Peritoneal Dialysis Procedure in Hyderabad | Indications and Cost
PACE Hospitals is one of the Best Peritoneal Dialysis Centers in Hyderabad, offering diagnosis, treatment and care for patients with kidney diseases. We have successfully treated patients who have dealt with issues ranging from acute kidney disease to chronic kidney disease and kidney failure.
Request an appointment for Peritoneal Dialysis Procedure
peritoneal dialysis procedure Appointment Enquiry
PACE Hospitals - A Peritoneal Dialysis Center in Hyderabad, India
What is Peritoneal Dialysis Procedure?
Peritoneal dialysis meaning
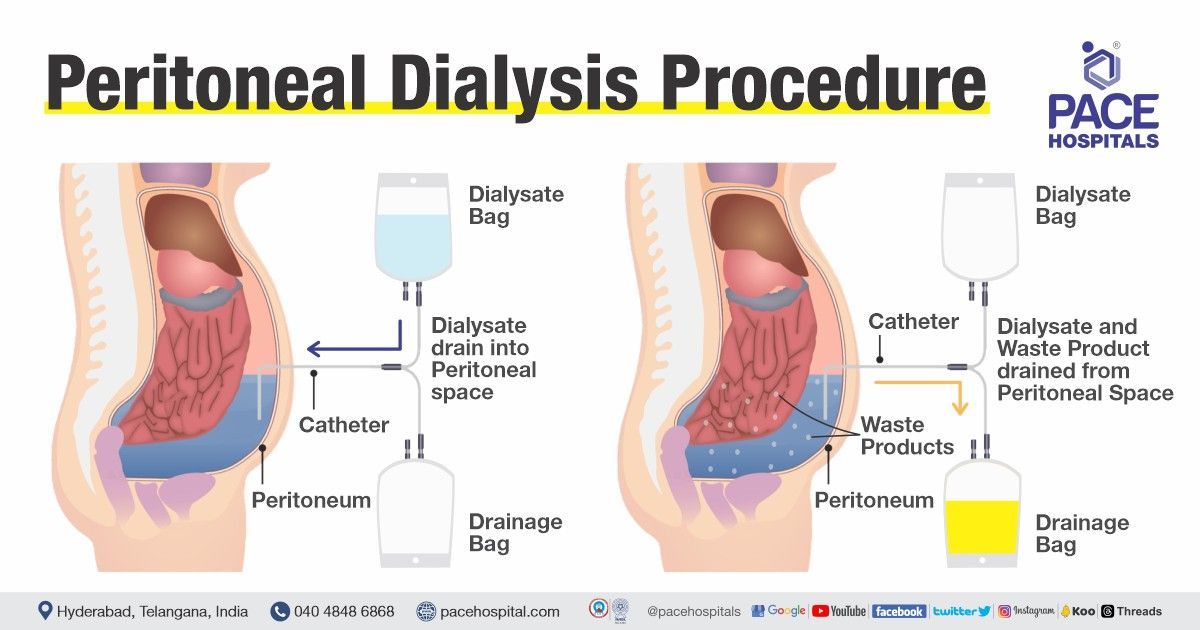
Peritoneal dialysis (PD dialysis) is a type of renal replacement therapy indicated for patients with end-stage kidney failure. It involves infusing or placing a dialysate (a sterile solution) into the patient's peritoneal cavity (abdomen) via a catheter and filtering the waste products and excess fluids from the blood using the peritoneal membrane as an exchange surface or filter.
The solution is infused and drained into the peritoneal cavity in two ways:
- Manually (continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis), in which the patient infuses the dialysate fluid by himself.
- Machine-assisted peritoneal dialysis (automated peritoneal dialysis), in which dialysis is performed with the help of a cycling machine that allows exchanges to happen overnight while the patient is sleeping.
These treatments can be performed at home or work under good hygiene conditions.
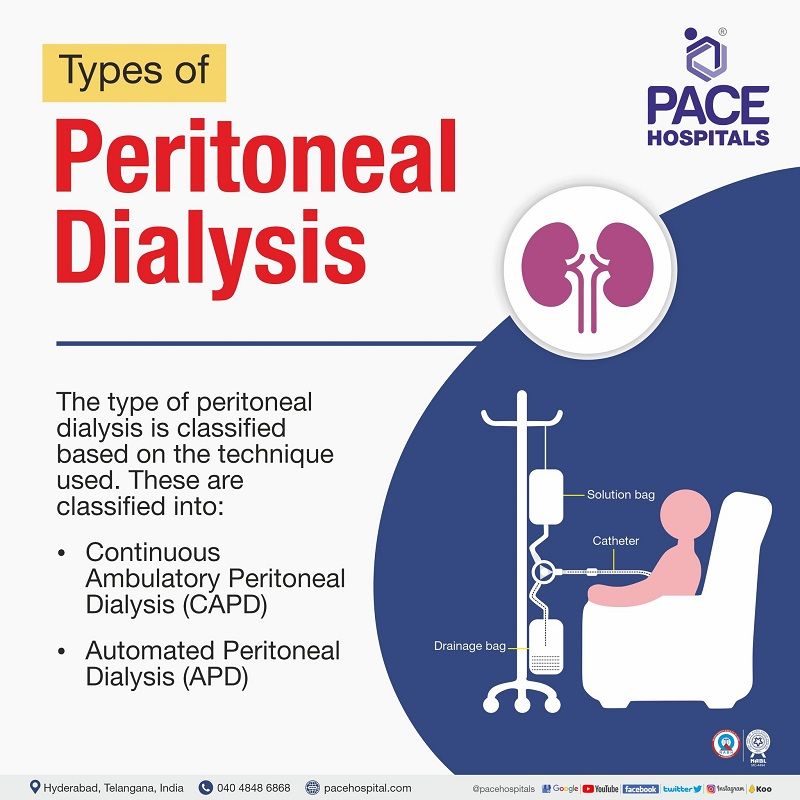
Types of Peritoneal Dialysis Procedure
The type of peritoneal dialysis is purely based on the technique used. These are classified into:
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD):
- 2 litres of dialysate fluid (cleaning fluid) will be inserted into the abdomen (belly) of the patient.
- To accomplish this, a Y-tube connects one of its ends to a plastic bag containing the dialysate fluid and the drain bag and the other side to the catheter located in the patient's abdomen.
- The plastic bag is raised to the patient's shoulder, and the fluid passes down into the patient's stomach due to gravity.
- After a certain amount of time, when a fluid exchange is complete, the dialysate in the patient's abdomen (which consists of wastes removed from the patient’s blood) should be drained off into the drain bag.
- This process is repeated 3–5 times during the day, and each exchange takes about 20 to 30 minutes
Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD):
Automated peritoneal dialysis works the same as continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis; the only difference in APD is that the exchange process is done through a machine (automatic cycler), which performs multiple exchanges while the patient is asleep. The cycler pumps and drains dialysate from the abdomen of the patient overnight according to the prescription provided by the nephrologist. This method is only appropriate for use at night because the patient must be attached to the machine for 10 to 12 hours. During daytime, a long dwell may be used based on the requirement of the patient as decided by the nephrologist.
Automated peritoneal dialysis consists of various forms, such as:
- Continuous cyclical peritoneal dialysis (CCPD): It comprises three to four exchanges during the night of 2 to 3 litres each and a long daytime dwell with 1.5 to 2 litres of dialysate. So the process is continuous 24 hours a day, so the name of continuous cyclical peritoneal dialysis.
- Nocturnal intermittent peritoneal dialysis (NIPD): Here the process of peritoneal dialysis is only done at night and there is no day dwell as in CCPD.
- Tidal peritoneal dialysis (TPD): TPD is an automated procedure that fills the patient's abdomen with dialysate and then exchanges only a portion of the volume, leaving an intra-abdominal reserve in the peritoneal cavity until the final drain.
