Hemorrhoidectomy - Procedure & Cost
PACE Hospitals is recognized for the hemorrhoidectomy procedure in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Our experienced colorectal surgeons and gastro specialists provide advanced care with a patient-focused approach. We specialize in minimally invasive hemorrhoidectomy surgery, ensuring less pain, faster recovery, and improved quality of life. With modern treatment options, transparent costs, and world-class facilities, PACE Hospitals is a trusted choice for hemorrhoids treatment in Hyderabad.
Book an Appointment for Hemorrhoids Treatment
Hemorrhoidectomy Procedure Online Appointment
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
WhatsApp: 8977889778
Regards,
PACE Hospitals
HITEC City and Madeenaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
WhatsApp: 8977889778
Regards,
PACE Hospitals
HITEC City and Madeenaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Hemorrhoidectomy Surgery?
State-of-the-Art Operation Theaters with Advanced Techniques for Conventional, Stapled & Laser Hemorrhoidectomy
Expert Gastro Surgeons/Surgical Gastroenterologists for Comprehensive Piles (Hemorrhoids) Treatment in Hyderabad
Hemorrhoidectomy Surgery with 99.9% High Success Rate, Minimal Pain & Faster Recovery
Affordable & Transparent Hemorrhoidectomy Surgery Cost with Insurance and Cashless Options
Hemorrhoidectomy definition
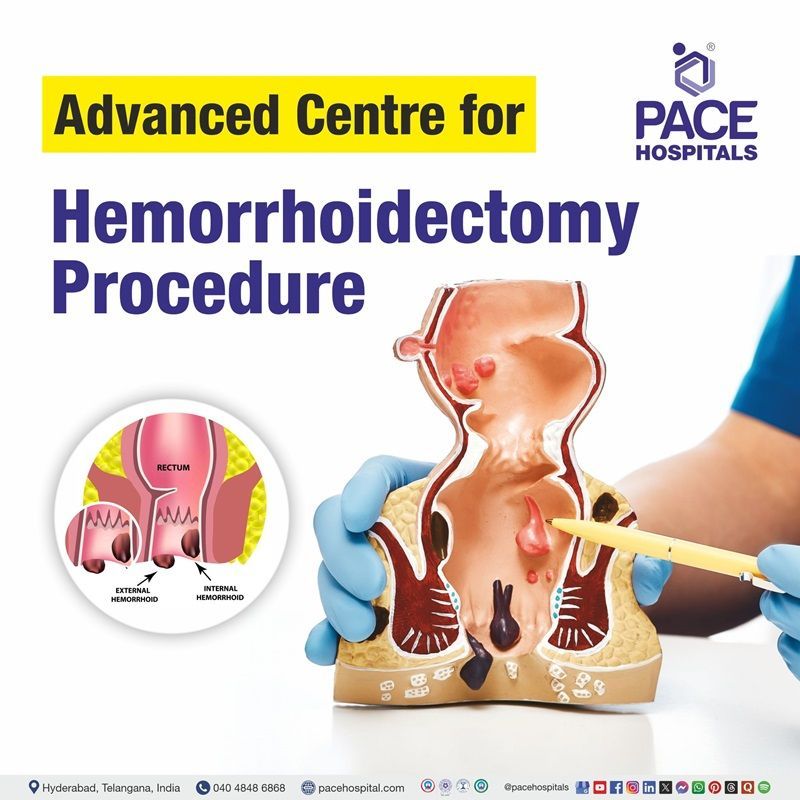
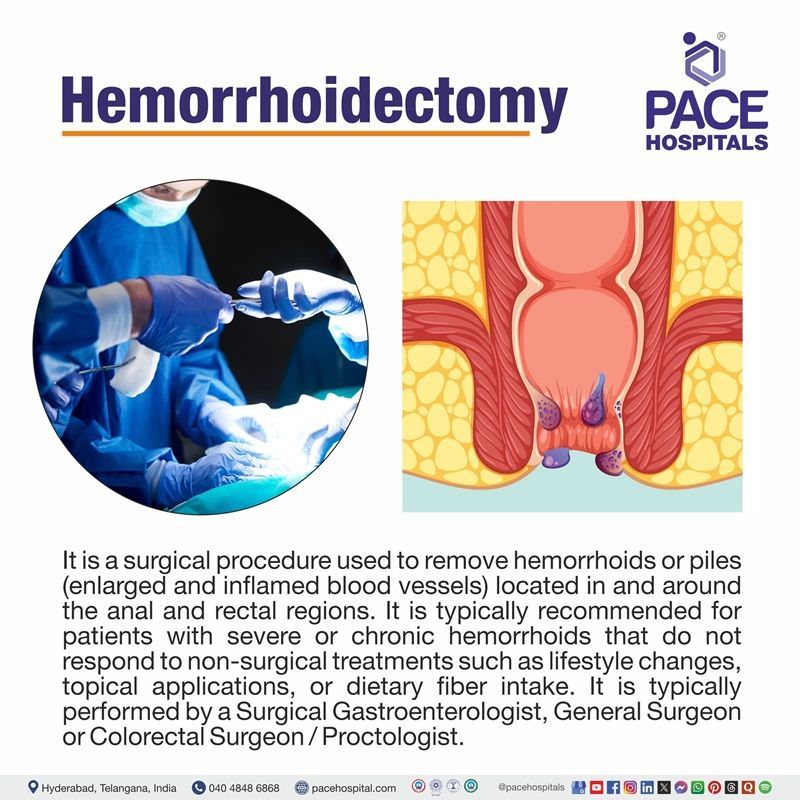
A hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure used to remove hemorrhoids or piles (enlarged and inflamed blood vessels) located in and around the anal and rectal regions. It is typically recommended for patients with severe or chronic hemorrhoids that do not respond to non-surgical treatments such as lifestyle changes, topical applications, or dietary fiber intake.
Hemorrhoids are a common anorectal condition affecting many individuals globally, and though they are not life-threatening, they can severely impact quality of life. When symptoms like pain, itching, swelling, bleeding, and prolapse become frequent and disruptive, a hemorrhoidectomy becomes an essential surgical option.
A hemorrhoidectomy is typically performed by a surgical team led by a general surgeon or a colorectal surgeon/proctologist, with a first opinion from a colorectal specialist or gastroenterologist often recommended for hemorrhoid treatment, especially if the condition is severe. However, this team includes an operating surgeon, a first assistant, a scrub technician, and an anesthesia team too.
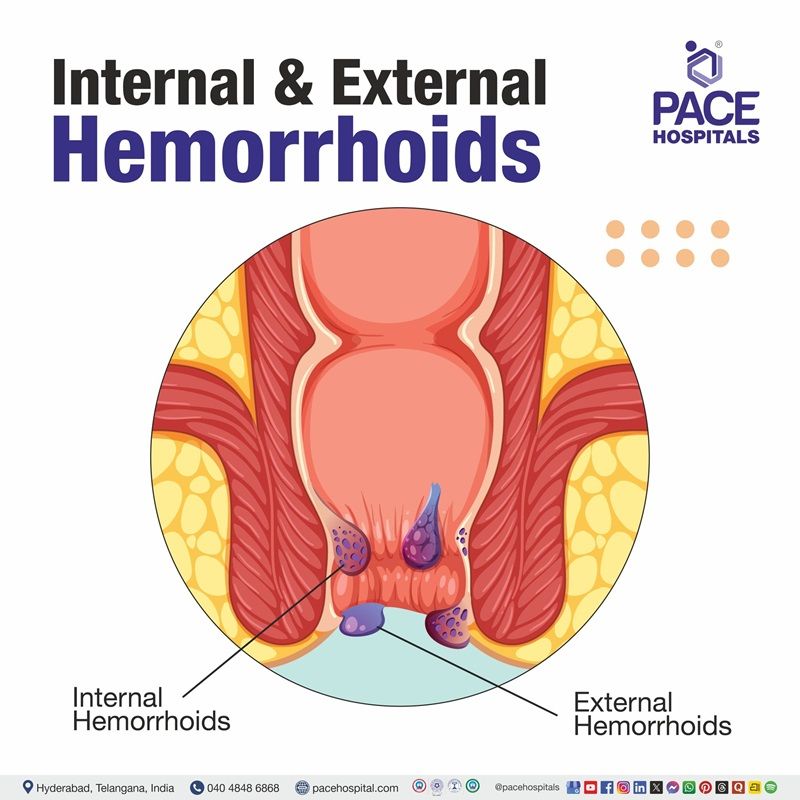
Types of Hemorrhoids
- Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum and are usually painless, often causing bright red bleeding or prolapse during bowel movements.
- External hemorrhoids form under the skin around the anus and tend to be painful, itchy, and swollen, especially if a blood clot forms.
Types of Hemorrhoidectomy
The type of hemorrhoidectomy performed depends on the severity, location, and individual health status. Below are the various types of hemorrhoidectomy:
- Open hemorrhoidectomy
- Closed hemorrhoidectomy
- Stapled hemorrhoidectomy
- Laser hemorrhoidectomy
- Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation (DG-HAL)
- Ligasure hemorrhoidectomy
Open hemorrhoidectomy
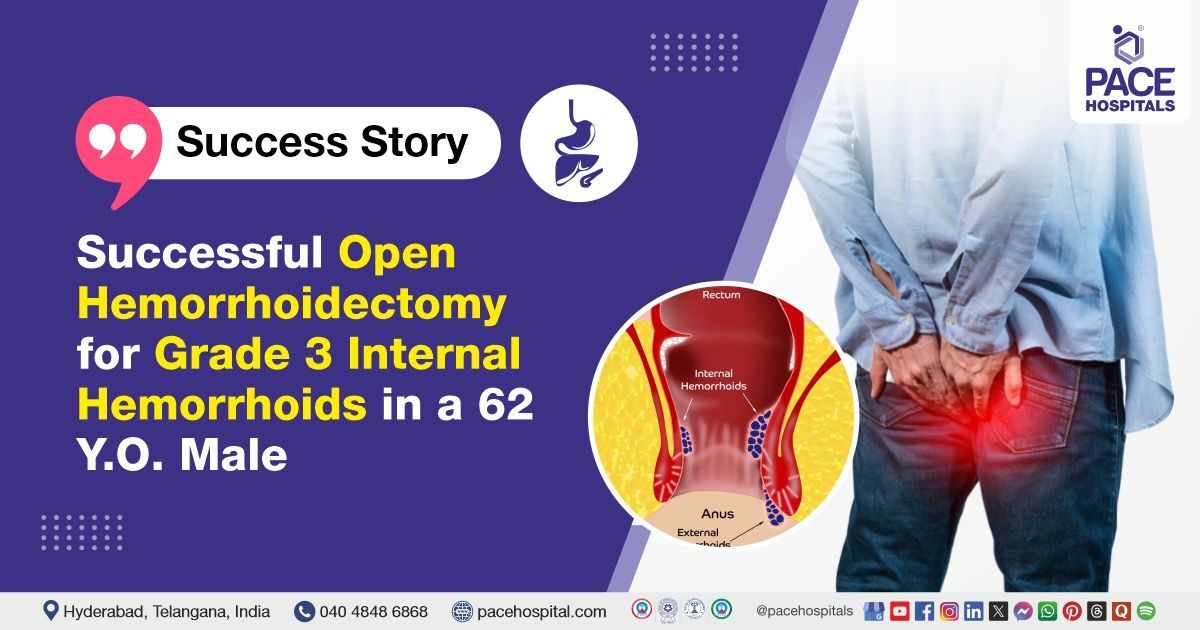
Also known as Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy in this traditional surgical method involves excising the hemorrhoidal tissue and intentionally leaving the wound open to heal naturally. Although healing may take longer, this approach minimizes the risk of infection. It is particularly effective for treating large, complex, or infected hemorrhoids.
Closed hemorrhoidectomy
Also known as Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy technique In this method, the hemorrhoid is surgically removed and the wound is closed with sutures. This technique generally results in faster healing and is commonly used for treating uncomplicated internal or mixed hemorrhoids.
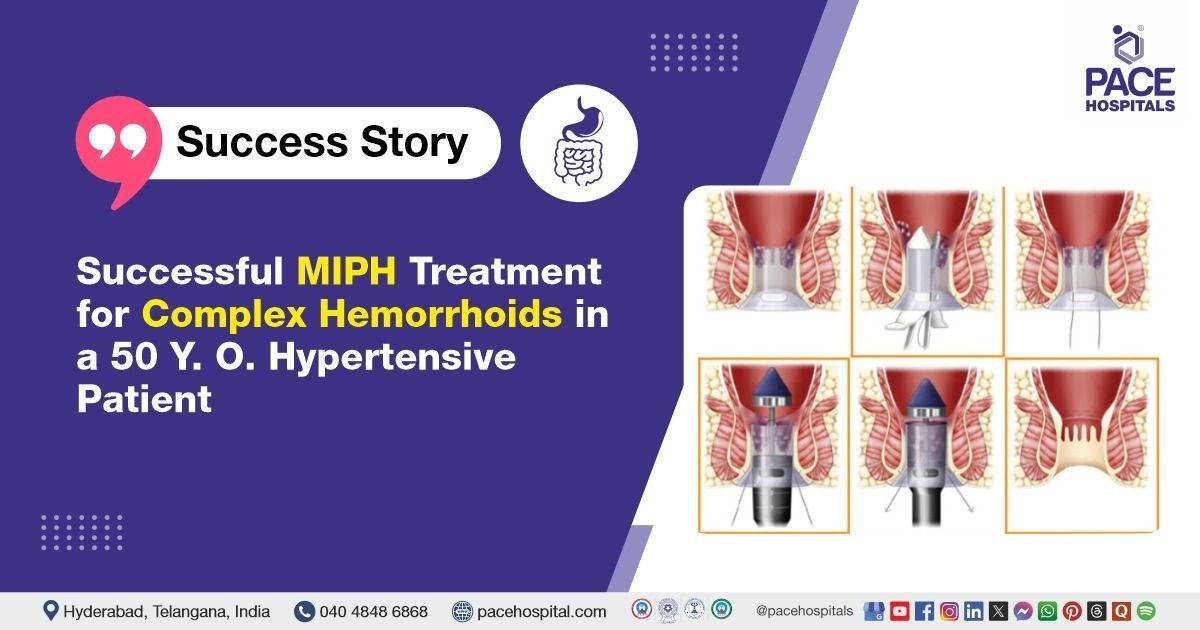
Stapled hemorrhoidectomy or Stapled hemorrhoidopexy
(Procedure for Prolapse and Hemorrhoids - PPH): A circular stapling device is used to reposition and secure prolapsed hemorrhoids. The stapler also cuts off the blood supply to the hemorrhoidal tissue, causing it to shrink over time. This minimally invasive technique is associated with reduced postoperative pain and quicker recovery, but is not suitable for external hemorrhoids.
Laser hemorrhoidectomy
This procedure uses focused laser energy to precisely vaporize or excise the hemorrhoidal tissue. It is linked to minimal bleeding, reduced postoperative pain, and faster healing. Often performed as a daycare procedure, it suits patients seeking a minimally invasive treatment with rapid return to daily activities.
Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation (DG-HAL)
Utilizing Doppler ultrasound, this procedure identifies and ligates the arteries supplying blood to the hemorrhoids. This reduces their size and alleviates symptoms with less postoperative pain and quicker recovery than traditional methods. However, it may be less effective for large or severely prolapsed hemorrhoids with significant tissue excess.
Ligasure hemorrhoidectomy
A bipolar vessel sealing device is used to simultaneously cut and seal blood vessels during hemorrhoidal tissue removal. This reduces intraoperative bleeding and often eliminates the need for sutures. The procedure offers minimal postoperative pain, faster wound healing, and shorter operative time. However, access to the specialised Ligasure device may be limited in certain healthcare settings.
