Liver Cirrhosis Treatment - Medical & Surgical Management | Cost
At PACE Hospitals, team of best liver specialist doctors in Hyderabad include hepatologist, liver transplant doctors are experienced in handling complex cases of liver related diseases and its complications such as cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, alcoholic liver disease, liver parenchymal disease, autoimmune liver disease, cholestatic liver disease.
Book Appointment for Liver Cirrhosis Treatment
Liver Cirrhosis Treatment - appointment
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Liver Cirrhosis Treatment in India?
Dedicated Liver Intensive Care Unit for Acute and Chronic Liver Injury
Equipped with latest technology, ERCP & SpyGlass Cholangioscopy
Team of the Best Liver Doctors and Surgeons with 35 + years of expertise
CGHS, ECHS and All insurance accepted for cashless treatment
Diagnosis for Liver Cirrhosis
Most people with compensated cirrhosis are asymptomatic, although symptomatic patients exist. Generally, the history of the patient and the physical examination are considered before taking the assistance of lab tests, imaging tests and other objective tests.
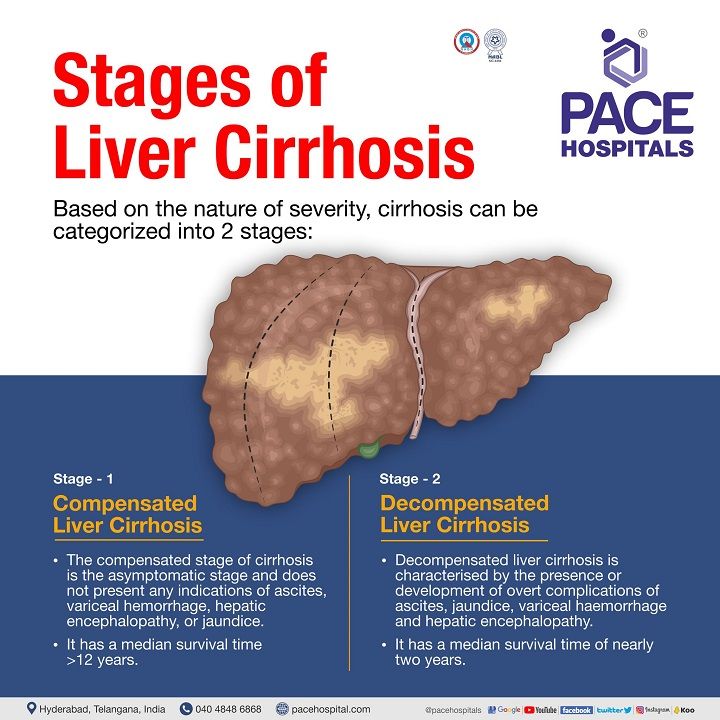
Liver Cirrhosis Stages
There are two stages of liver cirrhosis:
- Compensated liver cirrhosis
- Decompensated liver cirrhosis
These are the 2 clinical dynamic and progressive stages, but there is potential reversibility from the decompensated liver cirrhosis to the compensated liver cirrhosis.
Child-Turcotte-Pugh score method
The prognostic scoring system of the Child-Turcotte-Pugh score (CTP) in cirrhosis has based on the collection of symptom points:
Points for symptom/feature
- Ascites: none (1 point), diuretic-sensitive or mild/moderate (2 points) & diuretic-refractory or tense (3 points)
- Encephalopathy: none (1 point), episodic or overt grade 2 (2 points) & recurrent/chronic or grade 3 to 4 (3 points)
- Albumin in g/dL: > 3.5 (1 point), 3.4 to 2.8 (2 points) & < 2.8 (3 points)
- Bilirubin in mg/dL: < 2 (1 point), 2 to 3 (2 points) & 3 (3 points)
- Prothrombin time, expressed as an international normalised ratio (INR): < 1.7 (1 point), 1.7 to 2.3 (2 points) & >2.3 (3 points)
The prognostic scoring system of the Child-Turcotte-Pugh score (CTP) in cirrhosis has based on the collection of symptom points. Interpretation of the CTP scoring system:
- CTP A patients (5-6 points): mostly patients with compensated cirrhosis
- CTP B patients (7-9 points): mostly decompensated, but decompensation is "early."
- CTP C patients (10-15 points): decompensated (late or "further" decompensation)
Differential Diagnosis of Liver Cirrhosis
The sign and symptoms of liver cirrhosis are common with various other chronic diseases, such as:
- Acute fatty liver of pregnancy [a rare but severe condition of pregnancy in which an excessive accumulation of fat (triglycerides and fatty acids) in the hepatic cells]
- Amanita phalloides mushroom poisoning
- Acetaminophen (paracetamol) poisoning
- Bacillus cereus toxin
- Fructose intolerance (a disorder in which the patient is deficient in the protein needed to break down fructose)
- Galactosemia (inability to metabolisethe simple sugar galactose.)
- HELLP (haemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets) syndrome of pregnancy
- Haemorrhage viruses (Ebola virus, Lassa virus, Marburg virus)
- Idiopathic drug reaction
- Neonatal iron storage diseases
- Tyrosinemia (a rare, inherited disorder marked by high blood levels of tyrosine (amino acid))
Considerations and goals of a hepatologist / gastroenterologist in treating cirrhosis of the liver
A disease is defined as a physiological health failure, while sickness is determined by the inability to achieve critical objectives owing to physical or psychological dysfunction. Besides cirrhosis of liver, increasing physical and social losses from other chronic diseases severely influence the dignity of the afflicted individual in chronic conditions.
From the patient's point of view, the thoughts and expectations about the illness, energy loss, and/or chronic weariness differ from a healthy person, impacting the patient's psychological well-being. The considerations of hepatologists / gastroenterologists include:
Prognosis and quality of life: Numerous symptoms are seen in cirrhosis of liver which includes fluid retention (ascites), various degrees of confusion due to hepatic encephalopathy, acute gastrointestinal bleeding from varices or bacterial infections, etc. At least 50% of patients present one or more symptoms at the time of diagnosis. The deterioration of liver disease is indirectly proportional to the person's health‐related quality of life. Unless a curative liver transplant is possible, the symptom management is palliative.
Need for a holistic approach: This forms the basis for the holistic approach in treating a cirrhotic patient, as liver cirrhosis is a medically complex disease associated with poor health‐related quality of life, fatigue, psychological distress and abdominal symptoms.
Abolishing health ignorance: The holistic approach to treatment is also necessary as, combined with the aforementioned issues, the patients suffering from cirrhosis of liver demonstrate an air of ignorance about the disease, thus enhancing the prognosis and preventable hospital admissions. Therefore, patient education about the disease is necessary.
Address of psychological needs: According to Maslow's hierarchy of needs, patients must first meet their needs for safety, security, and stability before attaining the health behaviours required for successful care of advanced liver disease. Psychologist consultation can help.
Empathic staff: An educated understanding healthcare team which show empathy achieve a reduction in suffering from the patients by the patient‐centred care.
Intercommunication: Multidisciplinary healthcare teams display a high degree of communication and collaboration, aiding in accomplishing shared goals and including overall integrated healthcare.
Case management techniques used by mental health practitioners include screening, evaluation, risk stratification, follow-up, and care transfer, along with continuing treatment for liver cirrhosis.
Goals of a hepatologist / gastroenterologist in treating cirrhosis of liver
The goals of clinical manifestations of liver cirrhosis are adaptable, and it is difficult to provide overall management guidelines. General approaches to therapy should include:
- Identification and elimination: The possible causes of cirrhosis (e.g., alcohol abuse).
- Assessment of risk for variceal bleeding: Variceal bleeding risk assessment can instigate pharmacologic prophylaxis. Reserve prophylactic endoscopic therapy for patients with contraindications or intolerance to β-adrenergic blockers. Endoscopic treatment is also appropriate for patients suffering acute bleeding episodes. Variceal obliteration with endoscopic techniques is the recommended treatment of choice in patients with acute bleeding.
- Evaluation of ascites: The clinical signs of ascites are ascertained with pharmacologic therapy (usually diuretics and paracentesis). Careful monitoring for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis should be used in patients with ascites who undergo acute deterioration.
- Attention for hepatic encephalopathy: A complication of cirrhosis of liver requiring clinical vigilance involved with dietary restriction, and elimination of central nervous system depressants, apart from therapy to lower ammonia levels.
- Constant vigilance over:
- Hepatorenal syndrome [dysfunctional kidneys in patients with severe liver problems. Reduced urine promotes waste build-up containing nitrogen in the blood (azotaemia). Occurs in 1-10 hospitalised liver failure patients]
- Pulmonary insufficiency (incompetent pulmonary valve during diastole, which allows the backflow of blood from the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle of the heart)
- Endocrine dysfunction (impaired endocrine system causing wide-ranging effects on the body).
Treatment for Liver Cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis treatment depends on the cause and extent of your liver damage. The goals of treatment are to slow the progression of scar tissue in the liver and to prevent or treat symptoms and complications of cirrhosis. The various treatment modalities which can be administered to treat cirrhosis of liver.
Medical management of liver cirrhosis
Medical management of liver cirrhosis involves a combination of treatments designed to slow the progression of the disease and manage its symptoms. Some of the main goals of medical management for liver cirrhosis include:
- Management of the underlying cause: treating the underlying hepatitis virus infection (B or C), or blood extraction to lower iron levels in haemochromatosis etc.
- Dietary and lifestyle changes: People with liver cirrhosis often have difficulty absorbing nutrients from food, which can lead to malnutrition. Medical management may involve dietary changes; a nutritious, low-sodium diet, low-fat, high-protein diet and exercise in their routine can help people to avoid malnutrition and get enough nutrients.
- Immunisation for hepatitis (B or C).
- Reducing the load on the liver: This may involve reducing the intake of alcohol and certain medications, as well as treating underlying conditions that may be contributing to liver damage, such as viral hepatitis or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Managing complications: Liver cirrhosis can lead to a number of complications, such as ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen), varices (enlarged veins in the esophagus or stomach), and hepatic encephalopathy (a condition that causes confusion and difficulty thinking).
- Medications: Medical management of liver cirrhosis may involve medications such as Beta-blockers to reduce hypertension and risk of bleeding or diuretics to remove excess fluid, Antiviral drugs: to treat viral hepatitis, Steroids and immunosuppressive agents: to treat autoimmune hepatitis.
- Avoiding drug-induced liver injury: certain medications that can make the symptoms worse – such as opiates, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or sedatives. Upon the doctor's advice, they must be stopped, and alternatives must be administered.
- Regularised endoscopic procedures: Endoscopy can help in assessment of varices (enlarged veins in the esophagus or stomach) happen because of portal hypertension in cirrhosis patients. In most of severe cirrhosis cases, esophageal varices can burst and cause internal bleeding.
- Monitoring for liver cancer: People with liver cirrhosis have an increased risk in future of developing liver cancer. Medical management may involve regular monitoring, regular medical check-ups for signs of liver cancer, such as ultrasound exams or blood tests.
It's important to note that medical management of liver cirrhosis is not a cure for the condition. The focus is on slowing the progression of the disease and managing its symptoms. In advanced cases of liver cirrhosis, a liver transplant may be the best treatment option. It's important to work closely with liver specialist doctors to determine the best treatment plan for you.
Surgical management of liver cirrhosis
Surgical treatment for liver cirrhosis may be recommended in certain cases and may be used to treat more-severe complications of cirrhosis. Some possible surgical treatments for liver cirrhosis include:
- Liver transplant: This is the most effective treatment for advanced liver cirrhosis. A liver transplantation involves surgically removing the damaged liver and replacing it with a healthy liver from a donor.
- Shunt surgery: Shunt surgery may be an option for people with liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension (high blood pressure in the vein that carries blood to the liver). Shunt surgery involves creating an alternate pathway for blood to bypass the damaged liver, a small tube called a Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) may be placed in your vein to reduce blood pressure in your liver.
- Liver resection (hepatectomy): In some cases, a portion of the damaged liver may be surgically removed in a procedure called a liver resection. This may be an option for people with small, isolated areas of scarring in the liver.
- Copper chelating therapy: Copper chelating therapy is typically used to treat Wilson's disease, a rare genetic disorder that causes excessive amounts of copper to accumulate in the body. Copper chelating therapy can be effective in reducing copper levels in the body and improving symptoms of Wilson's disease
- Iron chelation and phlebotomy: to treat hemochromatosis, an inherited condition where the body absorb too much iron from the food after eating.
It's important to understand that surgical treatment for liver cirrhosis is not always possible, and it may not be the best option for everyone. Surgical treatment plan will depend on the severity of your liver damage, your overall health, and other factors. It's important to work closely with the liver specialist team to determine the best treatment plan for you.
Liver Cirrhosis Treatment Cost in Hyderabad, India
The
cost of Liver Cirrhosis Treatment in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹1,000 to ₹95,000 and above (approx. US $12 – US $1,145).
The exact cost varies depending on the stage of cirrhosis (compensated or decompensated), cause of liver damage (alcohol, hepatitis B/C, NASH, autoimmune), need for diagnostic tests (LFT, ultrasound, fibroscan, endoscopy), treatment (medications, paracentesis, endoscopic band ligation), hospitalization, and hospital facilities — including cashless insurance, TPA tie-ups, and documentation assistance wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of Liver Cirrhosis Treatment
- Gastroenterologist / Hepatologist Consultation – ₹800 – ₹1,800 (US $10 – US $22)
- Blood Tests (LFT, CBC, Kidney Function, INR) – ₹800 – ₹3,000 (US $10 – US $36)
- Viral Markers (HBV/HCV) – ₹500 – ₹1,800 (US $6 – US $22)
- Ultrasound Abdomen – ₹1,000 – ₹2,500 (US $12 – US $30)
- FibroScan (Liver Stiffness Test) – ₹2,000 – ₹4,500 (US $24 – US $54)
- Upper GI Endoscopy – ₹2,000 – ₹6,000 (US $24 – US $72)
- Endoscopic Variceal Ligation (If Required) – ₹12,000 – ₹28,000 (US $145 – US $335)
- Paracentesis (Fluid Removal) – ₹6,000 – ₹18,000 (US $72 – US $215)
- IV Medications & Albumin Infusion – ₹3,000 – ₹12,000 (US $36 – US $145)
- Hospitalization (1–5 Days) – ₹8,000 – ₹25,000 (US $95 – US $300)
- Management of Complications (Bleeding, Jaundice, Ascites, Encephalopathy) – ₹15,000 – ₹45,000 (US $180 – US $540)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Liver Cirrhosis
Can the liver recover from cirrhosis?
No, the liver can't recover from cirrhosis as the damage to the liver is far more extensive and beyond repair. Nevertheless, certain reformative steps can be taken to treat the underlying cause of cirrhosis. This could delay the worsening of cirrhosis and get time for a liver transplant.
What are the first signs of cirrhosis of the liver?
The first symptoms of cirrhosis of the liver may not develop in the early stage of cirrhosis as the liver can still function despite being damaged. Only severe damage to the liver can present symptoms. The main symptoms of cirrhosis include:
Tiredness and weakness
Feeling sick and loss of appetite
Red patches on palms and small, spider-like blood vessels on skin (spider angiomas) above waist level
Why is PACE Hospitals considered as the best hospital for liver cirrhosis in Hyderabad?
The Institute of Liver Sciences at PACE Hospitals is backed up by the top and highly skilled liver specialist doctors, and liver transplant surgeons with wide experience in treating all kinds of liver-related diseases and cancers through medical management and surgical management with high success rates. Department is among the famous hepatologists and liver transplant surgeons in Hyderabad, awarded nationally and internationally in their respective fields of study.
PACE Hospitals is equipped with cutting-edge infrastructure and equipment, including world's 1st Universal Surgical Robotic System, Liver Intensive Care Unit, advanced 3D HD laparoscopic system and world-class infrastructure to provide precision treatment. The multidisciplinary team is well-versed in the latest modalities. It is highly skilled in tackling critical cases, which makes PACE Hospitals, one of the best hospitals for liver cirrhosis treatment in Hyderabad, India.
How to prevent liver cirrhosis?
Preventative tips for cirrhosis include:
Abstinence from alcohol
Eating a healthy plant-based diet with rich fruits and vegetables.
Maintenance of a healthy weight and dietitian consultation for a weight-loss plan if obese
Reduce the risk of hepatitis with vaccines and avoid unhealthy practices such as sharing needles and unprotected sex.
What Is the cost of Liver Cirrhosis Treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of liver cirrhosis treatment typically ranges from ₹900 to ₹88,000 and above (approx. US $11 – US $1,060), making it an affordable and specialised option for patients requiring long-term liver care. However, the final cost depends on:
- Stage of cirrhosis (compensated vs. decompensated)
- Requirement for FibroScan, endoscopy, or CT imaging
- Medications and albumin infusion
- Need for hospitalization
- Frequency of paracentesis or endoscopic procedures
- Presence of complications (bleeding, infection, ascites, encephalopathy)
- Nutritional and long-term follow-up needs
Patients with mild, early-stage cirrhosis fall at the lower range, while those with advanced disease requiring frequent procedures and hospitalization fall toward the higher end.
After clinical evaluation, blood tests, and imaging, our liver care team will provide a personalised treatment plan and a transparent cost estimate based on your condition.
How long does it take fatty liver to become cirrhosis?
According to the research, it takes about ten years for 8-30% of the patients with alcoholic fatty liver disease who indulge in alcoholism daily to develop fibrosis or cirrhosis. It must be understood that the prognosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is uncertain.
Studies show that in predominantly non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients with aggressive natural history, the development of cirrhosis is seen in 26% of patients.
What are the 4 stages of cirrhosis of the liver?
Liver cirrhosis does not contain 4 stages. Actually, liver cirrhosis is one of the stage of liver disease / liver failure. Seemingly, liver failure has four stages. They are inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver failure.
- Stage 1: Inflammation: The early stages of liver disease. Here, swollen or hepatitis is seen as a natural response to injury. Increased toxins are one of the causative factors.
- Stage 2: Fibrosis: Untreated inflammation may lead to scarring of the liver, also called fibrosis which hinders the liver’s abilities, as it can restrict the blood flow. Scar tissue is usually not repairable. If detected early, the fibrotic patient can be saved.
- Stage 3: Cirrhosis: Severe and irreversible scarring of the liver. It may take several years to manifest. Most prone to liver cancer.
- Stage 4: Liver Failure (the final stage): Also called as hepatic failure or advanced liver disease where functioning of the liver is stopped. The liver cannot be repaired on its own or even with treatments; a liver transplant is the only option for recovery.
What is the best treatment for liver cirrhosis?
Initial stage, hepatology doctor may manage patients with medications, diet and lifestyle modifications to treat the underlying condition which caused liver cirrhosis in the first place. Doing this avoids further liver damage, and the deterioration can be slowed.
A
liver transplant is currently the best treatment for progressive cirrhosis and severe damage. This major operation involves extracting the damaged liver and replacing it with a healthy normal liver from a donor.
What are the symptoms of cirrhosis of the liver?
The symptoms of liver cirrhosis could be non-specific, i.e., the symptoms may not denote a defective liver. In a few cases, the patient could be asymptomatic (shows no symptoms at all). Some of the common signs and symptoms of liver cirrhosis include:
- Nausea & Fatigue
- Itchy skin
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Swelling in your legs
- Testicular atrophy in men
- Breast enlargement in men
- Easy bleeding and bruising
- Redness in the palms of the hands
- Spider-like blood vessels on the skin
- Confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech
- Ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen)
- Jaundice (yellow discolouration in the skin and eyes)
How does liver cirrhosis cause hyperglycemia (high blood sugar)?
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is higher in patients with liver diseases such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, chronic viral hepatitis, cirrhosis etc. Various mechanisms influence the pathogenic link between the presence of T2DM and the severity of the liver injury. Some of them include the following:
- Gut microbiota
- HCV infection
- Hepatic inflammation
- Obesity-associated insulin resistance
- Hepatic fat accumulation
- Reactive oxygen species
Gut microbiota: These are the bacterial organisms living in the gut. They can produce bacterial lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, contributing to low-grade inflammation in obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, diabetes and cardiovascular disease. A higher prevalence of bacteria in small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is seen in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
HCV infection: HCV infection can directly or indirectly alter glucose homeostasis. Intrahepatic inflammation results in insulin resistance & higher risk of developing T2DM.
Obesity-associated insulin resistance: Visceral adiposity (fat tissue) and chronic hepatic inflammation are intertwined and associated with chronic systemic inflammation in the pre-diabetic state.
Hepatic fat accumulation: Studies show that liver fat content, much more strongly than visceral fat, determines insulin sensitivity in humans and supports a direct and significant role of fatty liver in insulin resistance.
Reactive oxygen species: Oxidative stress has been long proposed as the root cause underlying the development of insulin, impaired glucose tolerance and T2DM. In both non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and experimental steatohepatitis, oxidative stress is increased, leading to T2DM.
Can cirrhosis of the liver be reversed?
No, cirrhosis of the liver cannot be reversed, but the damage to the body (and liver) may be slowed down if the steps are taken to treat the underlying disease and condition. In case of early detection, and the cause is treated, further damage can be stopped and, rarely, reversed.
What causes cirrhosis of the liver?
There are various causative factors of liver cirrhosis. the most common of them are:
- Alcoholism
- Obesity
- Poor diet/lifestyle
- Viral infections such as hepatitis B and C
- Underlying autoimmune disease
- Certain drugs, medications, and chemicals
- Genetics factor
Can liver function tests be normal with cirrhosis?
Yes. Liver function tests can be normal with cirrhosis and even at many stages of liver disease. This is why a usual series of tests, blood and urine tests, may be prescribed by the treating physician to detect the signs of liver impairment. Often, a liver biopsy could be the only way to confirm a diagnosis of cirrhosis.
How long can you live with cirrhosis of the liver?
Life expectancy in people with stage 3 cirrhosis of the liver is about 10 to 12 years (compensated cirrhosis). In liver cirrhosis, the deterioration of the fibrotic liver to the cirrhotic liver could take many years. This is why early diagnosis of liver impairment is of utmost important.
Can you come back from liver damage?
Yes. You can come back from liver cirrhosis. There are cases of people recovering from liver failure with appropriate treatment and transplantation. With permanent abstinence from alcohol (if alcoholism is the causative factor), the treated people can go back to their daily activities within six months. In the case of the
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) pathway, taking steps to remove fat build-up in the liver can help.
How do I know if my fatty liver is getting worse?
If the patient has been diagnosed with fatty liver disease, they must let the treating
gastroenterologist know about the increasing severity and intensity of the disease symptoms. These symptoms include loss of appetite, fatigue, weight loss, weakness, fluid retention, bleeding etc.
How alcohol causes cirrhosis of the liver?
Alcoholic liver cirrhosis is caused by frequent and heavy alcohol usage.
- When the liver tissue begins to scar, the liver no longer functions as effectively as it once did.
- Consequently, the body cannot create enough proteins or filter poisons from the blood as efficiently as it can.
- Cirrhosis of the liver may be caused by various factors. Alcoholic liver cirrhosis, on the other hand, is directly tied to alcohol use.
Can smoking cause liver cirrhosis?
Yes. Smoking can cause liver cirrhosis. Research from 2020 demonstrated the association between smoking cigarettes and the progression of fibrosis in chronic liver diseases (CLD), such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and primary biliary cholangitis.
- Developed liver cancer in patients with chronic hepatitis B or C virus infection.
- Lung function is affected, which can preclude liver transplantation.
- Post liver transplantation, smoking can cause various adverse effects such as:
- Increased risk of liver cancer
- Vascular complications (blood vessel problems) etc.
Is omega-3 good for liver cirrhosis?
Yes. Omega-3 fatty acids are good for liver cirrhosis.
- Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are the "essential fatty acids" as humans cannot synthesize them; therefore, they must be obtained through diet.
- Research suggested that it might be beneficial in reducing liver triglyceride levels, but not in other features of steatohepatitis.
Is ginger good for liver cirrhosis?
Yes. Ginger is considered a good supplement for stalling liver cirrhosis. Reduction of liver damage, cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, and inflammation in people with non-alcoholic liver disease can be seen with the ginger present in everyday diet. Ginger is generally considered safe. Gingerols and schools in ginger root help inhibit inflammation and protect against cellular damage.
Is curd good for liver cirrhosis?
Yes. Curd is good for liver cirrhosis. A 2018 study demonstrated that curd consumption improved liver features in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The various benefits include:
- Curd could improve hyperglycaemia condition by modifying the gut flora, increasing faecal pH, and reducing intestinal toxinsproduction.
- Beneficial effects of curd on fatty liver could result from the reversal of dysbiosis (imbalance in the gut-microbial community associated with liver disease).
Who is the best liver specialist doctor in Hyderabad for liver cirrhosis treatment?
The liver specialist doctor at PACE Hospitals, who are among the top 10 hepatologist in Hyderabad, with vast expertise in handling severe and critical cases of liver diseases with the help of the latest treatment modalities, are among the best liver specialist doctor in Hyderabad for liver cirrhosis treatment.
How do I book an appointment for liver cirrhosis treatment in Hyderabad?
If you are looking for a liver cirrhosis doctor near me or in the vicinity of Madhapur, Kondapur, Hitec city, Gachibowli, Kukatpally, or KPHB for liver cirrhosis treatment, then opt booking appointment with the top liver specialist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals by filling out an appointment form online or calling directly on 04048486868. The team of multidisciplinary team for liver disease treatment has a wide-range of experience in treating liver cirrhosis with a high success rate.
Are liver cirrhosis treatment covered by insurance in India?
Yes, liver cirrhosis treatment is covered by insurance in Hyderabad, India. Person need to cross-check with their respective health insurance companies and corporates about the partial or complete cashless treatment eligibility to get the benefits.