Bartholin’s Cyst - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Prevention
PACE Hospitals
Bartholin's cyst meaning
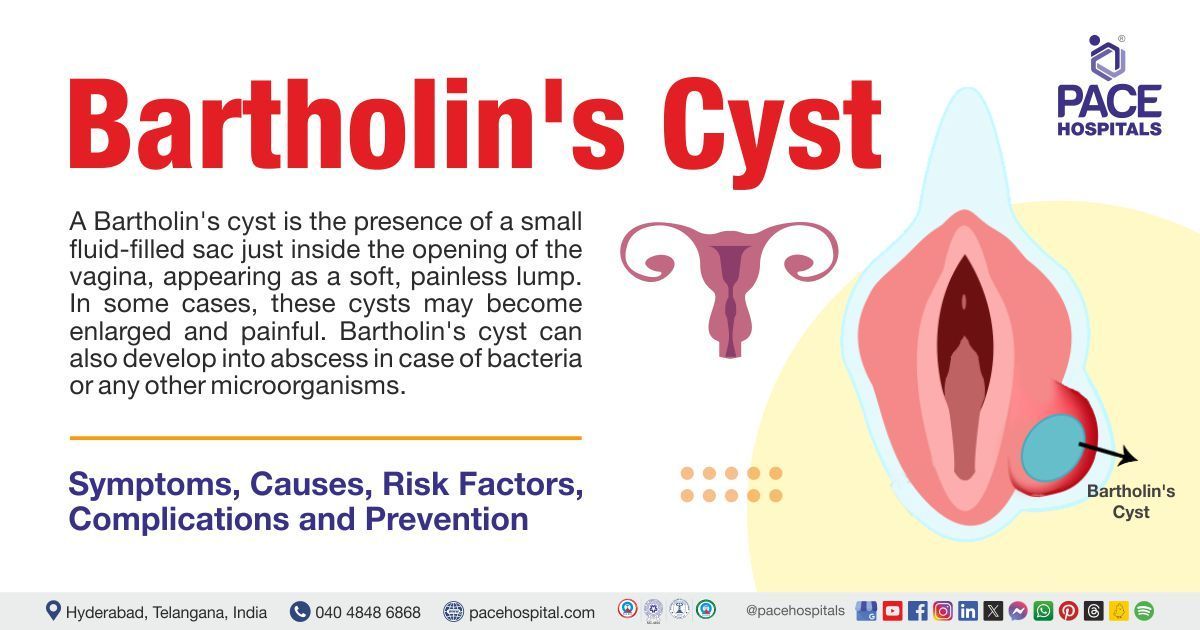
A Bartholin's cyst also called a Bartholin's duct cyst, characterized by the presence of a small fluid-filled sac just inside the opening of the vagina and appears as a soft, painless lump occurring at one side of the vagina (unilateral). In some cases, these cysts may become enlarge (noticeable) and painful. Bartholin's cyst can also develop into abscess in case of bacteria or any other microorganisms.
Bartholin’s cyst is formed in the Bartholin glands. These glands are round, very small, nonpalpable, and located on either side of the entrance to the vagina and produces and secrets mucus (fluid) to help the vagina stay moist (provide lubrication). Tiny tubes called ducts transport fluid downwards. A blockage or obstruction of the duct could occur due to oedema, infection, or trauma, leading to mucus build-up, which dilates the duct, resulting in cysts or abscesses.
Bartholin's Cyst Prevalence
The most common types of Bartholin gland masses are either cysts or abscesses. However, abscesses are three times more common than cysts. Symptomatic patients suffering from Bartholin cysts and abscesses account for approximately 2% of all gynaecologic visits per year, indicating 1 in 50 females may develop a Bartholin's cyst or abscess for reasons that are unclear (unknown).
Generally, these females are sexually active and range in between 20 and 30 years of age. Bartholin's cysts don't usually affect children and females above menopause age because Bartholin's glands functioning starts from puberty. Due to the shrinkage of the glands, after menopause, the condition is rarely seen. However, Bartholin's cysts/abscesses may occur at any age of a woman.
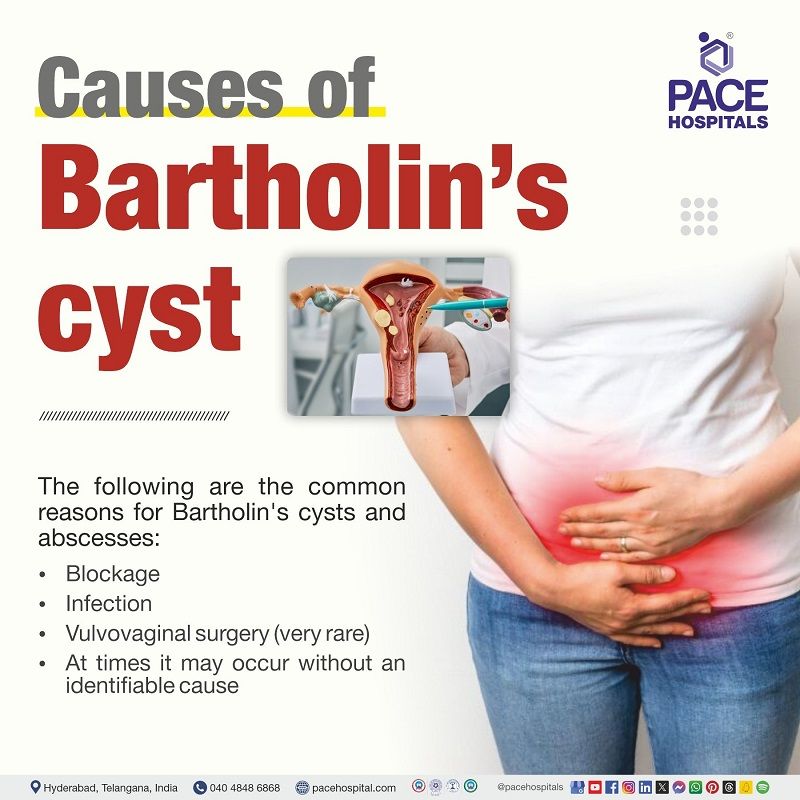
Bartholin’s Cyst Causes
The following are the common reasons for Bartholin's cysts and abscesses:
Bartholin's cyst:
- Blockage: Bartholin gland cyst occurs when the ducts of the glands that carry fluid from the glands gets blocked, and the fluid (mucus) builds up, causing cyst. A woman may feel quite dry in the vagina due to absence of lubrication.
An obstruction is often caused by local or diffuse vulvar oedema (widespread swelling of the tissues around the vulva), trauma to the area, episiotomy (an incision through the region (perineum) between a women's vaginal opening and anus), or childbirth. However, it may also happen without any identifiable cause.
Bartholin's abscess: An obstructed Bartholin duct can become infected and form an abscess.
- Infection: It's often not clear (unknown) why the ducts become blocked or obstructed, but some cases are linked to local infection, sexually transmitted infections, or an injury to the vulval area that can cause blockage and infection of the gland. The following are the microbes which may cause the abscess:
- Single or polymicrobial opportunistic organisms may cause Bartholin's gland abscesses. Most common isolates are Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Respiratory organisms, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae, are becoming more common, possibly due to the practice of oral sex.
- Sexually transmitted infections are responsible for only a small number of cases.
Vulvovaginal surgery: It is a rare cause of these cysts and abscesses.

Bartholin's Cyst Symptoms
Many Bartholin's cysts don't cause noticeable symptoms. However, usually, they are discovered when a woman detects a tiny, painless mass just outside the opening to the vagina because Bartholin's glands are palpable (feels) only if the duct becomes cystic or a gland abscess develops or when a gynaecologist notices it during a routine pelvic examination. The following are the common symptoms that will be observed in patients who have Bartholin cysts and abscesses:
Bartholin's cysts:
- Labial swelling: Painless, one-sided swelling of the labia (one of the skin folds of the vulva) mass without signs of surrounding cellulitis (inflammation of the surrounding tissue). Sometimes, the cyst affects the labia majora (outer pair of lips surrounding the vagina). One side may look swollen or bigger than usual.
- Discomfort or pain: However, if this cyst grows larger than 1 inch in diameter (large Bartholin cyst), discomfort or pain may be observed when pressure is applied while the patient is sitting or walking.
- Nonpurulent (no pus) discharge from a ruptured cyst.
- Vaginal dryness
Bartholin's abscesses:
- Presence of lump: A tender lump (painful sensation when touching it) on one side of the vagina where the ducts are situated.
- Smelly discharge: If a cyst becomes infected, it may fill with pus and become firm, swollen, and painful; the pus-filled cyst is known as abscess. Pus may begin to ooze from the area (abscess) and foul smell. It can increase temperatures up to 38°C (100.4°F) or above.
- Fever: Fever is uncommon in healthy patients. However, fever with other symptoms indicates infection.
- Redness and swelling: The area may look red, swollen and hot to touch
- Pain during intercourse: Patients may experience pain during sexual intercourse
- Stinging sensation: Patient may find it uncomfortable to pass urine
Sudden relief from symptoms may occur if the lump in the vulva drains or bursts on its own.
Bartholin's cyst Risk Factors
Risk factors associated with the development of a Bartholin's cyst and abscess includes:
- Nulliparity (haven’t had any baby)
- Sexually active women under the age of 40
- A previous Bartholin's cyst or abscess is a risk factor for recurrence.
- Previous history of vulval surgery or trauma, including female genital mutilation
- Abscesses are commonly caused by polymicrobial organisms, including Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and sexually transmitted organisms such as Gonorrhoea.
- Diabetics are more prone to abscesses.
Bartholin's Cyst Complications
Complications of Bartholin's cyst could be interlapped with Bartholin's abscess. The following are the possible complications of Bartholin's cyst and abscess:
Bartholin's cyst complications:
- Rectovaginal fistula (abnormal connection between vagina and rectum)
- Hydroureteronephrosis usually in neonates (dilation or (swelling) of ureter and the kidney resulting from the blockage of the urinary tract)
- Sepsis (body's overactive and extreme response to an already existing infection)
- Reoccurrence
Bartholin's abscess complications:
- Rectovaginal fistula and sepsis
- Reoccurrence
Bartholin Gland Cyst Diagnosis
The diagnosis of a Bartholin gland cyst or abscess is usually made by examination of the vulva. A gynecologists' may ask about the symptoms before physically inspection of the area. The following are the tests that would be recommended to diagnose Bartholin's cysts or abscesses:
- Physical examination: Physical examination includes visual inspection and palpation of the Bartholin gland. They may perform a pelvic exam by touching; if the patient presents with a cyst or abscess, they may clinically present as follows:
- Cyst: Painless, soft mass near the back of the vaginal opening at the site where the Bartholin duct and gland located.
- Abscess: A painful, warm, or pus-filled lump at the location of the Bartholin duct and gland, often surrounded by redness and inflammation (swelling).
- Abscess cultures: Gynaecologists send samples of vaginal discharge to look out for any infection. If purulent (pus) discharge is present, it will send to find the bacteria.
- Biopsy:
Biopsy is recommended in a woman over 40 years of age or postmenopausal women. For patients of any age with suspicion of malignancy of the Bartholin gland or other vulvar site, a biopsy is also suggested.
Bartholin's Cyst Treatment
If the Bartholin’s cyst is not causing pain or discomfort, treatment may not be required. However, some cysts can be managed by following the simple methods at home, where these methods are helpful to manage the pain and even make a cyst open and drain by itself:
- Sitz bath (warm water bath used for healing or cleansing purposes)
- Warm compress
- Painkillers
A gynaecologist may choose the treatment depending on the Bartholin's cyst size, how painful it is, and the presence of infection. Treatment options include the following:
- Antibiotics
- Drainage
- Surgery
- Other techniques
Antibiotics
If the Bartholin’s cyst becomes infected and an abscess accumulates, antibiotics will be recommended to clear the infection.
Bartholin's cyst drainage:
Once the infection has been treated, a gynaecologist may still recommend draining the cyst, especially if the abscess is large.
- Fistulization: It is sometimes called catheter placement or balloon catheter insertion, a traditional approach for treating symptomatic cysts or abscesses, although it is not appropriate for deep cysts.
Surgery
Bartholin's cyst surgery
Bartholin cyst removal surgery (Bartholin's cyst operation) may be required to open the cyst and stitch its walls to the surrounding skin to make it open. This procedure is called marsupialisation.
- Marsupialisation: It is appropriate for treating a primary or recurrent Bartholin duct cyst or gland abscess. Alternatively, a gynaecologist may need to remove a gland if the Bartholin cysts reoccur.
Bartholin gland removal
Surgery is recommended to remove the affected Bartholin's gland if other treatments have not been effective, and Bartholin's cysts or abscesses recurs or if cancer is suspected.
Other techniques:
The following are the other techniques that will be performed to treat the cysts. However, they are less commonly used or not widely available:
- Sclerotherapy: Using alcohol or silver nitrate may also be used to treat Bartholin duct cysts and gland abscesses.
- Carbon dioxide laser therapy: It includes cyst therapy, which is a safe and effective way to completely treat a Bartholin cyst.
- Silver nitrate gland ablation: As per some studies, this ablation following cyst drainage was as effective as marsupialization and caused less scar formation.
- Needle aspiration: A needle and syringe will be used to drain the Bartholin’s cyst during this process.
Why Choose PACE Hospitals?
Expert Super Specialist Doctors
Advanced Diagnostics & Treatment
Affordable & Transparent Care
24x7 Emergency & ICU Support

Bartholin's Cyst Prevention
It's not usually possible to prevent Bartholin cysts or abscesses due to lack of clarity in the development of Bartholin's cysts. Even while there is no way to prevent them totally, the following steps can help reduce the likelihood of getting these cysts or abscesses:
- Practicing safe intercourse: However, as some are thought to be linked to sexually transmitted infections (STIs), practice safe intercourse (using a condom during intercourse) can help reduce the chances of developing Bartholin's cysts.
- Maintaining hygiene: It is recommended to keep the vulvar and vaginal area clear.
- Surveillance: A gynaecologist also does a biopsy in the case of post-menopausal women or suspicion of malignancy to rule out cancer.
Differences between Bartholin’s cyst and Gartner’s Duct Cyst
Bartholin's cyst vs Gartner's duct cyst
Bartholin's cyst and Gartner duct cyst are both gynaecological issues that may cause problems to the vagina. Although they may appear similar, the following are the common differences:
| Elements | Bartholin's cysts | Gartner's duct cysts (vaginal cysts) |
|---|---|---|
| What it is? | These are the fluid filled sacs that occurs at Bartholin’s glands. | Gartner duct cysts are fluid filled sacs originate from remnants of embryonic tissue called Gartner’s duct. |
| Location | Near each side of the opening of the vagina | Develops on the side walls of the vagina |
| Size | May vary in size, usually smaller. | Less than 2 cm in diameter |
| Symptoms | If the cyst is small, it is painless, but if it is large, it may cause symptoms such as tenderness (pain) or discomfort. | Dysuria (burning sensation or pain while urinating), skin tag, pressure, itching, painful intercourse, pelvic pain. |
| Complications | If the cyst become infected it leads to abscess development. | In rare cases, with large cysts, problems in obstetric delivery may occur. |
| Treatment | Treatment options include sitz bath, warm compresses, painkillers, antibiotics (if it is infected), drainage and surgery. | Treatment options include, marsupialization into the vagina, partial removal of the cyst. |
Differences between Skene’s Gland Cyst and Bartholin’s Gland Cyst
Skene’s gland cyst vs Bartholin’s gland cyst
Skene gland cysts and Bartholin gland cysts are non-cancerous (benign) gynaecologic growths, that originate from the glands located in the female genital areas, potentially causing discomfort or pain. However, although they may appear similar, they have the following differences:
| Elements | Skene’s gland cysts | Bartholin gland cysts |
|---|---|---|
| What it is? | These are the fluid filled sacs that occurs at Skene’s glands | These are the fluid filled sacs that occurs at Bartholin’s glands. |
| Location | Near the opening of the urethra | Near each side of the opening of the vagina |
| Size | Most skene gland cysts are about 1 cm in diameter (less than ½ inch) | May vary in size, usually smaller. |
| Causes | Obstruction of skene’s ducts due to infection or inflammation. | Blockage or obstruction due to trauma, infection, inflammation. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms include frequent urination, painful urination (dysuria), painful sexual intercourse, frequent urinary tract infections. | If the cyst is small, it is painless, but if it is large, it may cause symptoms such as tenderness (pain) or discomfort. |
| Treatment | Treatment involves removal of the cyst, antibiotics (for abscesses) or creates permanent opening in it. | Treatment options include sitz bath, warm compresses, painkillers, antibiotics (if it is infected), drainage and surgery. |
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions on Bartholin's cyst
Is Bartholin's cyst dangerous?
A Bartholin's cysts are not life-threatening, but if they grow big, they can cause symptoms such as discomfort or pain while walking and sitting. However, they become problematic if infected, resulting in abscess formation, which may require medical intervention.For a healthy body, limited amounts of copper from meals are essential. However, excess copper is poisonous.
Why does Bartholin's cyst occur?
Bartholin cysts are commonly caused by the obstruction of the Bartholin's gland's ductal region. However, there is no identifiable reason why blockage occurs. As per some studies, the Bartholin gland obstruction may happen after trauma to the area, episiotomy (An incision through the region (perineum) between a women's vaginal opening and anus), or childbirth.
How do I know if I have a Bartholin gland cyst?
If anyone has a Bartholin cyst, it may appear as a round, painless fluid-filled sac within one of the vaginal lips, just near the opening of the vagina. It indicates a Bartholin gland cyst because the Bartholin gland is nonpalpable until it has developed any cyst or abscess. This cyst may remain the same size or may slowly grow into a big size. Larger Cysts that get infected by microbes are usually very tender. In extreme cases, walking may be painful. A gynaecologist can look at the area to see if that woman has a Bartholin gland cyst and find an infection.
Can a Bartholin's cyst spread?
Usually, Bartholin gland cysts are not infected and can't be spread to other people. Sometimes, they can be caused by an infection or become infected as they grow larger. In case of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) could be a cause of Bartholin cysts, which could be contagious.
Can Bartholin's cyst reoccur?
Women who already have a Bartholin cyst have a higher risk of recurrence than women without a Bartholin cyst. There is no guarantee that these cysts will not recur after treatment. They may recur due to poor hygiene in the affected area and lack of examination of the health of reproductive organs. Women of reproductive age who experience recurrent Bartholin's gland abscesses are often at risk of contracting a sexually transmitted polymicrobial infection.
How do you burst a Bartholin's cyst at home?
A Bartholin's cyst may drain or rupture on its own, or it can be effectively treated at home if the cyst is not causing pain by soaking the cyst for 10-15 minutes in a few inches of warm water (better while doing a bath), it is best to do this several times a day for 3 or 4 days if possible. It is recommended to hold a warm compress against the affected area. If it doesn't respond to home treatment or appears to have an infection, it is advised to consult a gynaecologist.
How do you pop a Bartholin's cyst yourself?
It is not advisable for Bartholin's cyst to pop, squeeze, or insert any sharp objects, such as needles, into a cyst to force it to open because it could cause injury, worsen symptoms, and lead to infection. Hence, seeking the right medical help at the right time for proper diagnosis and treatment is recommended.
Can you have intercourse with a Bartholin's cyst?
Bartholin's cysts are painless until they are big; there is no pain during intercourse. However, if they become big or infected, it may cause discomfort or pain when applying pressure while walking, sitting, and sexual intercourse. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a gynaecologist in case of pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Is Bartholin's cyst common?
Bartholin's duct cysts and gland abscesses are fairly common problems in women of reproductive age. Bartholin's cysts usually develop after puberty and before menopause of a woman. About 1 in 50 (2%) females may develop a Bartholin's cyst or abscess in their lifetime for reasons that are unclear (not known).
Will a Bartholin's cyst rupture on its own?
While smaller cysts may be asymptomatic (don't cause symptoms) and may be left untreated because they may go away on their own, larger cysts require medical attention. Some cysts may be effectively treated at home if they are not causing pain. To reduce the chance of infection, it's essential to keep the area clean and dry and to avoid squeezing or popping the cyst.
Can Bartholin's cyst become cancerous?
Bartholin's cysts are fluid-filled sacs that are typically non-cancerous; however, in very rare cases, there could be a possibility of the development of cancer called Bartholin gland carcinomas (BGCs), which are extremely rare tumours accounting for <1% of all female genital malignancies. Despite such negligible statistics, patients suffering from Bartholin cysts must undergo, regular medical examination as it is important to find abnormalities.
What does a Bartholin's cyst look like when it bursts?
A Bartholin's cyst is a painless fluid-filled sac; if infected, it could be filled with mucus, pus, bacteria, blood, or other fluids. This discharge may present as thick and range in colour from light yellow to brown or red. Infected Bartholin's cysts could have an unpleasant odour, such as a foul smell, when they rupture.
When to Consult a Doctor for Bartholin's Cyst?
When one of the tiny glands close to the vaginal entrance gets clogged, fluid accumulates, and a Bartholin's cyst develops. Since many cysts are tiny and painless, they may not need treatment.
Warning signs to look out for:
- A painful swelling near the vaginal opening
- Increasing size of the lump over a short period
- Difficulty while walking, sitting, or during intercourse
- Redness, warmth, or tenderness in the area
- Fever or chills
- Pus discharge or signs of infection
- Recurrent cysts in the same location
- Severe discomfort affecting daily activities
A general physician or gynaecologist may perform a physical examination and, if needed, suggest tests to rule out infection. Treatment options can include medications, drainage procedures, or minor surgical intervention, depending on the severity and recurrence.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868