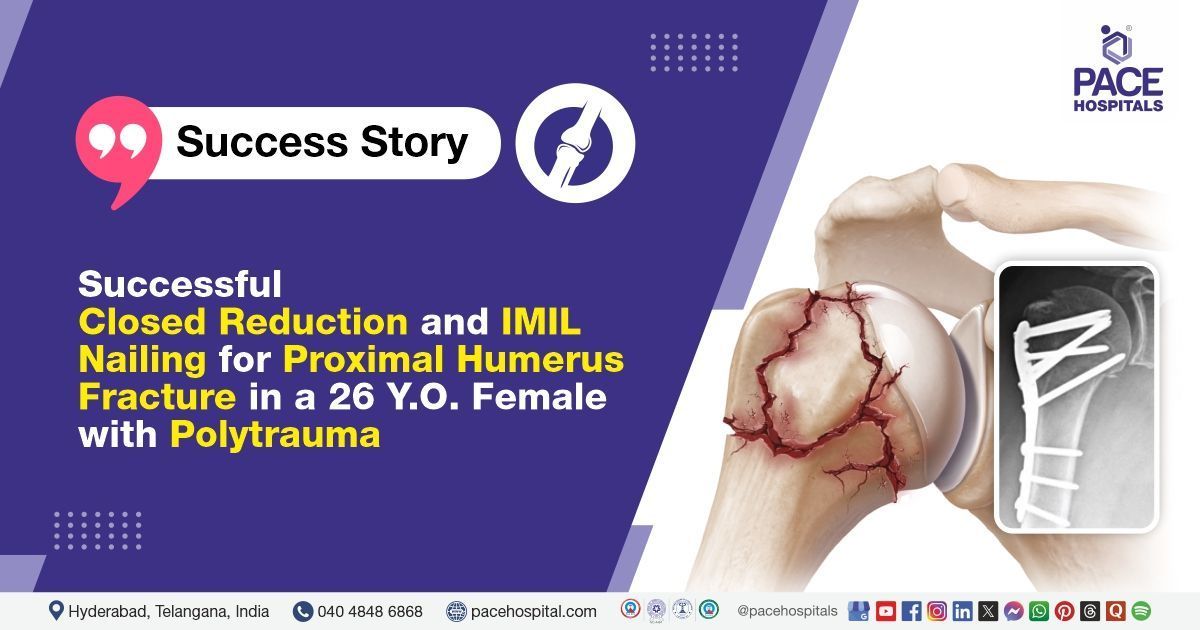
Successful Closed Reduction and IMIL Nailing for Proximal Humerus Fracture in a 26-Y.O Female with Polytrauma
PACE Hospitals
PACE Hospitals’ expert Orthopaedics team successfully performed a Closed Reduction and Internal Fixation with Interlocking Intramedullary Nail (IMIL) on a 26-year-old female patient who had sustained multiple injuries, including a displaced proximal right humerus fracture, right scapula and acromion fractures, rib fractures, mild pleural effusion, and a parietal bone contusion, following a road traffic accident. The procedure effectively stabilized the humerus fracture and contributed to the patient’s safe recovery.
Chief Complaints
A 26-year-old female patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 21 presented to the Orthopaedics Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, in a drowsy state following a road traffic accident (RTA). She sustained multiple injuries involving the right upper limb, chest, and head, with suspected intoxication at the time of the incident.
Past Medical History
The patient had no known history of hypertension or diabetes. The absence of comorbid conditions was considered clinically favourable, as it had minimized the risk of intraoperative and postoperative complications and had supported a smoother, more stable recovery in this case.
On Examination
On examination, the patient was drowsy with GCS: 10 /15 and Vital signs were stable. The patient had a deep laceration over the right occipital region with active bleeding and visible bony margins, along with abrasions over the right elbow and left thigh, and a superficial laceration over the right arm. Swelling and tenderness were noted over the right shoulder, with crepitus and abnormal mobility of the right arm. The range of movements at the right shoulder and arm was grossly restricted and painful. There was no distal vascular deficit.
Neurological status could not be fully assessed as the patient was in a drowsy state. Systemic examination revealed decreased air entry over the right side of the chest, while cardiovascular and abdominal examinations were normal. The central nervous system examination showed the patient responding to deep stimulus but remaining drowsy.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was thoroughly evaluated by the Orthopaedics team, including a detailed review of her medical history and a comprehensive clinical examination. She presented in a drowsy state, possibly intoxicated, following a four wheeler road traffic accident, with clinical suspicion of multiple traumatic injuries involving the right upper limb, chest, and head.
Comprehensive diagnostic investigations, including X-ray of the right shoulder, CT brain, and other imaging, confirmed a displaced proximal one-third right humerus fracture, undisplaced fracture of the right acromion process, minimally displaced right scapula fracture, undisplaced fractures of the right 2nd to 5th posterior ribs, mild right-sided pleural effusion with pulmonary contusion, and a parietal bone fracture with parietal contusion. Laboratory investigations, including complete blood picture, renal and liver function tests, coagulation profile, serum electrolytes were within normal limits except for anemia.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, she was advised to undergo for Proximal Right Humerus Fracture, Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the care of the Orthopaedic Department, ensuring comprehensive management.
Medical Decision Making
After consultation with Dr. Anand V Agroya, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, and cross-consultations with Dr. U L Sandeep Varma, a Neurosurgeon, Dr. S Pramod Kumar, a Neurologist, and Dr. Pradeep Kiran Panchadi, a Pulmonologist, a multidisciplinary team addressed the patients’ traumatic injuries. A comprehensive evaluation was carried out to determine the most appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan for the patients. Clinical assessment and imaging revealed a displaced proximal 1/3rd right humerus fracture, along with associated right scapular, acromion, rib, and parietal skull fractures, as well as mild pleural effusion and brain contusion.
It was determined that the patient had a road traffic accident (RTA), with multiple injuries involving the right upper limb, chest, and head, including suspected intoxication at the time of incident Closed Reduction and Internal Fixation (CRIF) using with Titanium Intramedullary Interlocking Nail (IMIL) Nail (Proximal Distal Locking) were identified as the most suitable surgical approach to stabilise the fracture and enable early mobilisation.
The patient and her family were informed about the diagnosis, the planned surgical procedure, its associated risks, and its potential to alleviate symptoms and improve her quality of life.
Surgical Procedure
Following the diagnosis, the patient was scheduled to undergo Closed Reduction and Internal Fixation (CRIF) surgery in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals with IMIL Nail for the displaced proximal right humerus fracture under the expert care of the Orthopaedic Department.
The procedure was performed in the following steps:
- Preoperative Preparation: The patient was shifted to the operating room and placed under general anesthesia after preoperative assessment. She was positioned in a beach chair or supine position, with the right arm draped and prepared in a sterile manner. C-arm fluoroscopy was arranged for intraoperative imaging.
- Closed Fracture Reduction: Closed manipulation was performed to align the fracture fragments of the proximal right humerus. Reduction was carefully monitored using intraoperative fluoroscopy (C-arm) to ensure anatomical alignment of the bone.
- Entry Point and Canal Preparation: A small incision was made near the greater tuberosity of the humerus. The entry point into the intramedullary canal was created using a bone awl. The canal was prepared to receive the nail; reaming was done only if necessary, depending on the bone diameter.
- Insertion of IMIL Nail: An orthopaedic implant, specifically an Intramedullary Interlocking Nail (IMIL) of 6.5 mm diameter, 240 mm length, was introduced into the intramedullary canal through the prepared entry point. Fluoroscopic imaging was used to guide the nail and confirm that fracture alignment was maintained during insertion.
- Locking Screw and K-wire Fixation: Once the nail was in position, proximal and distal locking screws were inserted using a targeting jig to provide rotational and axial stability. Orthopaedic implants K-wires were also used for additional temporary stabilization, if needed. The positioning of all fixation elements was confirmed using the C-arm.
- Final Position Check: A complete assessment was made under fluoroscopy to confirm proper placement of the IMIL nail, screws, and overall alignment of the humerus. No intraoperative complications were noted.
- Wound Closure and Dressing: The surgical site was irrigated with saline. The wound was closed in layers using absorbable sutures for deeper tissues and non-absorbable sutures for skin. A sterile dressing was applied, and the limb was placed in a shoulder immobilizer.
Postoperative Care
The postoperative period was uneventful. The patient was monitored in the recovery room for a few hours and later shifted to the ward in stable condition. On postoperative day 1, the surgical dressing was changed, and the wound appeared clean and dry. During her hospital stay, she was treated with intravenous antibiotics, analgesics, and supportive medications. Physiotherapy was initiated, focusing on finger movements of the right hand. The patient remained hemodynamically and neurologically stable and was discharged with clear instructions for wound care, medication, and follow-up.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed medications including oral antibiotics for infection prevention, analgesics for pain management, anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling, gastric protectors to prevent stomach irritation, supplements such as calcium and vitamin D to support bone healing and recovery and neuroprotective drugs were given to support brain injury recovery and reduce the risk of seizures. Anti-allergy medications were provided to prevent allergic reactions. Pulmonary support included nebulization to assist breathing due to pleural effusion and lung contusion, as well as low-flow oxygen therapy to maintain adequate oxygen saturation.
Advice on Discharge
The patient was instructed to use a shoulder immobilizer until further notice and to keep the dressing dry. Physiotherapy exercises for the right-hand fingers were advised to be continued as per recommendations.
Emergency Care
The patient and her family were advised to immediately contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of severe pain at the operated site, discoloration or swelling of the operated site or limb, excessive bleeding or discharge from the wound, chest pain, acute shortness of breath, altered sensorium, low urine output in the last 24 hours, nausea, vomiting, signs of allergy or drug intolerance, and high-grade fever.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up visit with the Orthopaedic Doctor in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals after one week for a wound dressing change. Additionally, follow-up consultations with the Pulmonologist, Neurophysician, and Neurosurgeon were recommended for further evaluation after 7 days.
Conclusion
This case highlights the successful management of a displaced proximal right humerus fracture managed by closed reduction and IMIL nail fixation. The patient’s postoperative course was stable and without complication. Proper follow-up and adherence to post-operative care were advised to ensure complete functional recovery.
Coordinated Multisystem Trauma Care Focused on Prioritized Injury Stabilization
In cases of multiple traumatic injuries, the orthopaedic doctor/orthopaedic surgeon plays a crucial role in prioritizing treatment based on the severity and functional importance of each injury. In this case, the team focused first on stabilizing the proximal humerus fracture, as it was essential for preserving arm function and enabling early movement. By using a minimally invasive surgical technique, they minimized additional tissue damage and promoted faster recovery. Early stabilization of major fractures helps prevent complications such as joint stiffness, muscle wasting, and prolonged immobility.
At the same time, associated injuries like rib fractures and brain contusion were carefully monitored and managed. This approach ensures that life-threatening and functionally significant injuries are addressed promptly, while also supporting overall patient recovery. Such prioritization by the orthopaedic doctor/orthopaedic surgeon is key to achieving the best possible outcomes in complex trauma cases.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles