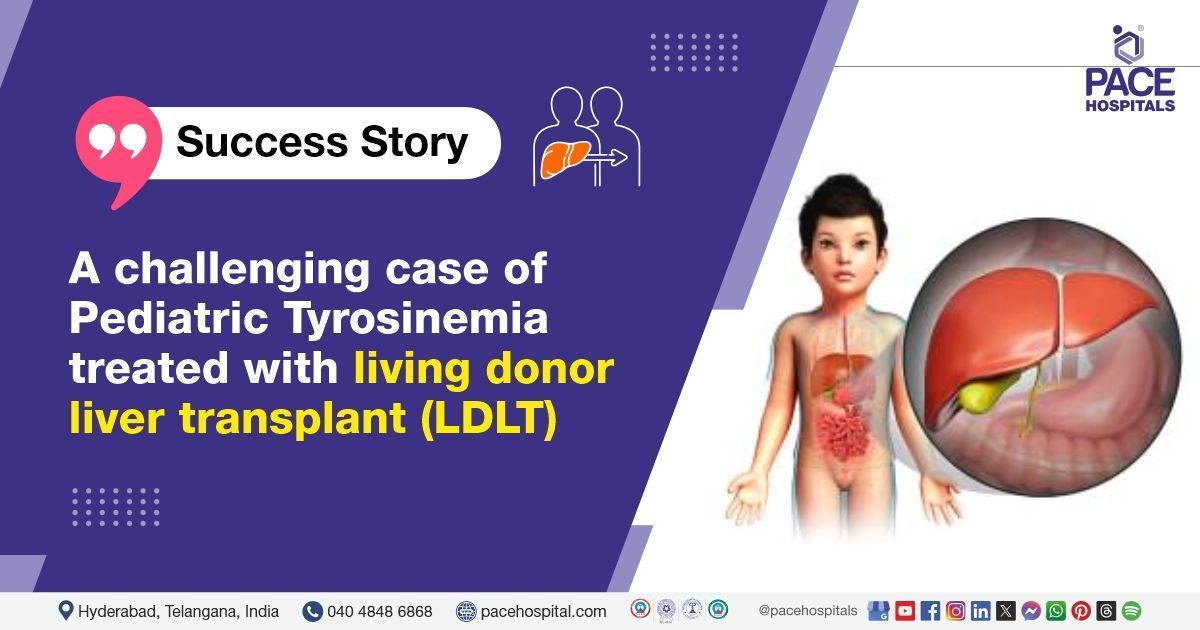
A paediatric liver transplant is a surgery that includes removing a non-functional liver from a child and replacing it with a functional liver from a deceased donor or a section of a living donor's liver to have proper liver function. Paediatric Liver transplant has proven to be an effective treatment option in treating children with acute and end-stage liver disease, providing an opportunity for a long and healthy life.
The majority of paediatric liver transplant surgery is from a deceased donor (deceased liver transplant), which involves an adult or child who has suffered severe injuries or diseases, is confirmed to be brain dead, and has been given permission to donate the liver by their family. On the other side, a close relative of the child or patient can donate a part of their liver (living donor liver transplant) to the patient. However, due to the presence of a hyperplastic response (increased cell number) in the human liver, the liver grows back to its normal position both in a child (if only half is inserted) and in a live donor.
Indications for liver transplantation in pediatrics
The most common cause of pediatric liver transplant are as follows:
- Extrahepatic cholestasis
- Intra-hepatic cholestasis
- Metabolic diseases
- Acute liver failure
- Others
Extrahepatic cholestasis
It is also called obstructive cholestasis, which occurs due to blockage of bile flow outside the liver and the extrahepatic bile ducts.
Intra-hepatic cholestasis
It is also known as functional cholestasis, which occurs due to the presence of a disease in the liver parenchyma cells and/or in the intrahepatic bile ducts.
- Alagille syndrome
- Non-syndromic paucity of intrahepatic bile ducts
- Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC)
- Sclerosing cholangitis
Metabolic diseases
These are a group of metabolic disorders that affects liver functions such as absorption, storage, transport, and breakdown.
- Wilson’s disease
- Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome
- Congenital impairment of bile acid metabolism
- Tyrosinemia
- Urea cycle disorders
- Organic acidemia
- Defect in acid lipase
- Type 1 oxaluria
- Carbohydrate metabolism disorders
Acute liver failure
It is defined as a rapid decline in liver function causing jaundice initial stage over the course of a few days to a few weeks in children.
Others:
These generally include primary liver tumours and cystic fibrosis.
Contraindications for liver transplant in paediatrics
Though liver transplant surgery is a major boon for children with end-stage liver disorder, it is not advised for everyone. Patients with the following conditions are contraindicated for a paediatric liver transplant:
- Non-resectable extrahepatic malignant tumour
- Concomitant end-stage organ failure that cannot be managed with a combined transplant
- Uncontrolled systemic infection
- Irreversible serious neurological damage
- Type C Niemann-Pick disease
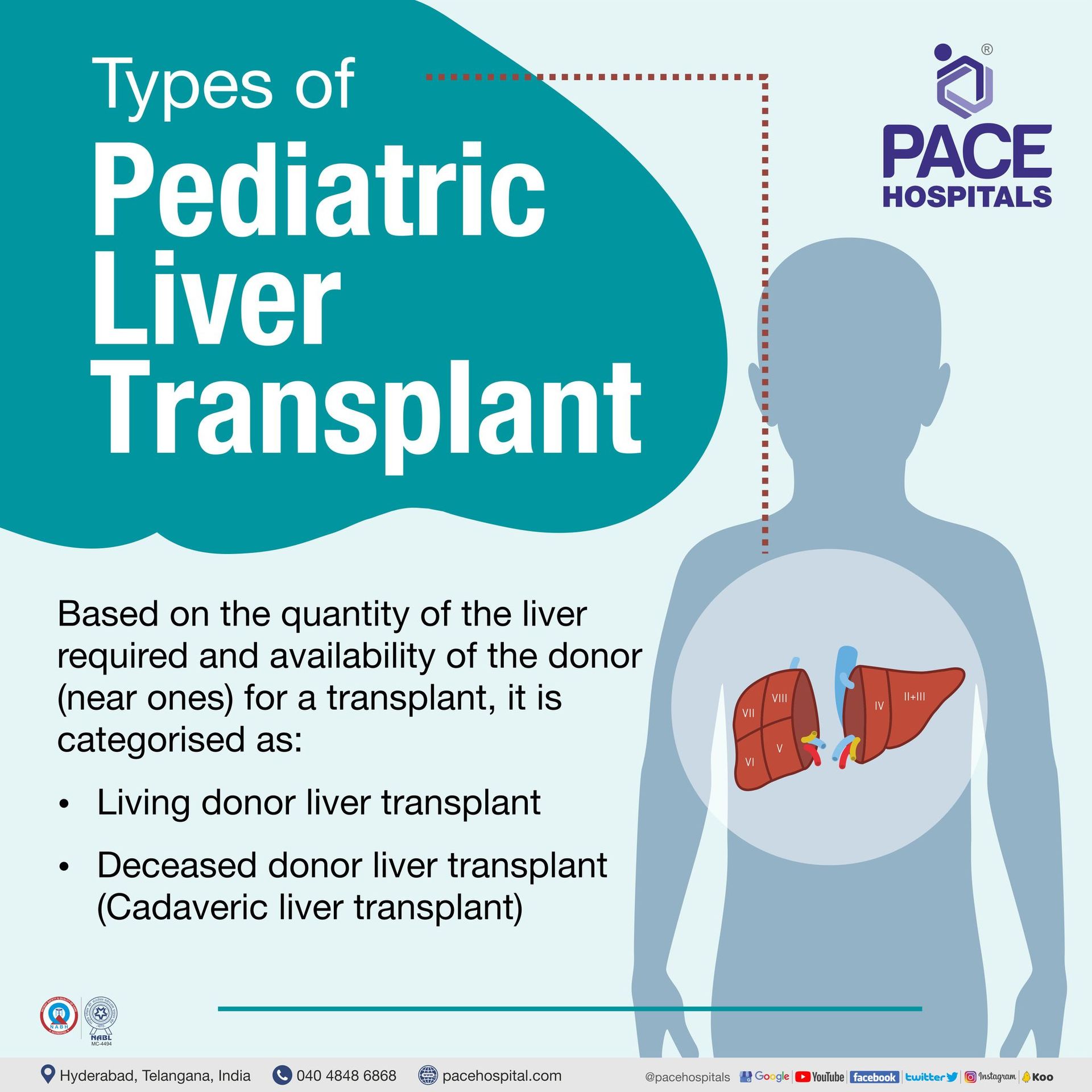
Type of paediatrics liver transplant
Based on the quantity of the liver and availability of the donor (near ones) to get a transplant, they are of the following types:
- Living donor liver transplant
- Deceased donor liver transplant (Cadaveric Liver Transplant)
Living donor liver transplant
Livining donor pediatric liver transplant normally involves a portion of the liver being transplanted from a living donor, usually a close relative, where an incision is made on the donor's abdomen, and a portion of the liver is removed based on the need (left or right). Post removal, the bile duct and major vessels of the liver, such as the portal vein, hepatic artery, and hepatic vein, will be cauterised (closed) in the donor.
The infant or newborn will undergo an abdominal incision around the liver, where the old liver will be carefully removed by detaching all the major vessels and bile ducts. The obtained part of the liver (from a live donor) will be replaced with the diseased liver, and all the patient’s main vessels will be attached to the donated part. The bile duct is linked to the child's small intestine. The child's replacement liver develops over time.
Deceased donor liver transplant
Deceased donor pediatric liver transplant involves a segment or whole liver transplant from a deceased or brain-dead patient, which is generally done when there is no availability of donors from near relatives. Based on the patient's condition and the requirement, the deceased donor's liver transplant can be of the following:
- Full graft liver transplant or Whole liver transplant
- Segmental liver transplant
- Split liver transplant
- Reduced-size liver transplant
Pre-procedure evaluations
Medical Evaluation: The primary goal is to find suitable candidates for transplantation and develop a pretransplant treatment strategy that will maximise survival before and after transplantation.
Identifying the right child for a liver transplant involves:
- The need of a transplant should be identified and confirmed
- Evaluating the primary disease severity
- Confirming the unavailability or the rejection of alternative treatments
- Absence of absolute contraindications to performing a transplantation
- Ruling out the presence of cardiopulmonary disease and vascular abnormalities that affect peri- and posttransplant survival
The pre-transplantation treatment plan includes:
- Evaluating a pediatric liver transplant vaccine status and providing immunisations
- Nutrition therapy for promoting optimal development, which may involve nasogastric tube feedings or complete parenteral nutrition (TPN).
Donor Considerations
The selection of an appropriate liver donor plays a crucial role in having immediate and long-term success of the transplant. The following are the suitable ones for paediatric recipients.
- Living or brain-dead donors should ideally be young (less than 45 years of age)
- Healthy and non-obese
- Should not be a drug user
- No evidence of liver disease
- Free of high-risk behaviour
Before a pediatric liver transplant surgery
The hepatologist would like to know the patient's (child's) medical history from their parents. The liver transplant surgeon also explains the entire process of the liver transplant, including the donor characteristics requirement or application for a donor, post-surgical complications, risk involved and recovery time in the transplantation.
The transplant team will request the following test to confirm the status of the child to be healthy enough for a transplant and to take post-surgery medications such as:
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests such as abdominal ultrasound or CT scan
- Biopsy if required
After having a positive sign of a transplant, the child’s name will be entered into the national organ (liver) waiting list if there are no nearby ones (donors) available to donate for living donor transplantation. The need and urgency of the transplant will be determined by the Pediatric End-Stage Liver Disease (PELD) score. More the PELD score, the faster the child will have the probability to allocate an organ.
During pediatric liver transplant
The donor and patient (DAP) will be provided with a surgical gown to change the dress. An intravenous line will be inserted into the DAP arm or hand, through which medications will be administered.
The DAP will be given general anaesthesia to make them sleep, and the anaesthesiologist will place a tube into the child's lungs that will be connected to a ventilator to breathe easily. During surgery, the DAP vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and blood oxygen level) will be monitored.
A sterile solution will be used to clean the skin above the surgery site, and the hepato-surgeon will make an incision in DAP’s abdomen. The associated arteries and veins will be constricted. Depending on the availability of a donor in the family, a liver transplant is of two types.
During cadaver donor liver transplant
The liver transplant surgeon removes the damaged liver through a hepatectomy procedure from the child’s body and replaces it with a liver obtained from a deceased donor (as required). The patient will be transferred to the intensive care unit once the surgery is complete.
Depending on the requirement, the transplant team performs either of the transplant procedures to obtain a liver from a deceased patient and replace it with the recipient's damaged liver.
- Split liver transplant
- Segmental liver transplant
- Full graft liver transplant
- Reduced-size liver transplant
During living donor liver transplant
After a thorough evaluation, the transplant team performs a hepatectomy surgery (also known as a liver resection) on a living donor. A part of a healthy liver (as required) will be removed and replaced with the recipient's damaged liver.
Once the donor’s liver is implanted in its position (child's body) and all the major vessels are connected, the surgical clamps will be removed to have blood flow. The surgeon will examine the site for any signs of bleeding at the site of stitches.
The bile duct will be connected, and the incision will be closed with the help of sutures, followed by placing a drain to reduce swelling.
Post pediatric liver transplant care
- After transplantation, both the recipient and donor will be shifted to the Intensive care unit, where the vital signs are being monitored continuously.
- The reintroduction of oral intake will be resumed within a week of surgery. The duration of the hospitalisation depends on the child's condition or recovery and typically last between two and three weeks. The hepatologist might request for few blood tests to confirm the functionality of the new liver, and it also helps in prescribing the medication doses.
- The patient (child/recipient) will be prescribed immunosuppressive therapy or anti-rejection medicines to prevent transplant rejections by reducing the child's immune response.
- The transplant team provides proper follow-up care and medication instructions to both donor (living donor) and the patient or parent's caretaker (parents) before they get discharged. Patients and their families will be instructed to stick with a rehabilitation programme that includes physical activity, healthy eating and to adhere to the prescribed immunosuppressants and other drugs.
Pediatric liver transplant complications
Despite the fact that neonates appear to have higher immunotolerance to donated organs, the combination of their underdeveloped immune system and usage of immunosuppressive drugs puts them at a higher risk for post-surgical infection.
In addition to this, paediatrics might have the following complications, but not limited to.
- Vascular problems such as hepatic artery and portal vein thrombosis
- Biliary complications such as bile leak
- Acute transplant rejections
- Osteoporosis
- Renal (kidney) and CNS toxicity
- Cardiovascular (heart) problems
- Psychosocial (mental) stress
Liver Transplant Patient Success Story
Transplant team at PACE Hospitals has successfully performed liver transplantation for a child with rare genetic disorder “Alagille Syndrome” in a very frail 8-year-old child.
Frequently asked questions:
Is pediatric liver transplant painful?
After a pediatric liver transplant operation, the patient may experience some pain, but it is unlikely to be as severe as after other abdominal surgeries. During surgery, nerves are severed, which results in numbness close to the incision. In accordance with the patient's specific conditions, the doctor might suggest appropriate medications.
Is a pediatric liver transplant permanent solution?
Patients (child) with end stage liver disease where liver no longer perform its function and cant repair itself, Pediatric Liver transplant surgery is the only solution. Till the patients dont get the donor medications can help in reliving symptoms of cirrhosis.
Does liver regenerate after a pediatric liver transplant?
The ability of the liver to regenerate in a situation of partial removal from the donor body is what makes it special. When a portion of the liver is transplanted, regeneration is also visible in the recipient's body. Within one week and six to eight weeks, respectively, the functional restoration and regeneration are visible.
Given that the liver serves as a key organ for detoxification and that toxins can harm it, the ability of the liver to regenerate is a sensible evolutionary adaptation. When the liver is damaged or removed in part, the regeneration process also involves mature liver cells—not stem cells.
Can a child donate a liver to a parent?
Yes, a child can donate a part of their liver to his/her parent. As per the transplant of the human organ (THO) act 2011, a near relative (son, daughter, mother, father, brother, sister, grandmother, grandfather, grandson and granddaughter) of the patient can be eligible for a living donor liver transplant.
Can I give my daughter part of my liver?
Yes, a mother can donate part of her liver to her daughter as she is a near relation to the patient. However, the mother should be eligible as a donor for a living donor liver transplantation. The following conditions can apply.
- The age should be less than 45 years of age
- Healthy weight with no associated cardiac and liver diseases
- Should not drink or smoke
- Should not be a drug user
Who gets a paediatric liver transplant first?
Patients waiting for a liver transplant are prioritised according to the severity of their condition. The severity of the children will be estimated by the PELD score. The higher the PELD score, the sooner the patient (child) will be able to receive the organ.
When was the first liver transplant performed?
The first pediatric liver transplant was performed by Thomas Starzl, MD, in 1963 on a 2-year-old kid with biliary atresia. However, the patient died during the surgery due to an uncontrolled haemorrhage.
Is pediatric liver transplant possible?
Yes, pediatric liver transplant is possible. Replacement of a damaged or diseased liver with a healthy liver from a donor requires extensive surgery. It frequently manifests in those whose livers are unable to function normally (mostly those with advanced liver disease or liver failure). Illness, or infections can cause the liver to steadily degrade, leading to cirrhosis, necrosis (death of tissue), and liver failure.
India has seen an increase in adult and pediatric liver transplant surgery since 1998. Over 1800 liver transplants per year have been performed up to this point.
Who all are involved in Pediatric Liver Transplantation?
Paedictric Liver transplant is a process where a team of medical and surgical staff are involved to evaluate the donor and recipient. The Liver Transplant Team at PACE Hospitals is trained specially in fulfilling the needs of liver transplant patients. The Liver Transplant Team members include:
- Liver specialist (transplant hepatologist)
- Transplant surgeons
- Pediatrician, Pediatric Hepatologist
- Transplant coordinator
- Intensivist, a critical care physician
- Radiologist, diagnosing injuries and diseases
- Psychiatrists who can help you cope with the psychological effects of the transplant
- Anesthesiologist, to discuss potential anesthesia risks
- Nutritionist, who can evaluate your current nutritional status
- Clinical Pharmacist, to review your medications for potential drug interactions
Can you live a normal life after a liver transplant?
Yes. It is possible to lead a normal live with a few precautions. After a liver transplant, most patients may return to most of their usual activities and enjoy a decent quality of life. Recovery might take up to a year, although they can normally start ramping up your activities after a few weeks without forgetting the regular follow-up appointments with the doctor. Among the therapeutic regimen, immunosuppressants are primarily prescribed.
A well-balanced healthy diet, avoiding alcohol indulgence and a routine exercise can help enhance the recovery process.
Is pediatric liver transplant successful in India?
Yes. Pediatric Liver transplant surgeries in India are as successful as anywhere else in the world. Various studies demonstrated 86% to 92% survival rate in Indian pediatric liver transplant surgeries in patients with acute liver failure.
Which are the Top 10 Pediatric Liver Transplant Hospitals in Hyderabad, India?
PACE hospitals is among the Top 10 Pediatric Liver Transplant Hospitals in Hyderabad, India, catering Living donor liver transplant and Deceased donor liver transplant (Cadaveric liver transplant) with a high success rate and 24x7 hassle-free comprehensive pre- and post-transplant support.
Is pediatric liver transplant safe for donor?
Yes. Pediatric Liver transplant is as safe procedure for donor as the liver can regenerate within 45 to 60 days. There are few possible surgical complications, which is common with any surgical procedure.
Does a pediatric liver transplant have to match?
To donate a part of the liver to a child who needs a pediatric liver transplant, both of them must be a good match. This is the reason the gastroenterologists or liver transplant doctors make sure that various vectors of surgery such as blood type, body size, and age etc. are evenly matched to that the transplant goes well for both – the donor and the recipient.
How long do you stay after a pediatric liver transplant in the hospital?
The living donor and recipient's condition determines the length of the hospital stay. In most cases, living donor will be hospitalised for 7 to 10 days after a living-donor pediatric liver transplant, whereas recipient or patients who got the healthy liver will be hospitalised for 15 to 20 days for monitoring and faster recovery. Then Afterward, patient generally recover at home and return to work or school after complete recovery.
Who can donate liver for transplant?
All living donors must complete in-person donor evaluation, which includes blood tests and medical imaging. In general, donor need to fulfil these conditions:
- In case of adult recipient, donor age can be in between 18 and 55 years whereas in case of children require liver, donor age can be up to 60 years.
- Donor should be healthy, physically and mentally strong enough for surgery, recovery and psychological impact of organ donation and its possible risks.
- Donor should not have any pre-existing medical conditions, specially related to clotting and bleeding.
- In case of smoking habit, donor should quit smoking.
What is pediatric liver transplant recovery time?
It is expected to have 90 to 180 days of recovery time after a successful pediatric liver transplant surgery. A child may be able to resume normal activities after a few months after the transplantation. The child will need to follow up with their doctors for the rest of their life. However, frequent visits might reduce after a couple of years.
What is the pediatric liver transplant success rate in India?
Pediatric Liver transplant is a successful surgery where a transplant surgeon replaces a patient’s damaged or partially damaged liver with a whole or partially healthy liver from another person called a donor.
Pediatric Liver transplant success rate in India is approximately 91% based on the current data, where pediatric liver transplant survival rate varies from 98% to 75% person to person.
Which is the best pediatric liver transplant hospital in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals is the one of the best pediatric liver transplant hospital in Hyderabad, India, backed up by a multidisciplinary Adult and Pediatric Liver Transplant Team and dedicated Liver ICU (intensive care units) and equipped with World’s 1st Universal Surgical Robotic System, the latest advanced laser treatment equipment, state-of-the-art facility and modern technology.
Is pediatric liver transplant covered by insurance in India?
Some of the health insurance companies cover liver transplant in India under the Transplantation of Human Organs Act 1994 and according to many insurance providers organ transplantation coverage starts after 3 to 4 years of the successful mediclaim policy completion.
It is advised to the patients to cross-check the cashless insurance coverage directly from the insurance provider. In India, most of the health insurance companies don't cover the pre- and post-hospitalization costs of the donor, pre- and post-surgery complications.
How much does pediatric liver transplant cost in India?
The average cost of a Pediatric Liver Transplant in India is approximately Rs. 26,45,000 (INR twenty-six lakh forty-five thousand). However, Pediatric Liver Transplant cost in India ranges vary from Rs. 20,50,000 to Rs. 28,25,000 (INR twenty lakh fifty thousand to twenty-eight twenty-five thousand) and also depends upon multiple factors and differs from case to case. However, cost may vary depending upon the different hospitals in different cities.
What is the cost of pediatric liver transplant in Hyderabad?
Pediatric Liver Transplant cost in Hyderabad ranges vary from Rs. 18,50,000 to Rs. 26,45,000 (INR eighteen lakh fifty thousands to twenty-six lakh forty-five thousands). However, cost of paediatric liver transplant in Hyderabad depends upon the multiple factors such as patient condition, age, associated conditions, hospital, room selection and insurance or corporate approvals for cashless facility.