Inguinal Hernia - Symptoms, Types, Causes, Risk Factors, Complications & Prevention
Pace Hospitals
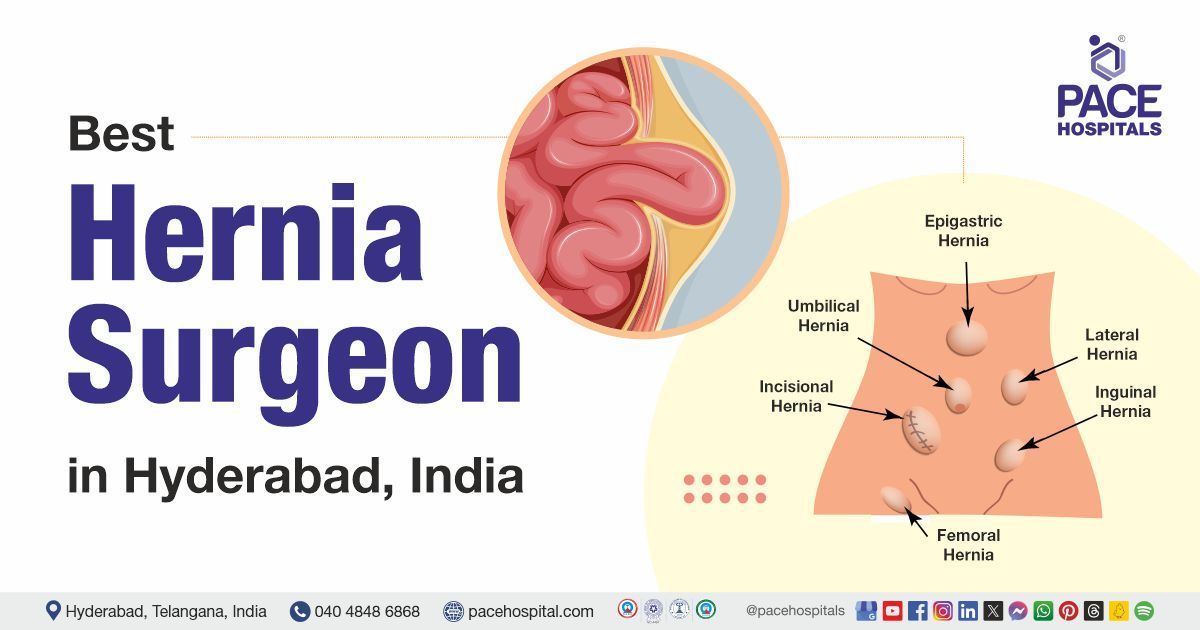
Inguinal Hernia definition / meaning
An inguinal hernia is often called a groin hernia due to the occurrence of a hernia in the groin area. An inguinal hernia is characterised by the bulging of abdominal contents through the weak regions of the abdominal wall. Groin hernias may happen at two passages, either through the inguinal or femoral canals. Hernia often bulges out through an opening that may be congenital (from birth) often called congenital inguinal hernia or due to muscle degeneration upon ageing.
Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia, and they are more common in men than in women.
Incidence of Inguinal hernia
75% of the abdominal wall hernias are inguinal hernias. A bimodal distribution of inguinal hernia incidence shows peaks around age 5 and after age 70.
Indirect hernias are the most familiar groin hernia in both males and females, accounting for two-thirds of all hernias. 90% of all inguinal hernias are seen in men, compared to 10% in women. Only 3% of inguinal hernias are femoral hernias, which are more common in women and makeup roughly 70% of all femoral hernias. Throughout an individual lifetime, less than 2% of women and almost 25% of men will develop an inguinal hernia.
Inguinal hernias occur frequently. According to researchers, around 27% of males and 3% of women will get an inguinal hernia at some point in their lives.
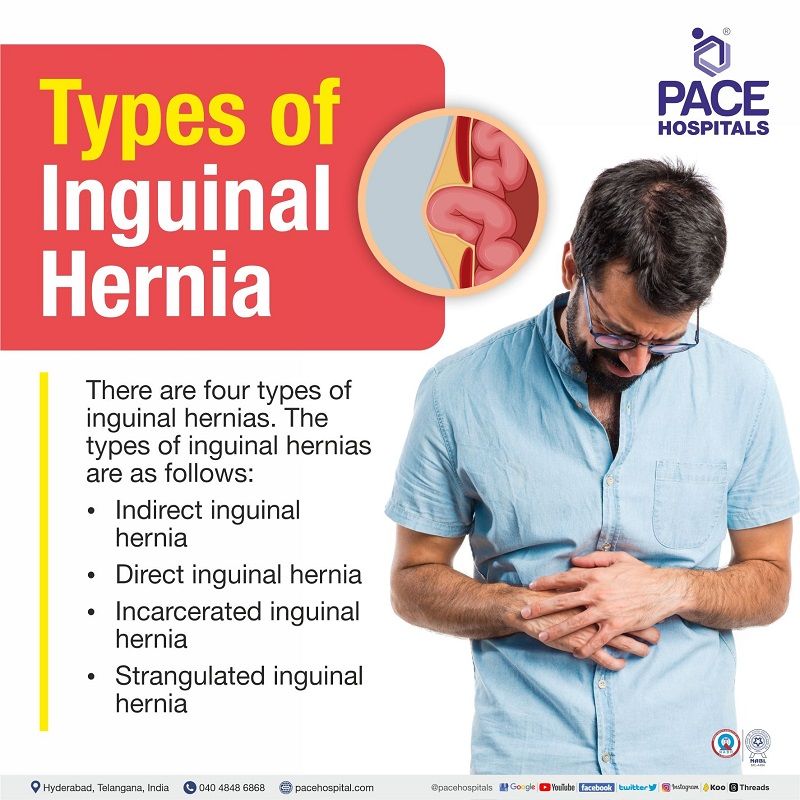
Inguinal hernia types
There are four types of inguinal hernias. They may occur in the left or right side of the groin regions and are often termed as left inguinal hernias or right inguinal hernias. The types of inguinal hernias are as follows:
- Indirect inguinal hernia
- Direct inguinal hernia
- Incarcerated inguinal hernia
- Strangulated inguinal hernia
- Indirect inguinal hernia: These are the most common and inborn type of hernias that might occur in males and females but are quite common in males. Usually, in males, the testicles start from the abdomen and descend to the groin area to reach the scrotum (a sac-like pouch that holds the testicles) through an opening; when this opening doesn't close at birth, a hernia forms. In females, this type of hernia (inguinal hernia female) is caused by the sliding of reproductive organs (sliding inguinal hernia) or small intestine into the groin area as a result of abdominal weakness.
- Direct inguinal hernia: Direct inguinal hernia is seen in adults, especially in men over ageing. On ageing, abdominal muscles weaken, leading to a direct inguinal hernia.
- Incarcerated inguinal hernia: When tissue in the groin becomes stuck, it results in an irreversible incarcerated inguinal hernia. This implies that it cannot be moved back to its original position. The blood supply to the tissue is intact in incarcerated inguinal hernias and tends to lead to strangulation (compression of blood or air-filled structures). It is common in all groin hernias, with an estimated frequency of 6%. In about 10% of cases, an inguinal hernia will become incarcerated, which can result in intestinal blockage, strangling, and infarction (obstruction of blood supply). The most dangerous and potentially fatal of these complications is strangling. Diagnosis is usually made by physical examination; the hernia sac content may vary in this condition.
- Strangulated inguinal hernia: Inguinal hernias that have been strangulated are more dangerous and occur when the blood supply to an intestine is interrupted. This condition frequently happens if there is a large amount of contents within the hernia and a small musculature opening.

Inguinal hernia symptoms
Inguinal or groin hernia signs and symptoms are as follows:
- Groin bulge (groin is the area between the thigh and lower abdomen).
- Discomfort, pain, or heaviness in the groin region.
- Scrotal bulge (scrotum is a sac-like pouch that holds testicles in males).
- Swelling in the scrotal region.
- Pain on coughing, exercising or bending.
- Aching or burning sensation at the hernial bulge.
Symptoms of strangulated inguinal hernia include:
- Fever.
- Severe pain on progression.
- Tachycardia (rapid heart rate).
- Nausea and vomiting.
NOTE: Inguinal hernia signs and symptoms may vary upon the type and severity of the hernia.

Inguinal hernia causes
The etiology of inguinal or groin hernias is as follows:
- A hole or weak area that exists from birth.
- Persistent coughing or sneezing.
- Long-term straining to urinate or defecate.
- Regular hard physical activities or heavy manual labour.
- Congenital variations in the collagen strength of the connective tissue.
- A gap or weak region left over from prior abdominal surgery.
- Multiple pregnancies and childbearing years.
- Jobs where standing is required for longer periods.
- Obesity, which may cause intra-abdominal pressure.
- Tissue deterioration on ageing.

Inguinal hernia risk factors
The risk factors for inguinal hernia are as follows:
- Heredity or family history: There is a genetic component regarding inguinal hernias, and the genes associated with inguinal hernia susceptibility have also been linked to connective tissue homeostasis.
- Male gender: Inguinal hernia is more common in men because they have a broader inguinal canal than women, so they are more likely to develop this type of hernia.
- Obesity or overweight: Obesity has been theorised to increase the risk of inguinal hernia through raising abdominal pressure.
- Chronic constipation: Constipated people who strain may have increased abdominal pressure and an increased risk of hernia formation.
- Cystic fibrosis (genetic disorder that affects the pancreas, lungs and digestive tract): A study has stated that there is a risk for hernia, hydrocele, and undescended testis in males with cystic fibrosis, and to a lesser extent in male siblings and fathers. This increased risk may be associated with the genes involved in cystic fibrosis and leads to the reflection of altered embryogenesis of the Wolffian-derived structures (duct from where the epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct and seminal vesicles of males will develop).
- Chronic cough: Severe or persistent coughing increases the pressure on the walls of abdominal muscles and might cause an inguinal hernia.
- Premature birth or premature infants: The inguinal canal from where the testes descend from the abdomen into the scrotum fails to close at birth, resulting in inguinal hernias (inguinal scrotal hernia). This condition is common in premature infants and is also seen in approximately 1 to 5% of children.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy increases intra-abdominal pressure due to the enlargement of the gravid uterus, which might cause a hernia. In addition, hormonal changes may lead to hernia formation in pregnant women.
- Men with a history of prostatectomy (surgical removal of the prostate gland): Men who have undergone surgery for prostatectomy, i.e., robotic-assisted radial prostatectomy, have a risk of developing an inguinal hernia due to incontinence.
- Ageing: In adults on ageing, there might be a chance to develop an inguinal hernia. On ageing, the connective tissues and muscles of the lower abdominal wall across the inguinal canal get weaker and tend to develop the inguinal hernia.
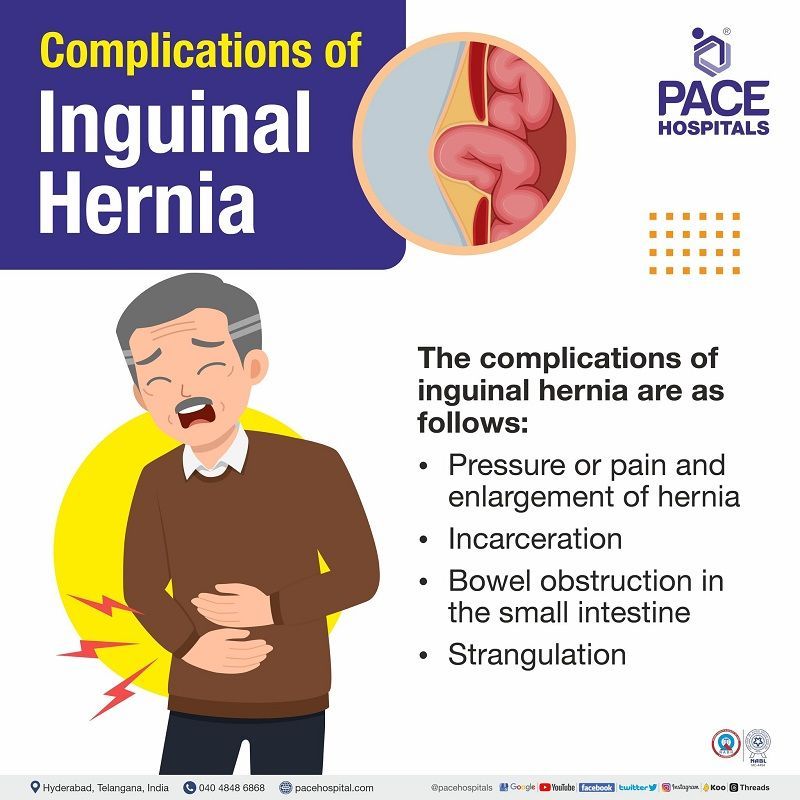
Inguinal hernia complications
The complications of inguinal hernia are as follows:
- Pressure or pain and enlargement of hernia: If the hernia is left untreated, it will become larger and create pressure. In men, this condition results in bulging down into the scrotum, which results in pain and swelling.
- Incarceration: Occurs when the hernia's protrusion (and its contents) become lodged in a weak spot of the abdominal wall. It may result in bowel obstruction, accompanied by excruciating pain, nausea, vomiting, and the inability to urinate.
- Bowel obstruction in the small intestine: Herniation of the small intestine becomes trapped and pinched, which may cause the blockage. This condition stops the individual from being able to poop or pass the gas, resulting in severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
- Strangulation: The blood flow to a strangulated hernia has been interrupted. As a result, the tissue may become inflamed, infected and eventually die (tissue necrosis). Strangulation is a medical emergency and requires immediate medical or surgical treatment.
Inguinal hernia diagnosis
Diagnosis for inguinal or groin hernias is as follows:
- Thorough history taking (family, medical or medication histories) of an individual.
- Physical examination
- Ultrasonography (USG)
- Computed tomography (CT scan)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan)
Inguinal hernia treatment
Inguinal or groin hernia treatment includes:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Wait and watch approach
Surgical approaches
- Open inguinal herniorrhaphy
- Tissue Repairs
- Prosthetic Repairs
- Laparoscopic inguinal herniorrhaphy
- Transversus Abdominis Muscle Release (TAR)
- Transabdominal Preperitoneal Procedure (TAPP)
- Total Extraperitoneal Procedure (TEP)
- Extended totally extraperitoneal repair (eTEP)
- Extended Transversus Abdominis Muscle Release (eTAR)

Inguinal hernia prevention
Indirect hernias (from birth) can’t be prevented. However, the direct inguinal or groin hernias may be prevented by the following measures:
- Learn proper lifting techniques for heavy goods
- Avoid constipation and cure it when necessary to avoid straining during bowel movements
- If the person has a chronic cough, treatment is needed for cough
- Get treated for an enlarged prostate who struggles to urinate
- Lose the additional weight and maintain a healthy weight
- Inguinal hernia exercises are needed to build core strength for the fitness of abdominal muscles
- Avoid or quit smoking. Get the doctor's cessation plan by talking to him
- Take a healthy diet which is rich in fibre
- Avoid lifting heavy objects
Direct vs Indirect inguinal hernia | Difference between direct and indirect inguinal hernia
On ageing, abdominal muscles get weak and tend to cause direct inguinal hernia. In indirect inguinal hernias, problems are associated with the abdominal wall since birth.
| Characteristics | Direct inguinal hernia | Indirect inguinal hernia |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Groin pain, bulging, burning sensation, enlarged or swollen scrotum (in males), etc | Symptoms are the same as direct inguinal hernia |
| Prevalence | Commonly occurs in adults | Commonly seen in infants and children |
| Causes | Ageing, stress or strain, weakened abdominal muscles, etc. | Failure of inguinal canal closure at birth. |
| Diagnosis and treatment | Diagnosis includes a physical examination, USG, CT scan, and MRI scan. Treatment includes a wait-and-watch approach, open surgery and laparoscopic surgeries. | Diagnosis and treatment procedures are the same as direct inguinal hernia. |
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868