Best Orthopedic Hospital in Hyderabad, India | Expert Ortho & Spine Care
PACE Hospitals is one of the Best Orthopedic Hospital in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, providing holistic and patient centric orthopedic treatment. The team of experienced and skilled orthopedic doctor, orthopedic surgeon and sports medicine doctor have vast expertise in managing all kind of deformities of bone, joints, muscles, ligament and tendons, including:
- Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoporosis
- Bone tumours, Bone infections (Osteomyelitis)
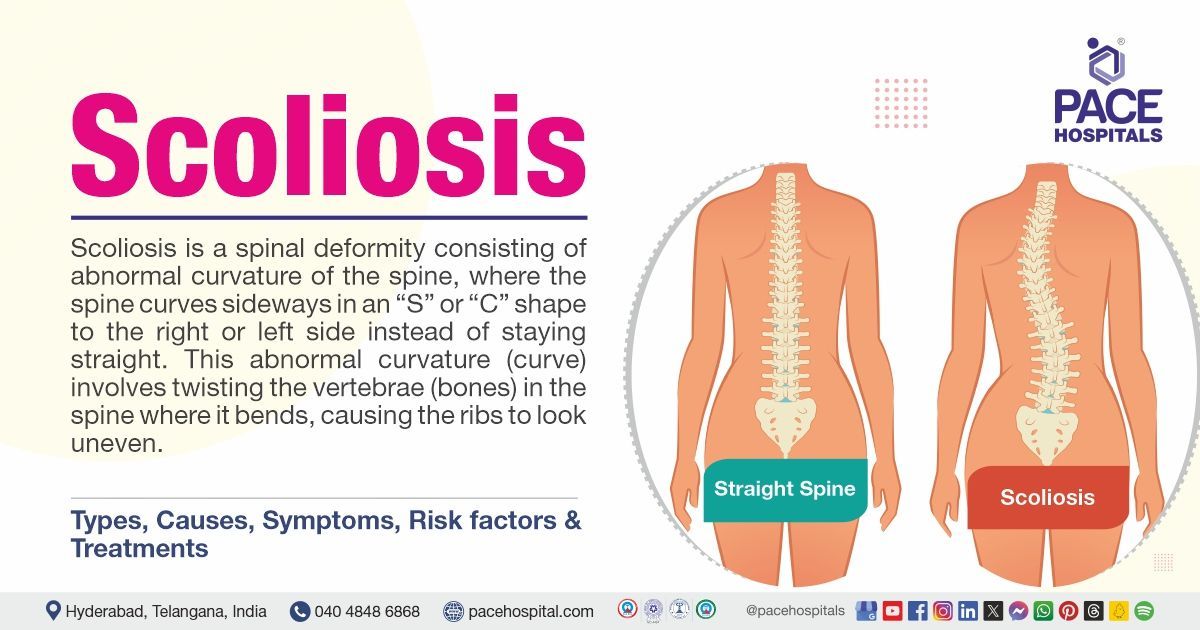
- Scoliosis, Spinal stenosis, Sciatica, Spondylolisthesis
- Tendonitis, Bursitis
- Frozen shoulder, Shoulder dislocation, Hip dysplasia
- Plantar fasciitis, Ankle sprains, Flat feet, Achilles tendon rupture
- Clubfoot, Leg length discrepancy, Growth plate injuries
- Runner's knee, Tennis elbow, Stress fractures, Meniscal tears
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL), Medial Collaterall Ligament (MCL)
- Compound fractures, Multiple fractures, Crush injuries, Pelvic fractures, Traumatic amputations
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Orthopedic Treatments?
Comprehensive Orthopaedic Care
Providing treatments to wide range of musculoskeletal disorder including deformities in the bone, joint, muscles, ligament, tendons and sports injuries.
Advanced State-of-the-art Facility
Equipped with advanced and latest diagnostic equipment, robotic and minimally invasive surgical facilities for musculoskeletal disorders treatment.
Skilled & Experienced Orthopaedic Specialist
Team of experienced orthopaedic doctor, orthopaedic physician, sports medicine doctor, orthopaedic surgeon with vast experience in minimally invasive procedures.
Advanced Centre for Orthopedic Treatment
in Hyderabad, Telangana

PACE Hospitals is one of the top 10 orthopedic hospitals in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, known for its patient-centric approach and consistently high success rates. The Department of Orthopaedics comprises a highly skilled team of orthopedic doctors, rheumatologists, sports injury specialists, and orthopedic surgeons, offering comprehensive care for a wide range of bone, joint, muscle, ligament, and tendon disorders.
