Kidney failure - End-Stage Renal Disease: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Kidney failure definition
The progressive loss of renal functions (kidney functions) such as inability to filter waste products from blood is collectively called kidney failure. This condition can either be rapidly developed (acute kidney failure) or has a history of insidious progression (chronic kidney disease).
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is the last stage (stage 5) of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in which the kidneys can no longer function properly. This can lead to a buildup of toxins and fluids in the body, which can be life-threatening.
ESRD is also called kidney failure and can be seen developing insidiously when the treatment of CKD is either delayed or not treated at all. As the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) drops below 15 mL/min/1.73 m2, the kidney function progressively worsens.
It is at this stage the nephrologist recommends renal replacement therapies such as dialysis or kidney transplantation to remove uremic toxins and maintain hemodynamic stability.
Types of Kidney failure
Usually, the two types of kidney failure are
- Acute kidney failure
- Chronic kidney failure
While acute kidney failure demonstrates an abrupt onset and potentially reversible, the chronic kidney failure occurs gradually and insidiously over the time - at least three months, which can lead to permanent kidney failure.
Acute Kidney (Renal) Failure
As there is a close relationship between Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and acute kidney injury (AKI), they could likely promote each other. Also, researchers found compelling evidence among a growing body of literature that AKI accentuates the progression of CKD into ESRD (kidney failure), especially in AKI patients requiring dialysis.
A 2009 study done in America demonstrated that patients who were diagnosed with an episode of AKI were more likely to develop ESRD (kidney failure) when compared with those patients without a history of either AKI or CKD. The risk of ESRD was 8 times higher in AKI patients compared with patients without a history of AKI or CKD.
Chronic Kidney (Renal) Failure
Chronic kidney failure, also known as chronic kidney disease (CKD), is a long-term condition in which the kidneys gradually lose their ability to function correctly. Kidneys are vital organs that filter waste & excess fluids from the blood, regulate electrolyte levels, and produce hormones that help control blood pressure and stimulate red blood cell production. When the kidneys become damaged or diseased over time, they may not perform these functions adequately.
CKD is typically categorized into five stages based on the level of kidney function, with Stage-1 being the mildest and Stage 5 being the most severe. These stages are determined by the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which measures how effectively the kidneys are filtering blood.
Kidney failure symptoms
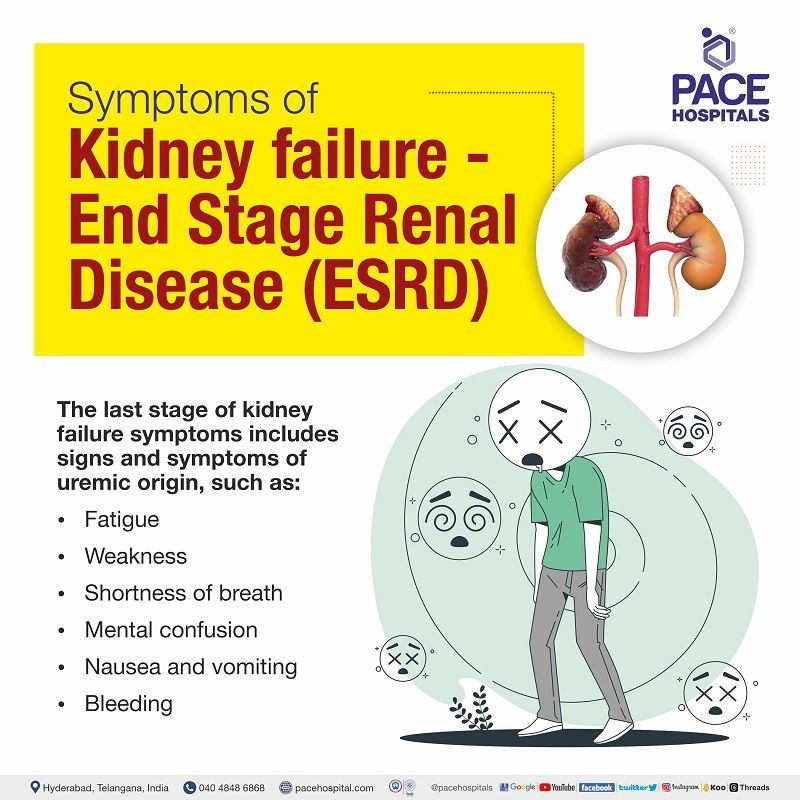
The last stage of kidney failure symptoms includes signs and symptoms of uremic origin, such as:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Mental confusion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bleeding
- Loss of appetite
- Itching
- Cold intolerance
- Weight gain
- Peripheral neuropathies
- Oedema
- Changes in urine output (volume and consistency),
- Foaming of urine (indicative of proteinuria)
- Abdominal distension.
Although ESRD symptoms certainly may develop in the earlier stages of chronic kidney disease, underscoring the importance of early intervention, they become more prominent as the disease worsens.
The early symptoms of kidney failure
It is rather difficult to categorise the early symptoms of kidney failure as it is difficult to predict the CKD complication, which further drives the advancement of CKD to kidney failure. In the case of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, the early symptoms of kidney failure include:
- Swelling
- Redness
- Pruritus
- Pain in the limbs
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty lifting their legs (as in climbing stairs or entering a car)
- Inflexibility of joints
Apart from marked decline in the frequency of intercourse, the kidney failure symptoms in men also include erectile dysfunction and decreased libido, while disturbances in menstruation and fertility are the prominent kidney failure symptoms in women.
Restlessness of legs in kidney failure
Among the other signs of kidney failure, restlessness of the legs is one of the prominent signs, especially in people undergoing dialysis therapy. The various other sleep disorders include - insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), sleep-disordered breathing, and movement disorders during sleep.
Risk factors of ESRD - Kidney failure
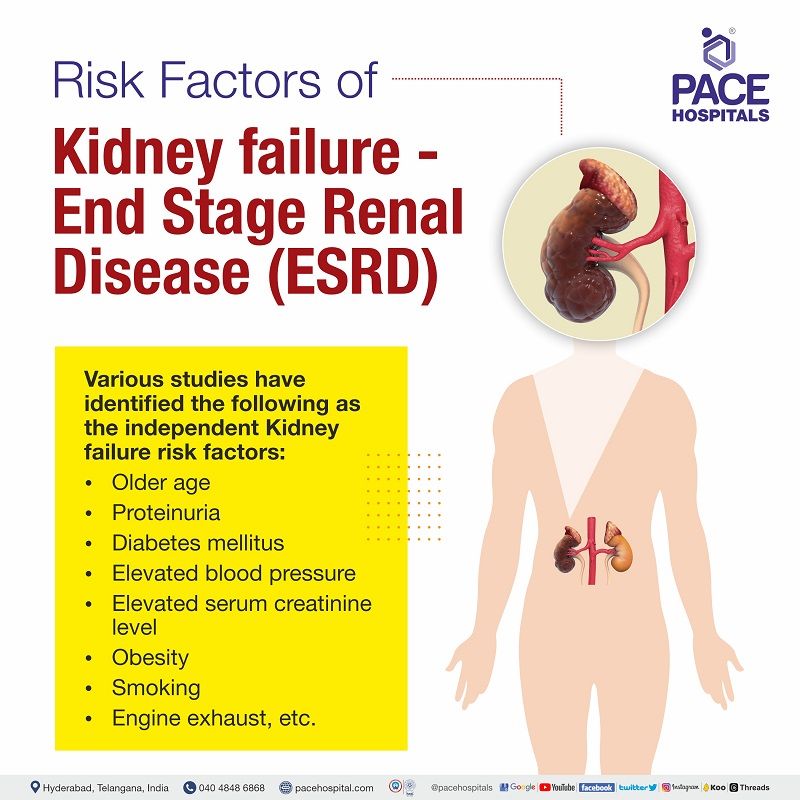
Various studies have identified the following as the independent kidney failure risk factors:
- Older age
- Proteinuria
- Diabetes mellitus (DM)
- Elevated blood pressure
- Elevated serum creatinine level
- Obesity
Apart from the above, a 2009 study demonstrated that there are other risk factors of ESRD, such as smoking, engine exhaust, etc.
Nocturia (urgency of urinating during sleep) could also be one of the risk factors for ESRD. Nocturia could be due to undiagnosed diabetes, and its presentation could prompt nephrologists to test diabetes.
Kidney failure risk
With the decline in kidney function due to the continued alteration in glomerular filtration rate in CKD and the probability of comorbid diseases, such as congestive heart failure or diabetes mellitus etc., the chances of kidney failure risk increase.
The kidney failure risk equation (KFRE) is a prediction tool developed in 2011 for nephrologists to accurately stratify and anticipate kidney failure. Its validation has been proven in numerous populations. The nephrology team and the hospital management utilise the tool to allocate resources to salvaging patients.
Causes of kidney failure - ESRD
While there are various causes of ESRD only the risk factors which progress the chronic kidney damage can be specified as the reasons for kidney failure. The major causes of kidney failure resulting from progression factors accelerating chronic kidney damage as follows:
- Proteinuria
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Hyperlipidaemia
- Obesity
Proteinuria (increased levels of protein in urine) - In diabetic kidney disease, an albumin excretion rate higher than 30 mg per 24 hours (microalbuminuria) can strongly predict nephropathy (proteinuria) and subsequent loss of kidney function.
Hypertension (high blood pressure) – Hypotension patients are 32% less likely to develop kidney failure than hypertensives. Controlling high blood pressure can reduce the progression of kidney failure.
Diabetes (persistent increase in blood sugar levels) – Diabetes leads to kidney failure. Large prospective studies from the early 1990s demonstrated the benefits of blood glucose control in both the development and progression of microvascular complications. Intensive control needs to achieve at least a ≤6.0% haemoglobin A1c.
Smoking – Smoking from nicotine sources can initiate and help in CKD progression, especially in diabetics, approximately twofold. It is also seen with microalbuminuria and the development of stage 5 CKD (ESRD).
Hyperlipidaemia (high lipid levels in the blood) – Hyperlipidaemia predicts incident CKD. The prevalence of hyperlipidaemia appears to increase as kidney function declines, and hyperlipidaemia is a characteristic of nephrotic syndrome. In 85-90% of patients with decreased kidney function and proteinuria greater than 3 g/day, elevated plasma total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol occur.
Obesity - Studies demonstrated a close relationship between increased body mass index (BMI) and ESRD development, especially in men and less in women.
Causes of acute kidney failure
The three main causes of acute kidney functions include:
- Factors which alter the blood flow to kidneys
- Factors which could block the flow of urine and
- Factors damaging the kidneys
Factors altering the renal blood flow could include:
- Liver failure
- Serious burns or dehydration
- An infection
- Heart failure
- Blood pressure medications
- Blood or fluid loss
Factors blocking the flow of urine include:
- Kidney calculi
- Blood clots in the urinary tract
- Enlarged prostate.
- Nerve damage in bladder
- Bladder, cervical, colon, or prostate cancer
Factors damaging the kidneys include:
- Cholesterol deposits
- Blood clots
- Drug induced renal disease.
- Glomerulonephritis.
Causes of kidney failure in child
The causes of kidney failure in young adults could be caused by either AKI or CKD. These conditions can be caused by:
- Hereditary Diseases
- Infection
- Nephrotic Syndrome
- Systemic Diseases
- Trauma
- Urine Blockage or Reflux
- Birth defects
Causes of death in ESRD patients
An Israeli study in 1992 demonstrated that infectious and cardiac diseases were the primary causes of death in ESRD patients undergoing dialysis.
Complications of kidney failure - ESRD
ESRD can be linked to various types of clinical manifestations complications of kidney failure, which can result in high morbidity and mortality and poor quality of life with the progressive decline of kidney function, which interact with each other. Some of the ESRD complications are of cardiovascular and neurologic origin, which can be quantified as follows:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy - thickening left ventricle wall.
- Cardiac chamber dilation - Enlarged heart chambers with difficulty in contraction.
- Ischemia - a restriction or reduction in a part of the body due to reduced blood circulation.
- Myocardial fibrosis - scarring of cardiac muscle with increased collagen deposition.
- Heart failure - Inability of the heart in pumping enough blood for the body's needs.
- Arrhythmias - Irregular heartbeat.
- About 25-30% of ESRD patients with angina had no evidence of significant coronary artery disease, but an undetermined number have silent coronary disease.
- Changes in the brain’s white matter - cause disturbed anatomical organisation, confusion, functional connectivity, etc.
- Cerebral atrophy (decrease in cerebral size) - loss of neurons causing dementia, seizures, etc.
- Osmotic demyelination syndrome - leads to brain cell dysfunction.
The complications of end stage renal disease can be attributed, at least partly, to the accumulation of uremic toxins. However, a cause-and-effect relationship between these compounds and the complications of kidney failure (uraemia) has not been clearly established.
Acute Kidney Failure Complications
The acute kidney failure complications include few or all the following:
- Oedema (fluid buildup)
- Chest pain (especially in the pericardial region)
- Acidosis (acidic blood)
- Muscle weakness (due to imbalanced electrolytes)
- Death
Kidney failure prevention
- The prevention of kidney failure starts with avoiding contracting AKI or CKD. Nevertheless, the prevention of kidney failure can be initiated if the treatment strategies which are effective in slowing the progression toward kidney failure are started at earlier stages of CKD.
- Avoiding or managing diabetes, hypertension, and other such health issues that cause kidney damage is the primary step in preventing kidney failure. Maintaining a healthy weight with healthy food and exercise helps both kidney failure patients as well as the risk population.
Kidney failure diet
The diet for kidney failure patients includes foods such as fresh fruits, whole grains, frozen or fresh vegetables, and low-fat or fat-free dairy products. Cutting back salts (< 2,300 mg sodium/day) and sugars can help. The diet for ESRD patients include:
- Choosing vegetables such as spinach, peppers, and broccoli.
- Baking meat items can be better than frying.
- Foods without added fats or gravy can be opted.
- Gradually shifting from whole milk to 2% milk.
- Whole grains foods (brown rice, whole wheat, oats, whole-grain corn, etc.) can be used instead of white rice.
- Reading food labels can help, resulting in avoiding foods low in saturated fats, trans fats, etc.
- A food diary can help to track food and food habits.
- The DASH diet plan can lower blood pressure.
Other kidney failure prevention tips include:
- Taking at least 30 minutes of rigorous physical activity daily, aiming for a healthy weight.
- Getting enough sleep (at least 7-8 hours each night)
- Abstaining from smoking and other tobacco product consumption.
- Limiting alcohol intake, thus avoiding weight gain.
- Exploring stress-reducing activities and sticking one (such as yoga) suiting your needs helps in relaxation and coping with emotional and physical health problems.
ESRD - kidney failure diagnosis
End stage renal disease diagnostic tests mainly include blood investigations which could reveal:
- Decreased levels of
- Serum bicarbonate
- Haemoglobin/haematocrit
- Iron stores
- Vitamin D levels.
- Albumin
- Increased levels of
- Serum creatinine
- Blood urea nitrogen
- Serum potassium
- Serum phosphorus
Kidney failure treatment
As ESRD becomes inevitable, the nephrologists prescribe appropriate dialysis modality based on patient preference and options for vascular access for haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. The ESRD treatment options include:
- Medicines – to manage and treat various other comorbid conditions.
- Diet restrictions – supplementing therapies.
- Fluid management – to treat acidosis.
- Renal (Kidney) transplant – to finally conclude kidney treatment
Kidney failure treatment without dialysis
Patients with ESRD require medicines to manage comorbid conditions and secondary complications. Kidney failure treatment can be completed only with renal replacement therapies such as continuous hemofiltration and haemodialysis, intermittent
haemodialysis,
peritoneal dialysis. These can extend the life until kidney transplantation is completed.
Acute kidney failure vs Chronic kidney disease - Differences between Acute kidney failure & Chronic kidney disease
Acute kidney injury (AKI) and Chronic kidney disease (CKD) are two different conditions that affect the kidneys. AKI is a sudden loss of kidney function, while CKD is a gradual decline in kidney function.
| Feature | Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) | Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) |
|---|---|---|
| What is it? | Acute kidney injury (AKI) - a sudden and reversible kidney disfunction seen with declined glomerular filtration rate (GFR) | Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive deterioration of kidney functions gradually over time characterized by irreversible |
| Causes | Illness, injury, or medication | Diabetes, high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis, polycystic kidney disease |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, fluid retention | Fatigue, weakness, anemia, poor appetite, changes in urination |
| Progression into | Upon severer kidney damage AKI can sometimes progress into CKD. | CKD progresses into ESRD requiring dialysis or renal transplant |
| Dialysis use | A short-term renal replacement therapy such as dialysis may be used until the kidney function recovers | Dialysis is a common treatment until kidney transplant especially in ESRD stage |
FAQs (frequently asked questions on Kidney failure - End-Stage Renal Disease)
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868