Enlarged prostate – Symptoms, Causes, Prevention and Treatment
Pace Hospitals
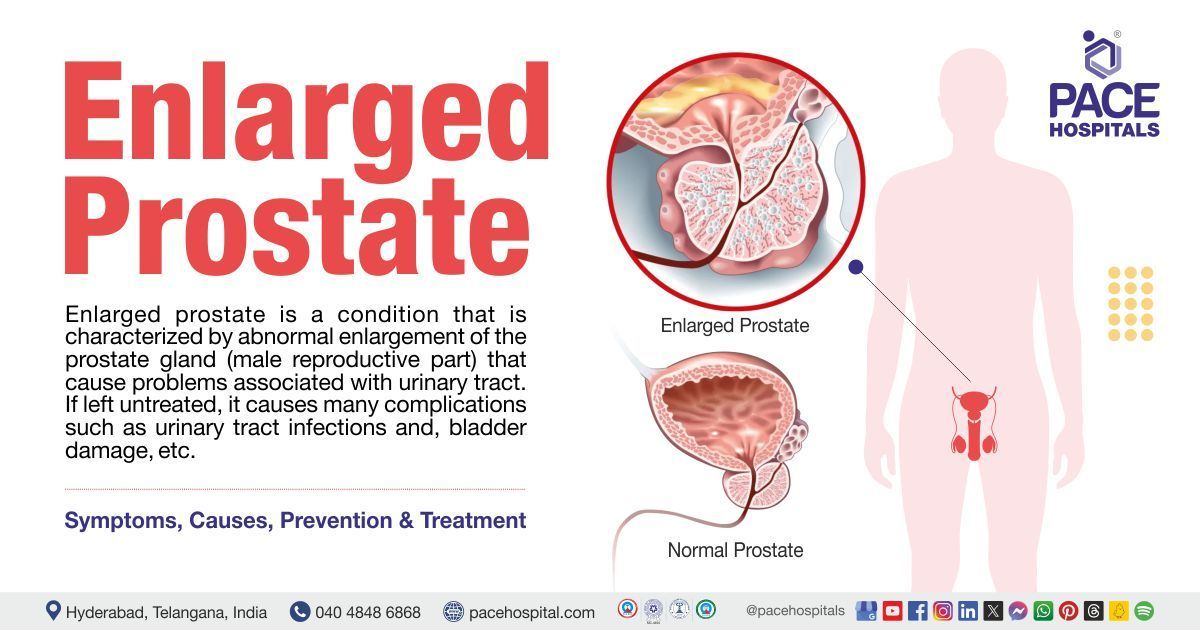
Enlarged prostate is a urological disorder seen in the male reproductive part that is characterized by a non-cancerous increase in the size of the prostate gland. It is usually seen in the elderly and leads to the development of lower urinary tract symptoms such as urinary retention (unable to empty the bladder) nocturia (frequent urination during nighttime) urethral compression (narrowing of the urethra, a tube that carries urine) etc.
Upon prostate enlargement, the gland strains the urethra making the bladder wall thicker, eventually leading to bladder weakness and the bladder may lose its capacity to empty urine entirely. If left untreated, it causes many complications such as urinary tract infections and, bladder damage, etc. The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system necessary for production of semen (fluid necessary to carry sperm after ejaculation.
The prostate is located below the urinary bladder and in front of the rectum (the final part of the large intestine).
Enlarged prostate is also known through various other medical terms such as
prostatomegaly, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), benign prostatic hypertrophy, benign prostatic obstruction, prostate enlargement etc.
This urological disorder (disease related to the urinary tract and reproduction) is very common in men aged 50 years and above. As such the growth of the prostate is non-cancerous, it is not a serious health threat, nevertheless; it is treated by a well-qualified urologist (a doctor trained in treating conditions related to the urinary tract and male reproductive parts).
Benign prostatic hyperplasia definition
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is defined as the abnormal growth of the prostate gland which cause lower urinary tract symptoms. Generally, the prostate is considered enlarged when the size of the prostate is greater than 30 cc (ml). The size of a normal prostate gland is about 25ml. The prostate weighs about 11 grams in normal adult men.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia meaning
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a combination of 3 words.
- 'Benign'-the term ‘benign’ is a French word which means ‘gentle’ ‘kind’.
- 'Prostatic' - relating to 'prostate gland'.
- 'Hyperplasia' -the term 'hyperplasia' is a Latin word in which hyper means ‘over’ ‘beyond’ and 'plasia' means ‘growth’ ‘development’.
Prostatomegaly meaning
The word prostatomegaly is a combination of 2 words. Both ‘prostato’ and ‘megaly’ are ancient Greek words, in which ‘Prostato’- means ‘leader’ or ‘guardian’. ‘Megaly’- means ‘large’ ‘great’.
While the term ‘prostato’ does not resemble anything keenly related to medical terminology, its metaphoric expression of “someone standing next to someone or something” has been taken into consideration. Ancient authors understood the contribution of the prostate gland in conjunction to the testicles, the spermatic ducts, which played an important role in “helping” procreation.
Mildly enlarged prostate meaning
Based on severity of symptom scores, the international prostate symptom score (IPSS) and American urological association (AUA) divides patients into three categories they are:
- mild (scores 0 to 9)
- moderate (scores 10 to 19)
- severe (scores 20 to 35)
Prevalence of enlarged prostate worldwide
Older men are more prone to enlarged prostate. The age-specific benign prostatic hyperplasia epidemiology was found to be:
- 8% in men aged between 40–50 years
- 50% in men aged between 60–70 years, and
- 80% in men aged between 80–90 years.
Studies conducted worldwide have revealed that people in the West have noticeably larger prostate sizes than people in other regions of the world, especially Southeast Asia.
Prevalence of enlarged prostate in India
The incidence of enlarged prostate cases is high in India. A 2003 study demonstrated an incidence of 92.97% enlarged prostate cases in the Indian subcontinent. A systematic review and meta-analysis study from 2017 demonstrated the prevalence of enlarged prostate age wise: They include:
- 25% in men aged between 40–49 years
- 37% in men aged between 50–59 years
- 37% in men aged between 60–69 years
- 50% in men aged between 70–79 years
Approximately 50% of men in India have enlarged prostate by the time they are 60 years old. Studies indicate that the imbalance of male reproductive hormones such as testosterone and oestrogen may be the cause of enlarged prostate. Prostate cell proliferation is enhanced by a larger percentage of oestrogen in the prostate.
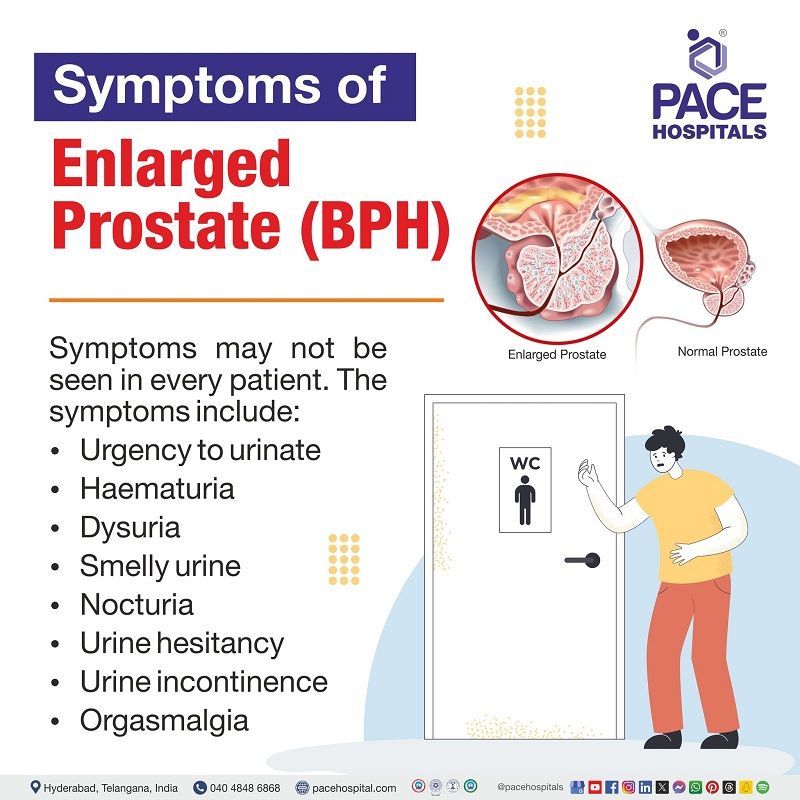
Not every man suffering from prostate enlargement (Benign prostatic hyperplasia-BPH) will experience the symptoms. Less than half of the men who are diagnosed with enlarged prostate will experience symptoms such as:
- Urgency to urinate
- Having weak flow of urine
- Finding difficulty in starting to urinate.
- Haematuria (blood in urine)
- Dysuria (Pain during urination)
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Smelly urine (urine that has unusual smell)
- Nocturia (frequent urination at night)
- Urine hesitancy (a condition that makes it difficult to maintain a steady urine stream)
- Urine incontinence (unintentional loss of urine)
- Orgasmalgia also called dyorgasmsia (pain after ejaculation)
Enlarged prostate symptoms usually occur due to:
- Blocked urethra
- A strained bladder, because of attempting to pass urine through the obstruction.
Enlarged prostate causes
The exact reasons for enlarged prostate are still unknown. Enlarged prostate mostly develops in aged men but is absent in men who were subjected to castration (removal of testicles before puberty) It will not develop in men who are 5 alpha reductase type-2 (an enzyme that converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone) deficient.
Research studies demonstrated that the hormones play a vital role in the development of enlarged prostate. With aging the active testosterone levels in males are reduced, and the oestrogen levels are increased, prompting the alteration in prostate gland which results in its enlargement. Benign prostatic hyperplasia causes are also seen with 5-alpha-reductase 2. The enzyme 5-alpha-reductase 2 converts any residual testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (another male reproductive hormone) which enhances the cell division and growth of the gland.
Some clinical studies suggest that there is a positive association between the development of enlarged prostate and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and some other studies emphasize diabetes (high blood sugar), which is a metabolic syndrome also causes enlarged prostate due to insulin resistance.
Some reports indicated that the increase in prolactin levels is directly related to the development of enlarged prostate. Prolactin is a hormone synthesized from various tissues such as testes, seminal glands, prostate, etc. There is evidence developed that there is a link between inflammation and the development of enlarged prostate. It is established that the growth of prostate epithelial cells (cells that covering the body surfaces) can be stimulated by cytokines (proteins that control inflammation).
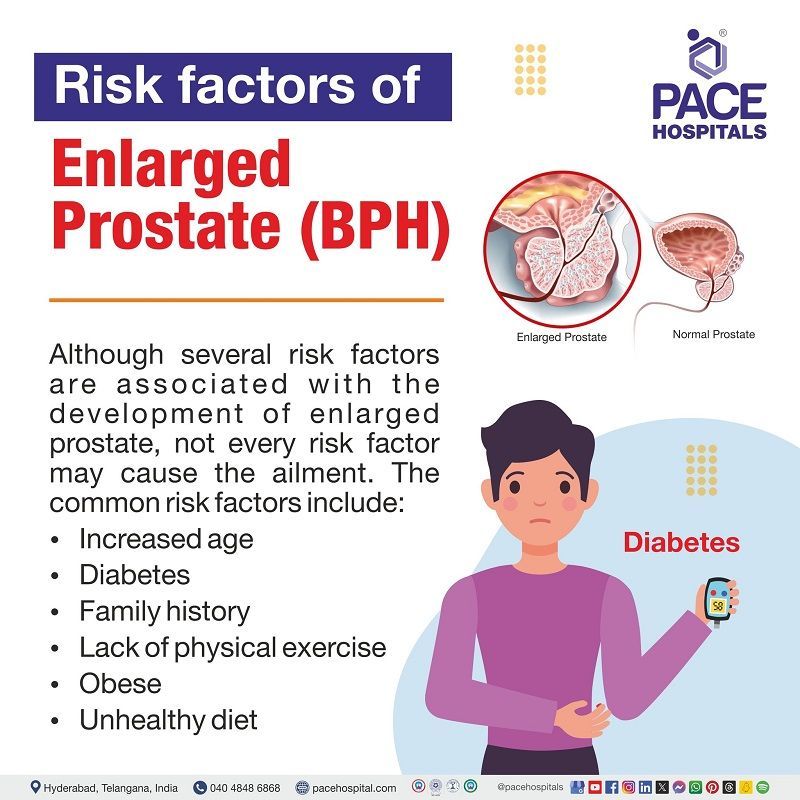
Enlarged prostate risk factors
Even though there are several risk factors associated with the development of enlarged prostate, not every risk factor may cause prostate enlargement. But men with the following risk factors are at more risk of developing enlarged prostate:
- Increased age: With aging, the active testosterone levels in the blood decreases and the levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This fluctuation in hormone levels lead to the development of enlarged prostate.
- Diabetes (high blood sugar): High blood sugar (Diabetes) cause insulin resistance, which increases insulin concentrations in the body. It in turn may exert a trophic effect, leading to enlarged prostate size.
- Family history: A 1994 study demonstrated a 4-fold increase in the risk of prostatectomy for BPH in the first-degree male relative. if the father required prostatectomy for BPH before the age of 64 years.
- Lack of physical exercise: It is demonstrated that there is an inverse link between physical activity and BPH symptoms. Men who were more physically active has a lower risk of developing BPH. Even low- to moderate-intensity physical activity, such as walking consistently at a moderate speed, is said to be beneficial.
- Obese (being overweight): Studies consistently demonstrated that an increase in the adipose tissue is associated with an increase in prostate volume, as determined by ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging tests. The greater the adiposity, the greater the prostate volume. Increased prostate volume strongly predicts BPH, acute urinary retention and renal failure.
- Unhealthy diet: The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) discovered a statistically significant link between a higher risk of BPH and a high consumption of lipids (type of fats) and red meat or low consumption of proteins and vegetables.
Possible risk factors that are not well understood include:
- High blood cholesterol.
- Smoking.
- High blood pressure.
Risk of cancer in benign prostatic hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia has a lower risk of developing prostate cancer, but the similarities between prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate) are close.
A 2016 meta-analysis of observational studies demonstrated that the development of enlarged prostate is detrimental particularly to the Asian population as they are more prone to avail both prostate cancer and bladder cancer.
Complications of enlarged prostate
The complications of enlarged prostate arise with the advancement in stages. In some cases of enlarged prostate, there are chances of complications such as:
- Acute urinary retention (inability to voluntarily pass urine)
- Vesicolithiasis (presence of stones in bladder)
- End stage renal disease (ESRD also called as Kidney failure)
- Urinary tract infections (UTI)
- Hydronephrosis (build-up of urine in the kidney)
- Urine hesitancy (weak urinary stream)
- Haematuria (blood in urine)
- Decompensated (loss of functional balance) urinary bladder.
- Erectile dysfunction (inability to maintain erections)
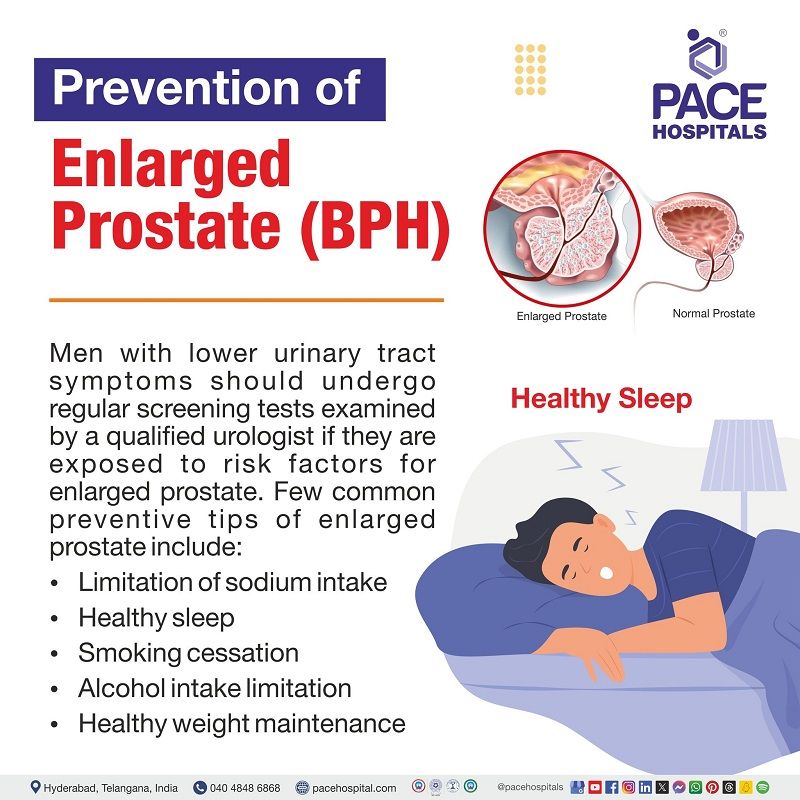
Enlarged prostate prevention
Currently, there are no preventive methods to stop enlarged prostate. The presence of lower urinary tract symptoms could depict an enlarged prostate. The patients can reduce the effects of enlarged prostate by through early diagnosis and receiving an early treatment. Some preventive measures that may help to prevent enlarged prostate include:
- Sodium intake limitation: Excess sodium as well as low sodium intake can increase the risk for developing enlarged prostate, so limiting sodium seemed beneficial.
- Healthy sleep: Getting enough sleep per day is as good as diet and exercise. Among middle-aged and older Indian males, a higher incidence of enlarged prostate was significantly linked with worse sleep quality.
- Smoking cessation: Cigarette smoking may have an impact on the size of the growing prostate, but only indirectly through its influence on factors that contribute to the development of BPH.
- Alcohol intake limitation: A study carried out in Italy states that BPH might develop in heavy alcoholics due to hormonal fluctuations caused by alcohol.
- Healthy weight maintenance: A 2016 study demonstrated that obesity has the potential to cause intra-abdominal pressure, abnormal endocrine (system that releases hormones) activity, and increased inflammation, which will eventually lead to BPH.
Men who have lower urinary tract symptoms should undergo regular screening tests examined by a qualified health care provider, if they have risk factors for enlarged prostate.
Difference between enlarged prostate and prostate cancer
(Enlarged prostate vs Prostate cancer)
| Parameter | Enlarged prostate | Prostate cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Cells | Cells are non-cancerous | Cells are cancerous |
| Chance of metastasis (spreading) | BPH will not spread | This cancer may spread to other parts of the body |
| Cause | Changes in male reproductive hormone levels, Excessive non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug use, Abnormal prolactin levels, Bodily inflammation | Mutation |
| Diagnosis | Digitorectal examination (DRE), Transrectal and transabdominal ultrasound, Computed tomography (CT) scan, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, Biopsy, Cystoscopy | PET (positron emission tomography) scan, Biopsy , Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) |
| Treatment | Pharmacological treatment(Treatment using medicine), Enlarged prostate can be treated with medicine such as: Phosphodiesterase (PDE-5) inhibitors, Alpha adrenergic blockers, 5 alpha reductase inhibitors etc., Surgical treatments include:, Transurethral resection of prostate , Transurethral incision of prostate, Open prostatectomy, Laser surgery etc | Pharmacological treatment(Treatment using medicine), Prostate cancer can be treated with medicine such as: Anti-androgens, Anti neoplastic agents etc., Surgical and interventional treatments include:, Radiation therapy, Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy, Cryosurgery, High-intensity–focused ultrasound therapy,Proton beam radiation therapy etc. |
| Life threatening | Usually not life threatening | Usually, life threatening as it can spread to other body organs, eventually damaging them. |
Benign prostatic hyperplasia vs benign prostatic hypertrophy
Since both benign prostatic hyperplasia and benign prostatic hypertrophy contribute to prostate enlargement, benign prostatic hyperplasia
increases cell count in the prostate whereas hypertrophy
increases the cells size in the prostate.
Enlarged prostate diagnosis
After taking the patient's entire history to find out whether the prostate gland is enlarged, the urologist initiates enlarged prostate diagnosis which includes physical examination, laboratory testing, and other tests.
Physical examination
- Digitorectal examination (DRE) to analyze the prostate volume.
- Penile and neurological examination is performed to check for any disorder associated with lower urinary tract symptoms.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia lab tests
- Urinalysis to identify haematuria (blood in urine) and glycosuria (glucose in urine)
- Serum creatinine (to check the kidney function)
- Serum test (to check whether it is enlarged prostate or prostate cancer)
Other tests
- Urinary cytology
- Transrectal and transabdominal ultrasound.
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
- Biopsy
- Cystoscopy
- Urodynamic tests
Enlarged prostate treatment
The treatment of enlarged prostate developed from addressing only life-threatening complications of severe obstruction, including the relief of minor levels of prostate gland enlargement symptoms.
Pharmacological treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
The common classes of benign prostatic hyperplasia medications are:
- Alpha adrenergic antagonists
- 5 alpha reductase inhibitors Anti-cholinergic drugs
- Diuretics
- Phosphodiesterase (PDE-5) inhibitors
- Combination therapy (combination of two or more medicine) may be given enlarged prostate treatment, especially if the cases are presented with severe symptoms.
Nonpharmacological treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
While modern innovations have developed medicine for enlarged prostate, urologists may initially opt for nonpharmacological treatment of prostate enlargement (treatment without using medicine). It includes:
- Avoidance of liquids at nighttime could reduce the chances of nocturia (frequent urination at night) that is seen with enlarged prostate.
- Exercise for enlarged prostate includes pelvic floor exercises which prepare stronger pelvic muscles, to support the urinary bladder and help control urine outflow.
- Avoid medicines such as decongestants (medicines used for blocked nose) and antihistamines (medicines used for allergies) as they make the muscle that controls urine outflow harder, eventually leading to difficulty in urination.
- Manage constipation.
- Avoiding the intake of alcohol and caffeinated liquids.
- Teaching the bladder to retain more urine over extended periods of time.
Foods to avoid with enlarged prostate
The nutritional aspects of enlarged prostate have received relatively little attention when compared with that of prostate cancer as prostate cancer has strong ecologic evidence of diet influences which the enlarged prostate lacks.
Nevertheless, a 1999 Greek study demonstrated that the consumption of fruits is helpful in reducing the risk of enlarged prostate. Similarly, foods that contain high fat (such as butter etc.) are not to be consumed among the aged communities as they can induce the risk of enlarged prostate. Olive oil does not present clear evidence in the development of enlarged prostate.
Enlarged prostate surgeries
When the symptoms of Benign prostatic hyperplasia are severe, that cannot be managed by medications alone, the urologist may opt for surgical treatments depending on the patient's condition, types of surgical methods include:
- Transurethral resection of prostate
- Transurethral incision of prostate
- Open prostatectomy
- Laser surgery
- Photo selective vaporization of the prostate (PVP)
- Prostatic urethral lift (urolift)
- Aquablation
- Holmium and thulium laser enucleation of the prostate
- Transurethral microwave thermotherapy
- Selective prostatic artery embolization
Phytotherapy (treatment using plants and herbs)
Despite widely used in Europe, phytotherapy is for the management of enlarged prostate demonstrated largely inconclusive and conflicting results. Due to this reason, treatment from plant agents are discouraged.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions on Enlarged prostate
What is the main cause of prostate enlargement?
Researchers are yet to understand the exact cause of prostate enlargement as this ailment has various factors that may not show uniformity across various patient populations. A study published in 2008 states that an enlarged prostate may develop due to
- Impaired homeostasis (balance between all body systems) of prostatic cellular proliferation and apoptosis (cell death).
- Excessive use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS).
- Abnormal fluctuations of male reproductive hormones.
What is the best treatment for enlarged prostate?
Aquablation therapy is considered as one of the best treatments for enlarged prostate. It is a minimally invasive surgery that removes prostate with robotic assisted water jet supervised by a urosurgeon. It is considered one of the best treatments as it is not only safe and effective treatment but also preserve the sexual function (upholding ejaculation and erectile function for a longer period) of the patient who experienced enlarged prostate ranging 25-80ml.
Does an enlarged prostate affect a man sexually?
Yes, enlarged prostate is frequently associated with sexual dysfunction such as erection and ejaculation problems. Patients suffering from severely enlarged prostate are often presented with:
- Decreased libido (low sexual desire)
- Lower levels of sexual satisfaction
- Premature ejaculation (when ejaculation happens before sexual intercourse)
What causes enlarged prostate at young age?
While usually, the condition of enlarged prostate is seen in the aged. nevertheless, there are fewer documented cases of enlarged prostate which occur in younger adults. The exact cause of an enlarged prostate at a young age is still unclear. Studies speculated that conditions like sexually transmitted diseases (STD) and progeroid syndromes (genetical disorders that cause physiological aging) may cause prostate enlargement.
What is enlarged prostate size?
The normal adult prostate measures about 20-25 cc(ml) and resembles a heart shape. Generally, the prostate is considered enlarged when the size of the prostate is greater than 30 cc (ml).
What is the latest treatment for enlarged prostate?
There have been the latest developments both in pharmacological (treated by medicine) and surgical treatments for enlarged prostate.
A 2024 study demonstrated that the combination of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs), phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors, and beta-3 agonists seemed to be beneficial in latest advancements in pharmacological therapy of BPH.
Previous study that conducted in 2023 emphasized that a new surgical intervention called Optilume BPH catheter system, not only improvises the urinary symptoms but also uphold the sexual function of the patient.
Is there laser treatment for enlarged prostate available?
Yes, there are laser treatments available for enlarged prostate. A 2023 study states that according to European Association of Urology guidelines, 4 laser treatment options are considered to treat enlarged prostate. The most common lasers used are:
- Holmium:YAG (Ho:YAG)
- Thulium:YAG (Tm:YAG)
- Greenlight laser
- Diode laser
How to cure prostate enlargement?
After diagnosing prostate enlargement (benign prostate prostatic hyperplasia), it can be cured by either pharmacological treatment (treatment using medicine) or surgery.
- Pharmacological treatment can be given by using Alpha adrenergic antagonists,5 alpha reductase inhibitors, Phosphodiesterase (PDE-5) inhibitors or by combining the medicine.
- Surgical interventions include, Transurethral resection of prostate, Transurethral incision of prostate, Open prostatectomy etc.
Can an enlarged prostate go back to normal?
No. The prostate once enlarged cannot revert to its normal shape and size on its own. Nevertheless, with early diagnosis and timely treatment which may include pharmacological therapy along with the use of surgical techniques, it can be brought back to its normal size and shape by shrinks the prostate. The advanced surgical techniques are especially used to remove the excess prostate.
Can an enlarged prostate lead to kidney problems?
Yes, as the prostate lies just below the bladder, the enlarged prostate often blocks the urine flow or shows symptoms of kidney problems, bladder or urinary track.
What is the average age for BPH?
The condition of enlarged prostate is commonly seen in aging men, which may start with 50 years. While around 50% of men of ages ranging between 51–60 years has enlarged prostate, the prevalence increases to 70% among those men who are aged between 60-69 and around 80% of men over 70 years of age. It is recommended for a male who crossed 50 years to get screened for enlarged prostate for at least once in every 2 years as a general practice.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868