Ear Wax Removal in Hyderabad, India
PACE Hospitals is a leading healthcare facility in Hyderabad, India, renowned for its expert care in ear wax removal. Our team of experienced ENT specialists is dedicated to providing safe and effective ear wax removal treatments tailored to each patient's needs. Utilizing state-of-the-art techniques and equipment, we ensure a comfortable and precise removal process, helping to maintain optimal ear health for patients of all ages.
Request an Appointment for Ear Wax Removal
Ear wax removal - appointment
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Ear Wax Removal?
8400+ Patients treated for ear wax buildup
Team of the Best ENT Doctor in Hyderabad
Precision Treatment with 99.9% success rate
All insurance accepted with No-cost EMI option
PACE Hospitals in Hyderabad, India offers professional and safe ear wax removal services, individuals of all ages receive exceptional care for ear wax removal, with a focus on comfort and precision. Our cutting-edge facilities and advanced diagnostic tools enable thorough assessment and effective removal of ear wax. Our dedicated team of ENT specialists collaborates with each patient to create a tailored treatment plan that suits their unique requirements.
Ear wax removal treatments at PACE Hospitals encompass a variety of methods, including gentle irrigation, microsuction, and manual extraction techniques. Our highly trained team of experienced ENT specialists and audiologists use the latest techniques and technology to ensure effective and comfortable ear wax removal and ensure each procedure is conducted with meticulous attention to detail, prioritizing patient comfort and safety. Whether you're experiencing minor discomfort or a significant blockage, PACE Hospitals is committed to providing thorough and compassionate care to restore your ear health.
Diagnosis of Ear Wax
An ENT specialist performs simple diagnostic tests to examine the ear canal and tympanic membrane to evaluate the extent and nature of the excess ear wax, which includes:
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Visual examination
- Otoscope
- Oto-microscopy
Medical history: Prior to physical examination of the external auditory canal (EAC), it is suggested that the patient talk with the healthcare professional about a detailed medical history and medication history and provide an explanation of any procedure(s) performed.
Physical examination: A healthcare professional can look into the ear canal and confirm that a plug of earwax has formed containing black/dark brown/yellow /dark orange chunky materials, partially or totally obstructing the external ear canal.
- Visual examination: During the process, the healthcare professional asks the patient to gently pull the tragus anteriorly with a finger to open the external ear canal (External auditory canal-EAC); simultaneously, the examiner gently pulls the pinna backwards and upward to examine the EAC with a light source (e.g., pen light, torchlight, cellular phone light).
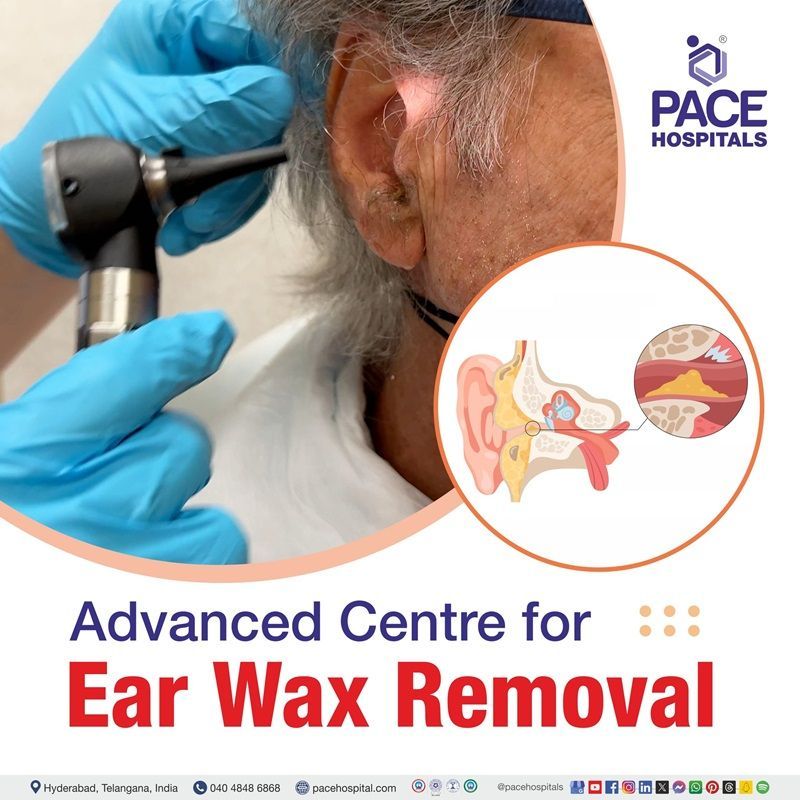
Otoscope: The diagnosis of ear wax blockage is made by direct visualization with an otoscope. This essential tool shines a beam of light to visualize and examine the eardrum and ear canal condition to detect ear wax blockage and reveal symptoms such as hearing loss, feeling of fullness in the ear, itching, etc. Otolaryngologists place the tip of the otoscope in the patient's ear, shine a light, and rotate the otoscope in all directions. Sometimes, they may use a pneumatic otoscope to see the fluid build-up and infection behind the eardrum.
Oto-microscopy: Otomicroscopy is the examination of the external auditory canal (EAC) and tympanic membrane (TM) using a surgical microscope. For purposes of this discussion, it is performed in an awake patient. For diagnostic purposes, otomicroscopy provides superior illumination and magnification compared to non-magnified otoscopy and gives the clinician freedom of both hands to perform therapeutic intervention.
✅Considerations of ENT specialist (otolaryngologist) before opting earwax removal
ENT (Ear, Nose, Throat) doctors (otolaryngologist’s) or audiologists considers multiple factors before opting to remove ear wax:
- Patient Age and Health: Considers the patient's age (child, adult, elderly) and overall health status, as well as any factors that may affect treatment tolerance or efficacy. For example, giving general anaesthesia is considered in the case of kids or mentally disabled patients as they cannot cooperate.
- Assessment of Symptoms: When patients have a cerumen impaction (earwax blockage) and develop new symptoms such as ear pain, drainage from the ear, fever, and hearing loss, and if the earwax is dry and has been in the ear canal for a long time, it can stick to the ear canal wall, and in some cases, a layer of skin can be removed along with the wax. These are frequently taken into consideration.
- Type of Ear Wax: The type of ear wax (cerumen) and consistency influence the removal method. Soft wax may respond efficiently to irrigation, while dry, hard or impacted wax may require manual removal.
- Underlying Conditions: Evaluates the underlying conditions that may influence the method of wax removal.
- Patient History: ENT doctors review a person's medical history to determine whether the patient had any previous infections, underlying conditions, allergies, or surgeries that may affect the treatment and to decide which treatment is best.
- Risk and benefits: ENT specialists consider the risks associated with different treatment methods, such as irrigation, suction, or manual removal. Risks such as ear canal injury or infection, and weigh these against the benefits of improved hearing and symptom relief.
- Expertise and Equipment: Foreign bodies should only be removed by a specialist using appropriate equipment, such as fine instruments, a headlight, or an oto-microscope. This is especially important for cases involving foreign bodies located in the lateral ear canal or for soft, easily grasped materials.
- Patient Preference: ENT specialist considers the patient's preferences while ensuring safe and effective removal.
Best ENT Specialist in Hyderabad, India
✅Treatment for Paediatrics and Children
- If the kid has no symptoms, treatment may not be needed. Over time, the problem may go away on its own. However, if the kid is having ear pain, itchiness, discomfort or any other symptoms, it is recommended to consult a paediatrician or ENT doctor (otolaryngologist).
- Never insert anything into a child's ears to remove wax (particularly cotton buds, cotton swabs, ear candles) as this can:
- Cause the wax to be moved by pushing it further into the ear,
- Damages the wall of the ear canal, and causes inflammation
- Perforate (tear) the eardrum
- Use an ear dropper to apply drops (only those approved by a health care professional) of mineral oil, baby oil, or glycerin to the ear.
- Check with the paediatrician first before using a bulb syringe.
Treatments that should only be done by a healthcare professional include:
- Ear irrigation (Syringing): Removing the wax by pumping the warm water into the ear canal using gentle pressure.
- Microsuction: Removing the wax via suction with a tiny probe
- Manual removal: Removing the earwax with small, special tools.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Ear Wax Removal
Should I use cotton swabs?
No. Avoid inserting cotton swabs or cotton buds, ear candles, match sticks or any objects because these small items are pushed into your ear canal, which can move the earwax deeper and cause it to form a plug, leading to ear wax problems even worse.
Which Is the best hospital for Ear Wax Removal in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad is regarded as one of the most reliable centres for ENT and otology care, including safe and effective ear wax removal.
Our experienced ENT specialists use advanced diagnostic tools and gentle, non-traumatic removal methods such as microsuction and endoscopic visualization to ensure complete wax clearance without discomfort.
With modern ENT suites, trained otology specialists, and a patient-friendly environment, PACE Hospitals ensures safe, hygienic, and painless ear wax removal — supported by cashless facility options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance processing for eligible patients.
What happens if earwax is not removed?
Normal earwax can help protect, lubricate, and clean the ear canal. However, excess earwax can block sound from entering the ear and cause various symptoms, including difficulty hearing, itchiness, dizziness, a feeling of fullness or pressure, and/or ringing in the ears (known as tinnitus). Sometimes, untreated ear wax leads to infection, causing drainage, which increases the risk of damage to the eardrum.
Is it necessary to treat your ears to prevent the accumulation of earwax?
Prevention is best for certain groups of people, yet not everyone needs it. The elderly, individuals with hearing aids, and those with a history of excessive earwax may be helped by prevention. Discussing this with an audiologist or ENT doctor (otolaryngologist) will help determine whether anything should be required based on the person's condition.
What are the safest ways to clean the ear wax?
Some of the safest ways to keep ears clean or soften earwax to help it come out of its own are using a damp washcloth and washing the ear's outer parts. Earwax softening drops can also help with earwax buildup when bathing or showering. However, using cerumen-softening agents (ear wax softening agents) is not recommended for everybody, especially if the person has a history of ear surgery. Hence, it is recommended that an ENT doctor (otolaryngologist) be consulted before proceeding with ear drops.
How much does it cost for ear wax removal in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of ear wax removal typically ranges from ₹450 to ₹2,200 and above (approximately US $5 – US $27), depending on:
- Whether wax is soft or hard/impacted
- Unilateral or bilateral removal
- Technique used (manual, irrigation, microsuction)
- ENT specialist expertise
- Need for ear examination, cleaning solutions, or follow-up
- Additional ENT procedures if required
For simple manual cleaning, costs fall at the lower end; for impacted wax requiring microsuction, costs are toward the higher end.
After an ENT evaluation and ear examination, our specialists provide a personalised treatment plan and a transparent cost estimate based on your condition.
How to remove baby earwax?
It is essential to clean the earwax from the baby's ear canal safely. A gentle approach is required to prevent damage to the delicate ear canal, which includes using a clean towel and soft cotton washcloth while bathing the baby, which helps remove the loosened wax, and a few drops of warm water or cellulolytic agents (recommended by a healthcare professional) can soften it. However, physicians strongly discourage inserting cotton swabs, paper clips or other objects into the ear canal as it pushes the wax deeper into the ear or causes damage. If concerns about excessive earwax or the baby shows signs of discomfort, it is advisable to consult a paediatrician.
What is earwax?
Earwax, also medically known as cerumen, is a natural substance that cleans, protects, and lubricates the ear canal .It is produced by special wax-forming ceruminous glands located in the skin of the outer one-third of the ear canal. Due to its acidic nature, earwax provides natural protection against infections and avoids dirt, dust, or foreign bodies entering the ear. The wax is gradually moved towards the opening of the ear canal, where it peels (flakes) off or is washed off during bathe by the skin's self-cleaning mechanism and the action of muscles used in chewing and talking.
What factors affect ear wax production?
Conditions such as eczema produce a lot of dry, flaky skin and cause hard earwax. As a person ages, there will be changes in the consistency of the glandular secretions, causing difficulty in travelling through the ear canal. Buildup of wax is more likely to develop in those who have narrow ear canals, in those who work in dusty environments and those who need to use earplugs to protect their hearing at work. Overproduction of earwax in case of picking more debris or sitting in the ear canal for a long time can get dry and hard; it is more likely to cause an obstruction or blockage causing symptoms such as hearing loss, ear pain itching in the ear and other problems.
What will happen at my ear wax removal appointment?
If anyone suspects earwax buildup, the audiologist or ENT doctor (otolaryngologist) may begin by looking into the ears with an otoscope. Earwax removal can be performed in several different ways. An audiologist or ENT doctor (otolaryngologist) may choose a method or type of instrumentation based on the amount and texture of the earwax, the person's age, and the presence and location of wax or discharge.
How to remove ear wax at home?
Audiologists and other medical professionals (paediatricians, ENT doctors) strongly discourage removing earwax at home using certain tools, including cotton swabs, cotton buds, matchsticks, curettes, picks, and ear candles. Incorrect usage of these tools can harm the ear canal, burn the skin, and puncture the eardrums.
What symptoms could be caused by excessive earwax?
Common complaints related to earwax buildup include hearing problems, earache, feeling of fullness in the ear, dizziness, and itchiness in the ear. Other issues include discharge, odour, cough, or ear pain. If left untreated, excessive earwax may cause earwax impaction symptoms to worsen. Therefore, it is recommended to consult an ENT doctor if anyone notices the above-mentioned symptoms.
Who do I see for earwax removal?
Earwax removal is usually performed by a trained and experienced healthcare professional, including an ENT specialist, audiologist, otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat doctor), or general physician for adults and paediatricians or specialised paediatric ENTs for children.
Does it hurt to remove earwax?
Earwax removal is usually performed in a physician's clinic or hospital. During the process, a person might feel a little bit of discomfort, but it is not painful. However, in the case of children or mentally disabled patients who are not cooperative or cannot sit properly, a healthcare professional injects general anaesthesia.
If earwax is removed, will my hearing get better?
If excess ear wax almost completely blocks the ear canal, removing the wax can help restore hearing. However, the extent of improvement relies on different factors, such as underlying conditions that affect hearing and the amount of earwax removed. Therefore, it is necessary to consult and discuss with healthcare professionals for appropriate evaluation and treatment to ensure safe and effective management of earwax-related hearing issues.
What factors affect earwax production?
Cleaning the ear using objects such as cotton-tipped swabs and pins can push the wax more inside, causing problems. Ear picking and its resultant ear infection, foreign body impaction, abnormalities of the external auditory canal, and excessive earwax production due to anxiety, fear, stress, and ageing are all significant factors in earwax impactions. The knowledge of the risk factors could greatly reduce earwax impaction and its associated complications.
What is the cost of ear wax removal in Hyderabad, India?
Ear wax removal cost in Hyderabad, India can range from ₹ 800 to ₹ 2,500 (INR eight hundred to two thousand five hundred) per session, depending on the hospital/clinic and the method used. The cost of ear wax cleaning in India can vary depending on several factors, including the patient condition, age, associated conditions, hospital, the complexity of the procedure.





