Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors and Complications
Pace Hospitals
Type 1 diabetes meaning
Diabetes mellitus type 1 also called as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, an autoimmune disease resulting in the destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells, leading to low or no insulin production. Insulin is a necessary hormone that regulates protein, glucose, lipid, and mineral metabolism, as well as growth.
Insulin plays several crucial roles in the body, including allowing glucose to enter muscle and adipose cells, stimulating the liver to store glucose as glycogen and synthesise fatty acids, stimulating the uptake of amino acids, inhibiting the breakdown of fat in adipose tissue, and stimulating the uptake of potassium into cells. Insulin replacement therapy is necessary for people with type 1 diabetes mellitus for the rest of their lives. Diabetic keto acidosis (DKA) is a condition that can occur without an insulin treatment.
Type 1 diabetes causes
The causes of diabetes mellitus type 1 include the destruction of the beta cells in the pancreatic islets. The pinpoint reason for beta cells damage is idiopathic (unknown), but researchers believe that there is a genetic predisposition (hereditary) with a strong relationship with specific HLA (DR and DQ) alleles, specifically DRB103-DQB10201 and DRB 10401-DQB10302H.
Without a family history, the risk of having type 1 diabetes is about 0.4%, while the risk is between 1% to 4% in children of afflicted mothers, 3% to 8% in children of affected fathers, and as high as 30% in children of both affected parents.
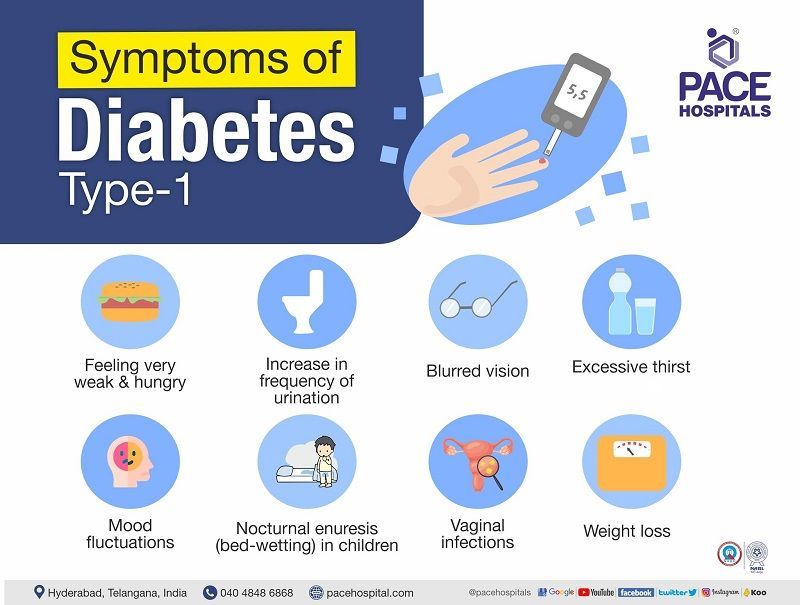
Type 1 diabetes symptoms
Diabetes mellitus type 1 symptoms in adults are of sudden onset that may include the following:
- Increase in frequency of urination
- Nocturnal enuresis (bed-wetting) in children
- Feeling very weak and hungry
- Mood fluctuations
- Excessive thirst
- Blurred vision
- Weight loss
- Vaginal infections
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in children
Diabetes mellitus type 1 symptoms in children usually develop quickly and may include
- Reduction in weight
- Increase urine frequency/bedwetting (in children more than four years)
- Feeling excess hunger and thirst
- Bad breath/ Fruity- smell
- Feeling tired or lack of energy

Type 1 diabetes risk factors
Several risk factors may increase the likelihood that a person may acquire type 1 diabetes, that includes
- Age
- Family history
- Genetics
- Viral exposure (in children)
- Age: Young individuals and children (less than 14 years) are more prone to develop type 1 diabetes. The initial peak might occur between the ages of 4 and 7 years. The second occurs in youngsters aged 10 to 14 years.
- Family history: The developing of type 1 diabetes risk is higher in people who have a parent or sibling with the condition. The risk is increased if both parents have type 1 diabetes.
- Genetics: The presence of specific genes may increase the risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
- Viral exposure: The autoimmune destruction of islet cells may be triggered by the presence of viral infections (enterovirus infection)

Type 1 diabetes complications
Diabetes mellitus type 1 complications that can occur over time, affects key organs.
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Heart and blood vessel disease
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Skin and mouth infections
- Pregnancy complications
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage): An excessive amount of sugar in the blood might cause damage to the capillary walls (tiny blood vessels), leading to a decrease in oxygen and nutrients supply to the nerves. In addition, high blood glucose can alter the nerves' chemicals, decreasing their ability to send impulses. This can cause pain, numbness and tingling sensations that usually start at the very ends of the digits (fingers or toes) and moves upward. Damage to the nerves can lead to erectile dysfunction in men and issues related to the digestive system, such as vomiting, loose stools or difficulty in passing stools.
- Heart and blood vessel disease: Long-term high blood sugar levels are associated with damage to blood vessels and the nerves that control the heart. Diabetic patients are also more likely to have additional diseases that increase their risk of heart disease such as increase in blood pressure, LDL and triglycerides levels.
- Diabetic nephropathy (Kidney damage): Increased blood sugar levels harm the blood vessels that prevent waste from entering the bloodstream. This system can be damaged by diabetes. Severe damage can result in irreversible renal failure or end-stage kidney disease.
- Diabetic retinopathy (Eye damage):Excess sugar in the blood can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to blindness. Diabetes also raises the risk of cataracts and glaucoma, which are significant eye disorders.
- Skin and mouth conditions: Type 1 diabetics are more prone to get oral and skin infections. The presence of bacterial and fungal infections causes these. Additionally, it raises the probability of gum disease and dry mouth.
- Pregnancy complications: The risk of miscarriage and birth abnormalities rises when blood sugar levels rise. In adult women, high blood glucose increases the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, retinopathy, pregnancy-induced high blood pressure, and preeclampsia.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: It develops due to the lack of insulin, where the sugar content in the blood is unable to enter into the tissues to generate energy, resulting in the increased process of fat break down by the liver (to generate energy) resulting formation of excess ketone bodies (acidic) in the blood.

Type 1 diabetes diagnosis
In the initial step of diagnosis, the diabetologist would like to assess the patient’s history, family history, obesity status, past medical history, signs and symptoms. Post that, the diabetologist would request diagnostic tests.
Diagnostic test for type 1 diabetes
The type 1 diabetes diagnosis tests includeHbA1c, which provides accurate measurement of blood glucose levels. The physician might request fasting blood sugar or random blood sugar based on the patient’s condition.
HbA1c: The haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test is an index of a patient’s average blood glucose level over the past 120 days, as the normal life span of red blood cells is about 110 to 120 days. This test is a widely accepted outcome measure for evaluating glycaemic control in individuals with type 1 diabetes. The glucose molecules in the blood attach to the haemoglobin (protein content part in RBC) and circulate over three months in the human body. A small amount of blood sample is collected by a phlebotomist by inserting a needle into the patient's vein, and the collected sample will be sent for analysis. The result might take 12 to 24 hours.
- The HbA1c% levels greater than 6.5% indicate the presence of hyperglycaemia (type 1diabetes).
- HbA1c% levels between 5.7% to 6.4% indicate the presence of risk of being hyperglycaemia.
Fasting blood sugar: This test provides the blood glucose levels under an overnight fasting state. The blood sample will be collected in the morning, at least eight hours after the patient’s last meal.
A fasting blood glucose level of higher than 126 mg/dL signifies the presence of hyperglycaemia.
A fasting blood glucose level between 100 to 125 mg/dL indicated the risk of hyperglycaemia.
Random blood sugar: This test is used to diagnose patients with high blood glucose levels, where a blood sample is collected at any time (randomly) and sent for analysis.
A random blood glucose level of more than 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) indicates the patient is suffering from hyperglycaemia.
Type 1 diabetes treatment
Diabetes mellitus type 1 treatment includes the use of synthetic insulin as a source of replacement for low insulin caused by the destruction of pancreatic beta Langerhans. There are several forms of insulin available. Depending on the patient's need, the diabetologist prescribes single or in combination.
Type 1 diabetes insulin: There are various types of insulin available depending on its onset, peak time and duration of action in the body. These are as follows:
- Rapid-acting
- Rapid-acting inhaled
- Short-acting
- Intermediate-acting
- Long-acting
- Ultra-long acting
- Combination (Premixed)
- Rapid-acting: As the name defines, the onset (time taken to show drug effect) is15 minutes post-administration with a peak time of 1 hour and exists for 2 to 4 hours in the body. It is taken before a meal.
- Rapid-acting inhaled: It has an onset time of 10-15 minutes with a peak time of 30 minutes and exists for 3 hours in the body. It is taken before a meal and can be given along with injectable long-acting insulin.
- Short-acting: The onset time is 30 minutes with a peak time of 120 to 180 minutes and exists for 3 to 6 hours in the body. It is taken one hour before a meal.
- Intermediate-acting: The onset time is 2 to 4 hours with a peak time of 4 to 12 hours and exists for 12 to 18 hours in the body. It is taken with rapid or short-acting insulin.
- Long-acting: The onset time is 2 hours and exists up to 24 hours. It is taken once daily, which covers the entire day's insulin.
- Ultra-long acting: The onset time is 6 hours and lasts more than 36 hours. Similar to long-acting, it is also taken once a day which covers the insulin needed for the entire day.
- Combination (Premixed): It is a combination of intermediate and short-acting insulin that is usually taken before breakfast and dinner. The onset time is 5 to 60 minutes with a varied peak time and exists for 10 to 16 hours in the body.
The other combinations include (based on the patient's condition)
- Rapid-acting + Long acting
- Rapid/short acting + Long acting
- Rapid/short-acting + Intermediate-acting
Insulin alternatives for type 1 diabetes:
Insulin can be administered through the following route:
- Subcutaneous: In this type, the insulin is inserted either through a needle or pen or pumped directly into the subcutaneous layer (fat layer under the skin).
- Inhalation: An oral inhaler is used to administer ultra-rapid-acting insulin via inhaled insulin before meals. Inhaled insulin is combined with a long-acting insulin injection.
Type 1 diabetes prevention
Prevention of type 1 diabetes mellitus is not possible as it is mainly caused by the destruction of the pancreas (beta cells of Langerhans) by the body's immune system.
Frequently asked questions
Related Articles


Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868