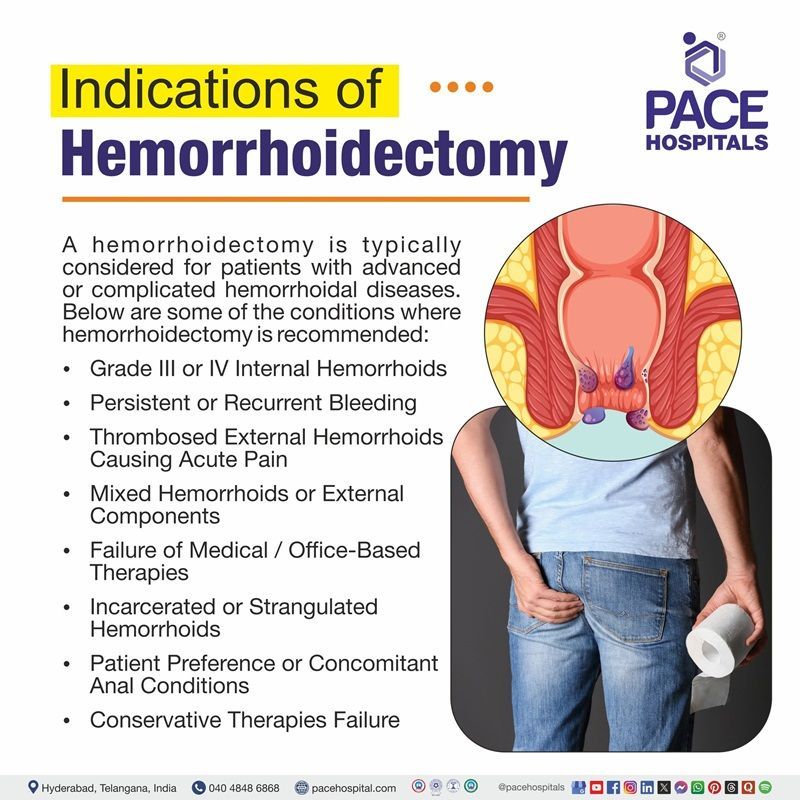
Hemorrhoidectomy Indications
A hemorrhoidectomy is typically considered for patients with advanced or complicated hemorrhoidal diseases. This procedure is typically indicated when non-surgical treatments fail, particularly in cases of large internal hemorrhoids (Grades III and IV) or painful, thrombosed external hemorrhoids. Below are some of the conditions where hemorrhoidectomy is recommended:
- Grade III or IV Internal Hemorrhoids: When hemorrhoids prolapse during bowel movements and do not reliably reduce (Grade III) or remain permanently prolapsed (Grade IV), surgery is often required.
- Persistent or Recurrent Bleeding: If ongoing bleeding unrelieved by conservative measures such as fiber intake, phlebotonics, or topical treatments may necessitate surgical removal through hemorrhoidectomy.
- Thrombosed External Hemorrhoids Causing Acute Pain: An acutely thrombosed hemorrhoid within 48–72 hours of onset significantly reduces pain and recurrence compared to conservative treatment, helps to find better treatment.
- Mixed Hemorrhoids or External Components: When symptomatic hemorrhoids include a significant external component or skin tags affecting hygiene or comfort, excisional hemorrhoidectomy offers the most durable resolution.
- Failure of Medical/Office-Based Therapies: If first-line interventions-such as increased fiber intake, band ligation, infrared coagulation, or sclerotherapy-fail to control symptoms (especially in Grade III or IV disease), hemorrhoidectomy becomes the definitive treatment.
- Incarcerated or Strangulated Hemorrhoids: Internal hemorrhoids that are irreducible or strangulated may cause pain, ischemia, or necrosis and require prompt surgical intervention.
- Patient Preference or Concomitant Anal Conditions: In some cases, patient preference plays an important role, particularly when associated with anorectal issues like fissures or fistulas require surgery.
- Conservative Therapies Failure: When intake of high-fiber diet, stool softeners and use of ointments have failed and are incapable of finding relief.
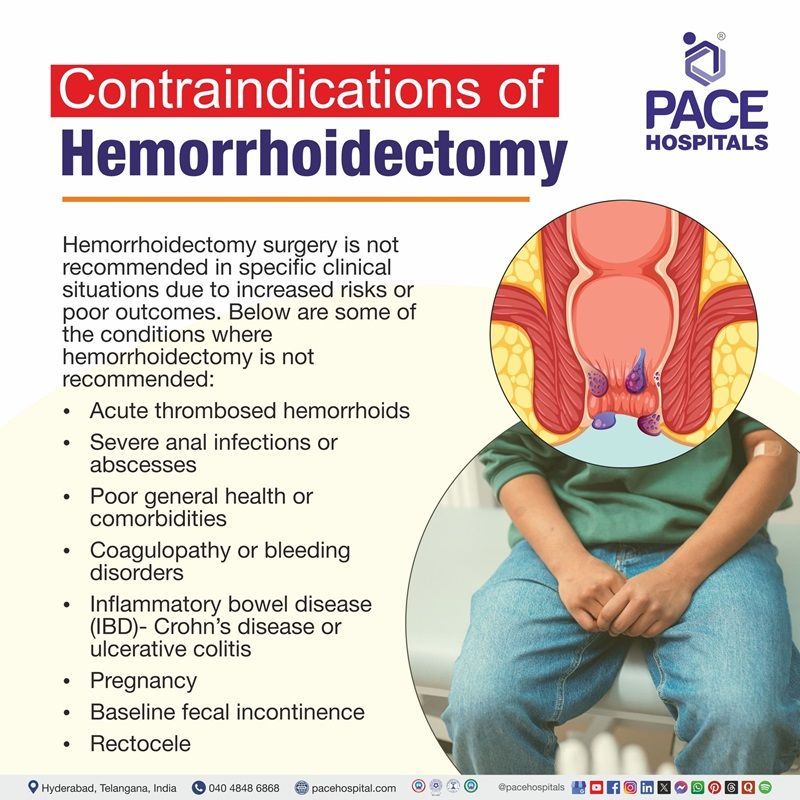
Hemorrhoidectomy Contraindications
Hemorrhoidectomy surgery is not recommended in specific clinical situations due to increased risks or poor outcomes. Below are some of the conditions where hemorrhoidectomy is not recommended:
- Acute thrombosed hemorrhoids: Surgery is generally avoided during the acute thrombosis phase because of severe pain and inflammation;
conservative treatment is preferred initially.
- Severe anal infections or abscesses: Active infections or abscesses increase the risk of postoperative infections, and may cause a delay in healing.
- Poor general health or comorbidities: When the patient has significant cardiovascular, pulmonary, or bleeding disorders, it may pose anesthesia and surgical risks.
- Coagulopathy or bleeding disorders: It can be dangerous for patients with clotting abnormalities or anticoagulants are at risk of excessive bleeding during surgery.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD):
Crohn’s disease or
ulcerative colitis involving the anorectal area may worsen with surgery or lead to poor healing.
- Pregnancy: Elective surgery is usually postponed during pregnancy to avoid risks to both mother and fetus unless it’s necessary.
- Baseline fecal incontinence: Existing fecal incontinence indicates potential anal sphincter or pelvic floor dysfunction, which may be exacerbated by surgery. It’s imperative to assess baseline incontinence thoroughly during the evaluation phase to tailor treatment and avoid worsening symptoms.
- Rectocele: A rectocele, where the rectum bulges into the vaginal wall, may lead to obstructed defecation, incomplete emptying, or leaking - especially in women. These symptoms can complicate surgical planning, and in cases without significant symptoms or “non-emptying” defects, conservative management (e.g., pelvic floor exercises, biofeedback) is recommended before considering surgery.
- Other conditions: In cases where patients unable to undergo general anesthesia due to medical comorbidities cannot undertake this method.

Hemorrhoidectomy Advantages
A hemorrhoidectomy is considered the gold standard for managing severe or complicated hemorrhoids. Below are some of the advantages of haemorrhoidectomy:
- Effective symptom relief: It helps to provide durable relief from bleeding, prolapse, pain, and itching.
- High success rate: This procedure significantly lowers recurrence rates compared to non-surgical treatments.
- Definitive treatment: It is often the only curative option for large, prolapsed, or thrombosed hemorrhoids is refractory to conservative care.
- Improved quality of life: Through applying these techniques, it helps to resolve persistent symptoms, enhancing daily comfort and well-being.
- Versatile techniques: It includes options such as open, closed, and stapled hemorrhoidectomies to enable tailored approaches based on individual patient needs.
- Potential improvement in erectile function: It has been observed that men with erectile dysfunction and hemorrhoids reported significant improvement in sexual function post-hemorrhoidectomy.
Hemorrhoidectomy Procedure Steps
Various processes followed before, during and after hemorrhoidectomy surgery steps are mentioned below:
Before Hemorrhoidectomy Surgery
- Medical Evaluation: Patients undergo a thorough clinical examination including digital rectal examination and anoscopy or proctoscopy to assess hemorrhoid severity and exclude other anorectal pathologies such as fissures or malignancies. Colonoscopy may be indicated in patients with rectal bleeding, especially in those over 40 years of age, to exclude colorectal malignancy.
- Preoperative Tests: Various preoperative tests, including a
complete blood count (CBC), coagulation profile, and renal function tests, need to be performed. Imaging studies are not typically required unless indicated by other symptoms. For intermediate-risk patients (e.g., older age or comorbidities), a serum creatinine may be useful. An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is recommended for individuals ≥ 45 years undergoing minor or intermediate surgery, and for all patients undergoing major surgery.
- Medication Management: Patients using blood thinners and newer anticoagulants must consult their surgeon and/or prescribing physician. A risk-benefit analysis is done to decide on discontinuation to minimize perioperative bleeding without increasing thrombotic risk. NSAIDs are usually stopped 1 week before surgery.
- Bowel Preparation: A bowel regimen, including mild laxatives or enemas, may be prescribed the day before surgery to empty the rectum, reducing contamination risk and facilitating the procedure. Experts may recommend laser hemorrhoidoplasty (LHP) with similar ambiguity; enemas may be used 2 hours before or omitted entirely, depending on the extent of the procedure.
- Fasting Guidelines: Patients are instructed to fast (not to take food or liquids) for at least 6 hours prior to surgery to minimize aspiration risk during anesthesia.
- Smoking and Lifestyle: Smoking cessation is strongly advised at least 2-3 weeks before and after surgery, as smoking impairs wound healing and increases postoperative complications.
- Informed Consent and Counseling: The surgeon explains the procedure, benefits, risks (bleeding, pain, infection, urinary retention), and postoperative care. Patients are required to sign an informed consent form and are encouraged to ask questions.
- Logistics: Patients must arrange for someone to accompany them on the day of surgery and assist with transportation home, as driving post-anesthesia is unsafe.
During Hemorrhoidectomy Surgery
- Anesthesia: The procedure is performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia (spinal or epidural), depending on patient factors and surgeon preference.
- Surgical Technique: Several approaches exist, chosen based on hemorrhoid type and severity:
- Open hemorrhoidectomy: In open hemorrhoidectomy, excision of hemorrhoidal tissue with wounds left open for secondary healing. It is suitable for large or thrombosed hemorrhoids. Lower infection risk but longer healing time.
- Closed hemorrhoidectomy: In closed hemorrhoidectomy, excision is followed by suturing of the wound edges. It helps with faster healing, but there is a slightly higher risk of infection.
- Stapled hemorrhoidectomy or Stapled hemorrhoidopexy: In this technique, a circular stapler resects a ring of prolapsed mucosa, repositioning hemorrhoids and reducing blood flow, ideal for prolapsed internal hemorrhoids without significant external components.
- Laser hemorrhoidectomy: It utilizes focused laser energy to vaporize hemorrhoidal tissue. Less bleeding and postoperative pain, minimally invasive.
- Procedure Duration: In general, surgery usually takes 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the number and extent of hemorrhoids. Stapled hemorrhoidectomy has a shorter operative time compared to open surgery-one study noted a mean reduction of ~12 to 22 minutes.
- Intraoperative Care: Hemostasis is carefully maintained to reduce bleeding. Absorbable sutures are often used. The surgeon ensures minimal damage to the anal sphincter muscles to preserve continence.
After Hemorrhoidectomy Surgery
- Recovery Room Monitoring: Patients are observed for vital signs stability, bleeding, and pain control in the post-anesthesia care unit.
- Pain Management: Oral analgesics, including Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), are prescribed. Opioids are reserved for severe pain. Sitz baths (warm water baths) are recommended several times daily to reduce pain and promote hygiene.
- Bowel Management: Stool softeners and a high-fiber diet are strongly advised to prevent straining during defecation, which could disrupt healing.
- Activity Restrictions: It is advised for patients to avoid heavy lifting, prolonged sitting, and strenuous activities for 3 to 4 weeks post-surgery to minimise swelling and bleeding risk.
- Wound Care: The anal area required to be kept clean and dry. Patients may gently cleanse with warm water after bowel movements and pat dry. Need to avoid harsh soaps or wipes.
- Hospital Stay: Most patients are discharged the same day as outpatient surgery. Overnight hospitalisation is rare, but may be required for complications or pain control.
- Follow-Up: Scheduled outpatient visits occur 1-2 weeks post-surgery to assess healing, manage complications (such as urinary retention or infection), and remove any non-absorbable sutures if present.
- Long-term Outcome: Full recovery may take 2 to 4 weeks. Most patients experience significant symptom relief and improved quality of life. Recurrence rates are low compared to non-surgical treatments.
Hemorrhoidectomy Complications
The occurrence and severity of complications following hemorrhoidectomy are influenced by multiple factors including the surgical technique used (open, closed, stapled, or energy-based methods), patient comorbidities, anesthesia type, perioperative management, and the extent of hemorrhoidal disease. While the procedure is generally safe and highly effective, a range of complications-from mild and transient to serious and prolonged-can occur. Below are the potential complications of hemorrhoidectomy:
- Pain: It is nearly universal phenomenon, especially early on felt commonly, especially during bowel movements or in the first postoperative week. In recent studies report immediate postoperative pain in up to 90% of patients.
- Bleeding: Small amounts of bleeding are expected; however, significant or delayed bleeding (up to ~2 weeks post-op) should be reported immediately. Primary hemorrhage occurs immediately; secondary hemorrhage may occur days later need to be taken care of. Bleeding rates range from 0.3% to 6% (average ~2%), with higher risk tied to inadequate hemostasis or high-grade disease.
- Urinary retention: A relatively common issue, influenced by anesthesia type and perioperative management. Occurs in approximately 1-36% of cases, more likely with spinal anesthesia, extensive surgery, or high intravenous fluid use.
- Infection and abscess formation: Rare but serious. Symptoms required to look out for fever, severe pain, or any discharge. Prompt evaluation is essential.
- Anal stenosis: A narrowing of the anal canal due to scarring after extensive tissue removal; it may require dilation if symptomatic, while it's uncommon (<1–6%), it can significantly affect quality of life if left untreated.
- Fecal incontinence: A rare and usually temporary complication, occurrence varies widely in reports, but typically resolves with time and conservative care. Very rare and usually temporary. It can result from sphincter or cushion disruption during surgery.
- Other rare risks: These include anal fistula, persistent skin tags, pelvic sepsis, chronic pain syndromes, and recurrence of hemorrhoidal disease, which needs proper examination.
Hemorrhoidectomy Recovery Tips
After Hemorrhoidectomy procedure is complete, following recovery tips are followed:
Hospital Stay and Return Home
- Same-day discharge is the norm for most patients, provided there are no complications or significant comorbidities observed.
- Overnight stay may be needed if issues like urinary retention, excessive bleeding, or severe pain arise in some cases.
Immediate Postoperative Period (Days 1-7)
- Patients may get mild to moderate discomfort, particularly during bowel movements.
- It can be managed with prescribed oral analgesics, warm sitz baths 3 times daily (especially after defecation), and stool softeners to ease bowel movements.
- If required, use of ice packs, topical numbing ointments, and cushioned seating (e.g., donut pillows) can enhance comfort.
Dietary Recommendations
- After surgery, patients are required to have a high-fiber diet and adequate hydration to avoid constipation, which can worsen postoperative pain and delay healing.
- Some patients are given a laxative made from lactose administered preoperatively intake and a fiber-rich diet (fruits, vegetables, whole grains), removing spicy, oily, or processed foods from the diet have been demonstrated to have benefits in reducing postoperative discomfort and complications.
Activity Restricted
- It is required to avoid prolonged sitting after the treatment, while light walking is encouraged.
- Depending on the nature of the job, a person can return to work within 7–10 days.
- It is advised to avoid heavy weightlifting after a hemorrhoidectomy.
Follow-Up Care
- Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor healing, remove any sutures (if needed) and need to check for any signs of complications such as infection or bleeding, an additional treatment is recommended if hemorrhoids recur.
Questions that patients can ask about hemorrhoidectomy surgery to the health care team?
- When can I go home after the hemorrhoidectomy?
- Will I need someone to assist me at home after surgery?
- Can I get itching after hemorrhoidectomy?
- What kind of pain or discomfort should I expect-and for how long?
- Can I go to gym after hemorrhoidectomy?
- What are post operative diet charts after hemorrhoidectomy?
- Can I drive after hemorrhoidectomy?
- Which sleeping position after hemorrhoidectomy is good?
- How long does full recovery usually take after a hemorrhoidectomy?What can I do to prevent constipation and straining after surgery?
- Can I get bleeding 6 months after hemorrhoidectomy?
- How to prevent stenosis after hemorrhoidectomy?
- When should I schedule my follow-up appointment?
Difference between Stapled Hemorrhoidectomy and Open Hemorrhoidectomy
Stapled hemorrhoidectomy vs open hemorrhoidectomy
Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure to treat severe or prolapsed hemorrhoids. There are two primary surgical approaches: Open hemorrhoidectomy (conventional method) and Stapled hemorrhoidectomy (also called Procedure for Prolapse and Hemorrhoids - PPH). Below are some of the parameters that differentiate Stapled hemorrhoidectomy and Open hemorrhoidectomy:
| Parameters | Stapled hemorrhoidectomy | Open hemorrhoidectomy |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A surgical technique that uses a circular stapling device to remove a ring of tissue above the hemorrhoids, pulling them back into place. | Traditional surgery where hemorrhoids are excised (cut out) using a scalpel or cautery. |
| Type of Procedure | Minimally invasive; performed above the dentate line, where there are fewer pain nerves. | More invasive; involves cutting in a more sensitive area with more pain receptors. |
| Level of Pain | Generally, causes less postoperative pain. | Often associated with more significant postoperative pain. |
| Recovery Time | Shorter recovery time - patients typically resume normal activities sooner. | Longer recovery time - healing may take 2-4 weeks depending on extent of surgery. |
| Hospital Stay | Often done as day surgery or with minimal stay. | May require a longer hospital stay if complications arise. |
| Recurrence Rate | Slightly higher recurrence rate, especially for external hemorrhoids. | Lower recurrence rate; more effective for large or mixed hemorrhoids. |
| Control for Bleeding | Less effective in treating external bleeding hemorrhoids. | Offers better control for bleeding hemorrhoids. |
| Suitability | Best for internal prolapsing hemorrhoids (Grade III). | Suitable for severe hemorrhoids (Grade III–IV), especially when external components are present. |
| Anesthesia | Usually requires regional or general anesthesia. | Also performed under general or spinal anesthesia. |
Stapled hemorrhoidectomy offers less pain and faster recovery but may not be suitable for all types of hemorrhoids, especially if external components are prominent. Open hemorrhoidectomy is more comprehensive and durable but involves more discomfort and a longer recovery.
Hemorrhoids Surgery Cost in Hyderabad, India
The cost of Hemorrhoidectomy in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹25,000 to ₹85,000 (approx. US $300 – US $1,025).
The exact hemorrhoidectomy surgery cost varies depending on factors such as the grade of hemorrhoids (Grade II–IV), type of surgery performed (open, closed, stapled, or laser), number of hemorrhoids, anaesthesia requirements, surgeon expertise, and hospital facilities — including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of Hemorrhoidectomy Procedure
- Conventional / Open Hemorrhoidectomy – ₹25,000 – ₹45,000 (US $300 – US $540)
- Closed Hemorrhoidectomy (Ferguson Technique) – ₹30,000 – ₹55,000 (US $360 – US $665)
- Stapler Hemorrhoidectomy (PPH Procedure) – ₹45,000 – ₹75,000 (US $540 – US $905)
- Laser Hemorrhoidectomy (Minimally Invasive) – ₹40,000 – ₹85,000 (US $480 – US $1,025)
- Hemorrhoidectomy with Fissure / Fistula Treatment (Combined Procedures) – ₹50,000 – ₹90,000 (US $600 – US $1,085)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Hemorrhoidectomy Procedure
Is hemorrhoidectomy a major surgery?
Yes, hemorrhoidectomy is considered a major anorectal surgery. Though it’s commonly performed, it can lead to complications such as bleeding, urinary retention, anal stenosis, recurrent hemorrhoids, incontinence, and in rare cases, sepsis. Proper postoperative care and follow-up are important to reduce these risks and ensure optimal recovery.
Which Is the best hospital for Hemorrhoids treatment in Hyderabad, India?
PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, is one of the most trusted centres for internal and external hemorrhoids treatment, offering advanced hemorrhoidectomy procedures using both conventional and minimally invasive techniques.
Our team of experienced general surgeons and colorectal specialists provides safe, effective, and long-term relief from Grade II, III, and IV hemorrhoids, chronic bleeding piles, and recurrent anal swelling.
With advanced surgical facilities, laser technology, dedicated day-care units, painless anaesthesia techniques, and structured recovery support, PACE Hospitals ensures precise, comfortable, and fast-recovery hemorrhoidectomy procedures — supported by cashless insurance options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and guided medical insurance processing.
What should a person expect after hemorrhoidectomy?
A slight pain is expected and a sensation of anal fullness during the first week is felt. Adequate postoperative care including pain management, stool softeners, and sitz bath can be crucial. Common early complications include bleeding and urinary retention, while late complications may involve anal stenosis, skin tags, and recurrent hemorrhoids.
How long does pain last after hemorrhoidectomy?
Moderate discomfort is expected during the first week or so. Pain can be significantly reduced using measures such as topical agents, anal dilation, or even partial sphincterotomy. Pain typically improves within 7-10 days, but mild sensitivity may persist for a few weeks.
When can a person walk after hemorrhoidectomy?
Most patients can begin light walking within 24 hours after a hemorrhoidectomy, as early mobility helps to minimize the risk of blood clots and promotes healing. Strenuous activities should be avoided for at least 1-2 weeks. Walking also helps regulate bowel function and reduces postoperative discomfort.
How much does Hemorrhoidectomy Cost in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals?
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, the cost of hemorrhoidectomy typically ranges from ₹24,000 to ₹78,000 and above (approx. US $290 – US $940), making it an affordable and specialised option for advanced piles treatment.
The final cost depends on:
- Grade and severity of hemorrhoids
- Type of surgery (open / closed / stapler / laser)
- Whether single or multiple hemorrhoids are removed
- Need for additional procedures (fissure / fistula repair)Surgeon expertise and type of anaesthesia used
- Duration of hospital stay (day-care vs overnight)
- Medications, consumables, and post-procedure care
For routine open hemorrhoidectomy, costs remain at the lower end; stapler and laser procedures fall toward the higher range due to advanced technology and faster recovery.
After a full proctology evaluation, anoscopy, and clinical assessment, our specialists provide a personalised treatment plan and transparent cost estimate based on your condition.
How can a person prevent anal stenosis after hemorrhoidectomy?
By use of a self-mechanical anal dilator early in the recovery period, the “pain-spasm-stenosis - pain” cycle can be prevented. This effectively reduces postoperative pain and the risk of anal stenosis. Incorporating lateral internal sphincterotomy (LIS) during excisional hemorrhoidectomy can lower rates of both anal stenosis and urinary retention.
Why is an individual not able to poop after hemorrhoidectomy?
Difficulty pooping after hemorrhoidectomy is usually due to postoperative pain, anal muscle spasm, or swelling. These factors can make passing stool painful, leading to voluntary stool withholding. Temporary issues like urinary retention or mild bleeding may also delay bowel movements.
When does bleeding stop after hemorrhoidectomy?
Mild bleeding after hemorrhoidectomy is common and usually resolves within a few days. Significant bleeding occurs in only 1-2% of cases. Urinary retention or straining during bowel movements may prolong or worsen bleeding.
What happens to the staples after a stapled hemorrhoidectomy (PPH)?
After a stapled hemorrhoidectomy (PPH), the staples typically remain in place and are gradually passed or absorbed. In some cases, they may contribute to scarring or stricture at the stapling site. Surgical technique adjustments, like using open-loop or tissue-selective methods, help reduce this risk.
Can a hemorrhoidectomy cause erectile dysfunction?
No-contrarily, hemorrhoidectomy may improve erectile function in men with preexisting erectile dysfunction. A prospective study showed a significant increase in International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) scores post-surgery compared to controls.
Does hemorrhoidectomy affect rectal anatomy?
Yes, surgical removal of hemorrhoidal tissue can alter the structure of the anal canal. Possible late changes include anal stenosis, skin tags, or scarring that can affect normal anatomy and function. In some cases, these changes may lead to symptoms like difficulty with bowel movements or a sensation feeling of incomplete evacuation.
Will sutures after hemorrhoidectomy fall away?
Typically, surgical sutures may either dissolve or require removal, depending on the technique used. While specifically, this aligns with standard surgical healing-any remaining suture usually gets absorbed or falls out as healing proceeds in most cases.
Is it normal to feel changes after hemorrhoidectomy?
Yes, it's normal to experience sensations such as tenderness, a feeling of fullness in the anal area, and sometimes temporary changes like mild incontinence or altered sensation after hemorrhoidectomy. These symptoms are usually temporary in nature and tend to improve gradually with proper care and regular follow-up.
This is paragraph text. Click it or hit the Manage Text button to change the font, color, size, format, and more. To set up site-wide paragraph and title styles, go to Site Theme.