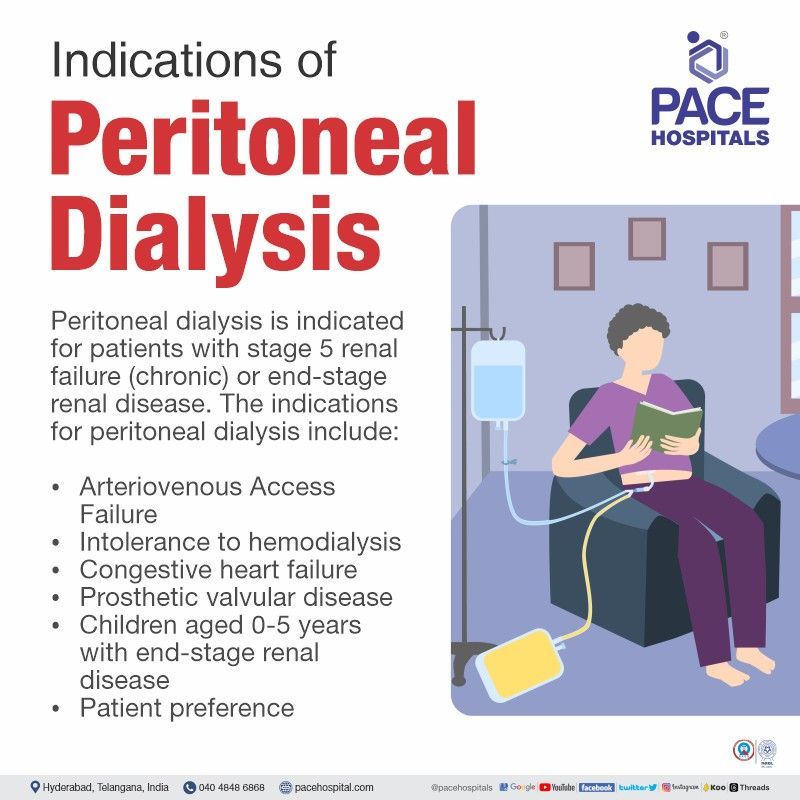
Indications of peritoneal dialysis procedure
Peritoneal dialysis is indicated for patients with stage 5 renal failure (chronic) or end-stage renal disease. The indications for peritoneal dialysis include:
- Arteriovenous Access Failure. In case if you cannot have a graft or fistula created in your arm or leg for haemodialysis.
- Intolerance to hemodialysis. Some people cannot tolerate hemodialysis because of its side effects, such as low blood pressure (hypotension), muscle cramps, nausea, anaemia or sleep problems.
- Congestive heart failure. Peritoneal dialysis may be a better option for people with congestive heart failure because it does not put as much stress on the heart as hemodialysis.
- Prosthetic valvular disease. People with prosthetic heart valves are at risk of blood clots during hemodialysis. Peritoneal dialysis may be a safer option for these people.
- Children aged 0–5 years. Peritoneal dialysis is the preferred treatment for children with end-stage renal disease because it is less invasive than hemodialysis.
- Patient preference. Some people simply prefer peritoneal dialysis to hemodialysis.
Contraindications of peritoneal dialysis procedure
Peritoneal dialysis is contraindicated (not suitable) for patients suffering from the following:
- An abdominal abscess (collection of infected fluid or pus, surrounded by inflamed tissue inside the abdomen)
- Severe inflammatory bowel disease
- Acute active diverticulitis (inflamed or infected diverticula)
- Severe active psychotic disorder and marked intellectual disability
- Active ischemic bowel disease
- Women in their third trimester (week 27) of pregnancy
- Multiple abdominal adhesions (scar-like tissue that form inside the abdomen)
- Ostomy (it is a surgical opening made in the skin in case any problem is not allowing a part of the body to function well)
- A person with upper limb amputation with no help at home
- The person with poor personal hygiene
- Dementia (forgetfulness)
Peritoneal dialysis preparation
Peritoneal dialysis preparation generally involves a minor surgery at least 2 weeks before the first exchange, where the nephrologist inserts a catheter into the patient's abdomen (belly).
- When the patient is under local anaesthesia (usually), the surgeon will make a small incision below and beside the belly button (navel) to insert the catheter into the peritoneal cavity.
- The site of the catheter placement should be allowed to heal for at least 15 to 20 days before starting a full schedule of exchanges for a better result.
- The patient will be provided with necessary training by the health care professionals for one to two weeks on how to use the peritoneal dialysis equipment without any infections.
- If the patient chooses automated peritoneal dialysis, the patient will be trained on:
- The preparation of the cycler
- Connection of the bags of dialysis solution
- Placement of the drain tube
- Execution of manual exchange in case of any power failure or if the patient requires an exchange during the day.
During peritoneal dialysis procedure
Peritoneal dialysis procedure is typically done at home or in any other clean, enclosed environment. During peritoneal dialysis at home:
The patient needs to attach a transfer set (a tube that is used to connect the catheter placed in the abdomen to the Y tube) to the catheter by opening the secure cap (which is present at the end of the catheter to prevent infections). Based on the dialysis technique, the patient can opt for one of the following methods:
- Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Automated peritoneal dialysis
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
- Before use, each bag of solution (dialysate) should be warmed up to body temperature.
- Connect the fresh dialysis solution bag and drain bag to the one end of the Y tube by hanging the fresh dialysis bag from a pole and placing the drain bag on the floor.
- All the air from the tubes should be removed before connecting to the catheter. This can be done by allowing a minute amount of fresh and warm solution of dialysate to flow directly into the drain bag from the new bag of solution.
- The disposable cap of the transfer set should be opened and connected to the other end of Y tube, and the patient’s abdomen will be filled with fresh dialysis solution from the hanging fresh dialysis bag.
- The dialysate liquid should be allowed to remain in the abdomen for a period of time.
- After the dwell time, the dialysis solution present in the abdomen of the patient will drain out into the drain bag. At the time of draining, the patient should wear a surgical mask.
- The process of filling dialysate solution into the patient’s abdomen and collecting waste products in the drain bag is termed “exchange”. In a day, the patient may need three to five CAPD exchanges.
Automated peritoneal dialysis
- Automated peritoneal dialysis is similar to CAPD; the only difference is that the exchange of fluid is done by a machine when the patient is asleep.
- The patient needs to clean the APD machine thoroughly with an alcohol wipe.
- The dialysis solution should be thoroughly checked for the presence of any leaks or contamination.
- The drain bags need to be placed on the bottom shelf.
- The cassette package should be inserted in the APD, with all the clamps on the organiser should be closed.
- Connect the organiser's heater line (red colour clamp) and supply line (white colour clamp) to the dialysis solution by opening their clamps, then connect the organiser's drain line (big white clamp) to the drain bag and close the drain bag clamp before beginning the process without touching the tips of their connectors.
- The organiser’s patient line should be attached to the transfer set (which is connected to the catheter placed in the patient’s abdomen).
- The organiser’s patient line and transfer set are connected using a connection shield. Once they are connected firmly, open the transfer set's twisting clamp and the patient line clamp to start the therapy.
- The patient should start the procedure before going to bed. As the patient sleeps, the machine automatically performs fluid exchanges, which take 8 to 10 hours to complete.
- At the end of the treatment session, a minute amount of dialysate fluid remains in the patient’s abdomen. This will be drained during the next session.
- During the nighttime treatment, the patient may experience interruptions such as a power outage or the need to use the restroom. However, it is normally safe to miss exchanges worth one night as long as treatment is resumed within 24 hours.
Post peritoneal dialysis procedure
- Post peritoneal dialysis at home session, the patient should carefully detach the transfer set from the dialysis apparatus, close it with a disposable cap, and carefully place it in a peritoneal dialysis belt or pouch.
- The fluid bag, which contains drained liquid (waste fluid that has been excreted out while on peritoneal dialysis), should be discarded.
- It's possible that the patient would experience discomfort and bloating in the abdominal region due to the constant presence of fluid throughout the day.
General mechanism of peritoneal dialysis procedure
During a peritoneal dialysis exchange, the removal of solutes and water depends on the balance between the movement of solutes and water into the peritoneal cavity and their absorption by the body.
- The dialysate solution, which contains a sugar called dextrose or icodextrin, flows into the abdomen of the patient and remains there for a certain amount of time (dwell time), which is usually four to six hours.
- Dextrose in the dialysate aids in the removal of waste and excess fluid from the patient's blood through microscopic blood vessels in the lining of the abdominal cavity.
- After the dwell time, the solution, along with waste products drawn from the patient’s blood, drains into a sterile collection bag or drain bag.
Measurement of peritoneal dialysis procedure
To determine the efficacy of peritoneal dialysis at home, clearance is calculated. Clearance test shows how much dose of dialysis is the patient receiving. The patient's dose of dialysis should be measured every four months. This measurement should be done when
- At the start of peritoneal dialysis (within one month)
- Change in the dialysis prescription
- At a request of a nephrologist
- When the patient’s residual kidney function goes down
Clearance test:
To figure out how much of a specific waste product is being eliminated from the patient’s blood during dialysis, a blood sample and a sample of dialysis (which consists of waste materials) will be collected and compared. The results estimate the functionality of peritoneal dialysis.
Peritoneal equilibration test (PET):
This test is done within 4 to 8 weeks after starting peritoneal dialysis . During the exchange, a few blood and dialysis solution test samples will be collected and compared. This test defines the rate of transfer of solute and water across the peritoneal barrier.
The test yields the following parameters:
- 4-hour dialysate to plasma ratio of creatinine
- 4- to 0-hour dialysate glucose ratio
- 4-hour ultrafiltration volume
The outcomes of the above signify the rate of waste removal from the blood into the dialysate. The results aid the nephrologist in making a decision on the following:
- A number of exchanges the patient needs each day.
- Duration of the dialysis fluid stay in the patient’s abdomen.
- Amount of dialysis and type of dialysate (higher or lower concentration of dextrose) fluid the patient need.
Advantages of peritoneal dialysis procedure
Peritoneal dialysis at home has the advantage of being physiologically gentle. In addition to this:
- Regular visits to the dialysis unit are not required
- Easy to do with less assistance
- Few restrictions on diet and fluid intake
- Fewer medications are to be taken because the patient is on dialysis daily
- Painless procedure
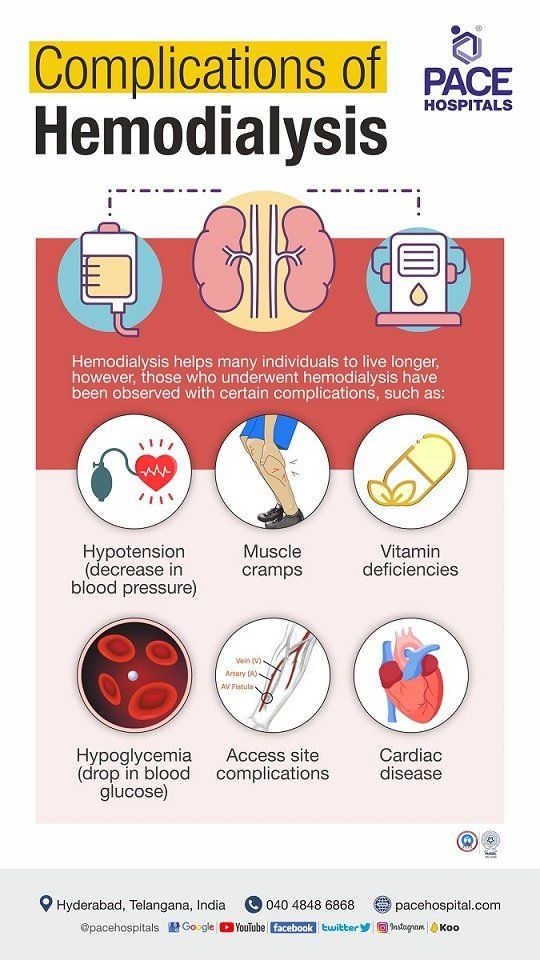
Peritoneal dialysis complications
Peritoneal dialysis comprises early and late complications. The early complications are related to catheter insertion, which might cause infection and further lead to peritoneal dialysis discontinuation.
