Gallstones, Gallbladder Stones – Symptoms, Causes, Types, Complications and Prevention
Pace Hospitals
Gallstones meaning
Gallstones or Gallbladder Stones are the hardened pebble-like particles that form in the gallbladder. The sizes of these gall bladder stones or gallstones can span from a few millimetres (as a grain of sand) to as large as 4.3 cm (as large as a golf ball). There could be a single massive gallstone, hundreds of smaller stones, or a combination of small and large stones in the gallbladder. In medical term, it is called cholelithiasis.
The gallbladder and bile - function, location & anatomy
The gallbladder is a sac-like structure located underneath the liver and functions not only as a reservoir of bile, but also concentrates it. The bile is a yellowish-green-coloured fluid produced by the liver, which aids in lipid and fat digestion. All the liver-secreted bile is collected into the gallbladder, where it is stored and concentrated, which is released in the duodenum (first part of the small intestine) to digest food (especially fats).
Although in the majority of the cases, neither the presence nor the development of gallstones causes pain which is why they could be dubbed as "silent gallstones", there are few cases in which the gallstones can cause pain in the upper right abdomen due to the gallbladder attack or biliary colic (blockage of bile ducts).
The treatment of gallstones depends on the case by case, but usually, they are painless; they do not require medical attention, but in cases of painful cases of biliary colics, it could cause various complications if not treated in time.
Prevalence of gallstone disease in India
The prevalence of gallbladder stones is common in a few regions when compared with the other regions of the world, which could be due to various factors such as dietary habits, the local endemics influencing gallstones etc. In India, approximately at least 4% of the population suffers from cholelithiasis, compared to 10% in the Western world.
Being a silent ailment, gallstone disease is commonly discovered by accident, usually through ultrasonography (USG), prescribed by the physician for other abdominal disease-related diagnoses. Apart from ultrasonography, the other diagnostic procedures which could accidentally reveal the presence of cholelithiasis include abdominal radiography, computed tomography scans and procedures such as laparotomy.
Every year, approximately 3% of those who are asymptomatic develop symptoms. Over a 20-year period, over two-thirds of asymptomatic gallstone patients remain symptom-free.
The increasing incidence of gallstone disease in India is mostly attributable to westernisation, the availability of ultrasonography in both urban and rural areas, as well as greater affordability because of changing socioeconomic structure and affordable investigative costs.
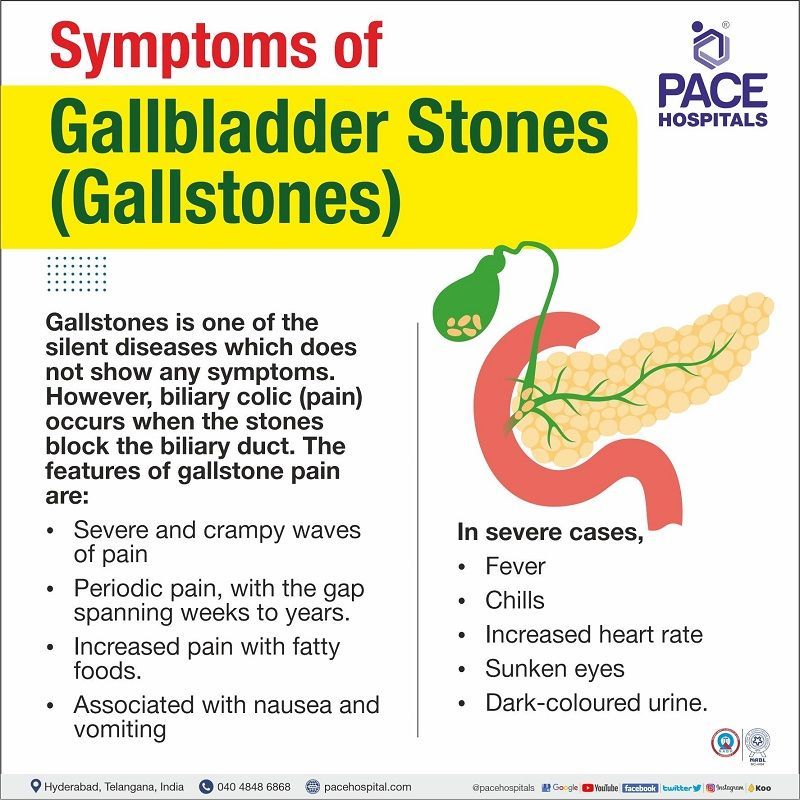
Gallstone or Gallbladder stone symptoms
As stated, gallstone disease is one of the silent diseases which does not show any signs of pain or discomfort. Nevertheless, biliary colic occurs when the stones increase in size, blocking the biliary duct. Some of the gallstone pain symptoms in both male and female are:
- The biliary colic pain occurs as severe, crampy waves of pain incapacitate the patient.
- The pain episodes are periodic, with the gap spanning weeks to years.
- Around 1-4 hours post-meal, the pain may begin. The pain intensity is very high, even at times awakening the patient during his/her sleep.
- The pain may be increased if meals include fatty foods.
- Nausea and vomiting are usually associated with colic.
- The pain could last more than 2–4 hours.
- Fever may be seen if the pain episodes last longer than 4-6.
- In a few cases, pain or tenderness or both may be seen near the liver area (around lower right ribs-right upper quadrant)
- In a few cases, depending upon the severity and other factors, pain could present across the entire upper abdomen, radiating to the back, right scapula, right flank, or chest.
In severe cases, apart from constant pain, fever, chills, increased heart rate, sunken eyes, and dark-coloured urine may manifest. The gallstones symptoms for female is same as that of male.
Types of gallstones or gallbladder stones
Gallbladder stones or Gallstones are usually two types based on the characterisation of their chemical composition.
- Cholesterol gallstones
- Calcium bilirubinate gallstones
Further, they are arbitrarily classified into cholesterol stones (>50% cholesterol content), mixed stones (20 to 50% cholesterol content), and pigment stones (<20% cholesterol content), the latter being composed primarily of calcium bilirubinate.
Gallbladder stone (Gallstone) Composition:
- Cholesterol stones: Here, the stones have more than >50% cholesterol content
- Mixed stones: The stones have about 20 to 50% cholesterol content
- Pigment stones: These stones have less than 20% of cholesterol content, but primarily contain calcium bilirubinate.
In 80% of cases arising from Western countries, either cholesterol or mixed stones heavily occur, but in Asia, 70% of all gall bladder stones are pigment stones. Pigmented stones are either black or brown.
While the black colour could be associated with haemolytic conditions containing calcium bilirubin and mucin glycoproteins, the brownstones are associated with parasitic or bacterial infections occurring in their Asian counterparts.
The black stones are commonly formed in the gallbladder, while the brown ones are seen in the biliary passages.
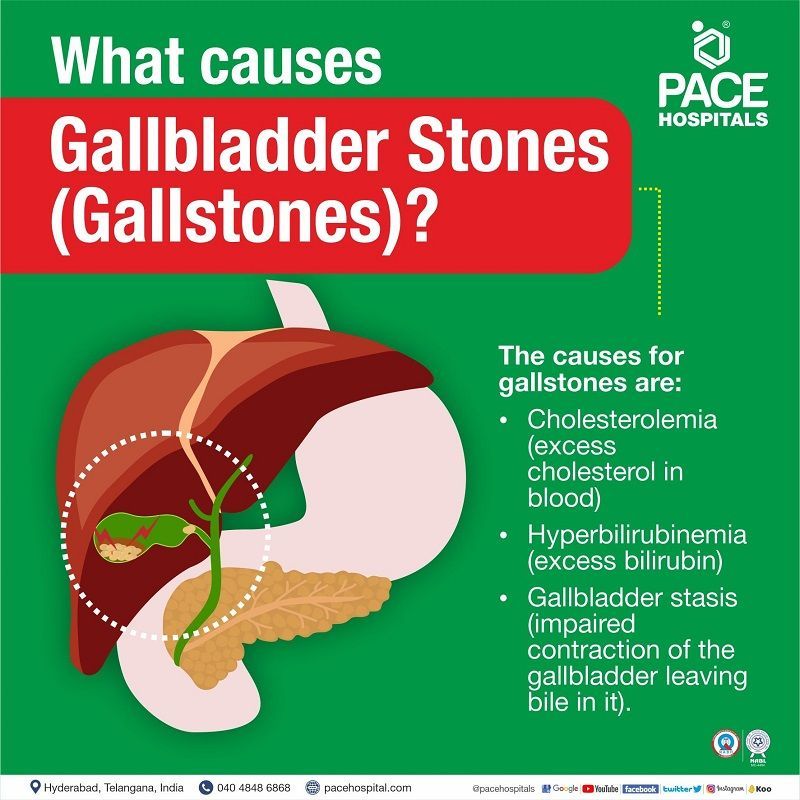
Gallstones or Gallbladder stones causes
Gallbladder stones (Gallstones) are common and are frequently discovered incidentally in asymptomatic patients. Although their spontaneous disappearance is a rare event—except for stones that formed during pregnancy or weight reduction - gallstone disease will remain “silent” in more than two-thirds of individuals.
Some of the causes of gallbladder stones (gallstones) are as follows:
- Cholesterolemia (excess cholesterol in blood): Cholesterolemia causes higher cholesterol content in the bile. While the bile chemicals (lecithin and bile salts) can dissolve cholesterol, either the lack of the same or the increase of cholesterol can cause stones. About 75% of gallstone cases are made up due to excess cholesterol.
- Hyperbilirubinemia (excess bilirubin): During the breakdown of red blood cells in the liver, bilirubin is produced. There are a few medical disorders and infections which can induce the liver to produce extra bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia also causes gallstones.
- Gallbladder stasis: To break down fats in the small intestine, the gallbladder releases bile. Proper contraction of the gallbladder is necessary to expel bile properly. However, disability in the contraction of the gallbladder can cause a few quantities of bile to be left behind. These nominal quantities of bile, over time, progressively concentrate into a sludge-like substance. Upon crystallisation, stones are formed.

Risk Factors for Gallstones or Gallbladder stones
While the conventional risk factors for gallstone disease could be attributed to the four “F’s, namely: female, fat, forty, and fertile”, various recent studies do recommend the inclusion of a 5th" F", which stands for "fair-skinned" as Caucasians have demonstrated moderately higher proportion cholelithiasis.
Delving deeper, there are various factors, such as genetic, environmental, metabolic, and related conditions, factors which implicate stone formations resulting from complex interactions of the same.
- Age: Gallstones are ten times more to form in people over 40 due to a decline in the activity of cholesterol 7 -hydroxylase, the limiting enzyme for bile acid synthesis. The decrease of this enzymatic activity increases biliary cholesterol, resulting in cholesterol saturation and decreased gallbladder emptying mobility. The drug group - cholecystectomies are more helpful in the elderly suffering from various symptoms and complications.
- Gender: Due to the naturally higher oestrogen levels, multiparty (giving birth to many children), or use of oestrogen-based oral contraceptives, women have a higher risk of cholelithiasis than men at all ages. Studies have also shown that women of all ages are more likely than men to undergo cholecystectomy.
- Lipid Profile: The most common ingredient in gallstones is cholesterol, a lipid largely generated in the liver and eliminated via the biliary system. Despite various studies, the relationship between lipids and gallstones remains controversial. There have been studies which report a positive correlation between the rise of lipid levels in the body to the occurrence of gallstones, but there are also studies which show an inverse relationship between the same.
Nevertheless, cholesterol hypersecretion and supersaturation, bile salt and phospholipid concentrations, crystal nucleation, gallbladder dysmotility, and gallbladder absorption and secretion functions are all associated with cholesterol gallstone formation, owing to these complicated and multivariate nature of cholelithiasis; treatment is difficult. - Diet: Westernised nutrition contains cholesterol which causes gallstones. High intakes of carbohydrates (especially refined sugar)and higher dietary glycaemic load increase the incidence of gallstone disease and cholecystectomy. Hyper-nutrition causes obesity, as it increases the risk of gallstones by increased cholesterol synthesis and secretion. Similarly, a high-calorie, low-fibre diet may lead to gallstone formation because it causes an increase in biliary cholesterol release and intestinal hypomobility (reduced movement in the intestine).
In contrast, diets high in unsaturated fat (such as coffee, fibre, ascorbic acid, calcium, fish oil, and fresh fruits and vegetables can reduce cholesterol gallstones risk. Men who eat nuts five times a week or more have a 30% reduction in the incidence of gallstone disease. Nuts are high in unsaturated fats, with favourable effects on blood cholesterol and lipoprotein profiles. - Obesity and Weight Loss: Body mass index (BMI) correlates with obesity and is also a well-known gallstone risk factor in both sexes, but mainly in women. Regional fat distribution worsens gallstone risk even further. Compared to lean women (BMI <24 kg/m2), obese women (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) exhibited a twofold increased risk and morbidly obese women (BMI ≥ 45 kg/m2) had a sevenfold increased risk of having symptomatic gallstones.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Low physical activity is demonstrated to increase the risk of symptomatic gallstones. In an American study, 45,813 men 40-75 years of age were followed from 1986 to 1994. It was shown that men who indulged in more than 40 hours per week of television time had a higher risk for symptomatic gallstones when compared with those men who watched less than 6 hours per week. Increased activity to 30 minutes of endurance-type training five times per week could prevent approximately 34% of cases of symptomatic gallstone disease.
- Diseases: In gallstone disease, metabolic syndrome, dyslipidaemia (disruption of lipid levels in the body),
diabetes, and insulin resistance/hyperinsulinemia usually co-occur. The prevalence of gallstone disease was 2-3 times greater in insulin-resistant individuals with
type 2 diabetes. Elevated hepatic cholesterol secretion, bile supersaturation, and gallbladder dysmotility increase the risks of metabolic syndrome and gallstone formation. Chronic infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) may potentially raise the risk of gallstones.
Liver cirrhosis and
Crohn's disease also increase risk factors for gallstones, in particular black pigment gallstones.
- Alcohol: Gallstone disease risk is negatively correlated with moderate alcohol use. By reducing bile cholesterol saturation and increasing HDL-cholesterol levels, moderate alcohol use may reduce the incidence of cholesterol gallstone disease. Nevertheless, severe alcoholism can cause cirrhosis - a strong independent risk factor for the formation of gallstones.
- Smoking: A 1992 study discovered that excessive smoking (more than 35 cigarettes per day) is a significant risk factor for gallstones in women.
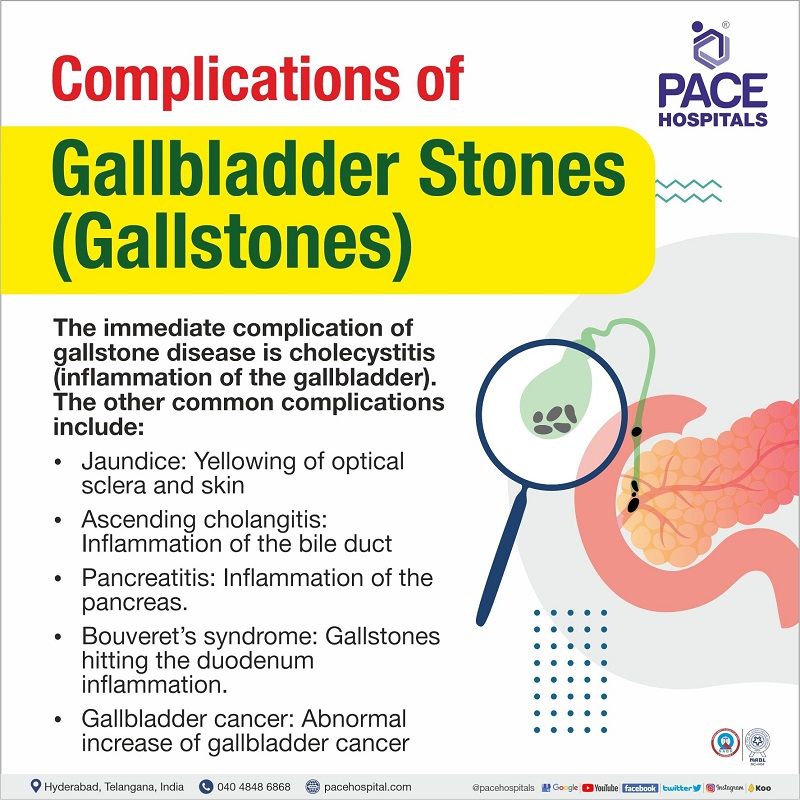
Complications of Gallstones or Gallbladder stones
The immediate complication of gallstone disease is cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder). It can cause severe pain in the upper-right belly and bloating. The other common gallstone disease complications include:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of optical sclera and skin. A partially or totally clogged bile duct can cause the levels of conjugated bilirubin to be leaked into the blood, causing blood levels to rise. This is jaundice, which causes the dark colouration of urine and pale stools.
- Ascending cholangitis: Inflammation of the bile duct, usually caused by bacteria. A partially or completely obstructed bile duct is prone to infections as stasis (stoppage of bile), resulting in ascending cholangitis.
- Bouveret’s syndrome: Gallstones can silently move directly from the gallbladder into the duodenum. The condition of stone hitting the duodenum causing pain and distress is called Bouveret's syndrome.
- Gallstone ileus: If the gallstone dislodges and moves into the duodenum, impacting the narrowest part of the healthy small bowel, which is situated in the terminal ileum, it is called gallstone ileus and could obstruct the small bowel movement.
- Gallbladder cancer: Although rare, gallstones could be a risk factor for gallbladder cancer. This rare cancer is usually discovered either at an advanced stage or as an incidental finding during cholecystectomy.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas. When stones move from the gallbladder to the bowel, they temporarily block the biliopancreatic duct (the common channel), initiating the activation of pancreatic enzymes and causing pancreatitis (gallstone migration theory).
- Gallstones-induced pancreatitis: Characterised by the inflammation of the pancreas, gallstones-induced pancreatitis is mainly caused by indulgence of the Western diet. Long-term follow-up studies reveal a 7% risk of biliary pancreatitis in patients with gallstones. Despite the numerous hypotheses which propose the path to explain the dislodging and movement of gallstones, invariably, the gallbladder stone must emerge through the cystic duct and induce severe pancreatitis by getting lodged at the pancreaticobiliary junction. Alternatively, a main bile duct stone or secondary gallbladder stone may pass through the ampulla of Vater.
The main hypothesis of gallstone-induced pancreatitis includes:
- Ampullary obstruction
- Local inflammation caused by gallstone passage at the level of the ampulla of Vater
- Temporary bile reflux into the pancreatic duct
The risk of gallstone pancreatitis increases with smaller gallstones (permitting more unrestricted movement into the common bile duct and over the ampulla) and higher gallstones count.
Asymptomatic Gallstones or Gallbladder stones
As reported by the Italian (GREPCO) study, asymptomatic gallstones do carry certain risks. The annual complication rate of asymptomatic stones could range between 0.3-1.2%, but in the case of initially symptomatic stones, the annual complication rate is 0.7-2%. The risk of developing gall bladder cancer is 0.3% over 30 years in one study and 0.25% for women, and 0.12% for men in another study over a similar period.
On the other hand, treating incidental asymptomatic gallstones could also risk patients being thrown into the pit of complications such as:
- Diarrhoea and gastro-oesophageal bile reflux, especially if the patient is associated with irritable bowel syndrome and loose stools.
- Elevated right-sided colon cancer risk after 15 years, especially in women.
- Bile duct injury during the procedure and the long-term morbidity.
Therefore, gastroenterologist take extreme measures to understand and confirm the treatment of asymptomatic gallstones, especially if cholecystectomy is the preferred treatment.
Unless there are specific exceptions, gastroenterologist usually follow the policy of not operating on patients suffering from asymptomatic gallstones.
Gallstones and pregnancy complications (gallstones while pregnant)
While pregnant women are more likely than males to have gallstones, the risk increases even more during pregnancy due to the increase of various hormones which influence gallstone formation through mechanisms such as:
- Increased cholesterol secretion in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters than constituents of the bile
- Increase of gall bladder volume due to reduced rate and volume of emptying bile
In 3rd trimester, around 8% of pregnant women develop gallstones, but fewer than 10% of symptomatic patients develop complications.
It is intriguing to note that despite the high incidence of gallstone production and remaining asymptomatic during pregnancy, women typically develop symptoms after giving birth. In fact, symptomatic gallstone disease continues to be the leading non-obstetric reason for hospitalisation in the year following delivery.
How to Prevent Gallstones?
Gallstones prevention can be followed with a few dietary tips (dietary management of gallstones), such as:
- Intake of high fibre, low saturated fatty acid and nut consumption are associated with a reduced risk of gallstones in the general population.
- At least mild-moderate physical activity appears to prevent gallstones.
- Limiting weight loss to a moderate rate (maximum 1.5 kg/week) with measures such as adding 10 g of fat to low-calorie diets and taking the hydrophilic bile salt ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA).
- Treatment of biliary colic by NSAIDs reduces the risk of acute cholecystitis.

Gallbladder Stones or Gallstones Diagnosis
The gastrointestinal specialist can diagnose the presence of gallstones through the following:
- Physical and clinical examinations
- Liver function tests
- Abdominal ultrasonography
Majority of the time, gallstones are discovered accidentally.
Gallstones or Gallbladder Stones Treatment
The usual treatment for gallstones is surgery – cholecystectomy. It could be either
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Open cholecystectomy
Nonsurgical treatments for gallstones:
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Oral dissolution therapy
- Shock wave lithotripsy
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868