Budd-Chiari Syndrome - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
Pace Hospitals
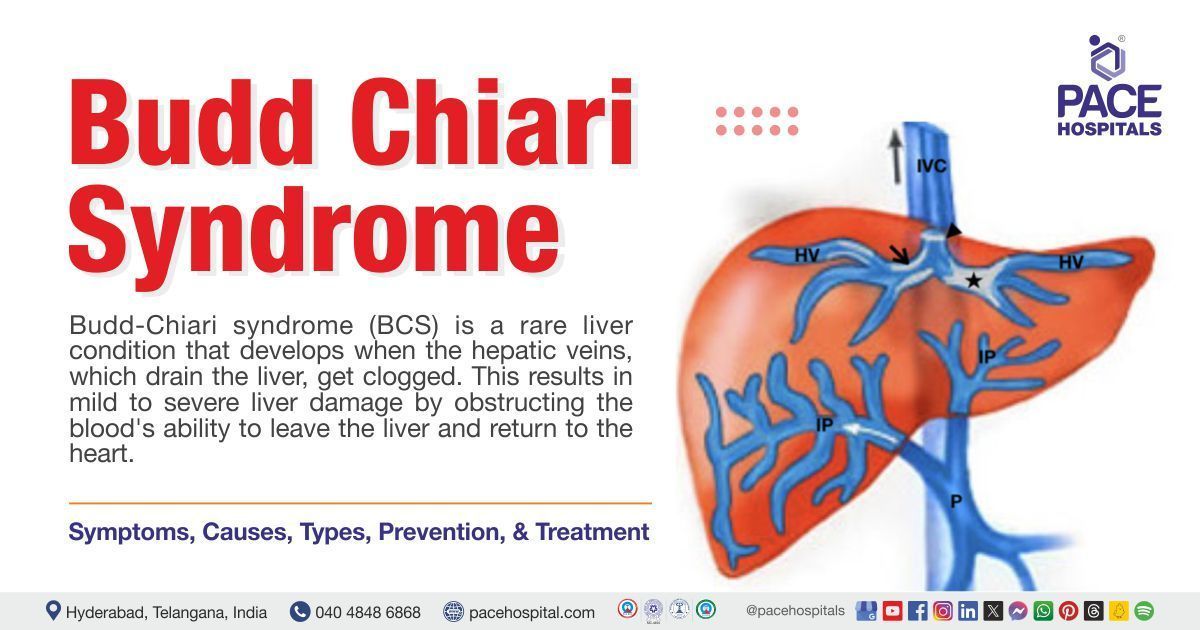
Budd chiari syndrome, the occlusion of hepatic veins (Obstruction of back flow of blood from liver to heart due to blockage) is an unusual condition which may be manifested by pain in the abdomen, ascites (build-up of fluid in the abdomen), hepatomegaly (liver enlargement) and a poor prognosis.
Anywhere throughout the vein's path, from the hepatic venules to the inferior vena cava (large vein that carry deoxygenated blood) junction and the right atrium (heart chamber), the obstruction could be thrombotic (related to blood clot) or non-thrombotic.
This disorder is an uncommon ailment considering its occurrence in 1 of 100000 individuals. In medical language Budd chiari syndrome is also known as hepatic venous outflow obstruction (HVOO).
Budd chiari syndrome is a diverse clinical disorder that can either be fatal if left untreated or may be managed with efficient treatment. When managed appropriately, the patients' prognosis is acceptable when compared to other chronic liver illnesses. Budd chiari syndrome can aggravate several conditions, including hematologic or malignant diseases, making it a rare significant syndrome.
Budd Chiari syndrome definition
Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare liver condition that is defined as, obstruction to the outflow of blood in hepatic veins at any point, ranging from the small hepatic vein to the junction of the right atrium (heart chamber) and inferior vena cava (largest vein in the body carrying deoxygenated blood).
Budd chiari syndrome meaning
The phrase "Budd-Chiari" was first used in the late 1800s in reference to the eminent work of internist George Budd a British physician and Austrian pathologist Hans Chiari.
A brief report on three patients who experienced hepatic vein blockage was published by George Budd in 1845. The illness, which has never been documented before, was linked to alcoholism and sepsis. 53 years later, Hans Chiari proposed the theory that syphilis was the reason for the hepatic vein blockage, adding pathological and clinical connections to the discussion postulated by George Budd.
Hepatic venous outflow obstruction meaning
Hepatic venous outflow obstruction is a union of 4 words in which.
- ‘Hepatic’- ‘hepatic’ is taken from latin word ‘hepaticus’ which means ‘pertaining to liver’
- ‘Venous’- ‘venous’ is derived from latin word ‘venosus’ that is used to describe ‘full of veins’
- ‘Outflow’- The word ‘outflow’ is derived from the Middle English word ‘outflowen’ which means ‘act or fact of flowing out’
- ‘Obstruction’- ‘obstruction’ is derived from latin word ‘obstructionem’ that is used to ‘express action of blocking up a way or passage’
Prevalence of Budd-Chiari syndrome
With a low incidence and prevalence in the general population, budd-chiari syndrome is an atypical serious liver condition. The incidence recorded in the literature varies from 0.2 to 4.1 cases per 10 lakh people annually, with an estimated prevalence of 1.4–4.0 cases per 10 lakh people in Western countries and 2.4–7.7 cases per million people in Asian countries. In Western studies, the prevalence was higher in women (52–69%), whereas in Asian studies, men were more often affected (48–70%).
Prevalence of budd chiari syndrome in India
Budd chiari syndrome has higher prevalence in developing countries like India.
- A study demonstrated that between 1967 and 2000, five investigations were conducted in India, and the results showed a prevalence that ranged from 3.8 to 21.5%.
- Another study of 2024 stated that, in India, it is believed that up to 7.4% of children suffering from chronic liver illness could have budd-chiari syndrome.
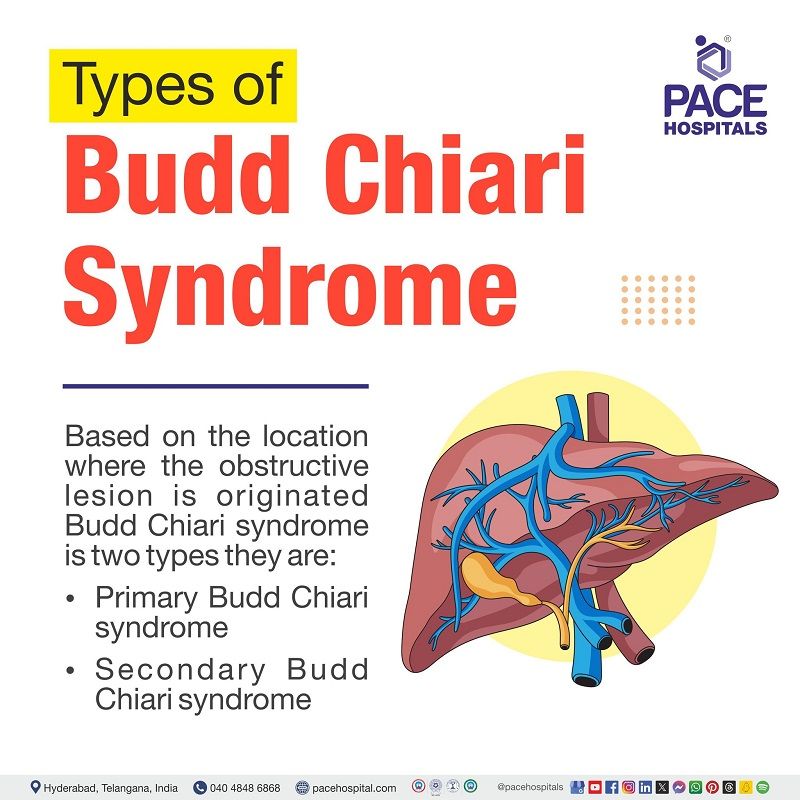
Types of Budd-Chiari syndrome
Based on the location where the obstructive lesion is originated, Budd Chiari syndrome can be categorized into two types they are:
- Primary: In cases when endoluminal venous lesion-like thrombosis is the cause of blockage, primary budd chiari syndrome is taken into consideration.
