Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment in Hyderabad, India
At PACE Hospitals, we understand that an ectopic pregnancy can be a distressing and potentially life-threatening condition for any woman. That's why we are committed to providing compassionate, personalized care to every patient who comes to us for ectopic pregnancy treatment. We have team of the Best Gynecologist in Hyderabad, India for ectopic pregnancy treatment, using the latest diagnostic tools and techniques to quickly and accurately diagnose ectopic pregnancies, and we work closely with our patients to develop individualized treatment plans that meet their unique needs.
Request an Appointment for Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment - appointment
Why to choose PACE Hospitals for Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment?
Our goal is always to provide the most effective and minimally invasive treatment for ruptured or unruptured ectopic pregnancy, while also ensuring the best possible outcomes for our patients' reproductive health. We believe that every woman deserves access to high-quality, comprehensive healthcare, and we are dedicated to providing that care with the utmost respect, dignity, and compassion.
If you or someone you love has been diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, we encourage you to reach out to PACE Hospitals today to learn more about how we can help.
200+ Laparoscopic Ectopic Pregnancy Surgery
Precision Treatment with 99.9% success rate
Team of the Best Gynecologist with 30+ years of expertise
All insurance accepted with No-cost EMI option
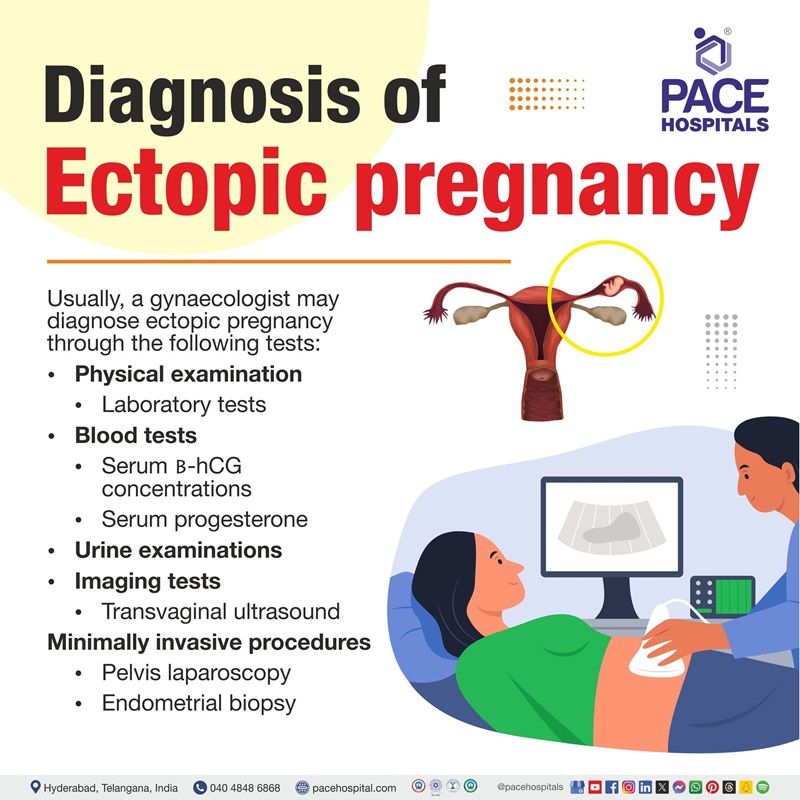
Diagnostic Evaluation of Ectopic Pregnancy
The nursing diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy may be challenging as the symptoms may often be mistaken for gastroenteritis (inflammation of the stomach and intestines), normal pregnancy, irritable bowel syndrome (common condition that affects the digestive system), miscarriage, or even appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix). However, early diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy plays a vital role in treating it.
The gynecologist evaluates the following before selecting the appropriate tests to diagnose ectopic pregnancy:
🔷 The presented signs and symptoms
Women with ectopic pregnancy may present with pelvic pain and vaginal bleeding in the first trimester (Each trimester is about 13 weeks or three months long) of pregnancy. These symptoms are not specific to pregnancy and may be associated with other complications, such as miscarriage.
Hence, gynaecologists always consider the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy in any woman of reproductive age who appears with any of the symptoms. They are also wary of pregnancy in any woman who exhibits abdominal or pelvic symptoms.
🔷 Age, family history, and general health of the suspected patient
The gynaecologist considers the age, family history, and general health of the suspected patient because in older age women, fallopian tubes likely have relatively decreased function, which may have the risk of getting tubal ectopic pregnancy. During the gynaecological assessment, the doctor may ask about the patient's family history and general health to evaluate the potential risks and guide diagnostic testing.
🔷 Medical and medication history
A gynaecologist may ask the patient about the patient's medical history, such as if a patient has had a prior confirmed history of ectopic pregnancy, known fallopian tube damage (due to the history of pelvic inflammatory disease, tubal surgery, obstruction, pelvic infections or achieved pregnancy through the use of infertility treatment.
A gynaecologist may want to know the medication history of the patient (e.g., fertility drugs or contraceptives) to find drugs that are increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy or interfering with treatment options.
🔷 The results of previous medical tests
A gynaecologist may ask about the reports of earlier medical tests to get valuable information to confirm the presence of ectopic pregnancy in a patient and to choose the proper diagnosis and treatment.
Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis
Usually, a gynaecologist can diagnose ectopic pregnancy through the following:
- Physical examination
- Laboratory blood tests
- Urine examinations
- Imaging tests
- Minimally invasive procedures
✅ Physical Examination
A physical exam alone is not enough for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy, but some physical findings may be predictive for ectopic pregnancy, such as:
- Presence of peritoneal signs (redness and swelling of the lining of the belly or abdomen).
- Cervical motion tenderness (severe feeling of pain or soreness of the cervix when moving it with the fingers during a bimanual examination; usually, it indicates peritoneal infection)
- Unilateral or bilateral abdominal or pelvic tenderness: (Pain on one or both sides of the abdomen or pelvis region, usually much worse on the affected side).
Pelvic examination may be preferred when ultrasonography and beta-human chorionic gonadotropin testing is unavailable, or the results are inconclusive. Speculum examination might be indicated in those presenting with severe bleeding or hypotension (low blood pressure), as removal of obstructing endocervical products may be a crucial resuscitative measure.
✅ Laboratory tests
Serum β-hCG concentrations (ectopic pregnancy test)
The pregnancy of unknown locations (PULs) has been predicted using the changes in human chorionic gonadotropin in blood (serum -hCG) concentrations over time.
- Serum hCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin is produced during pregnancy. The blood level of hCG, a hormone the placenta generates, should double every 48 hours in a normal pregnancy.
- The absence of these increased levels could be an early pregnancy failure.
- Rapid drops in -hCG levels, typically by 21-35% or more, are suggestive of an ectopic pregnancy that is ending or a spontaneous abortion.
Serum progesterone
Although no precise readings distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from an intrauterine pregnancy, the progesterone levels in blood are potentially helpful in finding pregnancies of unknown locations.
- A viable intrauterine pregnancy has serum progesterone values of more than 50 ng/ml.
- Although progesterone testing cannot clearly distinguish between an ectopic pregnancy and a failing intrauterine pregnancy, sometimes a low progesterone level (5 ng/ml) can be used to differentiate between:
- 'Low-risk' patients who can be managed conservatively with a pregnancy of unknown locations and
- 'at-risk' patients who require definitive treatment.
Urine examinations
β-hCG hormone can be detected in the blood and urine as early as one week before an expected menstrual period. Serum testing can detect levels as low as 5 IU/L, while urine testing can detect levels as low as 20-50 IU/L.
If the patient did not have a positive pregnancy test, then gynaecologist may take a urine sample to do the pregnancy test. If the test is negative, then the patient is very unlikely to have symptoms due to an ectopic pregnancy.
✅ Imaging Tests
Transvaginal ultrasonography
- Although it is usually used to confirm an intrauterine pregnancy (a normal, healthy pregnancy), ultrasonography is perhaps the most crucial method for diagnosing an extrauterine pregnancy.
- Transvaginal ultrasonography uses a tiny probe that can be introduced into the vagina.
- The probe produces sound waves which radiate through the abdomen and reflect back.
- A monitor displays a close-up image of the reproductive system due to the probe's reflected sound waves.
- Even though it can occasionally be challenging to detect, this will frequently indicate whether a fertilized egg has established itself in one of the fallopian tubes.
- At 5.5 weeks gestational age, a transvaginal ultrasound could correctly identify the intrauterine gestation sac in a healthy normal pregnancy (intrauterine pregnancy).
- If a collection of fluid in the endometrial cavity (pseudosac) is seen, it could be due to an ectopic pregnancy.
- After six weeks of gestation, further embryonic details, such as the yolk sac and heart activity, should be plainly seen.
In early pregnancy scanning, the gynaecologist/sonographer can distinguish between a pseudosac and an empty early intrauterine sac.
✅ Minimally invasive procedures
Diagnostic laparoscopy
A diagnostic laparoscopy may be performed if an ectopic pregnancy is suspected and an ultrasound is unclear.
- Many gynaecologists consider this to be the "gold standard" study in ectopic pregnancy. Delay in diagnostic laparoscopy has been identified as a risk factor in fatal situations.
- A laparoscope (a tiny telescope) is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small incision at the navel. If necessary, the ectopic pregnancy is usually removed by inserting special equipment through the laparoscope or by small incisions above the pubic area.
Endometrial biopsy (Dilation and Curettage in ectopic pregnancy)
In some cases of pregnancy of unknown locations, an endometrial biopsy may be performed to determine the presence or absence of chorionic villi.
- In the case of pregnancy failure or miscarriage or ineffective attachment of the embryo to the uterine wall, the surgical gynaecologist may gently scrape off the uterine lining.
- This operation, known as a dilation and curettage, is a form of endometrial biopsy and can be performed under anaesthesia.
- The pathologists examine the tissues retrieved from the uterus. If they detect the pregnant tissue in the sample, the chances of an ectopic pregnancy are pretty low.
- A double pregnancy, with one in the uterus and the other in the fallopian tube, can happen very rarely (called a heterotopic pregnancy).
- If there is no indication of pregnant tissue or hCG levels do not fall fast after a dilation and curettage, an ectopic pregnancy must be investigated.
Medical Treatment (Medical Management of Ectopic Pregnancy)
In some cases, gynaecologists give medical treatment for ectopic pregnancy. The fallopian tube will not be removed in these cases. A folic acid antagonist will be provided as an injection to prevent the ectopic pregnancy from growing, and it gradually disappears the ectopic pregnancy. Close follow-up with measurements of serum hCG will be required. A second course of treatment might be needed for some patients.
Our Team
At PACE Hospitals, we are proud to have some of the best doctors for ectopic pregnancy surgery in Hyderabad, India. Our team of experienced obstetricians & gynecologists who are experts in the latest surgical techniques for ectopic pregnancy, including laparoscopic surgery, using the latest diagnostic tools and techniques to quickly and accurately diagnose ectopic pregnancies, and they are dedicated to providing the most effective and minimally invasive treatment possible.
Dr. Mugdha Bandawar
Obstetrician, Gynecologist, Laparoscopic Surgeon and Infertility Consultant
Dr. Mugdha Bandawar
10+ years of exp.
Obstetrician, Gynecologist, Laparoscopic Surgeon and Infertility Consultant
Differential Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
The following are the essential differential diagnoses with ectopic pregnancies:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease: It's an infection in the female upper reproductive organs - ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes.
- Bleeding corpus luteal cyst: It is an ovarian cyst formed after ovulation, often resulting from spontaneous bleeding into a corpus luteum cyst.
- Torsion of an ovarian cyst: Partial or complete twisting of ovaries around the ligaments
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix
- Ovarian cyst rupture: Rupturing of the ovarian cyst (trigger severe pain and bleeding)
- Threatened miscarriage: Mild vaginal bleeding during pregnancy that could end in miscarriage.
- Incomplete miscarriage: It is a part of the pregnancy that remains in the uterus.
- Ureteral calculi: Kidney stones in one of the ureters
Surgical Considerations of ob-gyn surgeon before planning surgery
An ob-gyn surgeon considers the surgery as first-line treatment for ectopic pregnancy when some specific conditions aren't met for other treatment options, such as
- Beta hCG more than 5000
- Significant pain and hemoperitoneum (internal bleeding)
- Sac more than 35 mm
- Cardiac activity present
- Failure of expectant or medical management
- Urgent requirement for intervention due to the clinical status of the patient
- The patient's ability to take medicine properly is doubtful
The surgeon chooses the type of surgical approach based on the following factors:
- Clinical status of the patient
- The patient desires for future fertility
- Extent of tubal damage
- Condition of contralateral tube (health and function of the both fallopian tubes)
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
Treatment of the ectopic pregnancy cannot lead to the birth of the baby; all treatment approaches aims to end the pregnancy to reduce the risks to the woman's own health. Options of treatment may vary based on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and the results of diagnostic tests.
The treatment options may depend upon the following:
- How many weeks pregnant a patient is
- Symptoms and clinical condition
- Patient general health
- Results of scan
- Levels of βhCG
- Patient personal views and expectations (discussion about future pregnancy plan)
Treatment options for ectopic pregnancy may include follows:
- Expectant management
- Medical treatment
- Surgical treatment

✅ Expectant management (wait and see)
Expectant management refers to close monitoring or watchful waiting by medical professionals rather than immediate treatment because, sometimes, ectopic pregnancies may end on their own, like a miscarriage. However, it is not an option for all women. It may be preferred in the early stages only and when the patient has only a few or no symptoms.
The expectant management mainly depends on the pregnancy hormone levels, with higher serum βhCG levels linked with a lower chance of success. It is less commonly used than medical management, which is preferred for asymptomatic, vitally stable women who wish to avoid surgical approaches.
✅ Medical treatment (medical management of ectopic pregnancy)
In some cases, gynaecologists give medical treatment for ectopic pregnancy. The fallopian tube will not be removed in these cases. A folic acid antagonist will be provided as an injection to prevent the ectopic pregnancy from growing, and it gradually disappears the ectopic pregnancy. Close follow-up with measurements of serum hCG will be required. A second course of treatment might be needed for some patients.
✅ Surgical treatment of ectopic pregnancy (ectopic pregnancy surgery)
Seven in every 100 women with ectopic pregnancy may need surgery even after medical treatment.
Salpingectomy
It involves segmental or complete removal of the fallopian tube and is preferred when the tube is ruptured and damaged. Salpingectomy is a good treatment option because it minimizes the risk of ectopic mass persistence and does not seem to reduce future fertility.
- Unilateral salpingectomy: It involves the removal of one fallopian tube. A woman can become pregnant even with one fallopian tube.
- Bilateral salpingectomy: It involves the removal of both fallopian tubes. It should be considered a permanent form of birth control approach for people who do not desire future pregnancies.
To increase the chances of a successful future pregnancy and decrease the risk of another ectopic pregnancy, doctors may suggest removing the affected fallopian tube through salpingectomy.
Salpingotomy
It is also called neosalpingostomy, is a surgical creation of an opening in the fallopian tube without removing the tube itself. It is often preferred in unruptured ectopic.
Salpingotomy might be considered in women with a history of fertility-reducing factors such as previous ectopic pregnancy, previous pelvic inflammatory disease, fallopian tube damage, and previous abdominal surgery. In cases such as a patient having only one fallopian tube or the other tube that does not look healthy, the chances of conceiving are already affected. Salpingotomy may be advised to remove the ectopic pregnancy without removing the tube. This condition may carry a high risk of future ectopic pregnancy, although patients still have a chance to get pregnant through the uterus in the future.
Gynaecologist does the follow-up blood tests to check the pregnancy hormone levels after salpingotomy. Some women may need further medical treatment or another surgery to remove the fallopian tube later if the pregnancy has not been completely removed during salpingotomy. Surgeons may perform salpingectomy or salpingotomy either by using two common approaches, such as:
Laparoscopy
It is the gold standard for the management of unstable or ruptured ectopic pregnancy. It is a minimally invasive surgical (keyhole) approach that involves the removal of the affected fallopian tube containing the ectopic pregnancy.
The hospital stay required for laparoscopy is about 1 to 2 days, and the recovery is about 2 to 4 weeks. It is preferred over an open approach due to its minimally invasive nature (small incisions). The decision to perform salpingotomy or salpingectomy may sometimes only be made during laparoscopy under anaesthetic.
Laparotomy
Laparotomy (open surgery) is performed through a larger cut in the lower abdomen, and it is appropriate to deal with some cases, such as when the tubal rupture has happened, or there are adhesions in the pelvis region. However, sometimes, if laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy is not available, in urgent situations where immediate intervention is required to save a life, a laparotomy will be acceptable. The patient may need to stay in the hospital for 2 to 4 days and takes about 4 to 6 weeks to recover.
Before laparoscopy, laparotomy with salpingectomy was the standard therapy for managing ectopic pregnancy. Now, laparoscopic salpingostomy without fallopian tube removal is the preferred surgical method because laparoscopy has tubal patency and future fertility rates similar to medical treatment.
The type of surgical approach may depend on the patient's wishes, expectations, or plans for a future pregnancy and what the surgeon finds during the diagnostic laparoscopy.
Non-Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
The treatment of non-tubal ectopic pregnancy will depend on the location of the pregnancy is growing (sites of ectopic pregnancy). The gynaecologist will discuss treatment options with the patient based on factors such as blood hormone levels, location of ectopic pregnancy, and ultrasound results.
- Cervical ectopic pregnancy: First line of treatment - medical (conservative management), Indications for surgery - failure of medical management or life-threatening bleeding
- Caesarean scar ectopic pregnancy: Surgical approach might be preferred over medical management, Counselling regarding high risk of morbidity and mortality
- Interstitial ectopic pregnancy: First line of treatment - medical (conservative) treatment, Indications for surgery - failure of medical management or life-threatening bleeding
- Cornual/ rudimentary horn ectopic pregnancy: Surgical approach is the preferred approach, Laparoscopic or open excision of rudimentary horn
- Ovarian ectopic pregnancy treatment: Surgical approach is preferred, Laparoscopic or open removal of gestational products
- Heterotropic pregnancy: Medical or conservative approach if intrauterine pregnancy is non-viable
- Abdominal ectopic pregnancy: Surgical approach is preferable, Early first-trimester abdominal pregnancy – laparoscopic approach, Advanced abdominal pregnancy – laparotomy.
After Ectopic Pregnancy Surgery
Sometimes, it is expected to have some side effects after ectopic pregnancy surgery, and the patient may experience pain, swelling, and bruising around the incision sites and have to stay in the hospital for a few days (based on the type of surgery).
A gynecologist may prescribe pain medication to manage the pain and advise resting and avoid strenuous activity for a few weeks. Most patients are usually able to resume normal activities within 4 to 6 weeks after their surgery.
Fertility Ability After Surgery
During future pregnancies, be alert for any signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy until the gynaecologist confirms the subsequent pregnancy is growing in the uterus.
If a patient has had an ectopic pregnancy, they may have a higher risk of experiencing another ectopic pregnancy in the future. The risk of ectopic pregnancy in the general woman is 1 in 50 to 80 women. The risk of another ectopic pregnancy is 1 in 10.
HCG levels in Ectopic Pregnancy vs Normal Pregnancy
Differences between β-HCG levels in ectopic pregnancy and normal pregnancy:
| Elements | Normal pregnancy | Ectopic pregnancy |
|---|---|---|
| β-HCG levels | Level of β-HCG always double | Level of β-HCG may not double, usually increase less |
| Percentage | 50-66% increase may be seen for every 48 hours | Rapid drop by 21-35% or more |
| Pattern | No fluctuations | Fluctuations in both directions |
| Increasing rate | Faster | Slower |
β-HCG levels in blood tests suggests normal to abnormal pregnancy, such as either ectopic or failed intrauterine pregnancy. The following table shows the differences in hCG levels between ectopic and normal pregnancy.
Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment Cost in Hyderabad, India
The cost of Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹18,000 to ₹85,000 (approximately US $215 – US $1,020).
The exact treatment cost varies depending on factors such as whether the ectopic pregnancy is tubal, ovarian, cervical, or abdominal, whether medical management or surgical intervention (laparoscopic salpingostomy or salpingectomy) is required, severity of internal bleeding, surgeon expertise, and the hospital facilities chosen — including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance approvals wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
- Medical Management with Medicine Prescribed by Gynecologist– ₹18,000 – ₹35,000 (US $215 – US $425)
- Laparoscopic Salpingostomy (Tube-Preserving) – ₹40,000 – ₹60,000 (US $480 – US $720)
- Laparoscopic Salpingectomy (Tube Removal) – ₹50,000 – ₹75,000 (US $600 – US $900)
- Emergency Surgery for Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy – ₹60,000 – ₹85,000 (US $720 – US $1,020)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Ectopic Pregnancy
What is ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. Some women with ectopic pregnancies may not experience any symptoms at all, especially in the early stages.
The symptoms of ectopic pregnancy can vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and the extent of tissue damage. Some common symptoms include abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, shoulder pain, lightheadedness or fainting, and rectal pressure. These symptoms can develop suddenly or gradually over time, and they may be mild or severe.
Which Is the best hospital for Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad is regarded as one of the most trusted centres for the diagnosis and management of ectopic pregnancies.
We have team of highly experienced gynecologists and laparoscopic surgeons provides rapid assessment, precise diagnosis, and advanced minimally invasive treatment to ensure patient safety and reproductive health preservation.
With state-of-the-art operating theatres, 24×7 emergency care, modern anesthesia support, and dedicated post-operative monitoring, PACE Hospitals ensures prompt, safe, and effective treatment — supported by cashless facility options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance processing for eligible patients.
What happens if an ectopic pregnancy isn't treated?
The uterine muscle is designed to stretch and grow as the pregnancy develops. But other reproductive organs, such as fallopian tubes, cannot grow that way; if the embryo implants in the fallopian tube, the thin layer of it stretches and eventually ruptures. If the ectopic pregnancy is not treated, it may result in a life-threatening haemorrhage (internal bleeding).
Who is at risk of an ectopic pregnancy?
There are many different risk factors which could increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy, such as:
- Smoking
- Endometriosis
- Tubal ligation
- Inflammation or infection due to STI's
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- IVF treatments or undergoing fertility treatments
- Late maternal age (35-44)
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
What precautions should be taken during ectopic pregnancy?
It is advisable to avoid sudden movements or lifting heavy objects until the gynaecologist consents to everyday activities. In case of vaginal bleeding, the gynaecologist may recommend the use of sanitary pads. Regular checkups with the ob-gyn are necessary to monitor any potential complications.
How much does Ectopic Pregnancy surgery cost in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of ectopic pregnancy treatment typically ranges from ₹20,000 to ₹78,000 and above (approximately US $240 – US $940), depending on:
- Type of treatment (medical vs surgical)
- Whether the ectopic pregnancy is ruptured or unruptured
- Level of internal bleeding and emergency care required
- Laparoscopic vs open surgery
- Surgeon expertise and OT requirements
- Duration of hospital stay (day-care / overnight / ICU if needed)
- Additional diagnostics such as ultrasound, β-hCG tests, or blood transfusion
For non-ruptured cases requiring medication, costs fall at the lower end; for emergency surgeries or complex presentations, the higher end applies.
After a gynecological evaluation and ultrasound assessment, our specialists will provide a personalised treatment plan and a detailed, transparent cost estimate based on your clinical condition.
Is surgery for ectopic pregnancy safe?
Laparoscopic surgery for ectopic pregnancy is generally considered safe and effective, with a low risk of complications. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are some risks and potential complications associated with ectopic pregnancy surgery.
Some of the potential risks and complications of ectopic pregnancy surgery include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Damage to surrounding organs
- Adhesions
- Future fertility
It's important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of ectopic pregnancy surgery with your gynecologist, and to ask any questions you may have. At PACE Hospitals, our team of experienced gynecologists is committed to providing safe, effective, and personalized care for women undergoing ectopic pregnancy surgery, and to helping ensure the best possible outcomes for their reproductive health.
When ectopic pregnancy symptoms start?
Ectopic pregnancy symptoms can start at any time during the first few weeks of pregnancy. In some cases, symptoms may begin as early as 4 to 8 weeks after the last menstrual period. However, it's important to note that some women with ectopic pregnancies may not experience any symptoms at all, especially in the early stages.
The symptoms of ectopic pregnancy can vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and the extent of tissue damage. Some common symptoms include Abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding
- Shoulder pain
- Lightheadedness or fainting
- Rectal pressure
These symptoms can develop suddenly or gradually over time, and they may be mild or severe. If you are experiencing any symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, it's important to seek medical attention right away. Ectopic pregnancies can be life-threatening if not treated promptly, and early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent serious complications.
How can doctors tell if I have an ectopic pregnancy?
If a patient of childbearing age experiences lower abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding, faints, or goes into shock, a gynaecologist may perform a pregnancy test to determine if they are pregnant. If the pregnancy test is positive, the obstetrician-gynaecologist will perform a transvaginal ultrasound to locate the pregnancy and a blood test to measure the pregnancy hormone levels. Based on the reports of these tests, doctors tell if the patient has an ectopic pregnancy.
Why ectopic pregnancy occurs?
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including:
- Damage to the fallopian tubes
- Abnormal fallopian tube shape or function
- Hormonal imbalances
- Previous ectopic pregnancies
- Use of certain fertility treatments
It's important to note that ectopic pregnancies can occur even in women who do not have any of these risk factors. If you are concerned about the risk of ectopic pregnancy or are experiencing symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention right away.
Does ultrasound detect ectopic pregnancy?
Yes, ultrasound is a common diagnostic tool used to detect ectopic pregnancies. An ultrasound can help to confirm the location of the pregnancy and determine whether it is ectopic.
Transvaginal ultrasound is often used to diagnose ectopic pregnancies, as it can provide a clearer image of the reproductive organs than a transabdominal ultrasound. During a transvaginal ultrasound, a small probe is inserted into the vagina to produce images of the reproductive organs.
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, a gynecologist may perform an ultrasound as early as 4 to 5 weeks after the last menstrual period. However, it's important to note that in some cases, an ectopic pregnancy may not be visible on an ultrasound until several weeks later.
Can a baby survive an ectopic pregnancy?
No, a baby cannot survive ectopic pregnancy because it is impossible for the egg to survive and grow into a baby due to the lack of a protective, nourishing environment like the uterus. Even if it grows, it may cause the trouble for the tube to rupture (burst), leading to internal bleeding, which can be a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate surgery.
What to expect after laparoscopic surgery for ectopic pregnancy?
After laparoscopic surgery for ectopic pregnancy, a patient can expect to spend a few hours in the recovery room, where your vital signs will be monitored, and you will be given pain medication as needed. After the surgery, the patient may experience some abdominal pain, cramping, and bloating, which can be managed with pain medication. Patient may also experience some vaginal bleeding or spotting for a few days after the surgery.
It's important to rest and avoid strenuous activity for a few days after the surgery to allow your body to heal. A gynecologist will provide you with specific instructions on how to care for yourself after the surgery, including when to resume normal activities, how to manage pain and discomfort, and when to follow up.





