Liver abscess - Types, Causes, Symptoms, Risk factors and Prevention
PACE Hospitals
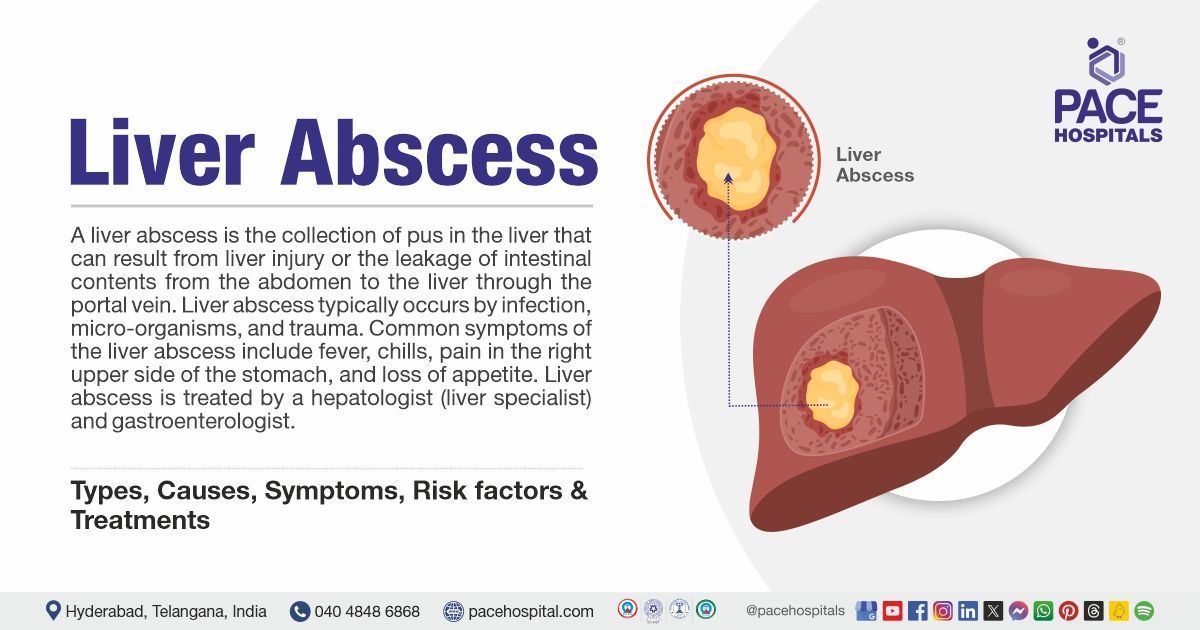
Liver abscess definition
Liver abscess, also called hepatic abscess, is a severe medical condition of the liver. It is the collection of pus in the liver that can result from liver injury or the leakage of intestinal contents from the abdomen to the liver through the portal vein (the vein that carries nutrients from the digestive organ to the liver). Liver abscess typically occurs due to infection by micro-organisms and by trauma.
Pus is a fluid formed when the body fights off an illness. It is made up of dead cells and white blood cells. Sometimes, pus gathers in a pocket inside the liver rather than emptying from the infection site. Stomach pain and swelling may result from it. Usually, there is swelling and inflammation around an abscess.
The most common symptoms of the liver abscess include fever (continuous or intermittent), chills, pain in the right upper side of the stomach, loss of appetite, and malaise (general feeling of discomfort or illness). The most common signs include right shoulder pain, jaundice, hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver), and pleural effusion (abnormal fluid buildup around the lungs). Complications include retroperitoneal extension (spread into the abdominal cavity), pulmonary emphysema (enlarged lung air sacs) and sepsis (a systemic infection causing organ dysfunction) are almost always incurable. Liver abscess is treated by a hepatologist (liver specialist) and gastroenterologist.
Liver abscess meaning
Liver abscess is the combination of two words.
- The word “Liver” is derived from the old German word ‘librn’, which means the secreting organ of the body.
- "Abscess" is derived from the Latin word ‘abscesus’ in 1960s, which means the collection of pus in a few parts of the body.
Prevalence of liver abscess worldwide
Globally, an estimated 4–5 crore people become infected with liver abscess disease each year; most cases arise in developing countries, where the incidence of infection exceeds 5–10% and can occasionally reach 55%. Tropical developing nations, including those in Mexico, India, and tropical regions of Asia and Africa, have the highest prevalence.
Prevalence in India
Based on research fever and stomachache were the most frequently occuring symptoms among the Indian individuals assessed, and the etiology was higher in pyogenic compared to amoebic, other than idiopathic factors.
When the gender of the patient was considered, the prevalence of amoebic liver abscess was found to be 6.9% in females and 93% in males. When socioeconomic conditions were considered, the individuals with amoebic liver abscesses were found to be 62.3% from low socioeconomic conditions and 37.6% from high socioeconomic conditions.
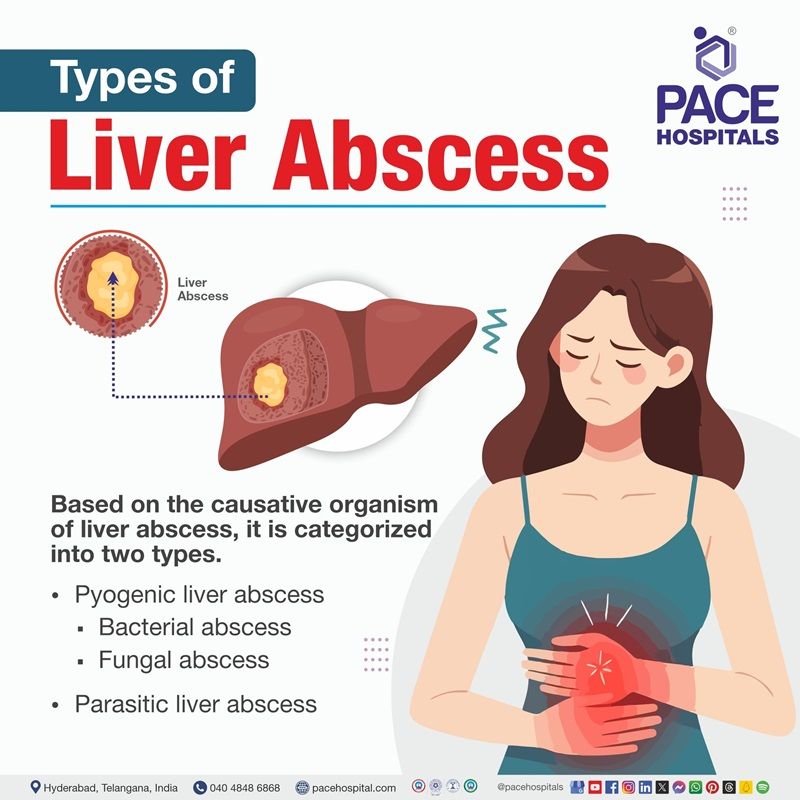
Types of liver abscess
Based on the causative organism of liver abscess, it is categorized into two types.
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- Bacterial abscess
- Fungal abscess
- Parasitic liver abscess
Pyogenic liver abscess
- Bacterial abscess: A common infectious condition called bacterial liver abscess is brought on by a variety of pathogens, including fungi, bacteria, and parasites. It is also called a pyogenic liver abscess (PLA). It can happen in several conditions, including trauma, colitis, pancreatitis, biliary tract disorders, and intravenous drug usage. Patients with weakened immune systems are frequently affected by a relatively new cause, Klebsiella pneumoniae. Symptoms related to endogenous endophthalmitis (EE), an uncommon and dangerous complications, may manifest before pyogenic liver abscess (PLA).
- Fungal abscess: The most common cause of fungal abscesses is Candida albicans, which frequently affects immunocompromised people. They are an indication of a widespread fungal infection. There have also been reports of aspergillus species and cryptococcus infections causing hepatic abscesses. In people with weakened immune systems, fungal micro abscesses are scattered throughout the liver, showing up as many small lesions, often less than a centimeter in size.
Parasitic abscess (Amoebic liver abscess)
An accumulation of pus in the liver caused by the intestinal parasite Entamoeba histolytica is an amoebic liver abscess. Other names for the amoebic liver abscess are amebiasis and amoebic dysentery. Following an extraintestinal infection, the parasite may travel through circulation from the intestines to the liver. Food and water contaminated with faeces spread amebiasis. The use of human waste as fertilizer will occasionally cause liver abscesses. Additionally, amebiasis is transmitted by person-to-person interaction. Globally, infection is present. It is more prevalent in tropical regions with crowded housing and inadequate sanitation. India, Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa have extensive health problems with this.
Humans can get hydatid disease, a parasitic infection, of which Echinococcus granulosus is the most common species. Dogs are the ultimate hosts of adult parasites, living in their stomachs. Cattle, horses, and sheep are intermediate hosts Humans are unusual hosts, as it is not common for them to become infected by consuming food and water contaminated with the stool of infected dogs. After being consumed, larvae of these eggs access the liver through the portal vein and are dispersed to various organs through the bloodstream.
Liver abscess causes
A liver abscess is a collection of pus(fluid) due to the infection caused by various micro-organisms, leading to inflammation. Based on the type of causative organism, they are divided into different types as mentioned below:
Pyogenic liver abscess causes
Different organisms causing pyogenic liver abscesses include Escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus anginosus group, clostridium species, Bacteroides species, and klebsiella pneumoniae. There are various causes of pyogenic liver abscesses, they are:
- Bile duct problems: The function of the bile duct is to collect bile from the liver and transport it to the small intestine. It acts as a bridge between the liver and the duodenum of the small intestine. Pyogenic liver abscess is an accumulation of pus in the liver because of bacterial infection, which destroys the liver parenchyma. This kind of infection is most frequently caused by biliary tract infection.
- Through portal vein: Pyogenic liver abscesses commonly originate from abdominal infection and bowel content leakage. The portal vein (the vein that carries nutrients from the digestive organ to the liver) carries bacteria to the liver, where they settle down causing infection. The biliary system may potentially be the source of an infection.
- Through hepatic artery: When bacterial endocarditis (heart infection) or systemic bacteremia (blood infection) occurs, the hepatic artery might become contaminated. Stones, strictures (narrowing of the tube), or tumors that break the bile flow cause contamination of the bile, which then causes cholangitis, which causes liver abscesses.
- From other parts of the abdomen: Pyogenic liver abscesses are frequently caused by the leakage of intraabdominal bowel contents, which travel to the liver through the portal circulation or directly spread when there is a biliary infection. Rarely a hepatic abscess caused by a foreign body that entered the digestive system is discovered. 80-90% of swallowed foreign bodies pass through the gut in less than a week without the patient realizing it and without any problems.
- Injury: Blunt or penetrating trauma can result in intestinal puncture, a fistula (abnormal internal connection) to the liver, and the subsequent formation of an abscess can also induce pyrogenic liver abscess. Hepatic artery thrombosis (clot) and narrowing of the bile duct can lead to vascular compromise, which can result in liver abscesses in a transplanted graft.
Amoebic liver abscess causes (Parasitic)
Parasites causing liver abscesses include Entamoeba histolytica, Echinococcus granulosus, protozoa, and helminths. The most common parasitic liver abscess is an amoebic liver abscess. Entamoeba histolytica is the protozoan that causes amebiasis, a parasitic infection spread through the fecal-oral pathway. The infection may show up as one or more liver abscess-related consequences, or it may be asymptomatic. The most typical extraintestinal sign of amebiasis is an amoebic liver abscess. It is the most prevalent organism. When it enters the portal system and migrates to the liver, it first causes amoebic colitis, followed by an amoebic liver abscess.
Echinococcus granulosus, another uncommon but important parasitic pathogen, creates a hepatic hydatid cyst leading to liver abscess.
Liver abscess symptoms
The patient's experiences act as the signs and symptoms of the illness. While symptoms are understandable to the patient, signs are the signals observed by the doctor. The below list includes signs and symptoms of liver abscess:
- Fever and shivering
- Vomiting
- Severe weight loss
- Right upper stomach pain
- Dark urine and faeces
- Nocturnal hyperhidrosis - sweating at nights
- Jaundice – yellowish discoloration of eyes and skin
- Hepatomegaly- Enlarged liver
- Loose stools
Liver abscess risk factors
Risk factors are the characteristics that increase the chance of developing a disease or a medical condition. Liver abscesses can arise because of several risk factors, including:
- Diabetes:
- Hyperglycemia is linked to gas formation in the body. When blood sugar levels are high, microorganisms can metabolize glucose vigorously, promoting increased gas production.
- Researchers have found gas in liver abscesses. Thus, managing blood sugar is important in reducing the risk of liver abscesses.
- Based on research, the incidence of liver abscess in a study population is 15.4% in diabetic patients.
- Diabetic patients with proper blood sugar control are at lower risk than patients with poor blood sugar control.
- Liver cirrhosis: It creates a major risk for both death and liver abscesses. Cirrhosis causes decreased immunity, loss of liver function, frequent gastrointestinal infections, and blood poisoning, leading the patient to be more prone to liver abscess.
- Gender: Based on the functioning of the immune system and lifestyle factors, males are more prone to liver abscesses than women.
- Age: Based on the research studies, people of age between 40-60 are more prone to liver abscess.
- Use of proton pump inhibitors: This class of drugs contributes to anti-inflammatory activity. Apart from the use of antibiotics, the immune system also needs to fight to control infections. Impaired immune function leads to an increased risk of infections.
- Impaired immune systems: The Liver’s Kupffer cells often ingest bacteria that enter the liver’s circulatory system. If the host’s immune system is impaired or the number of organisms exceeds the Kupffer cell’s capability due to an underlying liver illness, a liver abscess may arise.
Complications of liver abscess
Complications are the effects of the disease that are usually unexpected. These additional medical problems that arise because of the current disease require medical assistance. They are listed below:
- Peritonitis: Various studies have reported that ruptured liver abscess causes peritonitis (inflammation of the wall lining the abdominal cavity).
- Shock: Based on the study it was found that even after being administered with antibiotics and fluid resuscitation, patients with liver abscesses developed shock which is one of the major complications.
- Kidney failure: Studies have shown a high occurrence of kidney failure in patients with liver abscesses.
- Subphrenic abscess: A subphrenic abscess develops in the space between the diaphragm and the liver or spleen. It is a collection of infected fluids. Common causes of this pathology include damage from duodenal ulcers, inflammation of the intestine, appendicitis (swelling of the appendix), and amoebic liver abscesses. Fever, cough and abdominal pain are the discomforts caused by a subphrenic abscess.
- Fistula to adjacent organs: Injuries involving hydatid or pyogenic cysts result in penetration through the diaphragm, causing lower lung rupture and fistula formation.
- Acute pancreatitis: Cases show the simultaneous occurrence of pancreatitis and liver abscess, the reason may be the similar passage duct.
- Hepatic or abdominal venous thrombosis: There's a chance of localized inner blood clots in veins when an amoebic liver abscess bursts into a blood vessel like the Inferior vena cava, which could be the cause of pulmonary emboli.
- Liver pseudoaneurysm: Abscesses in vulnerable areas are linked to an increased risk of complications, such as the development of pseudoaneurysms (clots outside the blood vessel) because of regular percutaneous drainage treatments.
- Septic emboli in the central nervous system: The most impacted secondary sites are the central nervous system and the eyes. Bacteremia acts as a risk factor for both hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess frequently results in septic embolism, which may raise the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
- Endophthalmitis: Endogenous endophthalmitis (EE), a severe bacterially induced inflammation of the fluids and tissues inside the eye that quickly endangers the eye and eyesight, is the most frequent secondary spreading of liver abscess.
Liver abscess diagnosis
Liver abscesses may occur for several reasons and show various signs and symptoms. A detailed examination of the patient may help diagnose the condition. Diagnosis includes various steps. Liver abscess needs to be assessed in the following way:
- History: Including personal history, social history, past treatment, or medical history.
- Physical examination: Including signs and symptoms.
- Laboratory findings:
- Complete blood picture (CBP)- Checks for an increase in the number of white blood cells and a decrease in the number of red blood cells.
- Liver function test- For increase in alkaline phosphate, decrease in albumin and changes in liver enzymes.
- Blood culture- To check for organisms in case of amoebic liver abscess and to monitor for concomitant infection with bacterial, fungi and virus causing hepatitis.
- Imaging tests:
- Computed tomography- with contrast showing 90-100% accuracy.
- Ultrasonography- 80-90% accuracy.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Hepatic Radio nuclide scans – Technecium, gallium, and indium are the biomarkers used to detect the lesions in the liver.