- Secondary: when the cause arises from nearby structures such as extrinsic compression or tumor invasion, it is considered as secondary budd chiari syndrome.
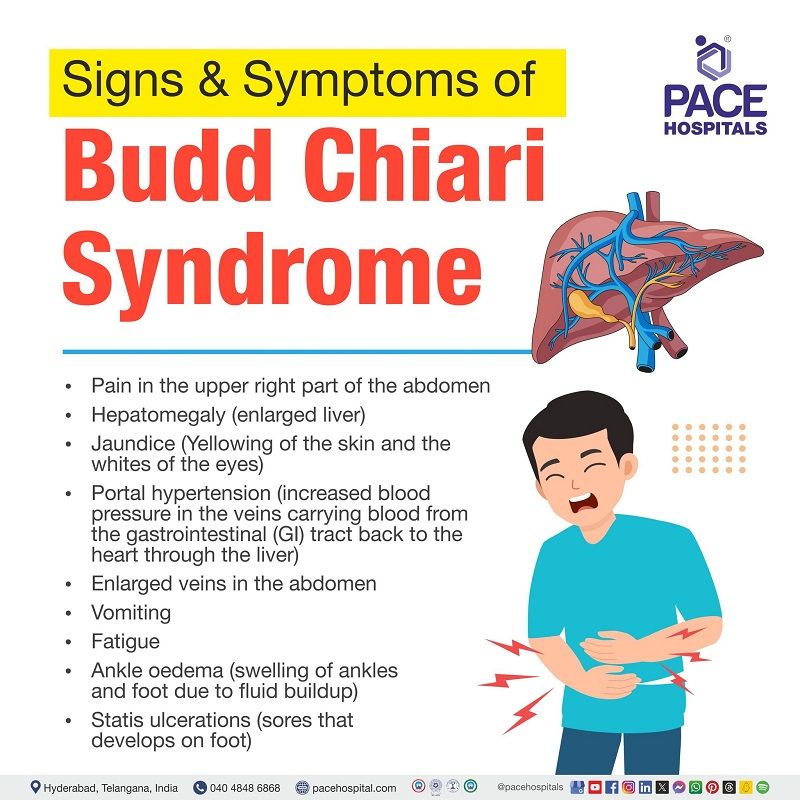
Budd-Chiari syndrome signs and symptoms
Depending on whether the obstruction happens suddenly or gradually, various signs and symptoms may be experienced which may include:
- Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen
- Enlarged liver (hepatomegaly)
- Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Increased blood pressure in the veins carrying blood from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract back to the heart through the liver (portal hypertension)
- Enlarged veins in the abdomen
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Ankle edema (swelling of ankles and foot due to fluid buildup)
- Statis ulcerations (sores that develop on foot)
Budd-Chiari syndrome causes
Budd-Chiari syndrome develops because of an underlying etiology in 80% of instances. These instances are primarily associated with a hypercoagulable state (a condition that increases the risk of blood clotting). The predominant causes of budd-chiari syndrome include:
- Thrombosis (blood clot with complete or partial blockage)
- Myeloproliferative disorders (blood cancers that result in an excessive production of blood cells in the body)
- Malignancy (the existence of cancerous cells with the potential to spread to different parts of the body)
- Liver lesions (abnormal cell growth in the liver that may be cancerous or non-cancerous)
- Pregnancy and use of oral contraceptive pills
- Idiopathic (disease with no identifiable cause)
- Gastric diseases
Thrombosis (blood clot with complete or partial blockage)
Hepatic vein blockage is primarily caused by thrombosis. Venous thrombosis, especially hepatic vein thrombosis, requires the coexistence of one or more thrombogenic (prone to blood clot formation) diseases and a triggering stimulus. The majority of budd chiari syndrome patients have a medical condition that makes them more susceptible to blood clotting.
Myeloproliferative disorders (blood cancers that result in an excessive production of blood cells in the body)
The primary cause of hepatic vein thrombosis is myeloproliferative disorders. Since some myeloproliferative illnesses, such as polycythemia vera (blood cancer) and essential thrombocythemia (blood cancer that increase platelet count), are invariably associated with hypercoagulability (condition that increases the risk of blood clotting), these conditions are linked to about half of the cases of Budd-Chiari syndrome.
Malignancy (the existence of cancerous cells with the potential to spread to different parts of the body)
Malignancy is linked to 10% of cases of Budd-Chiari syndrome, and it either directly compresses or invades blood vessels. Malignancy accompanied by hypercoagulability cause venous thrombosis and blockage. Other types of cancers that are more predominant to cause Budd Chiari syndrome include:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
- Adrenal gland carcinoma (adrenal gland cancer)
- Renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer)
- Leiomyosarcoma (cancer of smooth muscles in the body)
- Right atrial myxoma (cancer of right atrium [heart chamber])
- Wilms tumour (rare kidney cancer predominantly occurs in children)
Liver lesions (abnormal cell growth in the liver that may be cancerous or non-cancerous)
Compression of the vasculature can occasionally result from an infection or a lesion that takes up space in the liver. liver lesions can give rise to this disorder due to:
- Hepatic cysts (fluid filled sacs on liver)
- Adenomas (non-cancerous tumors)
- Cystadenomas (cancerous or non-cancerous tumors that occur in different body parts)
- Invasive aspergillosis (infection caused by fungus)
- Aortic aneurysms (bulge in blood vessel named aorta)
Pregnancy and use of oral contraceptive pills
An increased risk of budd chiari syndrome is associated with the use of oral contraceptives, especially those with a high estrogen level. Several reports states that patients in whom budd chiari syndrome was occurred due to oral contraceptives or pregnancy, may also have an underlying thrombophilia, either acquired or inherited.
Idiopathic (disease with no identifiable cause)
It is demonstrated that 20% cases of budd chiari syndrome occur due to unknown cause.
Gastric diseases
Studies have demonstrated that when underlying thrombophilias (condition that cause blood clots formation too easily) are present, budd chiari syndrome may be caused by ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, or abdominal trauma.
Budd-Chiari syndrome, may be caused by additional hypercoagulable conditions, such as:
- Bechet's disease:
(an unusual condition that makes blood vessels inflamed)
- Polycystic kidney disease: (a genetic condition where fluid filled sacs are formed on the kidney)
- Factor V Leiden: (a disorder that increase the risk of developing clots due to mutation in the blood clotting factor V).
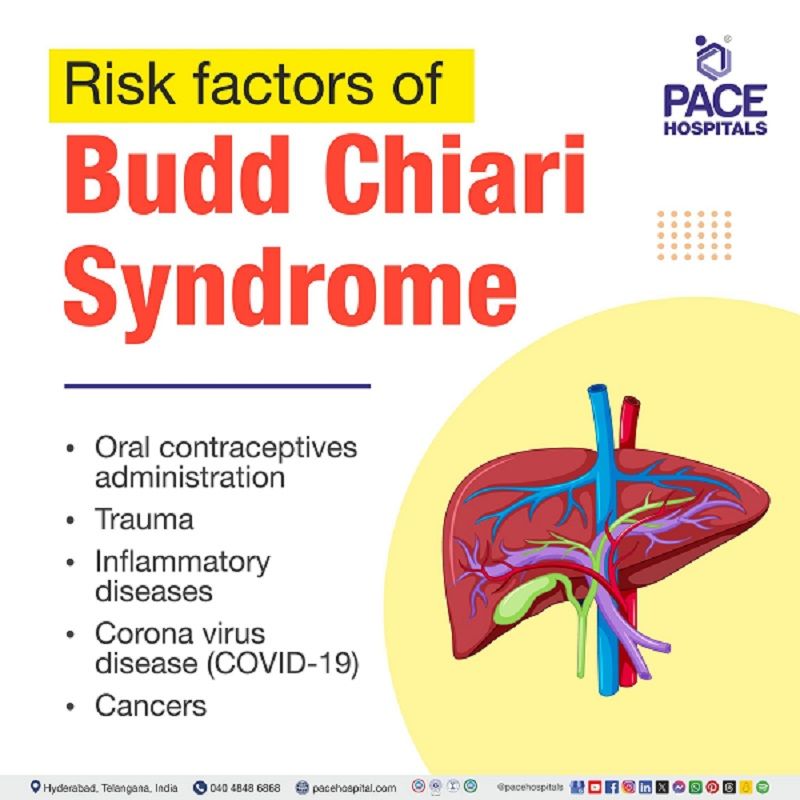
Budd-Chiari syndrome risk factors
Several risk factors have been linked to Budd-Chiari Syndrome, which may raise the chances of developing the disorder. Some of them include:
- Oral contraceptives administration: Those who use estrogen-containing oral contraceptives have a twofold greater risk of developing budd chiari syndrome. In individuals with various thrombogenic diseases, oral contraceptives seem to mainly increase the risk of thrombosis.
- Trauma: In case of severe traumatic instances, the veins over the liver may burst and this may result in a dramatic consequence of developing a syndrome (group of symptoms).
- Inflammatory diseases: people with inflammatory disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease, behchet’s disease etc are at a greater risk for developing thromboembolic complications which may eventually lead to budd chiari syndrome.
- Corona virus disease (COVID-19): A 2023 study had demonstrated that budd chiari syndrome is an uncommon and serious condition that can result from inflammatory and coagulation disorders associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Cancers: several cancers such as hepatocellular carcinoma etc may have the tendency to cause budd chiari syndrome through invasion of venous outflow.
Budd-Chiari syndrome Complications
Budd-Chiari syndrome complications are primarily associated with the severity of liver failure and underlying medical problems. Untreated Budd-Chiari syndrome generally may have complications such as:
- Hepatic encephalopathy (the loss of brain function resulting from the liver's inability to eliminate toxins from the blood)
- Variceal haemorrhage (rupture of blood vessels located all over the digestive system)
- Hepatorenal syndrome (Kidney failure due to liver dysfunction)
- Portal hypertension (increased blood pressure in the vein that caries deoxygenated blood to liver from intestines)
- Bacterial peritonitis (infection of abdominal fluid) in the presence of ascites
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
Prevention of Budd-Chiari syndrome
Managing the risk factors that give rise to Budd-Chiari Syndrome is the main strategy for preventing this disorder, along with general tactics that could aid in the prevention, such as:
- Thrombosis risk management: Taking care of diseases that raise the risk of thrombosis is essential since budd chiari syndrome is frequently brought on by blood clots in the hepatic veins.
- Surveillance throughout the pregnancy: Many women of childbearing age suffer from budd-chiari syndrome. If a woman has an underlying prothrombotic disease, pregnancy can exacerbate her condition and lead to budd chiari syndrome. Consequently, additional prothrombotic disease screening must be conducted for these women.
- Drug use monitoring: Certain drugs may make clotting more likely. Use of them should only be done under medical supervision.
- Lifestyle modifications: lack of exercise give rise to obesity which is affecting people around the globe and is causing a rise of thrombotic illnesses such as venous thromboembolism etc. Since thrombotic diseases can cause blockages in blood vessels it is highly recommended to maintain a healthy weight
Budd-Chiari syndrome diagnosis
The diagnosis of Budd-Chiari syndrome cannot be made with a single test. Based on traditional clinical signs and factors that increase the risk of thrombosis, such as the existence of cancer, the hepatologist / cardiologist may diagnose budd chiari syndrome by using below mentioned diagnostic procedures:
- Doppler ultrasonography
- Venography
- Liver function tests
- Liver biopsy
- Inferior vena cavography
- Echocardiography
- Sonography
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
Budd chiari syndrome radiology
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography (CT)
Budd-Chiari syndrome treatment
In order to reduce blockage, stop clot progression, minimize progressive liver injury and avoid or control consequences, this condition can be treated by below-mentioned treatment options:
Medical management (treatment using medicine)
- Anticoagulants
- Thrombolytics
- Diuretics
- Antibiotics
Interventional therapy (treatment involving minimally invasive techniques)
- Angioplasty
- Stenting
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
- Surgical decompression
- Liver transplant
The reason, how the symptoms manifest, and the extent of the sickness all influence the course of treatment for budd chiari syndrome. A multidisciplinary approach using a combination of medical and interventional therapy is necessary for the management, which is frequently challenging.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Budd-Chiari syndrome
Is Budd-Chiari syndrome curable?
Yes. Appropriate treatment may reverse this condition. According to a 2011–2016 study, the technical and clinical success rates of endovascular therapy for budd chiari syndrome of the hepatic vein type were 100% and 95.6%, respectively. After a year, the primary and secondary patency rates were 80.0% and 93.8%, 72.8% and 90.3%, and 67.9% and 91.2%, respectively. After one year, survival was 96.9%, followed by two years at 93.4% and five years at 91.2%.
What is the main cause of Budd-Chiari syndrome?
Eighty percent of cases have an underlying reason, most of which have to do with a hypercoagulable state, contributing to the development of budd-chiari syndrome. How ever conditions like liver lesions, cancers may have the potency to cause budd chiari syndrome.
What is the life expectancy with Budd-Chiari?
If budd chiari syndrome left untreated, the prognosis of the disease shall be poor. Death may occur in patients between 3months to 3 years of the diagnosis due to progressive degeneration of liver. Nonetheless, the 5-year survival rate for individuals with the condition after portosystemic shunting is 38–87 percent. After liver transplantation, the actuarial 5-year survival rate is 70%.
Is Budd-Chiari an autoimmune disease?
No. Budd chiari syndrome is not an autoimmune disease. However autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren syndrome, (an autoimmune condition characterized by the patient's white blood cells attacking the tear and salivary glands, resulting in persistently dry mouth and eyes) etc may increase the risk of patient to develop budd chiari syndrome.
What are classical Budd-Chiari syndrome triads?
Abdominal pain, ascites (buildup of fluid in the abdomen) and hepatomegaly (liver enlargement) are the three main classical traids that most individuals with budd-chiari syndrome express. It takes a high level of suspicion to identify this ailment because the signs are non-specific and present in a variety of ways.
What is acute and chronic Budd-Chiari syndrome?
The clinical manifestations of liver failure can differ; they might be acute or fulminant (severe and sudden in onset) subacute (signs or symptoms for less than six months without validation of liver cirrhosis), or chronic (signs or symptoms for more than six months with evidence of portal hypertension (increased blood pressure in the vein that carry blood to liver from intestines) and cirrhosis).
What is Budd-Chiari syndrome diet?
It is essential to incorporate items such as fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats etc that are beneficial to the liver into diet when managing budd-chiari syndrome. Two important aspects of treating the illness are lowering inflammation and promoting liver function, which are essential for controlling the condition.
What genders are predominantly affected by Budd-Chiari syndrome?
Both the males and females are equally affected by budd chiari syndrome. The majority of cases typically impact people in the twenty- to forty-year-old age range.
What is the difference between portal vein thrombosis and Budd-Chiari syndrome?
Venous outflow obstruction at the hepatic veins or inferior vena cava characterizes budd chiari syndrome. Whereas portal vein thrombosis results from occurs from occlusion in the extra hepatic venous system (veins outside liver)
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles