Hemodialysis Procedure in Hyderabad | Indications and Cost
PACE Hospitals is one of the Best Hemodialysis Centers in Hyderabad offering diagnosis, treatment and care for patients with kidney diseases. We have successfully treated patients who have dealt with issues ranging from acute kidney disease to chronic kidney disease and to kidney failure.
Request an appointment for Hemodialysis Procedure
Hemodialysis Appointment Enquiry
PACE Hospitals - One of the Best Hemodialysis Centers in Hyderabad
What is Hemodialysis Procedure?
hemodialysis meaning
Dialysis replaces some of the kidney functions when kidneys are not working properly. There are mainly two types of dialysis - hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Hemodialysis is a procedure to purify blood when kidney function has deteriorated to the point where the body can no longer remove waste products, salts, and excess fluid from the blood, which is commonly called end-stage kidney disease or renal failure. It is done through a special filter called a dialyzer (artificial kidney) with the help of a dialysis machine.
This procedure will be done in a hospital setting or a dialysis unit. Sometimes hemodialysis is done temporarily in hospitalised patients with acute kidney injury in whom kidney function usually recovers.
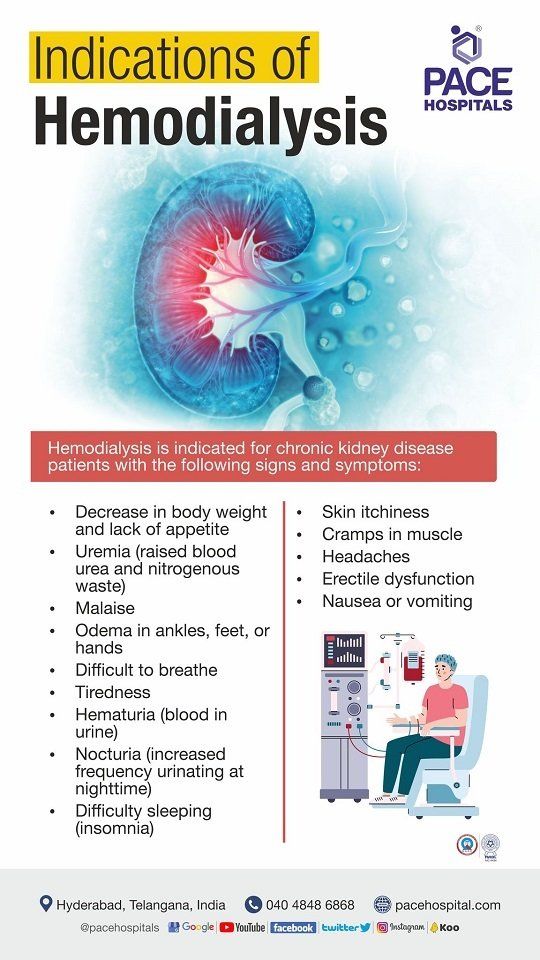
Indications of hemodialysis
Patient with stage-5 renal failure (chronic) where the kidney shows 10 to 15% or less functionality. Presence of signs and symptoms of chronic kidney failure, such as:
- Decrease in weight and lack of appetite
- Uremia (abnormally high levels of bodily waste or toxins waste products in the blood)
- Malaise (feeling of being not well or having zero energy)
- Edema in ankles, feet, or hands
- Difficult to breath
- Tiredness
- Hematuria (blood in urine)
- Nocturia (increased frequency urinating– particularly at night)
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- Skin itchiness
- Cramps in muscle
- Headaches
- Erectile dysfunction
- Nausea or vomiting
Contraindications of hemodialysis
Haemodialysis is an absolute contraindication in patients with an inability to secure vascular access. In addition to this, the relative hemodialysis contraindications include the presence of the following:
- Cardiac failure
- Coagulopathy (abnormality in bleeding cessation, leading to either excessive bleeding or clotting)
- Fear of needles
How to prepare for hemodialysis?
The patient needs to start his preparations several weeks (4 to 8) or months prior to the first haemodialysis procedure. The Nephrologist / Surgeon performs a minor surgery prior to the first hemodialysis to have vascular access to inject or remove blood while undergoing hemodialysis.
These are generally placed between blood vessels (artery and vein) of the patient’s arm or above the wrist, which helps in safely collection of a small amount of blood from the patient’s body circulation to the dialyzer and returning the same from the dialyzer to the patient’s body. Patients should maintain their access site properly, which can help prevent infection and other complications.
There are three types of accesses:
- Arteriovenous (AV) fistula
- Arteriovenous (AV) graft
- Central venous catheter
Arteriovenous (AV) fistula
An arteriovenous (AV) fistula is a setup in which an artery and veins are connected surgically, which is done typically in the less-used arm. This method is highly favoured because of:
- maximises dialysis blood flow
- reduces infection and clotting
- lasts longer
AV graft
Surgeons may use an arteriovenous graft, a flexible synthetic-tube, to connect an artery and a vein when the patient's blood vessels are too small for an AV fistula.
- This method can be used immediately after surgery.
- More chances of infection and clotting.
Central venous catheter
A plastic-tube (catheter) may be inserted into a major vein in the patient’s neck in the event of an emergency requiring hemodialysis. The catheter is only meant to be used temporarily.
Fluid and diet restrictions
Patients will be on strict fluid restrictions on hemodialysis, as the dialyser is unable to remove 2 to 3 days of excess fluid within 4 hours, which further leads to fluid accumulation in the blood, lungs, and tissues.
- The patient is allowed to drink less than 1L fluid per day.
- The patient needs to have a limited intake of salt, potassium, and phosphorus, as these can rapidly accumulate harmful levels in the patient’s body.
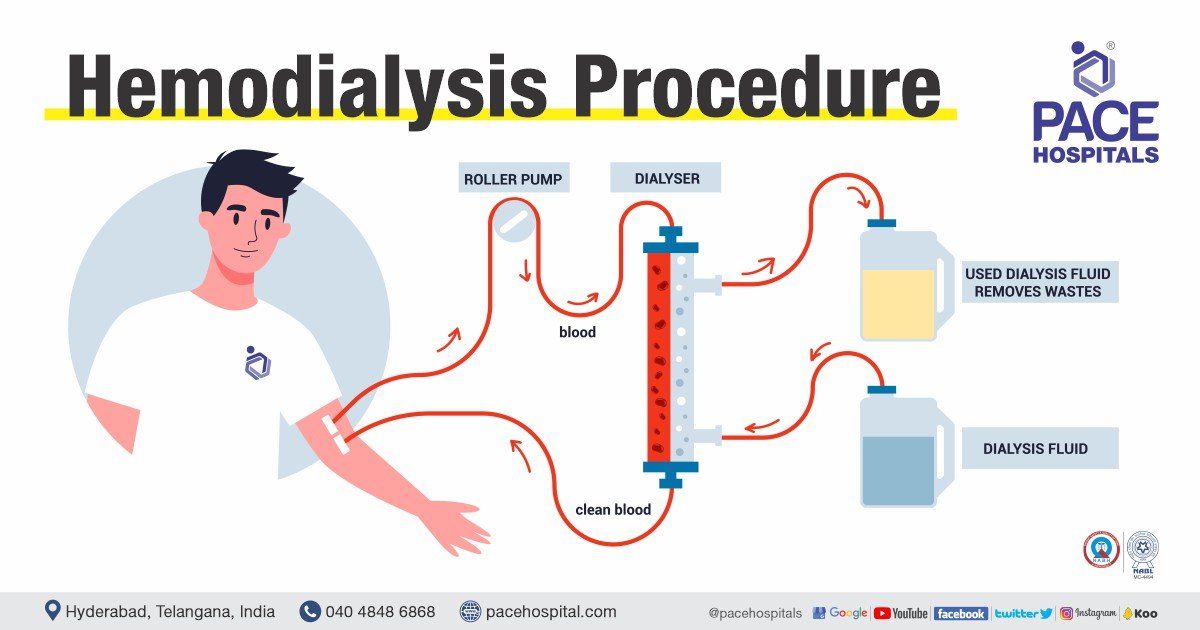
Hemodialysis procedure step by step
On the day of the haemodialysis procedure, the patient’s weight, blood pressure, pulse and temperature will be checked. The patient will be asked to rest on a bed. The arteriovenous fistula site will be cleaned thoroughly.
- During haemodialysis, two needles are inserted into the patient's arm via the access site (fistula/graft placed on the arm) and safely placed to remain secure, post that the dialyzer will be connected with each plastic tube. Through one tube, blood from the body goes into the dialyzer where the filtration of blood happens and the filtered blood returns to the body via the second tube.
- The dialyzer consists of a series of membranes, which act as a filter (artificial kidney) and a special liquid known as dialysate.
- The dialyzer filters the waste products and excess fluids in blood into a dialysate. The physician or the technician might inject an anticoagulant into the first tube to prevent blood coagulation. Through the second tube, the blood is reintroduced to the patient’s body after being purified.
- The patient’s blood pressure and heart rate are continuously monitored throughout the procedure. During the process, the patient can take rest, read, watch television, or speak with the caretaker or neighbours.
- When the treatment is completed, the needles will be removed from the patient's access site, it will be cleaned, and a pressure dressing will be applied to stop any bleeding. The patient’s weight will be checked after the completion of the procedure.
- When a lot of fluid has been filtered out, the patient may experience nausea, back pain, muscle cramps during the process, as the patient has put on more fluids between appointments. The patient needs to report to the physician about their symptoms so that they can be alleviated either by adjusting the speed of the dialyzer or by providing medication.
What happens after hemodialysis?
A patient may face complications post-haemodialysis, such as low blood pressure, dizziness, or faintness. In addition to these, they may also experience the following difficulties:
- Pain in the chest
- Restless legs syndrome
- Headache
- Skin itchiness
- Cramps in the muscle
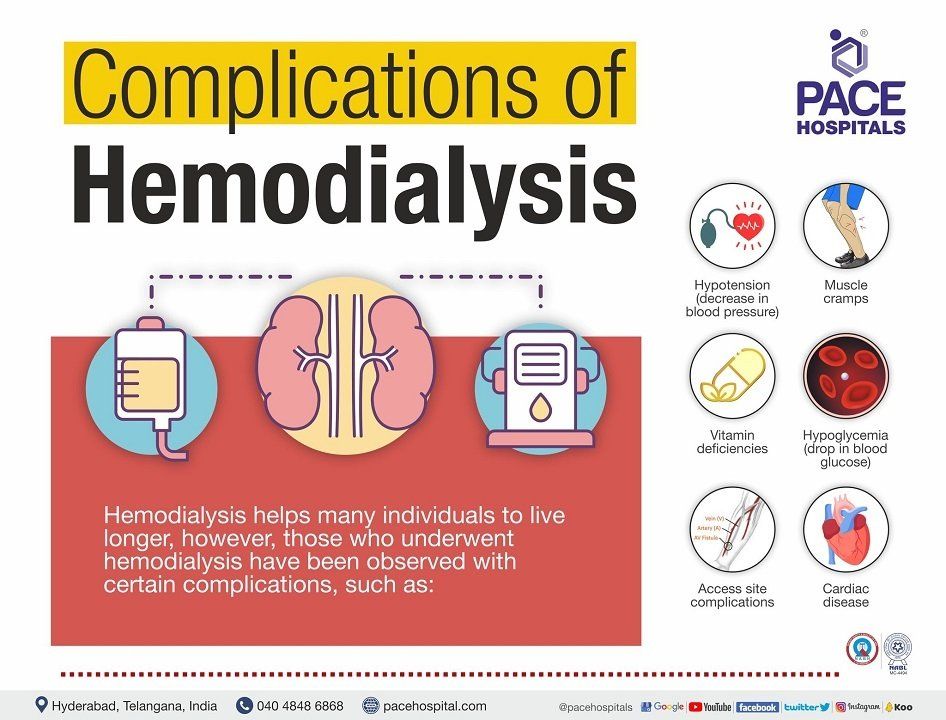
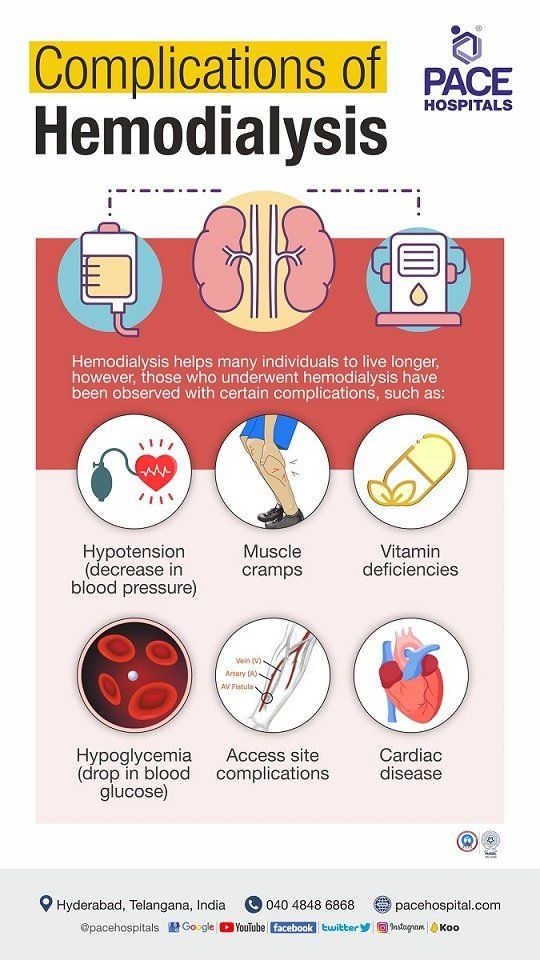
Hemodialysis complications
Most haemodialysis patients have many health issues. Although haemodialysis helps many individuals live longer, but those who undergoes hemodialysis have been observed certain complications.
Although hemodialysis is effective in restoring some kidney function, it is associated with a number of complications which will be managed by the dialysis staff. They are as follows:
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Muscle cramps
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Low blood sugars (Hypoglycemia)
- Access site complications
- Cardiac disease
Hypotension (low blood pressure): During the hemodialysis procedure, fluid is removed by ultrafiltration. The amount of fluid to be removed is determined by the weight gain of the patient in between dialysis sessions. If there is excess weight gain, the patient is prone to hypotension in the process of removal of that extra fluid from the body.
Muscle cramps: Hemodialysis patients frequently experience muscle cramps due to the changes in the fluid balance and electrolytes in the blood. Regulating fluid and sodium intake in between hemodialysis sessions may be useful for reducing symptoms experienced during treatment.
Vitamin deficiencies: Dialysis filters out water-soluble vitamins. In addition, the patient experiences bone loss as the damaged kidneys are unable to convert vitamin D (which absorbs calcium) to its active form. Therefore, dialysis patients are at risk of fractures and bone pains.
Low blood sugars (Hypoglycemia): Dialysis patients are prone to hypoglycemia during the dialysis procedure. Glucose monitoring during the procedure and management accordingly will prevent this complication.
Access site complications: The effectiveness of a patient’s hemodialysis treatment can be negatively impacted by complications like infection, the occurrence of an aneurysm (narrowing of the blood vessel wall), or blockage of the dialysis catheter of the arterio venous fistula.
Cardiac Disease: Some patients are prone to heart related complications like fluctuations in heart rate, heart attacks etc. This is due to:
- The effects of chronic anaemia, hypertension, and fluid overload on the heart's myocardium are almost certainly to blame.
- Pre-existing conditions like atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients with renal failure.
- Retaining too much phosphate can lead to aortic and mitral valve calcification in patients.
Hemodialysis vs Peritoneal dialysis | Difference between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis
Difference between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis can be catergorised under area of dialysis access, membrane used, complications and psychosocial considerations.
| S.No. | Hemodialysis | Peritoneal dialysis (PD) |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure | Hemodialysis takes 4 hours per session, 3 times a week. | Peritoneal dialysis (PD) using up to four exchanges/day or cycling at night |
| Location | Usually in hospitals | Done at home |
| Dialysis access | Accesses through an AV fistula or AV graft that needs to be inserted 2 to 3 months prior to the first procedure. | Access relatively easy to establish and can be used in 2 weeks |
| Membrane used | Selectively permeable membrane | Peritoneum |
| Complications | Adverse dialysis-related symptoms (Cramps, headache, etc.), Catheter infections and associated complications (septicaemia, subacute bacterial endocarditis etc.) can be life-threatening and Cardiovascular death from arrhythmias, myocardial infarction and stroke. | Peritonitis, Increased weight, Risk of high blood sugars, Abnormal lipid levels, Higher pressure in abdomen, which can cause hernias and fluid leaks |
| Psychosocial considerations | It can be inconvenient for patients and their families to have to arrange transportation to and from the unit three times a week for dialysis treatments and It's difficult to make leave plans when patients have to use nearby dialysis centres. | Home care can be less stressful, Getting to the hospital might require in case of emergency and Fluids for PD can be shipped anywhere in the world if notice is given in advance. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of catheter is used for hemodialysis?
Hemodialysis calls for a tunnelled catheter as it is placed under the skin. The catheters consist of two openings,
- Red: to draw unfiltered blood from the patient’s body and send it to dialyzer.
- Blue: to send back the filtered blood into the patient’s body from dialyzer.
There are of 2 types tunnelled categories:
- Cuffed: It is used for longer time (more than 3 weeks), when there is no option for usage of permanent access and when an AV fistula or graft has been placed which is not yet ready for use.
- Non-cuffed: These are used in case of emergencies and for shorter time period.
What happens during hemodialysis?
During hemodialysis, the patient’s blood moves from the patient's body into a dialysis machine through a network of tubes. A filter called a dialyzer is used to clean the blood by removing waste and excess fluid with the help of a liquid called dialysate while it's passing through the machine. After being purified, the patient’s blood is reintroduced into the patient’s body and needles will be removed from the patient's access site. A pressure dressing will be applied to stop any bleeding.
What is the common complication during hemodialysis procedure?
Most common complications associated with hemodialysis are a drop in blood pressure, headaches, weakness post hemodialysis and cramps.
Why does dialysis take 4 hours?
Dialysis session usually lasts 4 hours because it is the minimum amount of time which is required to remove the excess waste products from the body and it is based on the studies done in patients on dialysis.
Do dialysis patients still urinate?
Dialysis patients still urinate, but as the duration on dialysis increases, gradually urine output will decrease which is a known phenomenon.
Can kidneys start working again after dialysis?
Dialysis is not a form of treatment for the kidneys, which might have failed due to a variety of causes. Dialysis only provides support to the body in the place of kidneys in removal of waste products and excess water. If kidney failure is permanent, then the kidneys won’t start working after dialysis. Sometimes the kidneys temporarily stop working (acute kidney injury) and gradually recover their function. In that case dialysis will be done temporarily until the kidneys recover their function.
Can you miss a day of dialysis?
Once in a while missing a dialysis won’t cause many problems but if there is excess water accumulation in the body the patient may have breathing difficulty before next dialysis.
What is the most common cause of death in dialysis patients?
Cardiac related issues (arrythmias, coronary artery disease) are the most common reasons for death in dialysis patients.
Can you drink water during dialysis treatment?
Yes, patients can drink water during dialysis sessions but they should stay within the amount prescribed by the nephrologist in a day.
Can kidneys heal while on dialysis?
If it is a temporary kidney failure and the cause for it is reversed then kidneys may recover and dialysis may be stopped. But if the dialysis is due to permanent kidney failure kidneys won’t recover while on dialysis.
What should you eat after dialysis?
There is no specific diet that should be taken after dialysis other than what dietician and nephrologist has prescribed. In between dialysis sessions, a snack is provided for the patients as advised by the treating doctor.
Can your kidneys recover from stage 5?
Stage 5 means it is a chronic kidney disease which is irreversible and it is present for more than 3 months duration. Usually, recovery won’t happen in patients with chronic kidney disease unless.
How much does hemodialysis cost in India?
Cost of hemodialysis in India ranges vary from Rs. 1,500 to Rs. 5,800 per session (one thousand five hundred to five thousand eight hundred only) and depends upon multiple factors and differs from case to case. However, hemodialysis cost per session may vary depending upon the different hospitals in different cities.
What is the cost of hemodialysis in Hyderabad?
Hemodialysis cost in Hyderabad ranges vary from Rs. 1,600 to Rs. 3,800 per session (one thousand six hundred to three thousand five hundred only). However, cost of hemodialysis per session in Hyderabad depends upon the multiple factors such as dialyzer - single use, dialyzer - reuse, patient condition, age, associated conditions, hospital, CGHS, ESI, EHS, insurance or corporate approvals for cashless facility.