HbA1C Test - Indications, Range & Cost
Accurate HbA1c testing is essential for managing diabetes and monitoring blood sugar levels. At PACE Hospitals, you can rely on receiving trusted and high-quality care for this important test. Our NABH-accredited labs use advanced technology to deliver precise and reliable results. With experienced endocrinologists, diabetologists, and a dedicated healthcare team, we interpret your HbA1c levels and provide personalized treatment guidance, helping you manage diabetes more effectively.
Request an Appointment for HbA1c Test
HbA1c test appointment
Expert interpretation & Personalized care
Comfortable and convenient experience
What is HbA1c test?
HbA1c test meaning
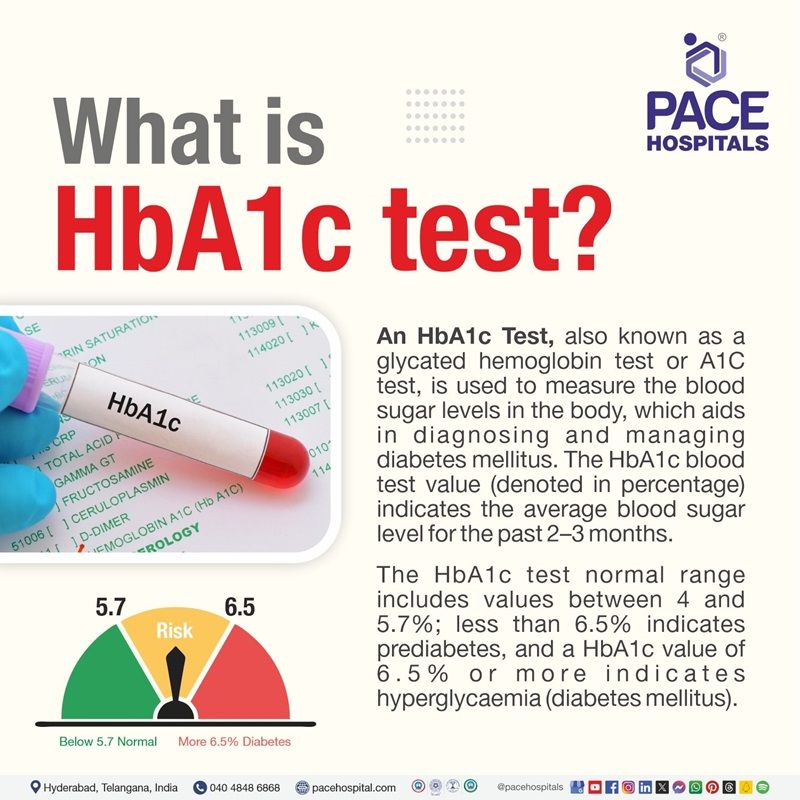
HbA1c test, also known as glycated hemoglobin A1c, is used to measure the blood sugar levels in the body, which aids in diagnosing and managing diabetes mellitus. The HbA1c blood test value (denoted in percentage) indicates the average blood sugar level for the past 2–3 months. The HbA1c blood test normal range includes values between 4 and 5.7%; less than 6.5% indicates prediabetes, and a HbA1c value of 6.5% or more indicates hyperglycaemia (diabetes mellitus).
The haemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells, providing a bright red colour to the blood. The haemoglobin consists of two alpha and two beta polypeptide chains with different amino acid sequences. The glycated hemoglobin or glycohemoglobin is formed due to the ketoamine reaction between the blood glucose (sugar molecules) and the N-terminal amino acid of the beta polypeptide chain of haemoglobin, resulting in the attachment of blood sugar molecule to the haemoglobin protein.
HbA1c Test Uses
HbA1c test full form in medical - Glycated hemoglobin or haemoglobin A1c
In general, healthy persons contain glycated haemoglobin; however, in prediabetics or diabetics, the excess amount of unutilised sugar molecules present in the blood (which might occur due to insulin resistance or absence of insulin production) attaches to the haemoglobin, resulting in higher levels of glycosylated haemoglobin. The amount of glycohemoglobin produced is directly proportional to the mean blood glucose during the 8-10-week period prior to the initiation of the HbA1c test, which thereby provides an average of 2-3 months days of blood sugar levels.
The blood sugar test HbA1c is used to screen and diagnose the following conditions:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Prediabetes
Diabetes mellitus: It is a metabolic disorder characterised by an increase in blood sugar levels or hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia is caused by decreased insulin secretion, poor glucose utilisation, and increased glucose production, all of which can be related to the underlying cause of diabetes mellitus.
Prediabetes:
It is a condition where there will be an increase in blood sugar levels than normal levels; however, it is not high enough to diagnose diabetes.

Importance of HbA1c Test
HbA1c importance
The HbA1c test is incredibly important for several reasons:
Diagnosis and Screening:
- Prediabetes detection: It helps identify prediabetes, a condition with higher than normal blood sugar levels but not yet high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. Early detection allows for lifestyle changes to potentially prevent or delay the onset of diabetes.
- Diabetes diagnosis: It aids in diagnosing type 2 diabetes by providing a snapshot of average blood sugar control over the past 3 months, offering a more reliable picture than a single finger-prick test.
Monitoring and Treatment:
- Risk assessment: A high HbA1c level indicates a greater risk of developing diabetes complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. Early detection and proactive management can help prevent or delay these complications.
- Treatment plan evaluation: For people with existing diabetes, the HbA1c test assesses how well their blood sugar levels are being managed under their current treatment plan. This information is crucial for making adjustments to medication, diet, or exercise recommendations.
Additional Benefits:
- Motivation: Regularly monitoring HbA1c levels can act as a motivator for people with diabetes to adhere to their treatment plan and maintain healthy habits.
- Convenience: Unlike finger-prick tests, which require multiple daily measurements, the HbA1c test only needs to be done every 3–6 months, depending on individual needs.
Overall, the HbA1c test is a valuable tool for managing diabetes and preventing its complications. It provides a comprehensive picture of long-term blood sugar control, allowing for informed treatment decisions and proactive risk management.
While the HbA1c test is highly reliable, certain factors like recent blood transfusions, certain medications, and some blood cell disorders can affect the results. Discussing any potential influencing factors with your primary care physician or doctor is crucial for accurate interpretation. The target HbA1c level may vary slightly depending on individual circumstances.
HbA1c Test Indications
For screening, diagnosis or managing diabetes, one might opt for an HbA1c test in the following scenarios.
Screening:
- Patients over the age of 45
- Overweight patients under the age of 45 and having one or more risk factors for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
Second test: If the patient is asymptomatic but still has an HbA1c value between 5.7% and 6.4% (prediabetes) or more than that (diabetes), a second test is recommended on a different day.
HbA1c test: Once every 1 to 2 years: In patients who are prediabetic and taking measures to control and lower the risk of diabetes mellitus.
HbA1c test: Once every 3 years: In normal HbA1c patients with age over 45 and having associated risk factors or ever had a history of gestational diabetes
In managing diabetes: In patients with uncontrolled diabetes and are on oral antidiabetic medications, the best time for HbA1c test, as per the American Diabetes Association (ADA) suggestions, is once every three months. In the case of stable and well-controlled patients, the sugar test HbA1c should be performed once in every six months.
Preparation for HbA1c Test Procedure
The patient needs to inform the diabetologist or endocrinologist about intake of their daily medications.
The patient can have food prior to the test, as the HbA1c test measures the average glucose concentration.
HbA1c test procedure:
- The HbA1c test can be done as a point of care or by sending the samples to the laboratory. The phlebotomist might draw 5 ml of blood by puncturing a vein from the arm with a small needle. The collected blood sample will be transferred into an HbA1c blood test vial and sent for further analysis.
- Once the sample is collected, with the help of any of the haemoglobin A1c measure methods (ion-exchange HPLC, immunoassay, boronate affinity HPLC or enzymatic assays) the glycated haemoglobin value is measured.
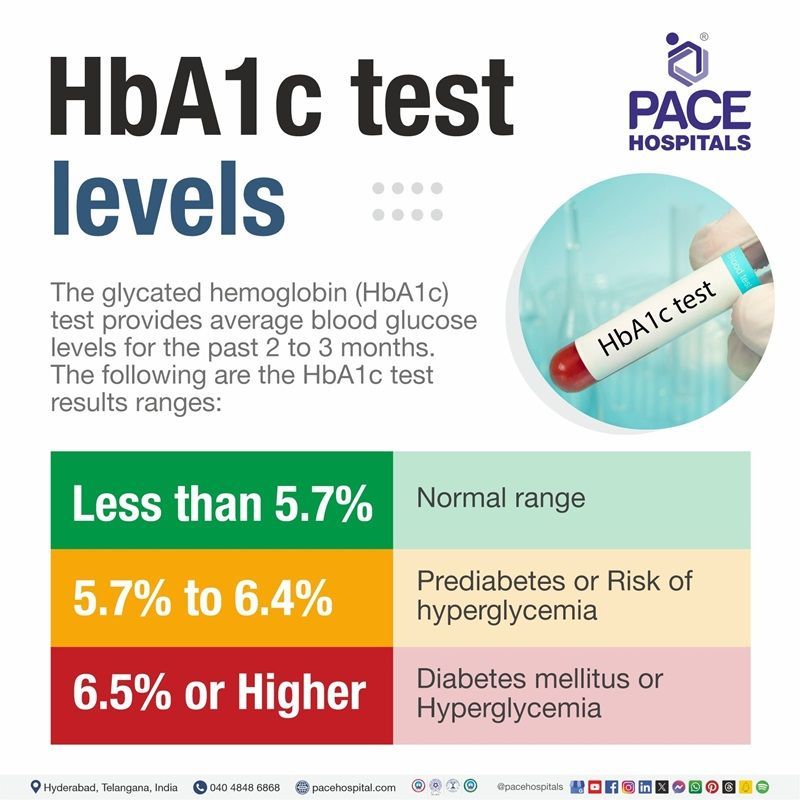
HbA1c Test Range
The glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test provides average blood glucose levels for the past two to three months. The following are the HbA1c test report values.
- The hemoglobin A1c normal range is between 4 and 5.6%.
- If the hemoglobin A1c level is between 5.7 to 6.4%, the patient is at risk of hyperglycemia (presence of high blood glucose levels) or prediabetes.
- If the hemoglobin A1c level is 6.5% or higher, it indicates hyperglycemia or diabetes mellitus condition.
Factors that Might Affect the HbA1c Test Result
The following conditions can alter (increase or decrease) the reading of HbA1c:
- Intake of vitamin C supplementations (depends on the method used for measurement)
Falsely low HbA1c values
- Residing at a high-altitude region
- Pregnancy
- Haemorrhage, liver cirrhosis, chronic kidney failure, sickle cell anaemia, haemolytic anaemia, and spherocytosis
- On erythropoietin administration and iron supplementation
Falsely high HbA1c values
- Low iron levels, which might be due to infection-induced anaemia, iron deficiency anaemia or tumour-induced anaemia,
- Presence of thalassemia and vitamin B12 deficiency
- Organ transplantation, hypertriglyceridemia and hyperglycation in some ethnic groups
- Intake of protease inhibitor agents or immunosuppressants
Correlation Between Haemoglobin A1c and Blood Sugar
As per the American Diabetes Association (ADA), the relationship between the haemoglobin A1c and estimated average blood sugar can be described by the following formula, which provides average blood glucose levels (estimated) for the past 70 to 90 days.
Estimated average blood glucose (mg/dL) = 28.7 x HbA1c value - 46.7.
| HbA1c value (%) | Estimated average blood glucose (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| 6 | 126 |
| 6.5 | 140 |
| 7 | 154 |
| 7.5 | 169 |
| 8 | 183 |
| 8.5 | 197 |
| 9 | 212 |
| 9.5 | 226 |
| 10 | 240 |
Difference Between Blood Glucose Test and HbA1c
HbA1c vs blood sugar
Both tests are used to measure blood glucose (sugar) levels; however, the following are the differences between them.
| Elements | Blood glucose test | HbA1c test |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Measures milligrams of glucose per decilitre of blood. | Measures the percentage of glucose bound to red blood cells (haemoglobin). |
| Fasting | Required fasting (overnight) to obtain fasting plasma glucose levels. | Not required fasting as it provides average glucose levels for the last 2-3 months. |
| Units of measurement | mg/dL | Percentage (%) |
| Use of Glucometer | Glucometer can be used to check for blood glucose. | Glucometer can’t provide HbA1c value. |
| Indicates | Blood glucose levels on the day of the test or 24 hours. | Average blood glucose levels for last the 2-3 months from the date of test. |
HbA1c Test Cost in Hyderabad, India
HbA1c test price in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹250 to ₹750 (approx. US $3 – US $9). The exact HbA1c test cost varies depending on the laboratory technology used (HPLC / immunoassay), whether it is part of a diabetes package, sample processing automation, urgency of reporting, and hospital laboratory facilities — including cashless options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of HbA1c Testing
- Standard HbA1c Test (Routine Screening) – ₹250 – ₹450 (US $3 – US $5)
- HbA1c Test with Estimated Average Glucose (eAG) – ₹300 – ₹600 (US $3.60 – US $7.20)
- HbA1c Test as Part of a Diabetes Monitoring Package – ₹350 – ₹750 (US $4.20 – US $9)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on HbA1c Test
What is the normal HbA1c level?
The HbA1c blood test normal range is between 4% and 5.6% in patients who are non-diabetic. In the case of prediabetic conditions (non-diabetes or risk of having diabetes), the value lies between 5.7% and 6.4%.
Which Is the best hospital for HbA1c Test in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, is one of the most trusted centres for diabetes screening and metabolic health evaluation, offering precise HbA1c testing using advanced, fully automated laboratory systems.
Our NABL-certified laboratories ensure accurate measurement of glycated hemoglobin levels, helping diagnose diabetes and monitor long-term blood sugar control effectively.
With expert pathologists, rapid sample processing, digital reporting, and comprehensive diabetic assessment support, PACE Hospitals ensures reliable, fast, and high-quality HbA1c testing — supported by cashless options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with insurance documentation where applicable.
How to reduce HbA1c level?
Lowering HbA1c levels can aid in the slow progression of diabetes mellitus, thereby reducing its complications. HbA1c level less than 7% should be a goal for most adults with diabetes mellitus. Changes in diet and lifestyle modifications and adherence to prescribed medication can help in reducing HbA1c levels.
Which is more accurate, HbA1c or fasting glucose?
Both tests help in diagnosing and managing hyperglycaemia. However, HbA1c can be more accurate in accessing diabetes conditions as it provides the average blood glucose levels for the past 2–3 months, whereas the fasting blood glucose provides the report of the fasting blood sugar (on the day of test), which can be inaccurate as it might depend on the previous day's food intake.
Is fasting required for HbA1c test?
No, fasting is not required for HbA1c as it provides the average blood glucose levels for the past 2 to 3 months. This test can be performed anytime as a part of diabetes screening and management.
What Is the cost of HbA1c Test at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of an HbA1c test typically ranges from
₹220 to ₹650 and above (approx. US $2.60 – US $7.80), making it an affordable and accurate option for diabetes diagnosis and monitoring.
The final cost depends on:
- Type of testing (standard / with eAG)
- Technology used (HPLC / immunoassay)
- Whether it is part of a diabetes blood panel
- Urgency of reporting (same-day / priority)
Additional tests recommended by the physician (FBS, PPBS, lipid profile)
For routine screening, costs remain at the lower end; tests performed as part of a comprehensive diabetes panel or urgent requests fall toward the higher range.
After clinical assessment, our team provides a personalised test plan and clear cost estimate based on your diagnostic needs.
What is normal HbA1c by age?
The HbA1c level can vary depending on a number of factors, including age, ethnicity, and health conditions. For example, the normal HbA1c level for children and adolescents is lower than the normal level for adults. And, the normal HbA1c level for pregnant women is also lower than the normal level for non-pregnant women. A high HbA1c level indicates that your blood sugar has been high for a long period of time, that indicates you have prediabetes or diabetes.
Following are the normal HbA1c levels for different age groups:
- Children and adolescents (6-17 years) - 4.8% –5.7%
- Adults (18–64 years) - 4.8%–5.7%
- Adults (65 years and older) - 5.7%–6.5%
- Pregnant women - 4.8%–5.3%
What is a dangerous level of HbA1c?
The dangerous level of HbA1c is more than 6.5%, where the patient might have the risk of complications related to diabetes mellitus such as eye problems, kidney problems, nerve damage, foot problems, gum diseases etc.
What is glycosylated haemoglobin?
Glycosylated haemoglobin is a biomarker for diagnosing diabetes mellitus. It is formed due to the occurrence of a ketoamine reaction between glucose (sugar molecule) and the N-terminal amino acid of the beta chain of haemoglobin, which results in the attachment of sugar molecules to the haemoglobin of red blood cells. The unutilised sugar molecules present in the blood (which might occur due to insulin resistance or absence of insulin production) attach to the haemoglobin, resulting in the formation of glycosylated haemoglobin.
What is estimated average glucose?
Estimated average glucose (eAG) is the estimated average blood glucose value (mg/dL) for the period of 2 to 3 months, which is calculated based on the values of glycosylated haemoglobin (%). The formula for calculating the estimated average glucose from HbA1c is 28.7 x HbA1c value - 46.7.
How much can HbA1c levels drop in 3 months?
It depends on the HbA1c levels; in the case of higher HbA1c levels, it is usually recommended to aim for an appropriate drop-in HbA1c level compared to moderate and low levels. However, it might vary depending on the patient's condition and the presence of comorbidities.
Is HbA1c 6 normal?
No, it is not considered as normal, as patients with HbA1c 6% are at risk of diabetes, as normal HbA1c levels are less than 5.7%. HbA1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% is considered a prediabetic condition.
Is 7.5 HbA1c high?
Yes, an HbA1c of 7.5 is considered high, falls into the diabetes range that indicates an average blood glucose concentration over the past 2–3 months. While the ideal HbA1c level is below 5.7%, most people with diabetes aim for a level below 7%.
It suggests that blood sugar levels have been consistently elevated over the past few months. It's important to note that individualized medical advice is crucial, and the interpretation of HbA1c levels may vary based on an individual's overall health, age, and specific medical conditions. If you have concerns about your HbA1c level, it's recommended to consult with an endocrinologist / diabetologist for a more accurate assessment and appropriate guidance.
Is a HbA1c of 9.5 high?
Yes, an HbA1c of 9.5 is considered significantly high. It falls well within the diabetic range. An HbA1c of 9.5 indicates consistently elevated blood sugar over the past 3 months. This significantly increases your risk of developing long-term complications of diabetes, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems.
It's crucial to discuss this result with an endocrinologist / diabetologist immediately. They can help you understand the specific implications for your health and develop a personalized plan to lower your HbA1c and manage your diabetes effectively.
Is HbA1c between 7 to 8 normal?
No, an HbA1c between 7 to 8 is not considered normal, although the interpretation can be slightly nuanced depending on your circumstances.
An HbA1c of 7-8 indicates consistently elevated blood sugar levels over the past 3 months. This puts you at an increased risk of developing long-term complications of diabetes, even if the risk orisk of developing long-term complications of diabetes, is not as high as with an HbA1c over and above 9%.
What is the HbA1c test cost in India?
HbA1c test cost in India ranges varies from ₹ 300 to ₹ 1400 (INR three hundred to one thousand four hundred).
The cost of the HbA1c test in India can vary depending on the city and the different diagnostic center & private hospitals.