Successful Spine Surgery for Lumbar Canal Stenosis, Spondylolisthesis, & Disc Prolapse in a 72-Y-O Male
PACE Hospitals
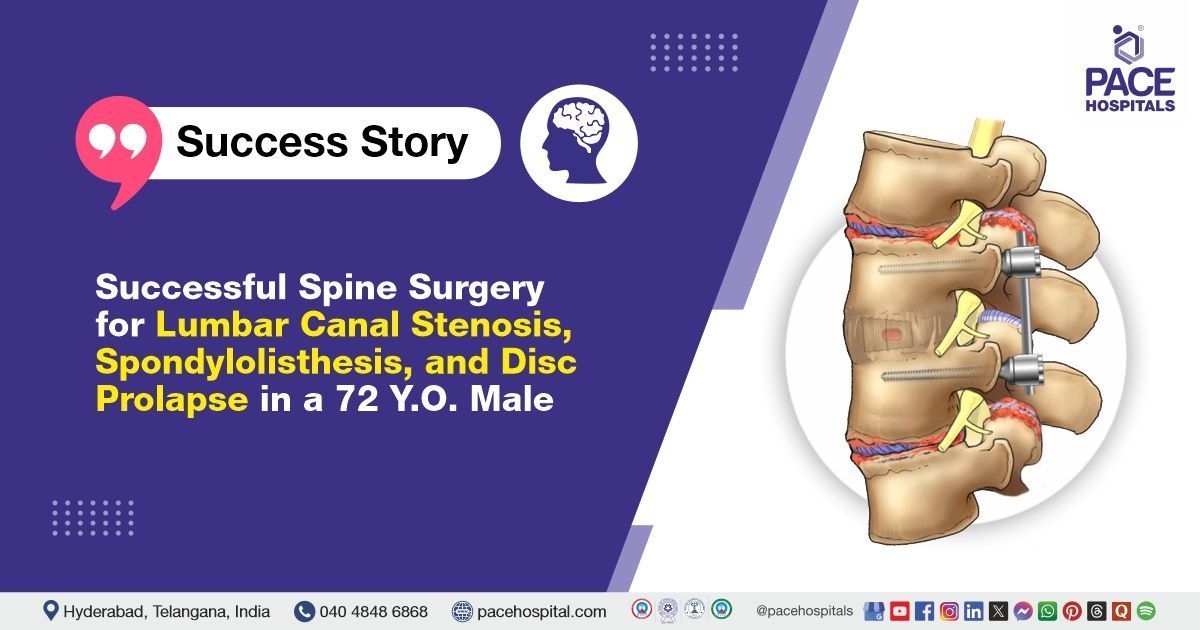
PACE Hospitals' expert neurosurgery team successfully performed L2–S1 spine stabilization, L2–L5 laminectomy, and discectomy at the L2–L3 and L4–L5 levels on a 72-year-old male patient who had been experiencing lower back pain and right lower limb weakness for the past 10 days. The procedure resulted in significant relief from lower back pain, improved neurological function, and enhanced overall quality of life for the patient.
Chief Complaints
A 72-year-old male patient with a BMI of 24 presented to the Neurosurgery Department at PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with complaints of lower back pain and right lower limb weakness that had been persisting for the past 10 days.
He had a prior history of similar symptoms; however, the pain had significantly worsened following a recent intramuscular injection. At the time of presentation, he could not walk even with support, indicating a marked decline in mobility and possible progression of neurological compromise. The patient denied any urinary complaints or bowel and bladder disturbances, suggesting the absence of cauda equina involvement, which typically presents with such symptoms and would have indicated a neurosurgical emergency. These findings pointed toward a severe lumbar spine pathology, likely compressive in nature, affecting motor function but sparing autonomic control.
Past Medical History
The patient had a known history of
hypertension and had been on regular antihypertensive medication. He followed a mixed diet and reported having normal sleep and appetite.
General Examination
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was hemodynamically stable. General examination revealed a moderately built and well-nourished elderly male with no clinical signs of systemic illness. Cardiovascular and respiratory assessments were unremarkable, with normal heart sounds (S1/S2) and clear breath sounds bilaterally. The abdominal examination showed a soft, non-tender abdomen with no organomegaly or abnormal findings.
Neurological evaluation revealed significant motor weakness in the lower limbs: power was reduced to 4+/5 in the left lower limb, 3/5 in the right ankle and hip, and 4/5 in the right knee flexion. Despite the motor deficits, sensory function remained intact, cranial nerve was normal, and no cerebellar or meningeal signs were observed, indicating localized involvement of the lumbosacral spine without central or cortical pathology.
His blood pressure was elevated at the time of presentation, consistent with his known history of hypertension, for which he had been on regular medication. His bowel and bladder functions were preserved, further ruling out involvement of the sacral nerve roots and cauda equina syndrome. Additionally, his glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) levels were in the prediabetic range, suggesting the need for ongoing metabolic monitoring and lifestyle modifications, which could influence long-term recovery and wound healing postoperatively.
Overall, the clinical findings pointed toward a localized compressive lumbar spine pathology causing motor weakness, while his general health remained relatively stable, with no systemic or metabolic derangements that could complicate his immediate management or surgical outcome.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient underwent a comprehensive evaluation, including a detailed review of his medical history and a thorough clinical examination by the neurosurgery team. Given his presenting symptoms of lower back pain, progressive right lower limb weakness, and recent inability to walk even with support, there was a strong clinical suspicion of a degenerative or compressive lumbar spine pathology.
The absence of sensory loss, bowel or bladder involvement, and cranial or cerebellar signs further supported a localized lumbosacral lesion. His known history of hypertension and newly detected prediabetic status were also considered during the assessment, as these factors could potentially influence surgical risk and postoperative recovery.
To support the clinical diagnosis and evaluate the extent of the underlying condition, a series of diagnostic investigations were performed, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbosacral spine and nerve conduction studies (NCS). These tests were aimed at identifying the source of the patient’s lower back pain and right lower limb weakness, which had raised a strong clinical suspicion of lumbar canal stenosis or nerve root compression.
The MRI findings confirmed significant L2–S1 Lumbar Canal Stenosis, along with Grade I Spondylolisthesis at the L2–L3 and L4–L5 levels, and Intervertebral Disc Prolapse (IVDP) at L2–L3 and L4–L5. These radiological findings correlated well with the patient's presenting symptoms of pain and motor weakness, confirming a compressive pathology as the primary cause.
Nerve conduction studies supported these findings, indicating impaired nerve function in the affected lower limb. No evidence was found to suggest involvement of the cauda equina or any acute central nervous system pathology, ruling out conditions such as spinal cord lesions or widespread polyneuropathy. Following a detailed clinical and radiological assessment, the patient was diagnosed with multi-level degenerative lumbar spine disease, causing severe neural compression.
He was therefore advised to undergo Multi-Level Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Neurosurgery Department for further management.
Medical Decision Making (MDM)
Following a thorough assessment and detailed discussion with the patient and his guardians, Dr. U.L. Sandeep Varma, Consultant Neurosurgeon, along with Dr. S. Pramod Kumar, Neurologist, recommended L2–S1 Spine stabilization, L2–L5 Laminectomy, and Discectomy at the L2–L3 and L4–L5 levels as the most appropriate course of action. The procedure was recommended to relieve neural compression, restore spinal stability, and improve functional outcomes. It was anticipated that the surgery would minimize postoperative pain, reduce tissue trauma, and promote a faster recovery.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled for Lumbar Spine Surgery in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, under the expert care of the Neurosurgery Department, to address the neural compression and improve spinal stability.
- Preoperative Evaluation and Consent: After a thorough pre-anaesthetic evaluation and informed consent, the patient underwent L2-S1 spine stabilization, L2-L5 laminectomy, and L2-3, L4-5 discectomy.
- Anaesthesia and Positioning: The surgery was performed under strict aseptic precautions and general anaesthesia. The patient was positioned prone, with adequate padding placed at all pressure points to prevent any pressure sores.
- Incision and Exposure: The surgical site was sterilized, and sterile drapes were applied. A vertical midline incision was made over the lumbar spine, and the incision was deepened through the subcutaneous tissues. The paraspinal muscles were carefully separated to expose the vertebrae.
- Pedicle Screw Fixation and Stabilization: Pedicle screw fixation was performed from L2 to S1, with bilateral screws inserted at L2, L5, and S1, and unilateral screws placed at L3 and L4. Stabilization was achieved by inserting titanium rods bilaterally from L2 to S1.
- Spinal Fusion: Posterolateral spinal fusion was carried out from L2 to S1 using autologous bone grafts harvested during the procedure.
- Osteoporotic Bone Consideration: During the surgery, the vertebral bones were noted to be osteoporotic (weak and brittle), which was considered during the fixation process.
- Wound Closure: An epidural drain was placed to prevent fluid accumulation postoperatively, and the surgical wound was closed in layers. The implants used included eight JAYON polyaxial pedicle screws (6.5 × 45 -8 mm), two titanium rods, and two Innie-8 connectors. The surgery was completed successfully without intraoperative complications.
Postoperative Care
The postoperative period remained uneventful. The patient was initially shifted to the ICU for overnight monitoring and subsequently transferred to a regular room. Intravenous antibiotics, analgesics, and other supportive treatments were administered as per protocol.
