हैदराबाद, भारत में कान का मैल हटाना
पेस हॉस्पिटल्स, हैदराबाद, भारत में स्थित एक अग्रणी स्वास्थ्य सेवा केंद्र है, जो कान के मैल को हटाने में अपनी विशेषज्ञ सेवाओं के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। अनुभवी ईएनटी विशेषज्ञों की हमारी टीम प्रत्येक रोगी की आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप सुरक्षित और प्रभावी कान के मैल को हटाने के उपचार प्रदान करने के लिए समर्पित है। अत्याधुनिक तकनीकों और उपकरणों का उपयोग करते हुए, हम एक आरामदायक और सटीक निष्कासन प्रक्रिया सुनिश्चित करते हैं, जिससे सभी उम्र के रोगियों के कान के स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर बनाए रखने में मदद मिलती है।
अपॉइंटमेंट के लिए अनुरोध करें कान का मैल हटाना
कान का मैल हटाना - अपॉइंटमेंट
हमें क्यों चुनें?
8400 मरीजों का कान में मैल जमने का इलाज किया गया
हैदराबाद में सर्वश्रेष्ठ ईएनटी डॉक्टर की टीम
99.9% सफलता दर के साथ सटीक उपचार
सभी बीमा बिना किसी लागत वाली EMI विकल्प के साथ स्वीकार्य हैं
हैदराबाद, भारत में स्थित पेस हॉस्पिटल्स पेशेवर और सुरक्षित कान का मैल हटाने की सेवाएँ प्रदान करता है। सभी उम्र के लोगों को आराम और सटीकता पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हुए, कान का मैल हटाने के लिए असाधारण देखभाल प्रदान की जाती है। हमारी अत्याधुनिक सुविधाएँ और उन्नत नैदानिक उपकरण कान के मैल का गहन मूल्यांकन और प्रभावी निष्कासन संभव बनाते हैं। ईएनटी विशेषज्ञों की हमारी समर्पित टीम प्रत्येक रोगी के साथ मिलकर उनकी विशिष्ट आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप एक अनुकूलित उपचार योजना तैयार करती है।
पेस हॉस्पिटल्स में कान के मैल को हटाने के उपचार में कई तरह की विधियाँ शामिल हैं, जिनमें सौम्य सिंचाई, माइक्रोसक्शन और मैन्युअल निष्कर्षण तकनीकें शामिल हैं। अनुभवी ईएनटी विशेषज्ञों और ऑडियोलॉजिस्टों की हमारी उच्च प्रशिक्षित टीम प्रभावी और आरामदायक कान के मैल को हटाने के लिए नवीनतम तकनीकों और प्रौद्योगिकी का उपयोग करती है और यह सुनिश्चित करती है कि प्रत्येक प्रक्रिया को रोगी के आराम और सुरक्षा को प्राथमिकता देते हुए, बारीकियों पर सावधानीपूर्वक ध्यान दिया जाए। चाहे आपको मामूली असुविधा हो या गंभीर रुकावट, पेस हॉस्पिटल्स आपके कान के स्वास्थ्य को बहाल करने के लिए संपूर्ण और संवेदनशील देखभाल प्रदान करने के लिए प्रतिबद्ध है।
कान के मैल का निदान
ईएनटी विशेषज्ञ कान की नली और टिम्पेनिक झिल्ली की जांच करने के लिए सरल नैदानिक परीक्षण करता है, ताकि अतिरिक्त कान के मैल की मात्रा और प्रकृति का मूल्यांकन किया जा सके, जिसमें शामिल हैं:
- चिकित्सा का इतिहास
- शारीरिक जाँच
- दृश्य परीक्षा
- ओटोस्काप
- ओटो-माइक्रोस्कोपी
चिकित्सा का इतिहास: बाह्य श्रवण नलिका (ईएसी) की शारीरिक जांच से पहले, यह सुझाव दिया जाता है कि रोगी स्वास्थ्य देखभाल पेशेवर से विस्तृत चिकित्सा इतिहास और दवा के इतिहास के बारे में बात करें और की गई किसी भी प्रक्रिया का स्पष्टीकरण प्रदान करें।
शारीरिक जाँच: एक स्वास्थ्य देखभाल पेशेवर कान की नली को देखकर पुष्टि कर सकता है कि कान के मैल का एक प्लग बन गया है जिसमें काले/गहरे भूरे/पीले/गहरे नारंगी रंग के मोटे पदार्थ हैं, जो आंशिक रूप से या पूरी तरह से बाहरी कान की नली को अवरुद्ध कर रहे हैं।
- दृश्य परीक्षण: प्रक्रिया के दौरान, स्वास्थ्य देखभाल पेशेवर रोगी को बाह्य कान नहर (बाह्य श्रवण नहर-ईएसी) को खोलने के लिए उंगली से ट्रागस को धीरे से आगे की ओर खींचने के लिए कहता है; साथ ही, परीक्षक प्रकाश स्रोत (जैसे, पेन लाइट, टॉर्च लाइट, सेलुलर फोन लाइट) के साथ ईएसी की जांच करने के लिए धीरे से पिन्ना को पीछे और ऊपर की ओर खींचता है।
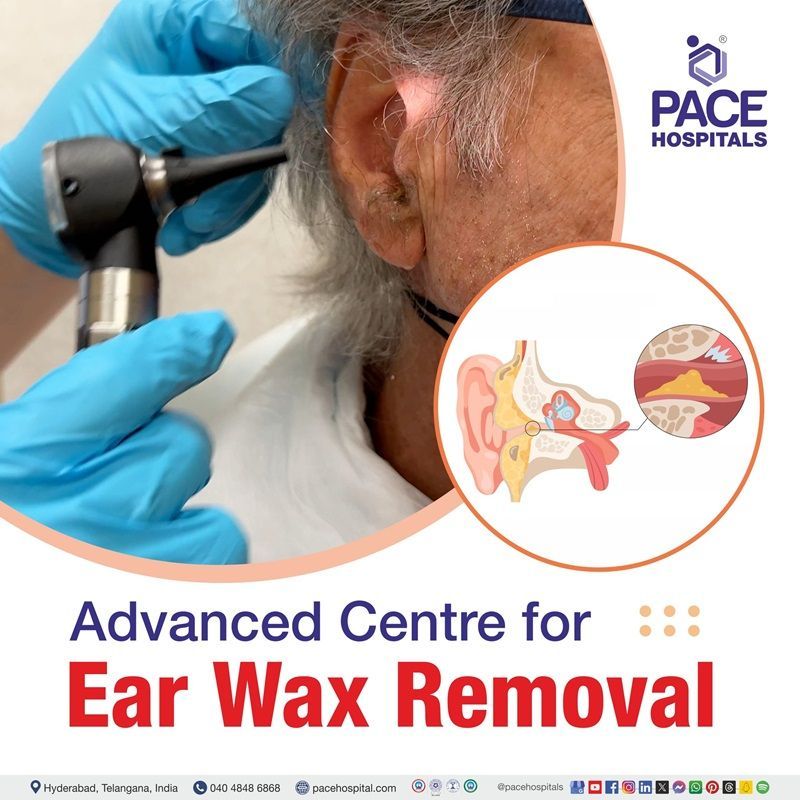
ओटोस्कापकान के मैल की रुकावट का निदान ओटोस्कोप से प्रत्यक्ष दृश्यांकन द्वारा किया जाता है। यह आवश्यक उपकरण प्रकाश की एक किरण डालकर कान के पर्दे और कर्ण नलिका की स्थिति का दृश्य और परीक्षण करता है ताकि कान के मैल की रुकावट का पता लगाया जा सके और सुनने की क्षमता में कमी, कान में भरापन, खुजली आदि जैसे लक्षणों का पता लगाया जा सके। ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट ओटोस्कोप की नोक को रोगी के कान में रखते हैं, प्रकाश डालते हैं और ओटोस्कोप को सभी दिशाओं में घुमाते हैं। कभी-कभी, वे कान के पर्दे के पीछे जमा तरल पदार्थ और संक्रमण को देखने के लिए न्यूमेटिक ओटोस्कोप का उपयोग भी कर सकते हैं।
ओटो-माइक्रोस्कोपीओटोमाइक्रोस्कोपी, सर्जिकल माइक्रोस्कोप का उपयोग करके बाह्य श्रवण नलिका (ईएसी) और टिम्पेनिक झिल्ली (टीएम) की जांच है। इस चर्चा के प्रयोजनों के लिए, यह एक जाग्रत रोगी पर किया जाता है। निदान के प्रयोजनों के लिए, ओटोमाइक्रोस्कोपी, गैर-आवर्धित ओटोस्कोपी की तुलना में बेहतर रोशनी और आवर्धन प्रदान करती है और चिकित्सक को चिकित्सीय हस्तक्षेप करने के लिए दोनों हाथों की स्वतंत्रता प्रदान करती है।
✅कान का मैल निकालने से पहले ईएनटी विशेषज्ञ (ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट) की सलाह
ईएनटी (कान, नाक, गला) डॉक्टर (ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट) या ऑडियोलॉजिस्ट कान का मैल निकालने का विकल्प चुनने से पहले कई कारकों पर विचार करते हैं:
- रोगी की आयु और स्वास्थ्य: रोगी की आयु (बच्चे, वयस्क, वृद्ध) और समग्र स्वास्थ्य स्थिति के साथ-साथ उपचार की सहनशीलता या प्रभावकारिता को प्रभावित करने वाले सभी कारकों पर विचार किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए, बच्चों या मानसिक रूप से विकलांग रोगियों के मामले में सामान्य एनेस्थीसिया देने पर विचार किया जाता है क्योंकि वे सहयोग नहीं कर सकते।
- लक्षणों का आकलन: जब मरीज़ों में सेरुमेन इम्पैक्शन (कान के मैल का रुकना) हो और कान में दर्द, कान से पानी बहना, बुखार और सुनने की क्षमता में कमी जैसे नए लक्षण दिखाई दें, और अगर कान का मैल सूखा हो और लंबे समय से कान की नली में हो, तो यह कान की नली की दीवार से चिपक सकता है, और कुछ मामलों में, मैल के साथ त्वचा की एक परत भी निकल सकती है। इन बातों को अक्सर ध्यान में रखा जाता है।
- कान के मैल के प्रकार: कान के मैल (सेरुमेन) का प्रकार और गाढ़ापन निकालने की विधि को प्रभावित करता है। नरम मैल सिंचाई से प्रभावी रूप से निकल सकता है, जबकि सूखे, सख्त या फंसे हुए मैल को हाथ से निकालना पड़ सकता है।
- अंतर्निहित स्थितियाँ: उन अंतर्निहित स्थितियों का मूल्यांकन करता है जो मोम हटाने की विधि को प्रभावित कर सकती हैं।
- रोगी का इतिहास: ईएनटी डॉक्टर व्यक्ति के चिकित्सा इतिहास की समीक्षा करके यह निर्धारित करते हैं कि रोगी को कोई बीमारी थी या नहीं। पिछले संक्रमण, अंतर्निहित स्थितियां, एलर्जी, या सर्जरी जो उपचार को प्रभावित कर सकती हैं और यह तय करने के लिए कि कौन सा उपचार सबसे अच्छा है।
- जोखिम और लाभ: ईएनटी विशेषज्ञ विभिन्न उपचार विधियों, जैसे सिंचाई, सक्शन या मैन्युअल निष्कासन, से जुड़े जोखिमों पर विचार करते हैं। कान की नली में चोट या संक्रमण जैसे जोखिम, और बेहतर सुनने की क्षमता और लक्षणों से राहत के लाभों के साथ इनका मूल्यांकन करते हैं।
- विशेषज्ञता और उपकरण: बाहरी वस्तुओं को केवल किसी विशेषज्ञ द्वारा उपयुक्त उपकरणों, जैसे कि सूक्ष्म उपकरणों, हेडलाइट या ओटो-माइक्रोस्कोप का उपयोग करके ही निकाला जाना चाहिए। यह विशेष रूप से पार्श्व कर्ण नलिका में स्थित बाहरी वस्तुओं या नरम, आसानी से पकड़ में आने वाली वस्तुओं के मामलों में महत्वपूर्ण है।
- रोगी की प्राथमिकता: ईएनटी विशेषज्ञ सुरक्षित और प्रभावी निष्कासन सुनिश्चित करते हुए रोगी की प्राथमिकताओं पर विचार करता है।
श्रेष्ठ ईएनटी विशेषज्ञ हैदराबाद, भारत में
✅बाल रोग और बच्चों के लिए उपचार
- अगर बच्चे में कोई लक्षण नहीं दिख रहे हैं, तो इलाज की ज़रूरत नहीं पड़ सकती। समय के साथ, समस्या अपने आप ठीक हो सकती है। हालाँकि, अगर बच्चे को कान में दर्द, खुजली, बेचैनी या कोई अन्य लक्षण हो, तो बाल रोग विशेषज्ञ या ईएनटी डॉक्टर (ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट) से परामर्श लेने की सलाह दी जाती है।
- बच्चे के कानों से मैल निकालने के लिए कभी भी उसमें कोई वस्तु न डालें (विशेषकर रुई के फाहे, रुई के फाहे, कान की मोमबत्तियाँ) क्योंकि इससे:
- कान में मोम को और अंदर धकेलकर उसे बाहर निकालें,
- कान की नली की दीवार को नुकसान पहुंचाता है, और सूजन पैदा करता है
- कान के पर्दे को छेदना (फाड़ना)
- कान में खनिज तेल, बेबी ऑयल या ग्लिसरीन की बूंदें (केवल स्वास्थ्य देखभाल पेशेवर द्वारा अनुमोदित) डालने के लिए ईयर ड्रॉपर का उपयोग करें।
- बल्ब सिरिंज का उपयोग करने से पहले बाल रोग विशेषज्ञ से जांच कराएं।
वे उपचार जो केवल स्वास्थ्य देखभाल पेशेवर द्वारा ही किए जाने चाहिए, उनमें शामिल हैं:
- कान की सिंचाई (सिरिंजिंग): हल्के दबाव का उपयोग करके गर्म पानी को कान की नली में डालकर मोम को निकालना।
- माइक्रोसक्शन: एक छोटी सी जांच के साथ सक्शन के माध्यम से मोम को हटाना
- मैन्युअल निष्कासनछोटे, विशेष उपकरणों से कान का मैल निकालना।
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न (FAQ) कान का मैल
क्या मुझे रुई के फाहे का उपयोग करना चाहिए?
नहीं। रूई के फाहे या रुई की कलियाँ, कान की मोमबत्तियाँ, माचिस की तीलियाँ या कोई भी वस्तु कान में डालने से बचें, क्योंकि ये छोटी-छोटी वस्तुएँ आपके कान की नली में चली जाती हैं, जिससे कान का मैल और गहरा हो जाता है और वह बंद हो जाता है, जिससे कान में मैल जमने की समस्या और भी बदतर हो जाती है।
यदि कान का मैल न निकाला जाए तो क्या होगा?
सामान्य कान का मैल कान की नली की सुरक्षा, चिकनाई और सफ़ाई में मदद कर सकता है। हालाँकि, अतिरिक्त मैल ध्वनि को कान में प्रवेश करने से रोक सकता है और कई लक्षण पैदा कर सकता है, जैसे सुनने में कठिनाई, खुजली, चक्कर आना, भरा हुआ या दबाव महसूस होना, और/या कानों में बजना (जिसे टिनिटस कहते हैं)। कभी-कभी, अनुपचारित कान का मैल संक्रमण का कारण बनता है, जिससे जल निकासी होती है, जिससे कान के पर्दे को नुकसान पहुँचने का खतरा बढ़ जाता है।
क्या कान में मैल जमा होने से रोकने के लिए कानों का उपचार कराना आवश्यक है?
कुछ लोगों के लिए रोकथाम सबसे अच्छी है, फिर भी सभी को इसकी ज़रूरत नहीं है। बुज़ुर्गों, श्रवण यंत्रों वाले लोगों और अत्यधिक कान के मैल के इतिहास वाले लोगों को रोकथाम से मदद मिल सकती है। किसी ऑडियोलॉजिस्ट या ईएनटी डॉक्टर (ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट) से इस बारे में बात करने से यह तय करने में मदद मिलेगी कि व्यक्ति की स्थिति के आधार पर क्या कुछ ज़रूरी है।
कान के मैल को साफ करने के सबसे सुरक्षित तरीके क्या हैं?
कानों को साफ़ रखने या मैल को नरम करके उसे अपने आप बाहर निकालने के कुछ सबसे सुरक्षित तरीके हैं, एक नम कपड़े का इस्तेमाल करके कान के बाहरी हिस्से को धोना। नहाते या शॉवर लेते समय कान के मैल को नरम करने वाली बूँदें भी जमा होने से राहत दिला सकती हैं। हालाँकि, हर किसी के लिए सेरुमेन-सॉफ्टनिंग एजेंट (कान के मैल को नरम करने वाले एजेंट) का इस्तेमाल करने की सलाह नहीं दी जाती है, खासकर अगर व्यक्ति का कान की सर्जरी का इतिहास रहा हो। इसलिए, कान की बूँदें इस्तेमाल करने से पहले किसी ईएनटी डॉक्टर (ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट) से सलाह लेने की सलाह दी जाती है।
शिशु के कान का मैल कैसे निकालें?
शिशु के कान की नली से मैल को सुरक्षित रूप से साफ़ करना ज़रूरी है। नाज़ुक कान की नली को नुकसान से बचाने के लिए एक सौम्य उपाय की आवश्यकता होती है, जिसमें शिशु को नहलाते समय एक साफ़ तौलिया और मुलायम सूती कपड़े का इस्तेमाल करना शामिल है, जो ढीले मैल को हटाने में मदद करता है, और गर्म पानी या सेल्युलोलिटिक एजेंट (स्वास्थ्य सेवा पेशेवर द्वारा अनुशंसित) की कुछ बूँदें इसे नरम कर सकती हैं। हालाँकि, चिकित्सक कान की नली में रुई के फाहे, पेपर क्लिप या अन्य वस्तुएँ डालने की सख़्त मनाही करते हैं क्योंकि इससे मैल कान में और गहराई तक चला जाता है या नुकसान पहुँचता है। अगर अत्यधिक मैल की चिंता हो या शिशु में बेचैनी के लक्षण दिखाई दें, तो बाल रोग विशेषज्ञ से परामर्श करना उचित है।
कान का मैल क्या है?
कान का मैल, जिसे चिकित्सकीय भाषा में सेरुमेन भी कहा जाता है, एक प्राकृतिक पदार्थ है जो कान की नली को साफ़, सुरक्षित और चिकना करता है। यह कान की नली के बाहरी एक-तिहाई हिस्से की त्वचा में स्थित विशेष मोम बनाने वाली सेरुमिनस ग्रंथियों द्वारा निर्मित होता है। अपनी अम्लीय प्रकृति के कारण, कान का मैल संक्रमणों से प्राकृतिक सुरक्षा प्रदान करता है और गंदगी, धूल या बाहरी पदार्थों को कान में प्रवेश करने से रोकता है। यह मैल धीरे-धीरे कान की नली के मुख की ओर बढ़ता है, जहाँ यह त्वचा की स्व-सफाई प्रणाली और चबाने व बात करने में प्रयुक्त मांसपेशियों की क्रिया द्वारा छिल जाता है (या छिल जाता है) या नहाने के दौरान धुल जाता है।
कान के मैल के उत्पादन को कौन से कारक प्रभावित करते हैं?
एक्ज़िमा जैसी बीमारियों के कारण त्वचा बहुत रूखी और परतदार हो जाती है और कान में मैल जम जाता है। जैसे-जैसे व्यक्ति की उम्र बढ़ती है, ग्रंथियों के स्राव की स्थिरता में बदलाव आते हैं, जिससे कान की नली से होकर गुज़रने में कठिनाई होती है। मैल जमने की संभावना उन लोगों में ज़्यादा होती है जिनकी कान की नली संकरी होती है, जो धूल भरे वातावरण में काम करते हैं और जिन्हें अपनी सुनने की क्षमता की रक्षा के लिए इयरप्लग का इस्तेमाल करना पड़ता है।काम नहीं करता। अधिक मलबा उठाने या लंबे समय तक कान की नली में रहने की स्थिति में कान के मैल का अधिक उत्पादन शुष्क और कठोर हो सकता है; इससे रुकावट या अवरोध उत्पन्न होने की अधिक संभावना होती है, जिससे सुनने की क्षमता में कमी, कान में दर्द, कान में खुजली और अन्य समस्याएं जैसे लक्षण उत्पन्न होते हैं।
मेरे कान का मैल हटाने की नियुक्ति पर क्या होगा?
अगर किसी को कान में मैल जमा होने का संदेह हो, तो ऑडियोलॉजिस्ट या ईएनटी डॉक्टर (ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट) ओटोस्कोप से कानों की जाँच करके शुरुआत कर सकते हैं। कान का मैल निकालने की प्रक्रिया कई अलग-अलग तरीकों से की जा सकती है। ऑडियोलॉजिस्ट या ईएनटी डॉक्टर (ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट) कान के मैल की मात्रा और बनावट, व्यक्ति की उम्र, और मैल या स्राव की उपस्थिति और स्थान के आधार पर एक विधि या उपकरण का प्रकार चुन सकते हैं।
घर पर कान का मैल कैसे निकालें?
ऑडियोलॉजिस्ट और अन्य चिकित्सा पेशेवर (बाल रोग विशेषज्ञ, ईएनटी डॉक्टर) घर पर कुछ खास औज़ारों, जैसे रुई के फाहे, रुई के फाहे, माचिस की तीली, क्यूरेट, पिक्स और ईयर कैंडल का इस्तेमाल करके कान का मैल निकालने की सख़्त मनाही करते हैं। इन औज़ारों का गलत इस्तेमाल कान की नली को नुकसान पहुँचा सकता है, त्वचा को जला सकता है और कान के पर्दों में छेद कर सकता है।
अत्यधिक कान के मैल के कारण क्या लक्षण हो सकते हैं?
कान में मैल जमने से जुड़ी आम शिकायतों में सुनने में दिक्कत, कान में दर्द, कान में भरापन महसूस होना, चक्कर आना और कान में खुजली शामिल हैं। इसके अलावा, कान से पानी आना, दुर्गंध आना, खांसी या कान में दर्द जैसी समस्याएं भी हो सकती हैं। अगर इलाज न किया जाए, तो अत्यधिक मैल जमा होने से मैल के लक्षण और भी बदतर हो सकते हैं। इसलिए, अगर किसी को ऊपर बताए गए लक्षण दिखाई दें, तो ईएनटी डॉक्टर से सलाह लेने की सलाह दी जाती है।
कान का मैल निकालने के लिए मैं किससे संपर्क करूं?
कान का मैल निकालने का कार्य आमतौर पर प्रशिक्षित और अनुभवी स्वास्थ्य देखभाल पेशेवर द्वारा किया जाता है, जिसमें ईएनटी विशेषज्ञ, ऑडियोलॉजिस्ट, ओटोलरींगोलॉजिस्ट (कान, नाक और गले के डॉक्टर), या वयस्कों के लिए सामान्य चिकित्सक और बच्चों के लिए बाल रोग विशेषज्ञ या विशेष बाल चिकित्सा ईएनटी शामिल हैं।
क्या कान का मैल निकालने में दर्द होता है?
कान का मैल निकालने की प्रक्रिया आमतौर पर किसी चिकित्सक के क्लिनिक या अस्पताल में की जाती है। इस प्रक्रिया के दौरान, व्यक्ति को थोड़ी असुविधा महसूस हो सकती है, लेकिन यह दर्दनाक नहीं होता। हालाँकि, बच्चों या मानसिक रूप से विकलांग रोगियों के मामले में, जो सहयोग नहीं कर सकते या ठीक से बैठ नहीं सकते, एक स्वास्थ्य सेवा पेशेवर सामान्य एनेस्थीसिया का इंजेक्शन लगाता है।
यदि कान का मैल निकाल दिया जाए तो क्या मेरी सुनने की शक्ति बेहतर हो जाएगी?
यदि अतिरिक्त कान का मैल कान की नली को लगभग पूरी तरह से अवरुद्ध कर देता है, तो मैल निकालने से सुनने की क्षमता बहाल हो सकती है। हालाँकि, सुधार की सीमा विभिन्न कारकों पर निर्भर करती है, जैसे कि सुनने की क्षमता को प्रभावित करने वाली अंतर्निहित स्थितियाँ और निकाले गए मैल की मात्रा। इसलिए, कान के मैल से संबंधित सुनने की समस्याओं के सुरक्षित और प्रभावी प्रबंधन को सुनिश्चित करने के लिए उचित मूल्यांकन और उपचार के लिए स्वास्थ्य सेवा पेशेवरों से परामर्श और चर्चा करना आवश्यक है।
कान के मैल के उत्पादन को कौन से कारक प्रभावित करते हैं?
रुई के फाहे और पिन जैसी चीज़ों से कान साफ़ करने से मैल और अंदर चला जाता है, जिससे समस्याएँ पैदा हो सकती हैं। कान में खुजलाना और उसके परिणामस्वरूप होने वाला संक्रमण, बाहरी वस्तु का अंदर जाना, बाहरी श्रवण नलिका की असामान्यताएँ, और चिंता, भय, तनाव और उम्र बढ़ने के कारण अत्यधिक मैल का बनना, ये सभी मैल के जमाव के महत्वपूर्ण कारक हैं। जोखिम कारकों की जानकारी से मैल के जमाव और उससे जुड़ी जटिलताओं को काफी हद तक कम किया जा सकता है।
हैदराबाद, भारत में कान का मैल निकालने की लागत क्या है?
हैदराबाद, भारत में कान का मैल हटाने की लागत प्रति सत्र ₹ 800 से ₹ 2,500 (INR आठ सौ से दो हजार पांच सौ) तक हो सकती हैअस्पताल/क्लिनिक और इस्तेमाल की जाने वाली विधि पर निर्भर करता है। भारत में कान के मैल की सफाई की लागत कई कारकों पर निर्भर करती है, जिनमें मरीज़ की स्थिति, उम्र, संबंधित स्थितियाँ, अस्पताल और प्रक्रिया की जटिलता शामिल हैं।