Our team has deep expertise in diagnosing and managing complex musculoskeletal conditions and is well-versed in the latest evidence-based treatment modalities.
The Orthopaedic Department at PACE Hospitals is widely regarded as the
best orthopedic in Hyderabad, India, and is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities including advanced digital X-rays, high-resolution MRI scanners, and robotic-assisted surgical systems. We specialize in minimally invasive procedures for joint and knee replacements, complex trauma care, and post-operative rehabilitation, ensuring our patients receive world-class orthopedic care under one roof.
3,28,338
99,825
684
2011
Best Orthopedic Doctors in Hyderabad | Top Orthopaedic Surgeons
A team of the best Orthopaedic Doctor in Hyderabad, India, having extensive expertise in diagnosing and managing a wide range of musculoskeletal diseases and disorders, including arthritis, fractures, osteoporosis, scoliosis, joint pain, ligament injuries, and sports-related injuries are committed to delivering patient-centric, evidence-based and compassionate musculoskeletal disorders treatment to the pediatric, adult and geriatric patients. The skilled and experienced team of orthopaedic specialists and sports injury doctor thoroughly analyse the diagnosis report to understand the root cause of discomforts to cater to complete orthopaedic care tailored to individual needs. Orthopaedic surgeons are highly skilled in using advanced procedures like joint & knee replacements and minimally invasive techniques to treat complex and critical musculoskeletal disorders with minimal complications and high success rates.
Dr. Anand Agroya
MBBS, D.Ortho, Fellow in Joint Replacement, Arthroscopy & Sports Medicine
Experience : 15+ years
Senior Orthopaedic Consultant, Trauma Surgeon & Sports Medicine Specialist | Expert in Knee & Joint Replacement & Arthroscopy Surgery
Specialist
Specialist in advanced orthopaedic care and comprehensive sports injury management, focusing on knee and joint replacement, arthroscopy surgery, ligament reconstruction, fracture management, cartilage preservation, and joint restoration techniques. He supports patients in regaining strength, alleviating pain, and enhancing their quality of life.
Expertise
- Knee & Joint Replacement
- Arthroscopy Surgery for ligament repairs and cartilage preservation
- Ligament Reconstruction & Repair procedures like ACL and PCL
- Fracture Management & Trauma Care: Expertise in managing complex fractures and orthopaedic trauma cases.
- Shoulder & Rotator Cuff Repair
- Cartilage Restoration & Preservation
- Sports Injury Prevention & Rehabilitation
- Joint Preservation Techniques
Consultation Timing:
Mon to Sat - 9 am to 6 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Hitec City
Dr. Raghuram
MBBS, DNB ORTHO, Fellowship in Joint Replacement and Arthroscopy, Fellowship in Shoulder and Upper limb, Sports medicine and Replacement
Experience : 10+ years
Orthopaedic Consultant, Trauma, Shoulder and Knee Arthroscopic Surgeon, Hip and Knee Joint Replacement Specialist
Specialist
Specialist in diagnosing, managing, treating problems and performing procedures related to Complex and Failed Traumas, Non-Union and Malunion Fractures, Joint Replacements, Revision Surgeries, Geriatric Trauma Surgeries, Spine Problems, Foot and Ankle Problems, Knee and Shoulder Pain, Sports Injuries, Arthritis etc.
Expertise
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR) & Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction, Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Reconstruction, Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Reconstruction
- Complex Traumas, Geriatric & Revision Trauma surgeries, Simple and Complex Intraarticular Fractures
- Shoulder Arthroscopy and Shoulder Arthroplasty
- Sports-Related Injuries - Meniscal
- Shoulder Ligament & Cartilage Injury
Consultation Timing:
Mon to Sat - 9 am to 6 pm
Location:
PACE Hospitals, Hitec City & Madeenaguda
Orthopaedic Diseases and Disorder Explained by Drs
Comprehensive Orthopedic Care Services
Struggling with chronic pain and swelling in your joints, dealing with a broken bone or injury, facing back pain, numbness or tingling in your hands, severe sports injuries or seeking treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, rotator cuff injuries, meniscus tear, torn ligaments (ACL & MCL), herniated disc problems, scoliosis, bone tumours, bone infections, tendonitis, bursitis, tennis elbow, hip dysplasia, compound fractures, multiple fractures, we provide evidence-based treatment tailored to your needs. Our team of skilled and experienced orthopaedic doctors, sports medicine physician, orthopaedic surgeon provides comprehensive and compassionate care for geriatric, adult and pediatric patients.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) on Orthopedic
What is Orthopaedics?
Orthopaedics is the medical branch that deals with diseases and injuries of the human musculoskeletal system, which includes joints, bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles.
What kind of diseases and conditions treated at Orthopedic Department?
Orthopaedic departments at any multi-speciality hospital specialize in diagnosing, managing, and treating an extensive range of common and critical orthopedic conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system. As a leading orthopedic specialist hospital in Hyderabad, Telangana, PACE Hospitals offers expert care for various bone, joint, muscle, ligament, and tendon disorders through a multidisciplinary approach.
Some of the most common orthopedic diseases and disorders we treat include:
- Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Tendonitis
- Bursitis
- Bone infections (osteomyelitis)
- Frozen shoulder
- Shoulder dislocation
- Hip dysplasia
- Runner's knee
- Tennis elbow
- Meniscal tears
- Ankle sprains
- Clubfoot
- Compound fractures
- Multiple fractures
- Pelvic fractures
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injuries
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) injuries
At PACE Hospitals, our expert team of orthopaedic doctors, surgeons, and sports medicine specialists delivers comprehensive, precise, and advanced orthopedic care to help patients regain mobility and improve quality of life.
What are the most common Orthopaedic Problems?
The most common musculoskeletal conditions for which they might need ortho medical care are arthritis (osteo, rheumatoid, elbow), fibromyalgia, sprains or strains, fractures, back and neck pain, hand and knee pain, bursitis, hip fracture, foot pain, shoulder pain, osteoporosis, kyphosis, Paget's disease, and soft tissue injuries.
How do I know if I have a fracture?
The person with a fracture may have heard or felt a grinding or snap noise during the injury. In addition to these, bruising, swelling, pain and tenderness are seen at the site of the injury. In some severe cases, the injured part looks deformed, and the affected person may feel dizzy or faint as a result of shock due to bone fracture.
When should I see an orthopaedic specialist?
You should see an orthopedic doctor if you are experiencing any of the following symptoms:
- Pain in your bones, joints, or muscles that doesn't go away after a few days.
- Limited mobility or difficulty moving a joint or limb.
- Deformities or misaligned bones or joints.
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around a joint.
- A feeling of tingling or numbness in your arms or legs.
- A recent injury to your bones, joints, or muscles.
- A chronic condition, such as arthritis, that is affecting your mobility.
When should I see an orthopaedic specialist?
You should consider seeing an orthopedic specialist if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Persistent pain in your bones, joints, or muscles that doesn’t improve after a few days.
- Limited mobility or difficulty moving a joint or limb.
- Visible deformities or misalignment in bones or joints.
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around a joint, especially if accompanied by pain.
- A tingling or numb sensation in your arms, hands, legs, or feet.
- A recent injury involving bones, joints, ligaments, or muscles.
- A chronic orthopedic condition, such as arthritis, impacting your daily movement and quality of life.
If you are facing any of these symptoms, it's important to consult one of the best orthopedic doctors in Hyderabad, Telangana, at PACE Hospitals. Our experienced team offers accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and advanced surgical and non-surgical interventions to help you regain mobility and live pain-free.
Which is the best orthopedic hospital in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals is widely regarded as one of the best orthopedic hospitals in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. It stands out for its:
- Highly experienced orthopedic specialists – including top orthopedic surgeons, rheumatologists, and sports medicine doctors.
- Comprehensive care – treating a wide range of musculoskeletal disorders affecting bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
- Cutting-edge technology – including robotic-assisted joint replacement, minimally invasive procedures, digital X-rays, and high-resolution MRI.
- Advanced rehabilitation and post-op care – ensuring faster recovery and long-term results.
- Multiple specialties under one roof – managing everything from fractures and arthritis to complex spinal conditions and orthopedic oncology.
- Convenient locations – accessible from Hitech City, Madhapur, Kondapur, Gachibowli, Kukatpally, and KPHB.
Whether you're dealing with a sports injury, joint pain, or a need for total joint replacement, PACE Hospitals offers expert, evidence-based, and patient-centric care—making it one of the top choices for orthopedic treatment in Hyderabad, India.
What are the most common procedures done at Orthopedic Department?
The most common orthopedic procedures done by orthopedic surgeons are:
- Knee replacement surgery
- Joint Replacement surgery
- Hip Replacement
- Shoulder Replacement
- ACL Reconstruction Surgery
- Meniscal repair surgeries
- Arthroscopy
- Spine surgeries
- Fracture repair
- Tendon repair
What are the common Diagnostic Tests done at Orthopedic Department?
Some of the common diagnostic tests and examinations performed to assess musculoskeletal system disabilities are as follows:
- X-rays
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
- Bone Scan
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA:
- Ultrasound
- Arthroscopy
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
- Muscle Biopsy
- Genetic Testing
What is the difference between an Orthopaedist and a Rheumatologist?
Orthopedists are specialists in the musculoskeletal system, which consists of bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and nerves. These experts are trained in diagnosing and treating bone and joint diseases and injuries, which may involve orthopaedic surgery.
Rheumatologists are specialists in the management of inflammatory autoimmune diseases. In diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system of the patient attacks healthy body tissue rather than invading foreign pathogens.
Is PACE Hospitals empaneled under the Aarogyasri scheme for orthopedic treatments in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals is proud to be associated with the Aarogyasri Health Care Trust, offering comprehensive orthopedic care in Hyderabad under the Aarogyasri scheme. As one of the most trusted names among Aarogyasri orthopedic hospitals in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, we are committed to delivering high-quality and affordable treatment for patients covered under the Aarogyasri initiative.
We are:
✅ Aarogyasri-approved hospital for orthopedic surgeries and trauma care
✅ Team of experienced orthopedic surgeons and joint replacement specialists
✅ Treatment for fractures, arthritis, spine issues, sports injuries, and joint disorders
✅ Advanced diagnostic imaging, physiotherapy, and surgical care
✅ Personalized rehabilitation plans for faster recovery
✅ Compassionate care in a modern, patient-friendly environment
Whether you need knee replacement, hip replacement, spine surgery, or treatment for a sports injury, our expert team at PACE Hospitals ensures world-class orthopedic care under the Aarogyasri scheme in Hyderabad.
How to book an appointment in the Top Orthopedic Hospital in Hyderabad?
Anyone seeking famous orthopedic hospitals in Hyderabad, Telangana for the treatment of bone, joint, muscle, ligament, or tendon disorders in the locations nearby Hitech City, Madhapur, Kondapur, Gachibowli, KPHB, or Kukatpally can visit the PACE Hospitals' Orthopedic Department webpage and fill out the Appointment Form. They can also directly visit the hospital located near the Hi-Tech City metro station or call 04048486868 to book a hassle-free appointment.
Do you provide free online doctor consultations in Hyderabad, India for Orthopedic care?
Yes, PACE Hospitals, a trusted name among top orthopedic hospitals in Hyderabad, Telangana, offers free online and offline doctor consultations with experienced orthopaedic specialists for all Teachers, Police, and Army Officials. Whether you're dealing with joint pain, arthritis, fractures, or planning for knee or hip replacement surgery, our expert team is here to guide you with personalized care and medical advice.
✅ Free consultations with top orthopaedic doctors
✅ Evaluation of bone, joint & spine conditions
✅ Medical second opinions for surgeries & treatments
✅ Advanced diagnostics, physiotherapy & surgical care
📞 Call: 04048486868 or 💬 WhatsApp: +918977889778. 📅 Book your free orthopaedic consultation today!
Our Specialized Orthopedic Treatments & Services
At PACE Hospitals, we specialize in treating and managing a wide range of orthopaedic diseases and disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system, including the bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. As a top orthopedic hospital in Hyderabad, Telangana, India, we are equipped to handle everything from common sports injuries to the most complex orthopedic conditions with a compassionate and patient-centric approach.
