BMI Calculator for Men & Women | Chart, Range & Health Info
Pace Hospitals
How to Use the Free BMI Calculator for Men & Women?
BMI Calculator (Age 2–120 years)
A healthy weight is the appropriate height and body weight for adults.
- People who are overweight (BMI of 25-29.9) have too much body weight for their size.
- People who are obese (BMI of 30 or above) almost always have more amount of body fat than their height.
BMI full form in medical - Body Mass Index
BMI is a statistical index that is necessary to measure the amount of body fat. A person’s weight and height are used to estimate their obesity status, thereby understanding the risk of obesity-related comorbidities.
BMI meaning
Body Mass Index meaning is a value acquired from height and weight. It categorizes a person's weight status and assesses whether they are underweight, average, overweight, or obese.
BMI is an estimation of the body mass and a good gauge of a person's risk for conditions that can occur with more body fat; the higher the BMI, the higher the risk for diseases such as cardiovascular disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, gallstones, pulmonary conditions, and other cancers.
BMI formula
As explained earlier, the weight and height of an individual is necessary for the BMI calculation formula. Usually, the BMI formula in kg and meter is calculated.
BMI = weight (in kg)/ height^2 (in m^2), the weight of a person (in kilograms) divided by their height in meters squared.
The number obtained through this equation is the individual's BMI. Instead of traditional height vs weight charts, the National Institute of Health (NIH) uses BMI to differentiate a person as underweight, average, overweight, or obese.
Importance of BMI
Although BMI doesn't measure body fat directly, it's strongly correlated with it. BMI helps assess a person's weight's appropriateness and guides health actions.
- Weight and Health Evaluation: A higher BMI often means higher risks like heart disease, diabetes, etc. Understanding the BMI enables the management of risks through diet and activity changes.
- Weight Management: Monitoring BMI changes aids weight loss, improving health and energy levels.
- Personalized Health: BMI guides doctors in tailoring recommendations for patients, addressing specific needs effectively.
- Heightened Awareness: BMI awareness encourages healthier habits, preventing future health issues.
Prevalence of obesity and the necessity of body mass index (BMI) calculator
One of the significant public health crises in the world is obesity. Recent studies have revealed that more than 190 crore adults are overweight, and 65 crore people are obese. Nearly 28 lakh deaths are reported because of being overweight or obese. Various studies have revealed that the prevalence of obesity is higher among women than compared to men.
Necessity of BMI Calculator in India
More than 13.5 crores of Indians suffer from obesity. The obesity of the Indian diaspora can be dependent on various factors such as socio-economic status, gender, age, geographical environment, etc, among others. While obesity rates range from 11.8% to 31.3%, the central obesity could vary from 16.9% to 36.3%. Abdominal obesity is one of the significant risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVDs) among Indians.
Consideration of specific issues by the patients and caretakers before opting for the BMI calculator
A high BMI value indicates high body fat. It only screens for weight categories, which may lead to health problems, but it does not diagnose an individual's body fatness or health. The determination of BMI as a health risk by the general physician necessitates the requirement of further assessments, such as:
- Skin fold thickness measurements
- Diet evaluations
- Physical activity and
- Family history
BMI is merely an inexpensive but productive and accessible tool, requiring only calculating height and weight. Despite its versatile usability, BMI does have some limits:
- It may approximate body fat in athletes and those with a muscular build.
- It might underestimate body fat in older persons.
Although BMI often corresponds with body fat, the higher the score, the more body fat a person may have; it isn't always reliable. BMI is not a diagnostic device for health. Doctors use BMI and other tools and tests to evaluate a patient's health and risk factors.
Even though BMI is calculated using the same BMI formula as BMI for adults, BMI for children and teens is interpreted differently. The BMI calculator for kids and teenagers must be age and gender-specific because the amount of body mass changes with age and differs between girls and boys.
In general,
- Women often have higher body fat percentages than males at the same BMI (BMI calculator for females Vs. BMI calculator for men).
- Depending on the racial/ethnic group, the percentage of body fat may vary at the same BMI.
- On average, older persons have more body fat than younger adults with the same BMI.
- At the same BMI, athletes have less body fat than non-athletes.

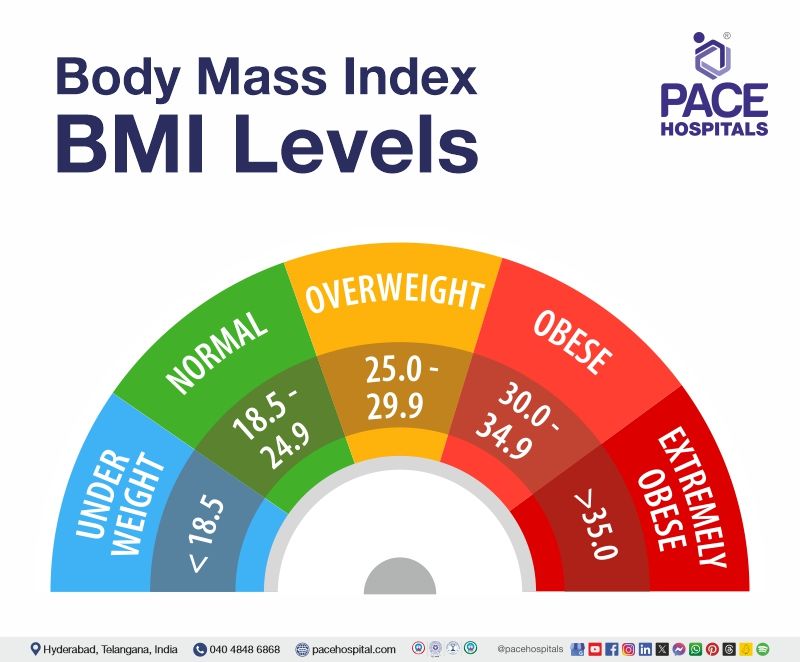
BMI classification
In general, the below-mentioned BMI chart (in kg/m2) classifies different weight types:
- Severe Thinness: Less than 16
- Moderate Thinness: 16 to 17
- Mild Thinness: 17 to 18.5
- Normal: 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: 25 to 29.9
- Class I obesity: 30 to 34.9
- Class II obesity: 35 to 39.9
- Class III obesity (Morbid Obesity): More than 40
BMI normal value
The body mass index normal range is typically considered between 18.5 and 24.9.
Realizing that body fat isn't the sole factor influencing overall health is crucial. Other factors such as heredity, activity level, smoking or using tobacco, alcohol consumption, and mental health disorders all have an impact on individuals' overall health and likelihood of getting a chance for specific medical conditions.
The BMI calculator is not a source of clinical guidance. It is not a substitute for a doctor's advice, as BMI measures body fat based on weight and height. However, individuals with the same BMI may have different amounts of body fat. Persons may seek advice on healthy weight status from an experienced general physician.
The general physician may perform additional testing among individuals whose BMI is more than 30 kg/m2 and whose BMI is less than 18 kg/m2.
In obese people (BMI greater than 30 kg/m2), these additional testing could include
- Fasting lipid panel
- Thyroid function tests
- Liver function tests
- Fasting glucose and
- Haemoglobin A1C (HbA1C)
In underweight people (BMI less than 18 kg/m2), the additional testing is:
- Thyroid level
- Comprehensive metabolic panel
- Psychiatric screening for eating disorders, malabsorption conditions, etc.
If a patient experiences sudden unintentional weight loss, malignancy screening should be done.
Limitations of BMI
BMI has its limits, despite its everyday use as a helpful predictor of a healthy body weight. Body composition cannot be considered by BMI, which is merely an estimate, because there are many different body types and variations in the distribution of fat, muscle, and bone mass; BMI should not only use as a metric to determine an individual's healthy body weight. Instead, it should be used in conjunction with other metrics.
Limitations of using BMI to help diagnose different weight types: Body Mass Index (BMI) does not differentiate between lean body mass (the weight of everything but fat in the body) and fat mass. As a result, a person with a high BMI (due to muscle mass) can have a shallow fat mass and vice versa.
- BMI for adults: It is incorrect since BMI calculates excess weight rather than excess fat. Age, sex, ethnicity, muscle mass, body fat percentage, and activity level impact a person's BMI. Athletes may be at a healthy weight for their body composition, especially bodybuilders who are deemed overweight because their muscle mass exceeds their fat mass.
- BMI calculator for kids and adolescents: Children and adolescents can also be affected by the same variables that restrict the effectiveness of BMI in adults. Furthermore, a child's BMI and body fat can be influenced by their height and stage of sexual development compared to overweight children, whose BMI may result from higher amounts of fat or fat-free mass (all body components other than fat, such as water, organs, muscle, etc.), BMI is the best measure of excess body fat in obese children. The variation in BMI in lean children may result from fat-free mass.
BMI is a good predictor of body mass for 90-95% of the population and can be used with other measurements to establish an individual's appropriate body weight.
Limitations of BMI screening as a tool for different health-related conditions: While BMI screening could assess the risk of certain health disorders such as diabetes type 2 and heart diseases, it has its limitations, such as:
- The BMI does not account for the distribution or location of body fat. This is a problem because more fat stored in specific places in the body, such as the belly (abdomen), is linked to a greater risk of health problems than excess fat accumulation in other areas, such as the thighs.
- Family history of diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and high cholesterol (dyslipidemia); familial length (average lifespan); or family history of cancer are sometimes overlooked in the link between BMI and death rate.
Risk of obesity-related comorbidities
Obesity is one of the most neglected health problems, which leads to diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Overweight and obesity have become a significant public health problem in both developing and developed countries. In the Indian sub-context, the country is in a transitional state of undernutrition due to poverty and obesity due to industrialization and rapid urbanization.
Given below are a few of the typical overweight BMI risks that increase the affinity of several severe diseases and health conditions:
- Diabetes BMI risk
- High blood pressure
- LDL cholesterol, often called "bad cholesterol," can increase the risk of heart disease. HDL cholesterol, known as "good cholesterol," helps remove LDL from arteries. High levels of triglycerides can also raise the risk of heart disease.
- Stroke
- Gallbladder disease
- Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease when the cartilage between joints breaks down.
- Sleep apnea and respiratory problems
- Certain cancers like endometrial cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, kidney cancer, gallbladder cancer, liver cancers
- Poor life quality
- Mental illnesses such as clinical depression, panic attacks, anxiety, and other
- Body pains and difficulty with some physical functions
- Generally, there is an increased risk of mortality compared to those with a healthy BMI
BMI and diabetes relationship: A research study conducted by Chan et al. revealed that people with a BMI of more than 35 kg/m2 had more risk of developing type 2 diabetes than compared to people whose BMI is less than 23 kg/m2. Hence, the study revealed that obesity increases the risk of disease. Other factors, such as fat distribution, genetics, and fitness level, contribute to an individual's disease risk assessment.
BMI and cardiovascular disease risk: It is a term used to describe various health problems that affect the heart, such as heart attack (blood flow to the heart is restricted or blocked), angina (chest pain due to reduced blood flow to heart muscles), heart failure (failure of heart in pumping blood adequately), and arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms). The heart must work hard to send blood to all body cells if the patient is obese or overweight. Hence, being overweight or obese increases the risk of heart disease, which can be overcome by reducing weight. It includes.
High blood pressure: It is also known as hypertension, A condition where blood flows through the blood vessels with a force greater than usual is known as hypertension. Increased blood pressure occurs commonly in patients with increased body sizes as the heart needs to be pumped, which is much more complicated to supply blood to all the cells. More fat may also cause damage to the kidneys, which help regulate blood pressure.
High blood pressure can affect the heart and damage blood vessels, and heart attack risk is increased stroke, kidney disease, and even death. High blood pressure may be lowered by reaching a healthy body mass index by losing enough weight. Thus, through weight reduction, obesity-related health problems associated with hypertension can be prevented or controlled.
BMI stroke risk: A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain or neck is busted or blocked, decreasing the blood flow to the brain, thus damaging the brain's tissue and making the individual aphasic (unable to speak) or paralytic (unable to move body parts). High pressure in the blood, high cholesterol, and high glucose levels are some of the risk factors for stroke. Losing weight may overcome these risk factors.
BMI gallbladder risk: High levels of cholesterol in the bile are seen in people who are obese. They cause gallstones. Gall bladder size may increase in some cases, and its working is affected. In obese people, having more amount of fat around the waist may increase the chances of getting gallstones. To overcome this, weight should be decreased, but the sudden decrease in weight, in turn, leads to other complications. Hence, before losing weight, get the help of a healthcare practitioner and follow accordingly.
BMI osteoarthritis risk: Being obese or overweight causes extra pressure on joints and cartilage, which in turn increases the risk of developing osteoarthritis. The blood of individuals suffering from excess body fat contains higher levels of inflammation, which increases the risk of osteoarthritis.
BMI and sleep apnea, breathing risk: In obese and overweight patients, fat stored around the neck is increased, compressing the airway, causing breathlessness, snoring, etc. Losing weight helps in overcoming sleep apnea. The working capacity of the lungs is also affected by weight. Being overweight or obese can affect the lungs and increase breathing problems.
BMI cancer risk: Overweight or obese men are at an increased risk of colon, rectum, and prostate cancer development, while overweight and obese females are at an increased risk of breast cancer.
BMI mental health risk: Being overweight or obese also affects the mental health of people. These people are likely to face some challenges like body-shaming and weight-related bias at school, college, or the workplace, which affects their quality of life. Losing weight will help reduce the symptoms of depression, improve body image and self-esteem, and decrease stress.
BMI pregnancy risk: People who are obese and overweight have higher chances of developing gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and increased health risks for the baby. So, a healthy weight should be maintained during pregnancy.
Being overweight can have several detrimental and occasionally fatal effects, as the above list illustrates. In general, one should aim to keep their BMI around 25 kg/m2, but ideally should consult a doctor to determine if any lifestyle adjustments are necessary to get healthier.
Underweight BMI risks
Being underweight has its associated risks, including:
- Malnutrition, vitamin deficiencies, anemia
- Osteoporosis (bone disease increasing the chance of fractures).
- Immunocompromised state (decreased immune function).
- Growth and development problems, particularly in children and teenagers
- Possible reproductive problems for females due to hormonal imbalances that can disrupt the menstrual cycle. Underweight females also have a high chance of miscarriage in the first trimester (first third of pregnancy, from the first day of your last period to the end of the 13th week)
- Potential complications because of surgery
- Generally, there is an increased risk of mortality compared to those with a healthy BMI.
- Hypothermia (an abnormally low body temperature)
- Decreased muscle strength.
Being underweight may be an indication of underlying medical conditions, including the risk of anorexia nervosa. A doctor consultation is needed if the reason for being underweight does not seem obvious.
BMI Normalisation in Overweight
To maintain a normal BMI and avoid various diseases, these types of therapy are followed:
1. Conventional Therapy: The treatment that is widely accepted and it includes:
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Pharmacotherapy
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in weight management and promoting overall health. Here are some practical and sustainable lifestyle changes for individuals who are overweight:
Healthy Eating Habits:
- Focusing on a balanced diet, which includes various types of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Take good protein and more fiber.
- Limit the quantity of salt, sugar, and fat in the diet.
- To avoid overeating, we should be mindful of the meal size.
- Planning meals and snacks to make healthier choices and avoid impulsive eating.
- Consuming water throughout the day can help control hunger and support overall health.
- It includes lower energy intake than expenditure.
- A deficit of 600 kcal/day is recommended for sustainable weight loss.
- A reduced-calorie diet is a dietary treatment for people with high BMI.
Regular Physical Activity:
- Engaging in moderate physical activity, with a goal of at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week
- Including activities such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming to burn calories and improve cardiovascular health.
- Incorporating strength training exercises to build muscle, which can boost metabolism.
- Finding activities one can enjoy, making exercise a sustainable routine.
- To burn calories throughout the day, add ordinary movements like walking around the neighborhood, getting up from your desk, and moving regularly.
- Muscle strengthening exercises should be done at least twice a week.
Behavioral Changes:
- Listen to hunger and fullness signs, and avoid distractions like screens during meals.
- Having food slowly allows the body to register when it's complete.
- Identifying emotional triggers for overeating and finding other coping mechanisms, such as confiding in a friend or engaging in a hobby, can help address the issue.
- Aiming for 7–9 hours of high-quality sleep per night is essential, as poor sleep can affect hunger and stress-regulating hormones.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking.
Stress Management:
- Practicing stress-reducing activities such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness
- Avoiding food is a primary way to cope with stress and find alternative outlets for stress relief.
Hygiene and Habits:
- Choosing healthy snacks and being mindful of portion sizes
- Preparing meals at home to have better control over ingredients and portion sizes.
- Reducing intake of processed and high-calorie foods
Pharmacotherapy:
In addition to dietary therapy and lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy is also followed as the treatment for high BMI people. For patients whose BMI is greater than 27 kg/m2 with associated risk factors or people with a BMI of greater than or equal to 30kg/m2, the below-mentioned drugs are used in the weight loss management of obese or overweight patients.
Pharmacotherapy includes lipase inhibitors, incretin mimetics, and opiate antagonists.
2. Interventional therapies:
There have been a few surgical procedures that can help in reducing weight in obese individuals. A few of them are:
- Intragastric balloon
- Bariatric surgery
Intragastric balloon: Since 1985, this anti-obesity intervention, an intragastric balloon (IGB), has been used. Through an endoscope, it deploys a silicone balloon filled with saline is into the stomach, which remains inflated for at least six months. It is used in patients who decline or are not fit for bariatric surgery as an alternative option for weight loss.
Bariatric surgery: When all the interventions fail, the treatment of choice is bariatric surgery. It is superior to the other non-surgical interventions. Usually, the patients are referred for bariatric surgery only if the following criteria are achieved:
- BMI ≥35 kg/m2 with associated comorbidities that could be improved with weight loss.
- BMI ≥40 kg/m2
- BMI of 30–34.9 kg/m2 with a recent onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- When all the other conservative and medical weight loss options have been tried but have failed
- The patient is fit for anesthesia.
- The patient shows commitment to long-term follow-up.
All types of bariatric surgery have advantages and disadvantages. There are common types of bariatric surgery:
- Roux-en-Y (roo-en-wy) gastric bypass: Here, the stomach and distal part of the intestine are divided and attached, thus limiting the amount of food intake. It is the most popular method of gastric bypass surgery. This operation is usually irreversible. Mostly done laparoscopically, the RYGB yields an estimated weight loss of 73% within a year,
- Sleeve gastrectomy: Sleeve gastrectomy involves removing 80% of the stomach, leaving a tube-like pouch. This smaller stomach can't hold as much food, thus reducing the caloric intake.
- Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS): The Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD-DS) involves creating a tube-shaped stomach pouch, like a sleeve gastrectomy. BPD-DS is a complex procedure, and perioperative anastomotic leaks, splenectomy, internal bowel herniation, and small bowel obstruction could be the complications.
- Adjustable Gastric Band (AGB): The Adjustable Gastric Band involves a silicone band wrapped around the top of the stomach to limit the food intake. The impact on obesity-related diseases and long-term weight loss is less significant than with other types of surgery. As a result, its use has decreased during the last decade.
BMI normalisation in underweight
Being underweight means vitamins and minerals are deficient in the body, which leads to a weak immune system. To gain weight, the following things could be followed:
- Adults could add 300-500 extra calories per day to gain weight
- By eating smaller meals and taking healthy snacks in between meals
- Consume more cheese, nuts, and seeds
- Consume more high-calorie drinks like milkshakes
- Practice yoga and weight-gaining exercises to increase appetite
Frequently Asked Questions on Body Mass Index (BMI)
How good is BMI as an indicator of body fat?
The correlation between BMI and body fatness is strong, but even if two individuals have the same BMI, their level of body mass may differ. Age, sex, ethnicity, and muscle mass affect the relationship between body fat and BMI.
BMI cannot differentiate between excess fat, muscle, or bone mass nor indicates fat distribution among individuals. Individuals with higher levels of body mass and BMI also have better accuracy rates for BMI as an indicator of body fatness. Although a very high BMI (35 kg/m2) is undoubtedly obese, a somewhat high BMI can also indicate a high proportion of lean body mass (bone and muscle).
How to check BMI?
Body mass index (BMI) is a screening device used in medical screening that calculates the ratio of height to weight to measure how much body mass a person has. Medical professionals use the formula of weight in kilograms (kg) divided by the square of height in meters (m2) to determine BMI.
Is BMI a reliable indicator of health?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a valuable health indicator at the population level; it does not consider factors like muscle mass, bone density, and fat distribution.
Can a low BMI indicate good health?
A low BMI (less than 18.5) can indicate underweight, which may be associated with health risks.
Why is BMI important?
BMI is important as it provides a quick and accessible way to assess a person's weight status with height. It is a valuable screening device for identifying health risks associated with underweight, overweight, or obesity.
How often should I check my BMI?
It's recommended to check BMI periodically, especially during significant life changes or as part of regular health check-ups.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles