Spyglass Cholangioscopy - Procedure Indications & Cost
Dept. of Gastroenterology at PACE Hospitals, is equipped with advanced Third-Space Endoscopy, The SpyGlass® Direct Visualization System and Laparoscopic surgery equipment to perform complex and supra-major precancerous and cancerous conditions of gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Our team of the Top Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad, India; are having extensive experience in performing endoscopic Resection and third space endoscopy techniques such as endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), and submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection (STER) to treat conditions of gastrointestinal system.
Request Appointment for Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure
Spyglass Cholangioscopy - appointment
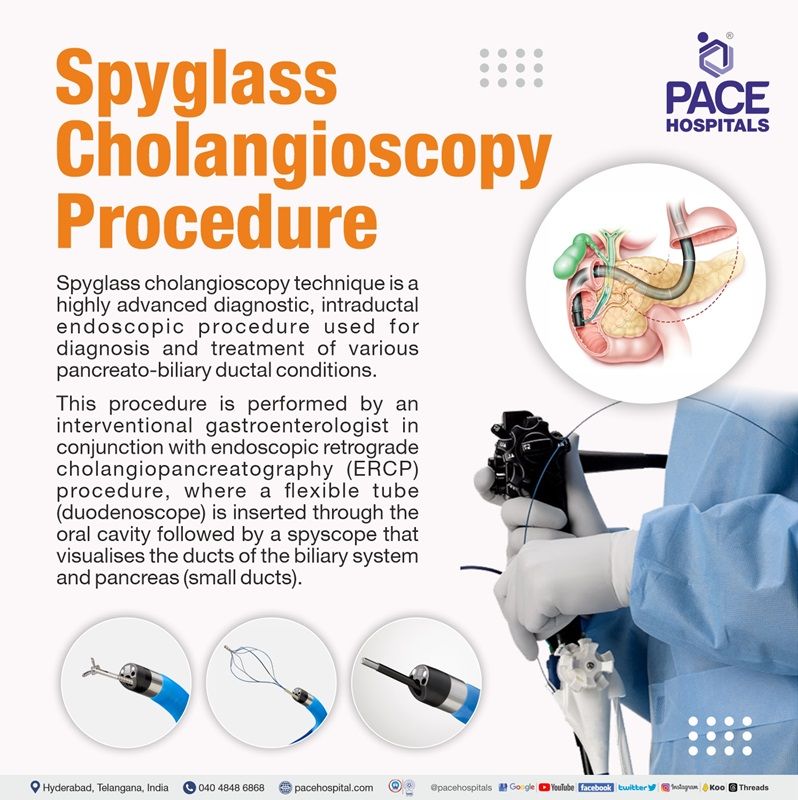
What is Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure?
Spyglass cholangioscopy technique is a highly advanced diagnostic, intraductal endoscopic procedure used for direct visualisation (diagnosis) and treatment of various pancreato-biliary ductal conditions. This procedure is performed by an interventional gastroenterologist in conjunction with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedure, also known as ERCP spyglass cholangioscopy, where a flexible tube (duodenoscope) is inserted through the oral cavity followed by a spyscope that visualises the ducts of the biliary system and pancreas (small ducts).
The spyglass cholangioscopy procedure will be done with the help of a standard endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) scope. Spyglass cholangioscopy procedure, a single-operator cholangioscopy technology (SpyScope catheter 10F is attached to the duodenoscope using a silastic belt) used by experienced, skilled
interventional gastroenterologists or gastro endoscopists that address the constraints of traditional 'mother-baby' cholangioscopy, where two endoscopists are required to operate (one for duodenoscope and other for cholangioscope).