On postoperative examination, the surgical wound appeared healthy, with no signs of infection or complications. The patient’s vital signs remained stable throughout the recovery period. On postoperative day (POD) 3, both the Foleys catheter and epidural drain were removed, and the patient was mobilized successfully.
A postoperative X-ray confirmed that the implants were well-aligned and in proper position. The patient showed symptomatic improvement and was prepared for discharge with detailed post-discharge care instructions and follow-up recommendations.
Discharge Notes
The patient demonstrated a satisfactory postoperative recovery and was discharged in a stable condition. He was provided with comprehensive instructions for continued care, which included dietary modifications to support healing, proper wound care to prevent infection, and scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor his recovery progress.
In addition, he was counselled on the importance of adhering to the prescribed medications, maintaining good wound hygiene, engaging in light daily activities, and avoiding strenuous physical exertion to ensure a safe and smooth recovery.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed a comprehensive and individualized medication regimen to support postoperative recovery and minimize the risk of complications. The prescribed medications included antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections, muscle relaxants and analgesics to manage postoperative pain and discomfort, and anticonvulsants to address nerve-related symptoms.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) were also prescribed to protect the gastric lining from irritation associated with prolonged use of pain medications. Additionally, nutritional supplements and supportive therapies were recommended to promote healing and restore strength. The patient was advised to continue his regular antihypertensive medications to maintain stable blood pressure throughout the recovery period.
Advice on Discharge
The patient was advised to follow a set of specific postoperative care measures to ensure a smooth and safe recovery. These instructions included avoiding all forms of strenuous activity and using a lumbar support belt as recommended by the medical team. He was instructed to adhere strictly to the prescribed medication regimen to aid healing and prevent complications.
Proper wound care was emphasized, and the patient was allowed to bathe with caution, ensuring that the surgical site always remained clean and dry. He was also advised to avoid sitting on the floor, refrain from lifting heavy objects, and begin physiotherapy as per the rehabilitation plan to help restore mobility, muscle strength, and functional independence.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the Emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms like fever, severe pain, weakness of limbs, wound discharge.
Review and Follow-Up
The patient was also advised to return for a follow-up visit with the Neurosurgeon in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals two weeks after discharge for staple removal. This scheduled follow-up was intended to allow a thorough evaluation of his postoperative recovery, monitor wound healing, and ensure that there were no signs of infection or other complications.
It also provided an opportunity to address any ongoing symptoms, review his adherence to postoperative care instructions, and make any necessary adjustments to his treatment plan for optimal recovery and long-term spinal stability
Conclusion
This case highlighted the effectiveness of spinal decompression surgery as a definitive approach for managing L2–S1 lumbar canal stenosis, L2–L3 and L4–L5 spondylolisthesis, and intervertebral disc prolapse (IVDP) (Slipped Disc) in an elderly patient. The surgical intervention successfully alleviated his neurological symptoms and lower back pain, resulting in improved functional mobility and a better quality of life. The timely and appropriate management further contributed to a smoother and faster postoperative recovery, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and expert surgical care in such complex spinal conditions.
Interconnected Pathologies of the Lumbar Spine: Understanding and Managing Spinal Stenosis, Disc Prolapse, and Spondylolisthesis
Lumbar spinal stenosis, intervertebral disc prolapses (IVDP), and spondylolisthesis are closely interrelated spinal conditions that often coexist and contribute to a common clinical picture of lower back pain and neurological deficits. An intervertebral disc prolapse occurs when the disc between the vertebrae degenerates or herniates, compressing nearby nerve roots or the spinal cord. This disc degeneration can lead to instability of the spinal segment, increasing the risk of spondylolisthesis, where one vertebra slips over the one below it. The instability and vertebral slippage caused by spondylolisthesis can further narrow the spinal canal, resulting in lumbar spinal stenosis—a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal and compression of spinal nerves. Together, these pathologies cause chronic back pain, radiculopathy, leg weakness, numbness, and difficulty walking. In severe cases, untreated compression may lead to bladder and bowel dysfunction and permanent neurological damage.
If left unmanaged, these conditions progressively worse, leading to significant loss of mobility, diminished quality of life, and permanent disability. Management typically includes conservative measures such as physiotherapy, pain relief medications, and lifestyle modifications in the early stages. However, in moderate to severe cases, a comprehensive surgical approach—including spinal decompression (laminectomy/discectomy) to relieve nerve compression, and spinal stabilization/fusion to correct spondylolisthesis and maintain spinal alignment—is often necessary. When performed timely and appropriately, these surgical interventions can address all three conditions simultaneously, restoring function and preventing further neurological deterioration under the expert care of a
neurosurgeon/neurosurgery doctor.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868