Ankylosing Spondylitis Diagnosis, Treatment and Cost
PACE Hospitals provides expert care for ankylosing spondylitis in Hyderabad, India, focusing on early relief, long-term mobility, and improved quality of life. Backed by experienced ankylosing spondylitis specialist and doctors, our rheumatology team delivers precise diagnosis using advanced tests to assess disease activity and progression, ensuring a personalized and effective treatment plan for every patient.
Book an Appointment for Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment
Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment Appointment
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment?
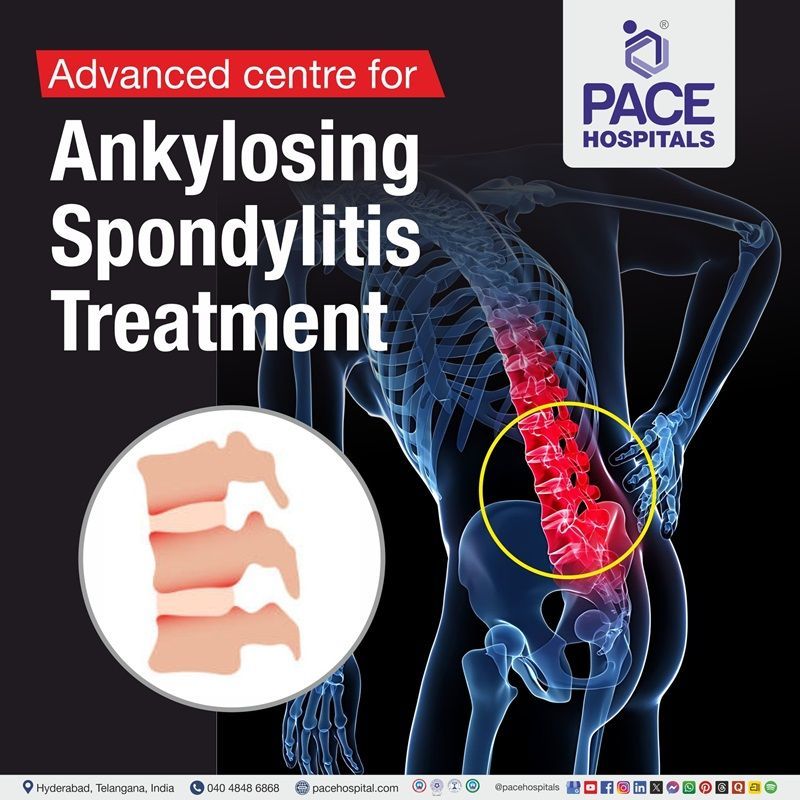
Advanced Diagnostic Facilities: Autoimmune Blood Tests, ANA Profile, Nailfold Capillaroscopy, PFT, HRCT Chest & Echocardiography
Best Rheumatologists & Ankylosing spondylitis specialist for ankylosing spondylitis management
Moderate to Severe Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment with Advanced Medical Therapy & Rehabilitation Support
Transparent Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment with Insurance & Cashless Options
Ankylosing Spondylitis Diagnosis
For diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis, a comprehensive evaluation of the entire body is suggested because of the disease nature and its potential involvement in multiple organ systems.
The following are the steps involved in diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis:
Initial evaluation
A rheumatologist may consider the following before selecting the appropriate tests:
- Medical history: A detailed medical and family history is important for the initial assessment of the patient. The patient may be asked about the symptoms, how long he/she been having the pain, the location where the pain is present, and what is making the pain worse and better. The patient also enquired about whether any family member had a history of back pain, joint pain, or arthritis.
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination is conducted. The joints, spine, pelvis, heels, and chest are examined. The patient is also examined for flexibility, watching how the patient moves and bends in different directions. The patient is also asked to breathe deeply to check for rib stiffness and inflammation.
Diagnostic evaluation
After gathering the above information, the rheumatologist may recommend for the following ankylosing spondylitis investigations:
Laboratory testing
- Complete blood count (CBC): Complete blood count does not directly diagnose ankylosing spondylitis, but may help in knowing the general health of the patient.
- C–reactive protein (CRP): Elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) is a marker of inflammation and is found in 50 to 70 percent of people with ankylosing spondylitis. Ankylosing spondylitis patients may have C-reactive protein levels ranging from greater than 6 mg/L (slightly elevated) to 20 to 30 mg/L.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): It is a blood test for detecting inflammation. In about one-third of the ankylosing spondylitis patients, there is a raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which is observable in exacerbations of the disease, but other conditions may also cause a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA): This gene variant is positive in 80 to 90 percent of ankylosing spondylitis patients, more so in the Caucasian population and African Americans. This antigen is also present in other inflammatory conditions of the intestines or joints.
Imaging studies
- X-ray: X-ray can show areas where the bone has been worn away by the condition. The vertebrae of the spine start to fuse together as the ligaments between them become calcified. A single anteroposterior pelvis X-ray is adequate to assess the sacroiliac joints. Ankylosing spondylitis is defined by inflammatory back pain.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This imaging technique is employed when X-rays are normal, but there is a clinical suspicion of axial spondyloarthritis (SpA). Magnetic resonance imaging may be particularly helpful in early disease, although it can be normal even in active axial spondyloarthritis, and the chronic changes of sacroiliitis are better observed on plain X-rays.
- Fat-suppressed short T1 inversion recovery (STIR) sequences generally demonstrate marrow oedema at the sacroiliac joints and vertebral corners. This marrow oedema is associated with later development of bony sclerosis or fusion, either of the sacroiliac joints or spine.
- Ultrasound: It is useful in detecting enthesitis, such as Achilles tendonitis. The role of ultrasound in the detection of sacroiliitis remains to be determined, as this modality is largely operator dependent. Colour Doppler ultrasound is used to diagnose early sacroiliitis and helps in monitoring response to therapy.
Genetic testing: This test may be performed to see if the patient is carrying the HLA-B27 gene variant, which is found in most individuals with ankylosing spondylitis. This test contributes towards a diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis, but this is not entirely reliable, as not everyone with the condition has this gene variant, and some people may have the gene variant, but there is no development of ankylosing spondylitis.
✅Ankylosing Spondylitis Differential Diagnosis
Several diseases share similarities with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), particularly in presenting symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Therefore, a careful differentiation is necessary for accurate diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis. The differential diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis includes the following:
- Mechanical low back pain: Ankylosing spondylitis and mechanical back pain can be distinguished on the basis of several factors, with the onset of symptoms being the key differentiating factor. Mechanical back pain occurs at any age, while ankylosing spondylitis presents before the age of 40. Mechanical back pain improves with rest, and morning stiffness is mild and short-lived.
- Lumbar spinal stenosis: It is a condition which is characterized by the spinal canal narrowing that leads to spinal cord compression. It presents symptoms of chronic back pain and morning stiffness similar to ankylosing spondylitis. It presents in older patients aged 60 and above, whereas ankylosing spondylitis occurs before the age of 40.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: It is another chronic inflammatory disorder of the joints, which often presents with progressive back pain and morning stiffness in patients aged 40 or younger, similar to ankylosing spondylitis. The prevalence of peripheral arthritis is higher in rheumatoid arthritis compared to ankylosing spondylitis. The presence of rheumatoid nodules that are pathognomonic for rheumatoid arthritis is another distinguishing feature of rheumatoid arthritis, which is not observed in ankylosing spondylitis patients.
- Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): It is a degenerative disorder which is characterized by ossification in the spine, primarily in the anterior longitudinal ligament, paravertebral tissues, and the peripheral aspect of the annulus fibrosus. It may present a history of postural changes and back pain similar to ankylosing spondylitis.
✅Treatment Goals of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Though there is no cure for ankylosing spondylitis, the treatment may help in managing the symptoms. The common goal of ankylosing spondylitis includes the following:
- The primary aim of ankylosing spondylitis is to alleviate pain and stiffness
- To preserve spine mobility and functional ability
- To ease the symptoms
- It helps in maintaining good posture, flexibility, and strength.
- To prevent the disease from progressing or slow down its progression.
- To prevent spine complications.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment
There is no cure for ankylosing spondylitis, and the treatment usually involves managing the symptoms and preventing further disease progression.
The following are the steps involved in the ankylosing spondylitis management:
Physiotherapy and exercise: Being physically active can improve posture and range of spinal movement and also prevent the spine from becoming stiff and painful. Physiotherapy is an important part of treating ankylosing spondylitis, and also for being physically active. Physiotherapists may advise the patient to maintain good posture and may help to offer hydrotherapy, which is also known as aquatic therapy. This involves exercises for the spine, hips and shoulders that are carried out in a special warm-water pool.
Drug therapy
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS): Pain killers and non–steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are usually the first choice of treatment for ankylosing spondylitis. These drugs for ankylosing spondylitis can improve spinal pain, peripheral joint pain, and function in ankylosing spondylitis.
- Biologic therapies
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors: These are drugs that inhibit tumor necrosis factor; they have revolutionized the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Introduction of these inhibitors has dramatically changed the management of autoimmune inflammatory disorders, including ankylosing spondylitis.
- Monoclonal antibody: This antibody treatment may be recommended to people with ankylosing spondylitis who do not respond to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or anti-medicine, or as an alternative to anti-tumor necrosis factor medicine.
- Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors: These are medications which are prescribed to ankylosing spondylitis patients who do not respond to anti-tumor necrosis factor. They work by blocking the enzymes that are proteins, which are utilized by the immune system to trigger inflammation.
- Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These drugs are an alternative often used to treat other types of arthritis. These may be prescribed for ankylosing spondylitis patients; they only benefit in treating joint pain and inflammation in areas of the body other than the spine.
- Corticosteroids: These drugs have a strong anti-inflammatory effect and can be taken as injections by patients with ankylosing spondylitis. These drugs may be injected directly into the joint when a particular joint is inflamed. It is recommended to limit corticosteroid injections to not more than 3 times in a year, with at least 3 months between injections in the same joint.
- Bisphosphonates: These drugs play potential, but they still not been fully established in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) because of their anti-osteoclastic and anti-inflammatory properties. They may help in reducing bone loss and in improving symptoms in some patients, particularly those with osteoporosis.
Surgery: The majority of patients with ankylosing spondylitis may not require surgical procedures. Sometimes joint replacement surgery is recommended for improving pain and movement in the affected joint when the joint has severely damaged. A hip replacement surgery is performed when the hips get damaged. Corrective surgeries are carried out in rare cases, may be required when the spine badly bents.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Prognosis
In ankylosing spondylitis, the symptoms and progression of the disease can vary widely from patient to patient. Ankylosing spondylitis progression may affect around 20 to 30 percent of patients. Patients who experience an earlier onset of ankylosing spondylitis are usually associated with poorer functional outcomes. It is important to know that severe physical disability is uncommon in ankylosing spondylitis patients.
The majority of the patients maintain a reasonable level of physical function and can lead active and fulfilling lives. There is an increased risk of disease mortality compared to the general population in patients with severe and long-standing disease, and the increased mortality is primarily attributed to cardiovascular complications.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment Cost in Hyderabad, India
The cost of Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) treatment in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹30,000 to ₹4,50,000 (approx. US $360 – US $5,420).
The exact cost of treatment varies depending on disease severity, duration of symptoms, degree of spinal and joint involvement, response to initial therapy, and whether advanced medications such as biologics are required. Other factors include frequency of follow-up visits, physiotherapy needs, diagnostic investigations, and hospital facilities — including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment
- Conservative Treatment (NSAIDs + Physiotherapy) – ₹30,000 – ₹70,000 (US $360 – US $840)
- Disease-Modifying Therapy (DMARDs) – ₹50,000 – ₹1,20,000 (US $600 – US $1,445)
- Biologic Therapy (Anti-TNF / IL-17 Inhibitors) – ₹1,20,000 – ₹4,50,000 (US $1,445 – US $5,420)
- Advanced Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation Programs – ₹40,000 – ₹1,00,000 (US $480 – US $1,205)
- Surgical Management for Severe Spinal Deformity or Hip Involvement – ₹2,50,000 – ₹4,50,000 (US $3,010 – US $5,420)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Ankylosing Spondylitis
Which is the most common joint affected in ankylosing spondylitis?
The sacroiliac joint, a joint that connects the lower spine to the pelvis, is the most common joint affected in ankylosing spondylitis. This condition causes inflammation of the spine and also affects other organs of the body, such as the eyes, lungs, kidneys, shoulders, knees, hips, heart, and ankles.
What is the hallmark of ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic, inflammatory disease which primarily affects the axial spine, manifesting a range of clinical signs and symptoms. Chronic back pain and progressive spinal stiffness are the hallmark features of this condition.
Which Is the best hospital for Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, is a trusted centre for the diagnosis and long-term management of ankylosing spondylitis and inflammatory spine disorders, offering comprehensive care for patients with chronic back pain, spinal stiffness, and reduced mobility.
We have experienced rheumatologists, orthopedic spine specialists, physiotherapists, pain management experts, and internal medicine specialists working together to manage ankylosing spondylitis using evidence-based treatment protocols focused on pain control, inflammation reduction, and preservation of spinal flexibility.
We are equipped with sophisticated technically sound instruments along with access to advanced imaging (X-ray, MRI), autoimmune testing, biologic therapy administration, structured physiotherapy units, and long-term follow-up programs, PACE Hospitals ensures safe, effective, and patient-centred AS care — supported by cashless insurance facilities, TPA corporate tie-ups, and smooth documentation assistance.
Which organs are affected by ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis which causes chronic inflammation of the spine and sacroiliac joints. It also affects other organs of the body, such as the eyes, lungs, kidneys, shoulders, knees, hips, heart, and ankles.
What are the complications of ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis is a complex disease which can affect different parts of the body. It can cause some serious complications affecting day-to-day life and leading to additional health problems. Joint damage, osteoporosis, spinal fractures, cardiovascular disease, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease are some of the complications of ankylosing spondylitis.
What Is the cost of Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of ankylosing spondylitis treatment typically ranges from ₹28,000 to ₹4,20,000 and above (approx. US $335 – US $5,060), making it a cost-effective option for specialised rheumatology care compared to others. However, the final cost depends on:
- Severity and stage of ankylosing spondylitis
- Requirement for long-term medications or biologic therapy
- Frequency of rheumatology consultations and monitoring
- Diagnostic tests (HLA-B27, ESR/CRP, MRI spine, X-rays)
- Physiotherapy and rehabilitation needs
- Presence of complications (hip involvement, spinal deformity)
- Hospitalisation, if required
For early-stage ankylosing spondylitis, costs remain toward the lower end with medications and physiotherapy, while advanced disease requiring biologics or surgical intervention may fall toward the higher range.
After a detailed rheumatology evaluation, imaging review, and functional assessment, our specialists provide a personalised treatment plan and transparent cost estimate, aligned with symptom control goals, mobility preservation, and long-term disease management.
What factors influence the survival rates for ankylosing spondylitis patients?
Disease severity, age of onset, comorbidities, and genetic factors are some of the factors which influence the survival rate in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients. Early disease onset and severe conditions, including hip joints or limited spinal mobility, are generally linked to a poorer prognosis. Cardiovascular complications are the major contributors to increased mortality, with a 35 to 60 percent higher risk of mortality from cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in patients with ankylosing spondylitis compared to the general population.
What is ankylosing spondylitis?
It is a type of arthritis which causes inflammation or swelling in the joints and ligaments of the spine and can also affect peripheral joints such as knees, ankles, and hips. Chronic back pain and spinal stiffness are the most common features.
What are the causes of ankylosing spondylitis?
There is no exact known cause of ankylosing spondylitis, but a few studies show that both genes and the environment may lead to the development of the disease. The HLA-B27 gene can increase the risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis.
What are the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis?
The symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis may come and go over time. Back pain, spinal stiffness, loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, fever, anemia, joint pain, organ damage, such as to the heart, lungs, and eyes, are some of the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis.
Who is at risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis?
Individuals who are young, with a family history of ankylosing spondylitis, individuals with HLA-B gene variants, and who are exposed to certain infections, toxins, and pollutants, individuals with underlying disease conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease and uveitis, are at increased risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis.
How common is ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis is common in individuals aged below 40, with approximately 80 percent of the patients experiencing their first symptoms before the age of 30, and less than 5 percent are diagnosed after the age of 45. It is more prevalent in men than women.
Can ankylosing spondylitis cause weight loss?
Yes, ankylosing spondylitis can cause loss of weight in patients. Due to chronic inflammation and fatigue, patients may experience a loss of appetite, and they decrease intake of food. Long term of decreased food intake can lead to subsequent weight loss.
How does ankylosing spondylitis affect daily life?
Ankylosing spondylitis can affect daily life through pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, particularly in the spine and hips. All this can make it difficult for the patient to perform daily routine activities such as getting dressed, lifting objects, standing up from a seat, nodding, or turning the head.
How does the duration of symptoms affect treatment outcomes in ankylosing spondylitis?
The duration of symptoms before diagnosis and treatment can affect the outcomes in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The longer symptom duration, because of delays in diagnosis, results in poorer functional outcomes and more structural damage, such as spinal fusion. When the disease is left untreated for many years, it can lead to permanent damage to the spine and joints.
Is ankylosing spondylitis a disability?
Based on the severity of the disease and impact on an individual's ability to work and perform daily activities, ankylosing spondylitis can be considered a disability. The Social Security Administration (SSA) recognizes in the United States recognizes ankylosing spondylitis under the category of spondyloarthropathy and may grant disability benefits when the condition severely limits a person's ability to work or engage in various activities.