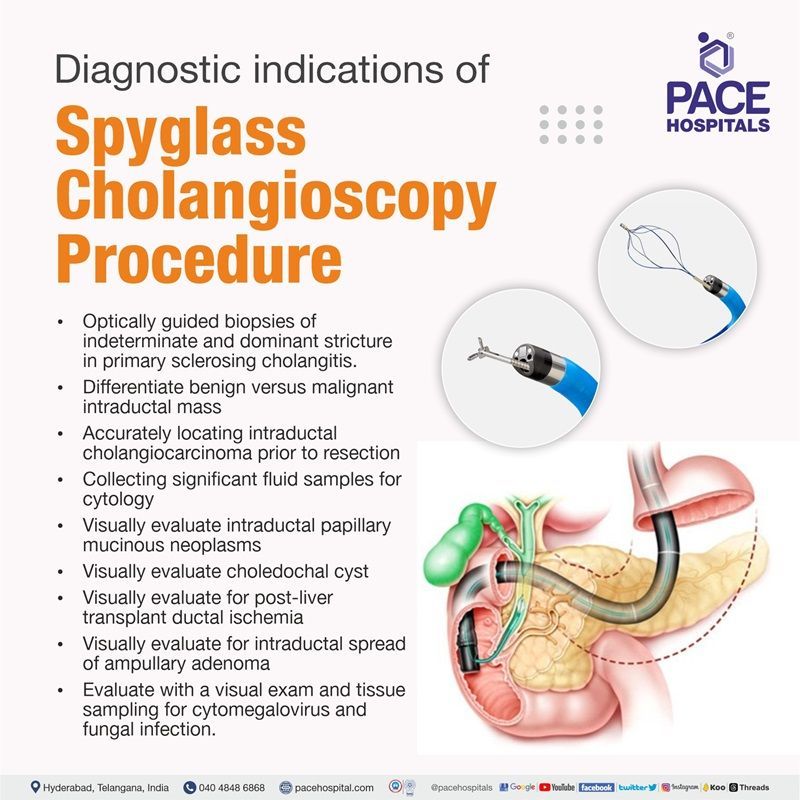
Indications for Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure
Spyglass cholangioscopy procedure is indicated to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting the pancreato-biliary ducts.
Diagnostic:
In comparison to standard imaging and ERCP techniques, direct vision of the ducts by various endoscopic modalities such as Spyglass has been proven to differentiate and diagnose lesions more precisely. The following are the diagnostic indications for
- Optically guided biopsies of indeterminate and dominant stricture in primary sclerosing cholangitis.
- Differentiate benign versus malignant intraductal mass
- Accurately locating intraductal cholangiocarcinoma prior to resection
- Collecting significant fluid samples for cytology
- Visually evaluate intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms
- Visually evaluate choledochal cyst
- Visually evaluate for post-liver transplant ductal ischemia
- Visually evaluate for intraductal spread of ampullary adenoma
- Evaluate with a visual exam and tissue sampling for cytomegalovirus and fungal infection.
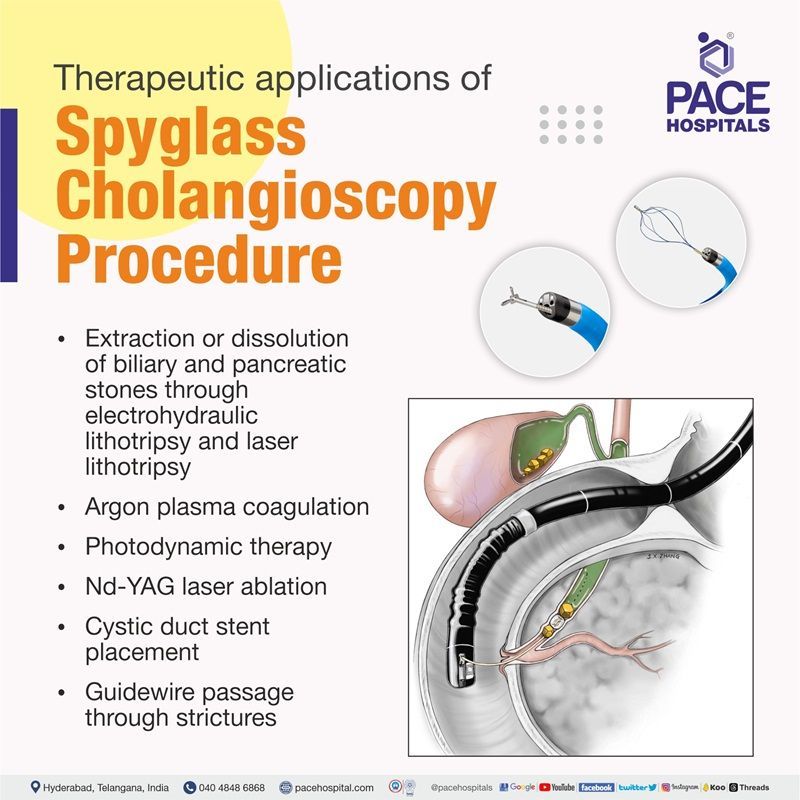
Treatment:
Spyglass cholangioscopy procedure is also indicated for therapeutic applications where normal ERCP procedures are unable to remove stones from within the ducts due to their size, location, or adherence to the biliary epithelium. The following are the therapeutic applications of Spyglass cholangioscopy procedure.