Early complications include:
- Bowel perforation: Bowel perforation is rare (less than 1%) and occurs while insertion of the peritoneal dialysis catheter into the abdomen.
- Bleeding: Bleeding at the exit site is rarely a severe issue during peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion.
- Wound infection: Rare but can be treatable.
Late complications include:
- Peritonitis (peritoneum membrane lining inflammation): It is the most important complication which needs to be identified early and treated to prevent outcomes. It is an infection of the abdominal lining caused by skin bacterium contamination, which is a typical consequence of peritoneal dialysis. Infections can also form near the site where the catheter is inserted to transport the cleansing fluid (dialysate) into and out of the patient's abdomen.
- Cuff extrusion or infection: There is a cuff on the peritoneal dialysis catheter which is positioned under the skin. It adheres to the surrounding tissues and forms a barrier to infections entering the peritoneal cavity from the skin surface. Cuffs may sometimes come out or may get infected. Usually develops when the exit location is located beneath the belt line. Closely positioned superficial cuffs may protrude or get contaminated. In such cases, the catheter should be swapped, and a new exit site should be chosen.
- Weight gain: The patient will have a weight gain as the dialysate used in peritoneal dialysis contains sugar. In the case of diabetes patients, absorbing some of the dialysate might cause an increase in blood sugar.
- Hernia: Long periods holding liquids in the abdomen may cause muscle strain.
- Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis: It is rare and late complication of peritoneal dialysis. It is a serious complication where peritoneal membrane gets thickened. It leads to peritoneal dialysis failure, abdominal discomfort and may cause intestinal obstruction.
- Back pain, genital swelling (abdominal pain)

Peritoneal dialysis precautions
Precautions during peritoneal dialysis at home should be followed by the patient to have hygiene and an effective process without any catheter-related infections.
- Low-calorie diet with low sodium and phosphorus and the right amount of potassium and protein.
- Record maintenance of the amount of liquid and food consumed.
- Adjusted doses for diabetic patients' medicines, as dialysate containing glucose enters the patient's abdomen, raises the patient’s blood glucose levels.
- Refrainment of swimming for two weeks following catheter administration due to the possible contamination at the site.
- Avoidance of over-the-counter medications that damage kidney function, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Every time the patient needs to touch the catheter, they must wash their hands thoroughly.
- Before performing exchanges, the patient should wear a surgical mask.
- Before using a dialysate solution, the patient must be sure there is no scope for contamination in the packaging, such as cloudiness.
- The skin around the surgical site, where the catheter is placed, should be thoroughly cleaned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is peritoneal dialysis safe?
Yes, peritoneal dialysis is a safe and painless procedure that should be performed in a clean environment, preferably at home. Some patients, however, may experience side effects such as peritonitis, weight gain, abdominal hernia, etc.
What happens when peritoneal dialysis is stopped or not effective?
Peritoneal dialysis is used to treat kidney failure, where the kidney is unable to perform its functions, especially the excretion of waste and excess fluid. If the peritoneal dialysis stopped or not effective, the waste accumulates in the human body, leading to toxicosis. The patient immediately needs to shift to haemodialysis.
How many times a week is peritoneal dialysis done?
It depends on the type of peritoneal dialysis. In the case of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, it is done multiple times during the day, typically three to five times while the patient is awake during normal activities. About 20 to 30 minutes are averaged for each exchange under continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.
In automated peritoneal dialysis, it is done once with a long duration of 8 to 10 hours and one exchange with a dwell time that lasts the whole day. Therefore, it is generally used at night when the patient is sleeping.
Can you take a shower with peritoneal dialysis catheter?
For the first two weeks after peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion, the patient should avoid bathing or swimming because the skin around the catheter must be kept dry until it has healed completely. The patient is at significant risk of exit site contamination during bathing or swimming. It is acceptable to clean the body with a wash cloth or sponge, as long as the catheter and bandage are kept dry at all times. After the catheter insertion site heals fully, a shower can be done.
Why can't you drink excess water while on dialysis?
Dialysis is an artificial filtration process used when the patient's kidneys are unable to maintain fluid balance. In peritoneal dialysis or haemodialysis, based on the native urine output patient is advised to restrict fluid intake including water to avoid excess weight gain. If excess water is consumed it leads to accumulation in the body. This condition can harm the patient's health, such as difficulty breathing, heart problems, high blood pressure, and swelling.
How to insert a peritoneal dialysis catheter?
A peritoneal dialysis catheter can be inserted into the patient's abdominal cavity through several methods. Due to their safety and promising early outcomes, percutaneous insertion by nephrologist is becoming common. Open surgery and laparoscopic procedures are among the other options.
What solution is used in peritoneal dialysis?
The dialysate solution is a sterile aqueous electrolyte solution that contains six electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, and bicarbonate) and sugars such as icodextrin (glucose polymer) or dextrose that help in the removal of toxins and excess fluid from the body. These concentrates vary as per the available bag sizes (1.5 to 3 liters).
Why do you warm peritoneal dialysis fluid?
Dialysate has the potent capability to change the blood temperature, which directly influences the body’s core temperature. Warm peritoneal dialysis fluid that enters the patient's abdomen causes blood vessels to dilate (widen) and more toxins to be released into the bloodstream. These toxins are then disposed of in the drain bag. Hence, it is recommended to warm the peritoneal dialysis fluid before the procedure starts.
Does peritoneal dialysis remove phosphorus?
Yes, peritoneal dialysis removes phosphorus when the patient is on the dialysis procedure. Peritoneal dialysis removes approximately 300 mg of phosphorus each day.
How to unclog a peritoneal dialysis catheter?
The first approach to remove clots developed in the catheter is usually manual compression of the dialysis fluid container. In some cases, urokinase can help dissolve fibrin clots. Clots (especially fibrin clot) form after catheter insertion, as an early consequence of peritoneal dialysis.
What exercises can I do while on peritoneal dialysis?
Patients on peritoneal dialysis therapy can participate in aerobic exercises, including walking, jogging, dancing, seated marching, and seated cycling, as well as muscle strength training exercises like push-ups and squats. As per World Health Organisation, patients on peritoneal dialysis therapy with very low activity levels should gradually work towards 150-300 mins of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per week, or they should indulge in 75–150 mins of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, followed by two or more days per week of muscle-strengthening activities.
What can you not eat with peritoneal dialysis?
The patient should limit their daily phosphorus and sodium intake and eat the right amount of high-quality protein and adequate caloric foods. Due to the impairment of the patient’s kidney function, certain dietary limitations must be observed.
What is the peritoneal dialysis price in India?
Peritoneal dialysis price in India ranges vary from ₹ 20,000 to ₹ 30,000 per month (INR twenty thousand to thirty thousand). However, cost of peritoneal dialysis in India depends upon the multiple factors such patient condition, no of session, peritoneal dialysis fluid price, PD machine price, no of dialysate bag, drainage bag, cyclers, injectable medications.
How much does peritoneal dialysis cost in Hyderabad?
Peritoneal dialysis cost in Hyderabad ranges vary from ₹ 23,000 to ₹ 28,000 per month (INR twenty-three thousand to twenty-eight thousand). However, price of peritoneal dialysis in Hyderabad depends upon the multiple factors such as type of PD procedure (CAPD and APD), patient condition, peritoneal dialysis machine cost, dialysate bag, drainage bag, cyclers, injectable medications.