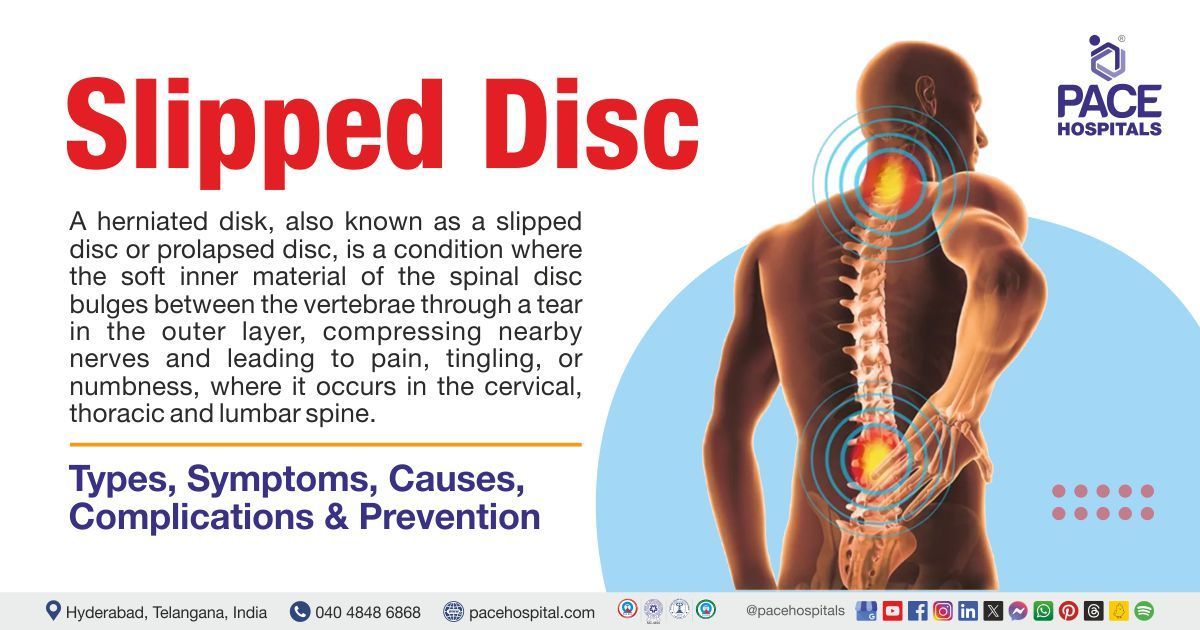
Our expertise spans across various conditions such as osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, osteomyelitis (bone infections), fractures, tendonitis, bursitis, frozen shoulder, shoulder dislocation, ankle sprains, clubfoot, tennis elbow, runner's knee, meniscus tears, and compound fractures. We also manage critical and chronic disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, bone tumors, herniated or slipped discs, kyphosis, degenerative disc disease, sciatica, torn ligaments (ACL, MCL tears), hip dysplasia, developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), multiple fractures, pelvic fractures, and traumatic amputations. Our multidisciplinary team of orthopaedic physicians, orthopedic surgeons, and sports medicine specialists is dedicated to delivering comprehensive, precise, and compassionate orthopedic care, ensuring optimal outcomes for your bone and joint health.

Google Reviews and Patient Testimonials
A Patient from Somalia with Osteoarthritis in both knee with 90-degree Flexon Deformity, treated successfully with
Total Knee Replacement.
Orthopedic Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
At PACE Hospitals, we provide comprehensive and precise orthopedic diagnostics to deliver evidence-based treatments for a wide range of musculoskeletal impairments. Our advanced screening protocols are designed to detect and evaluate abnormalities in the bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons at an early stage, ensuring accurate diagnosis and timely intervention.
Using the latest imaging technology and diagnostic tools, our team of orthopedists, sports injury doctors, and orthopedic surgeons can make well-informed clinical decisions to proceed with the most suitable treatment modalities or surgical procedures. This approach not only ensures better outcomes but also minimizes recovery time and improves long-term joint function.
Recognized among the
best hospitals in Hyderabad for orthopedic care, PACE Hospitals is committed to delivering patient-centered, high-precision orthopedic services that restore mobility, relieve pain, and enhance overall quality of life.
1.Electromyography (EMG): Electrodiagnostic studies are used to detect neuromuscular abnormalities, measuring the electrical activity in muscles and nerves to assess nerve function and evaluate injuries. These studies include electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS), which are commonly ordered during the assessment of patients with suspected peripheral nerve compression. These tests are often conducted together, and the combined evaluation is commonly referred to as two and abbreviated as an EMG/NCS or commonly called an EMG test. During the test, thin needles are placed in specific muscles, and then a healthcare professional asks the patient to mobilize the muscle to look at the electrical signals.
2. Bone Scan: A bone scan is also called a skeletal scintigraphy, a specialized radiology procedure used to examine the abnormal areas or damage in various bones of the skeleton, which is performed to detect areas of chemical and physical changes in bone. During this procedure, a tiny amount of radioactive material is injected into a person's vein, travels through the blood, collects in the bones and is detected by a special camera that takes images of the inside of the body called a scanner. This scan is advised to detect bone non-cancerous tumours or cancers that have spread to the bone and to diagnose other bone conditions, including bone infections, fractures, etc.
3. Arthroscopy: Arthroscopy is a keyhole surgery (minimally invasive surgical procedure) used to examine and treat problems inside the joint. During this test, a surgeon inserts a thin tube attached to a camera (arthroscope) into the joint through small incisions to view the joint on a monitor and address issues such as cartilage damage, tears, or loose fragments.
4. Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) is a medical imaging technique primarily used to assess bone mineral density (BMD) and body composition. It employs two different X-ray energy levels to distinguish between bone and soft tissue, providing precise measurements of bone density, which is crucial for diagnosing conditions like osteoporosis, monitoring the effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments and predicting the likelihood of bone fractures can also include measuring muscle and fat composition in specific body areas.
5. Nerve Conduction Studies: A nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test is performed to measure how fast (velocity) an movement of electrical impulse moves through the person's nerve. During this examination, two electrodes are placed on the skin over a muscle or over a nerve where one electrode stimulates the nerve with a very mild electrical impulse, and others record it, which is repeated for each nerve being tested. Healthcare professionals measure the distance between electrodes and the time taken for electrical impulses to travel between them to calculate the speed of electrical impulses.
6. Muscle Biopsy: Muscle biopsy is a common diagnostic procedure used by clinicians to evaluate patients with weakness that may be caused by muscle disease. It involves removing a small tissue sample for testing in a laboratory to diagnose neuromuscular disorders, infections that affect muscle, and other abnormalities in muscle tissue, including muscular dystrophy (MD), myasthenia gravis (MG), polymyositis (chronic disease involving skeletal muscles) etc.
Orthopaedic Procedures Performed:
1. Arthroplasty: Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure that is done to restore the functionality of a joint by resurfacing the bones. An artificial joint (often called a prosthesis) is used in this procedure. This surgical procedure is indicated when other medical treatments are no longer effective in relieving joint pain and disability.
2. Achilles Tendon Repair: Achilles tendon repair is a type of surgery that is done to fix the damaged Achilles tendon. During this procedure, an incision is made in the backside of the calf. The surgeon will stitch the tendon if it ruptures. In some occasional scenarios, the Achilles tendon repair surgery will be minimally invasive with several small incisions. A special scope with a tiny camera and a light is used in this procedure to help or guide during the surgery.
3. ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) Reconstruction: ACL reconstruction surgery is indicated to reconstruct the ligament in the centre of the knee. This procedure is usually done with the help of knee arthroscopy by inserting a tiny camera into the knee through a small surgical cut. The surgeon will make necessary small cuts around the knee and insert medical instruments to fix or correct the abnormality. After the insertion, the surgeon will stitch with sutures and covers the area with a dressing.
4. Bracing and casting: Hip and knee braces are commonly used to support post-surgery patients to prevent or reduce the severity of injuries. The braces are meant for stabilization, mechanical correction, immobilization, and rehabilitation. The casting material is a Plaster of Paris or synthetic used to immobilize the fractures and complex ligament injuries of the lower leg and maintain the foot position during conservative management. Casting is a temporary measure for definitive fracture fixation.
5. Bunionectomy: Bunion surgery, or bunionectomy, is a treatment that is used to correct bunions. A bunion (hallux valgus), is a bony bump-like structure present aside from the big toe joint. There are a few types of bunion surgery that are involved in repositioning the big toe to get relief from the pain and to improve its function. This surgery uses different techniques such as Exostectomy, Osteotomy, and Arthrodesis.
6. Carpal Tunnel Release: Carpal tunnel release is a kind of surgery indicated to treat and heal painful carpal tunnel syndrome. During this procedure, the surgeon cuts through the ligament, pressing down on the carpal tunnel, making more space for the tendons and median nerve to pass through the tunnel, thereby reducing the pain and improving the function. This outpatient procedure is usually done in traditional or open carpal tunnel release and endoscopic carpal tunnel release.
7. Decompression Surgery: Decompression surgery is indicated to treat chronic lower back pain. This surgery involves either the partial or complete removal of anatomical structures from the lumbar spine, which causes neural impingement. The types of decompression surgery are laminectomy and discectomy, whereas the procedures include open conventional and microscopic. The indications of decompression surgery are disc herniations, neurological dysfunction and spinal stenosis.
8. Electrical Stimulation: Electrical stimulation is a therapy developed in recent years for healing bone abnormalities or fractures related to bones. Bone stimulators are the devices that are often used in this procedure to treat fractures which are failed to heal on their own. These types of fractures are called "non-unions."
9. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT): Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive treatment used to treat several conditions, such as chronic plantar fasciitis, tendonitis, and Achilles tendonitis. Shockwave therapy helps to induce the body's normal healing process. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy works by using either focused shockwaves or radial pressure waves. These are outpatient procedures that last for 5–15 minutes. On turning on the ESTW machine, the instrument or shockwave gun is pressed against the affected site to deliver rapid impulses to the patient.
10. Fracture Repair: Bone fracture repair is a type of surgical procedure that fixes a broken bone using pins, plates, metal screws, or rods to hold the bone in its place. This procedure is also called open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) surgery.
11. Hammertoe correction: Hammer toe surgery is one of the outpatient procedure which requires anaesthesia or numbing medications. The type of procedure is suggested based on the severity of the hammer toe. A flexible toe requires tendon transfer, whereas joint resection or joint fusion is suggested for stiff or fixed toes.
12. Hip Replacement: Hip replacement, often called hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure used to treat hip pain. This surgery replaces parts of the hip joint with an artificial implant. Hip replacement surgery may require replacement of one or both parts. The motto of hip replacement is to allow the individual to resume daily activities and exercises.
13. Joint Aspiration: Joint aspiration is a procedure that removes the fluid from the space surrounding a joint using a needle and syringe. This procedure requires local or regional anaesthesia to relieve swelling or obtain fluid for analysis to diagnose a patient with a joint disorder or problem. Joint aspiration is mostly done on the knee. However, this procedure can also be used to remove the fluid from other joints, such as the hip, shoulder, elbow, ankle, or wrist.
14. Joint Debridement: Debridement is referred to as the surgical removal of damaged tissue. This procedure is usually done with an arthroscopy technique and requires general or local anaesthesia; Arthroscopic debridement is an accessible treatment modality that involves chondroplasty, synovectomy, toilet lavage, and meniscectomy which aims to reduce the symptoms by removal of inflammatory factors and cartilaginous debris. It is well-indicated for mild to moderate osteoarthritis, especially in the knee and joints. Irrigation, often known as "lavage," is essential to rinse out the fluid from the knee.
15. Joint Distension: Joint distension, commonly known as arthrographic or hydrodialtion, is performed under local anaesthesia. This procedure initially injects a dye into the joint to visualize it clearly on an imaging device. This procedure involves injecting sterile water into the joint to expand the area and make the adhesions loose and pull away. This frees up the space near the joints and improves the range of movement. It is a less invasive and the best alternative to shoulder injury procedures.
16. Joint Manipulation: Joint manipulation is a procedure that involves the synovial joint's opposing articular surfaces being split apart (gapped) and thereby causing cavitation in the joint's synovial fluid. Joint manipulation is a brief manual therapy technique that only affects the target joint and may produce a slight pop. Joint manipulations can offer short-term pain relief and mobility improvement in a dysfunctional location.
17. Knee Replacement: Knee replacement, commonly called as knee athroplasty, is a surgical procedure to resurface a knee damaged due to arthritis. Metal and plastic parts are incorporated to seal the bones' ends that form a knee joint alongside the kneecap. This surgery is considered for individuals with severe arthritis or a severe knee injury.
18. Laminectomy: Laminectomy is a type of procedure involving the removal of a part or total of the vertebral bone (lamina). This procedure reduces pressure on the spinal cord or the nerve roots that are caused by injury, stenosis, herniated disc, or tumours. The laminectomy is suggested if the medical therapy is failed. This procedure is usually done for neck or back pain that continues on medical treatment or is done when the pain is due to nerve damage, such as numbness / weakness in the arms or legs.
19. Meniscus Repair: Meniscus repair will be done based on the grade of the condition (meniscus tear). The meniscus tear of grade-3 is suggested with surgeries such as either arthroscopic repair or arthroscopic partial meniscectomy, or total meniscectomy. The arthroscopic procedure is done by inserting the arthroscope to look at the tear and placing small devices like darts to stitch it. Arthroscopic partial meniscectomy involves the removal of a piece of the torn meniscus to make the knee functional, whereas total meniscectomy involves the complete removal of the meniscus.
20. Osteotomy: An osteotomy is a type of surgical procedure used to cut and reshape the bones. This procedure is commonly used to repair the joint and to shorten or lengthen the deformed bones. During this osteotomy procedure, general or regional anaesthesia is given prior to the procedure, and then the surgeon will make a small cut in the skin to guide a special wire that measures the bone. The section is taken out by using a special surgical saw, followed by filling the open space. Tiny screws and metal plates are commonly used in this procedure to hold the bones. The types of osteotomy are knee, hip, spine, toe, chin, and jaw.
21. Rotator Cuff Repair: Rotator cuff (tendons and muscles that form a cuff on the shoulder) repair is a surgery used to correct a torn tendon in the shoulder. The procedure can be done with an open incision or with arthroscopy. Prior to this procedure, general anaesthesia is given. Three common techniques that are used to repair the rotator cuff tear are open repair (used for large or complex tears), shoulder arthroscopy, and mini-open repair surgery.
22. Spinal Fusion: Spinal fusion is a type of surgical procedure indicated to correct the problems that are found in the bones of vertebrae (spine). Spine fusion is a welding process done to eliminate pain and restore the spine's stability. This surgery is usually recommended when the ortho surgeon confirms the source of the pain. This procedure uses an imaging test, such as X-rays, computed tomography scans (CT-scan), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
23. Synovectomy: Synovectomy is a surgical procedure involving destroying or removing the synovial membrane. A synovial joint is the largest articulation, is frequently affected by chronic inflammation, and often undergoes synovectomy. Open surgical, radiation, chemical, and arthroscopic synovectomies are the surgical types indicated to remove potentially damaging synovium from the knee. The common indications for synovectomy are chronic inflammatory arthritis conditions, benign neoplastic disorders and recurrent hemarthrosis.
24. Tendon Repair: Tendon repair is a surgical procedure indicated to treat a damaged or torn tendon. Tendon repair surgery is commonly suggested to people with tendon injuries (lacerations and sports injuries) that are painful and make it difficult to move. The aim of this surgery is to bring back the normal movement. This procedure requires a small incision followed by sewing the torn ends of tendons; thereby, the incision is closed with stitches and dressings. Prior to the procedure, regional or local anaesthesia is given.
25. Total Joint Replacement: Total joint replacement is a surgical technique in which arthritic or diseased joint pieces are taken out and replaced with a metal, plastic, or ceramic prosthesis. The prosthesis can replace a natural, healthy joint's motion. Joint replacement surgery can be done on various joints, such as the elbow, shoulder, ankle, and wrist. Hip and knee replacements are the most often performed joint replacements.
26. Visco-supplementation: Visco supplementation is a procedure where the ortho surgeon injects hyaluronic acid into the joints. This fluid reduces the pain and swelling in the joints. Before this procedure, numbing medicine is injected into the space around your knee joint, followed by draining of fluid that causes swelling and pain. This method is commonly indicated to treat arthritis conditions.
27. Prolotherapy: Prolotherapy is a type of medical therapy indicated to treat joint and muscle pain. Prolotherapy is commonly called proliferation therapy or regenerative injection therapy. This procedure involves an injection of saline or sugar substance into the muscle or sore joints, this substance acts as an irritant, and thereby the body sends the immune cells and other chemicals to the injected area, which in turn starts the natural healing process. This process is used to repair the damaged soft tissue in muscle or joint areas such as muscle tissues, nerves and blood vessels.
Patient Education and Health Blogs
Why choose PACE Hospitals?
- A Multi-Super Speciality Hospital.
- NABH, NABL, NBE & NABH - Nursing Excellence accreditation.
- State-of-the-art Liver and Kidney transplant centre.
- Empanelled with all TPAs for smooth cashless benefits.
- Centralized HIMS (Hospital Information System).
- Computerized health records available via website.
- Minimum waiting time for Inpatient and Outpatient.
- Round-the-clock guidance from highly qualified super specialist doctors, surgeons and physicians.
- Standardization of ethical medical care.
- 24X7 Outpatient & Inpatient Pharmacy Services.
- State-of-the-art operation theaters.
- Intensive Care Units (Surgical and Medical) with ISO-9001 accreditation.