- Extraction or dissolution of biliary and pancreatic stones through electrohydraulic lithotripsy and laser lithotripsy
- Argon plasma coagulation
- Photodynamic therapy
- Nd-YAG laser ablation
- Cystic duct stent placement
- Guidewire passage through strictures
Contraindications of Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure
The spyglass cholangioscopy procedureis contraindicated if the patient is having:
- Inadequate surgical back-up
- Inadequate access to the ampulla of Vater
- History of recent acute pancreatitis, which is not related to gallstones.
- High levels of anticoagulation predispose to bleeding
- Other general factors that are contraindicated for an endoscopy or ERCP.
Preparing for Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure
The gastroenterologist might ask for the following before initiating the procedure:
- Blood tests and imaging studies
- Current ongoing medications and presence of any chronic health conditions
- Any allergies related to drugs or sedatives
- The interventional gastroenterologist would advise not eating for at least eight to twelve hours before the procedure and stopping certain medications before surgery.
- The entire procedure and risk (if any) of the spyglass cholangioscopy will be explained clearly to the patient, upon which the patient can provide his/her consent for the procedure only after all doubts and concerns are cleared by the interventional gastroenterologist.
- After consulting with the prescribing physician, the endoscopist suggests stopping anticoagulants before the procedure if sphincterotomy is expected.
During Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure
- Clothing, jewellery, and other objects that could obstruct the process should be removed, and the patient will be provided with a surgical gown to wear.
- Experienced therapeutic gastroendoscopists or interventional gastroenterologists performed this procedure under conscious sedation.
- A side-viewing video duodenoscope was used to do the ERCP procedure to identify abnormalities in the biliary system.
- The patient will be positioned prone on an x-ray table.
- The patient will be administered prophylactic antibiotics if clinically indicated.
- The interventional gastroenterologist might administer strong sedatives during the procedure, but general anaesthesia may be prescribed if clinically necessary.
- A small mouthguard will be placed inside the patient's mouth to prevent accidental bites.
- The interventional gastroenterologist will insert the standard therapeutic duodenoscope(ERCP scope) through the mouth, slowly extend it to the stomach through the oesophagus, and reach near the ampulla of Vater or major duodenal papilla (a small opening that connects the common bile duct and pancreatic duct).
- Standard ERCP procedures are used to cannulate the duct of interest. The interventional gastroenterologist might perform a sphincterotomy to improve access to the intended ductal system and to permit duct drainage during irrigation.
- The SpyScope cholangioscope is advanced through the duodenoscope's channel and into the pancreatic or biliary ductal system to provide access for direct visualisation by repeatedly moving the SpyScope forth and backwards with the help of the four-way tip deflection.
Spyglass-guided lithotripsy procedure steps
- The spyscope catheter and optical probe will be inserted into the duodenoscope together and advanced through the papilla of Vater for direct visualisation of biliary ducts. The spyglass will be inserted until it reaches the most distal common bile duct stone (as noted before).
- If a suspicious lesion in the biliary ducts is discovered, the spybite forceps are inserted into the working channel to take samples (2 to 6) from the targeted area.
- Once the stone is identified within a bile duct, the interventional gastroenterologist will flush water through irrigation channels to clear the debris.
- Then water, along with debris, is sucked through the therapeutic channel, which is manually drained out with the help of a syringe attached (outside, the other end) to the spyglass cholangioscope. Based on the type of lithotripsy procedures used, two types of probes can be introduced through the working channel of a spyglass.
- An EHL (Electrohydraulic lithotripsy) probe with the tip positioned directly towards the stone will be introduced through the working channel of the Spyglass cholangioscope. The interventional gastroenterologist may release water through the irrigation channels, and shockwaves are generated by releasing an electric spark (50-90W) at the end of the probe to achieve stone fragmentation under visual guidance. Fragmented stones will be flushed into the intestinal lumen or removed using a balloon and/or basket.
- A laser probe will be introduced through the cholangioscope's working channel, with the tip positioned directly at the stone at a specific distance. A laser beam will be passed through the stone to break it into small bits, which are further flushed out into the intestinal lumen.
- The lithotripsy techniques described above were designed to break the stones. If the stones were not completely removed during the first attempt, an additional attempt will be made. If the first two efforts are unsuccessful, the patient will be referred for surgery.
Post Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure
- The patient will be transferred to the recovery room until the sedative effect wears off while the patient's vital signs are being monitored.
- The patient might have a painful throat and find it difficult to swallow, which is quite normal, for which the gastroenterologist might prescribe medication and suggest not eating anything until the day following the procedure.
- The patient will resume a regular diet based on the dietician's guidelines and previous medication (which was stopped before the surgery).
- Based on the patient's condition, the patient might be discharged within a couple of days after the procedure.
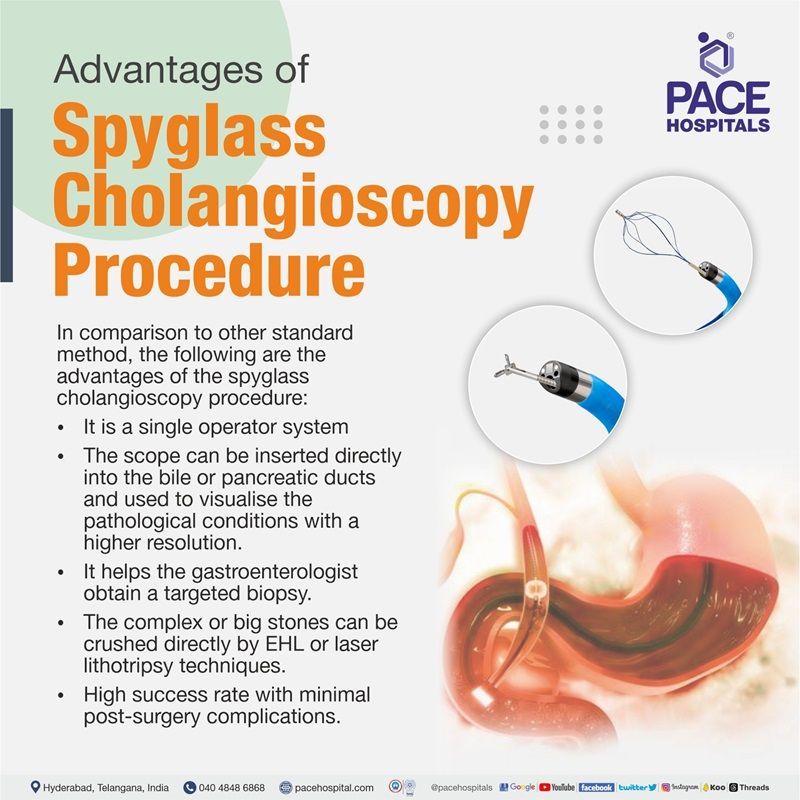
Advantages of Spyglass Cholangioscopy technique
In comparison to other standard method, the following are the advantages of the spyglass cholangioscopy procedure:
- It is a single-operator system
- The scope can be inserted directly into the bile or pancreatic ducts and used to visualise the pathological conditions with a higher resolution.
- It helps the gastroenterologist obtain a targeted biopsy.
- The complex or big stones can be crushed directly by EHL or laser lithotripsy techniques.
- High success rate with minimal post-surgery complications.
Patient questions post Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure
- What is the size of the stone removed?
- Is the stone completely removed?
- What are the chances of stone reformation?
- What kind of diet should I follow post-procedure?
- When should I visit back for a follow-up?
- When can I go back to my work?
- Whom to contact if I have any complications?
History of Cholangioscopy (Spyglass cholangioscopy technique)
Cholangioscopy is the term for the visual examination of the biliary tree. The concept of cholangioscopy dates back to the 1950s, with significant technology limits at the time. In the 1960s, intraoperative cholangioscopy was first effectively applied. In the middle of the 1970s, peroral cholangioscopy was first described. A 1977 research report demonstrated that, following an endoscopic papillotomy, a fiberscope with an 8.8 mm diameter can be placed straight through the mouth into the biliary system without the requirement for a second scope to be used as a guide. However, this process failed to provide a biopsy channel to collect tissue samples.
Later the practice of inserting a small calibre "baby" cholangioscope into the common bile duct (CBD) through the channel of a "mother" duodenoscope, which is known as duodenoscope-assisted cholangiopancreatoscopy (mother-baby) that had gained acceptance.
The "mother-baby" method was the most widely utilised cholangioscopy technology for many years, though it had the following challenges.
- Breaking of optical fibres often
- Limited two-way tip deflection for the baby scope
- Time-consuming procedure
- Required two endoscopists.
Several smaller scopes have been created in an effort to see the pancreatic duct and biliary tree up close. Some of these scopes have the benefit of being able to be advanced using a standard therapeutic duodenoscope.
With the introduction of the SpyGlass direct visualisation device in recent years, interventional gastroenterologists may now directly view the pancreatic duct and biliary tree, which is a major advancement.
To promote accessibility, this system additionally employs four-way tip deflection (up, down, left, and right). In addition, the SpyScope has two independent light-emitting diode (LED) lights and two dedicated irrigation channels (to flush water that aids in viewing and clearing mucus and debris) that are independent from the 1.2 mm working channel. The SpyBite Biopsy Forceps, guidewire, laser or electrohydraulic lithotripsy probes will be introduced through a working channel that can be used for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes.
Complications of Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure
Spyglass cholangioscopy is a safe procedure. However, it does have certain complications, including:
- Infections
- Pain in abdomen
- Inflammation of the pancreas
- Nausea/vomiting
- Bile duct Injury
- Increased pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase) without clinical pancreatitis
- Inflammatory syndrome
- Decrease in blood pressure
- Liver abscess (collection of pus in the liver)
- Minor bleeding at the time of sphincterotomy
SpyGlass Cholangioscopy Procedure Cost in Hyderabad, India
The cost of SpyGlass Cholangioscopy Procedure in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹55,000 to ₹1,80,000 (approx. US $660 – US $2,165).
The exact SpyGlass procedure cost varies depending on factors such as whether it is diagnostic or therapeutic, need for biopsy, stone removal difficulty, stricture evaluation, use of laser lithotripsy, anesthesia duration, specialist expertise, and hospital facilities — including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of SpyGlass Cholangioscopy
- Diagnostic SpyGlass Cholangioscopy – ₹55,000 – ₹90,000 (US $660 – US $1,085)
- SpyGlass-Guided Biopsy (Targeted Sampling) – ₹65,000 – ₹1,10,000 (US $780 – US $1,325)
- SpyGlass-Guided Stone Removal (Difficult Stones) – ₹80,000 – ₹1,50,000 (US $960 – US $1,810)
- SpyGlass With Laser Lithotripsy (Hard/Impacted Stones) – ₹1,00,000 – ₹1,80,000 (US $1,205 – US $2,165)
- SpyGlass for Biliary/Pancreatic Stricture Evaluation – ₹70,000 – ₹1,40,000 (US $845 – US $1,690)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Spyglass Cholangioscopy
How much does Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure cost in India?
Spyglass Cholangioscopy cost in India, ranges vary from ₹ 1,85,000 to ₹ 2,62,000 (Rupees one lakh eighty-five thousand to two lakh sixty-two thousand). However, cost of Spyglass Cholangioscopy Procedure in India vary in different private hospitals in different cities.