Prevention of liver abscess
Liver abscess prevention requires various lifestyle modifications, as mentioned below:
- Food and water: Having food and water contaminated by feces will lead to infection-causing liver abscesses as they may contain parasites. Cleaning fruits and vegetables before eating and avoiding uncooked meat can help prevent infections.
- Hygiene: Developing countries need to care more about creating awareness among the people and maintaining a hygienic environment.
- Safe sexual practice: Especially in men engaging in sexual relations with men and involved in oral-anal sex need to take care of hygiene to avoid the spread of infection.
Liver abscess treatment
There are several methods for treating liver abscesses. Treatment depends on the cause of liver abscess and the severity of the infection. An untreated hepatic abscess is life-threatening due to its potential complications. Below are the treatment options for liver abscess:
Pyogenic liver abscess treatment
The choice of treatment for pyogenic liver abscess depends on the clinical presentation, characteristic organism, and size of the abscess. Pharmacological therapy and drainage are used in the treatment based on the requirement.
- Pharmacological therapy: Includes pyogenic liver abscess antibiotic treatment, including aminoglycosides, beta-lactam antibiotics, penicillinase-resistant penicillin, and cephalosporins (1st generation).
- Liver abscess drainage procedure: The main treatment for pyogenic liver abscesses. It includes percutaneous drainage, which is performed superficially.
- Liver abscess Surgery: Open or laparoscopic surgical drainage, which is performed using ultrasonography (US) and computerized tomography (CT scan), is recommended only when both percutaneous drainage and antibiotic therapy do not treat the condition.
Amoebic liver abscess treatment
Drugs of choice are amoebicidal drugs, and drainage is not usually recommended, but needle aspiration is used in required cases, whereas open surgical drainage is used only when all other methods fail to treat the condition.
Difference between amoebic and pyogenic liver abscess
Amoebic vs pyogenic liver abscess
Liver abscesses are categorized into two types based on the causative organism and is the most important cause of hospitalization in low- and middle-income countries. Proper diagnosis is important for appropriate treatment. Below are some of the parameters that help in differentiating amoebic liver abscess and pyogenic liver abscess:
| TYPES | AMOEBIC LIVER ABSCESS | PYOGENIC LIVER ABSCESS |
|---|---|---|
| PATHOGEN | Entamoeba histolytica, Echinococcus granulosus, protozoa and helminths. | Escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus anginosus group, clostridium species, Bacteroides species, klebsiella pneumoniae. |
| INCIDENCE | Globally, 80% of all liver abscess patients | Globally, 20% of all liver abscess patients |
| TREATMENT | Antibiotics, including amoebicidal drugs. Drainage and surgical treatments are rarely recommended. | Antibiotics including aminoglycosides, beta-lactam antibiotics, penicillinase-resistant penicillin, and cephalosporins are used. Drainage is the main procedure of the treatment. Surgery is recommended only when other procedures fail to treat. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Liver abscess
Is liver abscess cancerous?
Liver abscesses have been reported to be predictive of cancer, particularly colon and hepato-biliary cancer. Compared to the general population, patients with liver abscesses have noticeably increased chances of liver cancer, biliary tract cancer, and other cancers. Within 90 days of follow-up, the chances of liver cancer, biliary tract cancer, and all cancers are substantially higher in liver abscesses patients. Additionally, younger liver abscess patients (those under 60) are at higher risk than older.
Can a liver abscess burst?
Yes, if untreated, liver abscess can rupture, releasing infectious fluid into the body and causing severe complications. It ruptures due to the pressure buildup in the abscess or external trauma. So, early treatment of liver abscess is recommended.
Can liver abscess spread in the body?
Yes, under high internal pressure within the abscess or external trauma, the abscess bursts out and spreads in the body, causing severe complications. It is the most significant complication of the liver abscess.
Can liver abscess go away by itself?
A liver abscess requires treatment under the supervision of a health care professional. If left untreated, it may be life-threatening. Allowing the abscess to resolve on its own without treatment can result in significant health risks and complications.
What is the difference between a cyst and an abscess on the liver?
A liver abscess is an infectious condition filled with pus, typically causing pain and discomfort. In contrast, liver cysts are noninfectious sacs filled with fluid, often remaining asymptomatic until they reach a large size.
What is a liver abscess?
A liver abscess is a pocket within the liver filled with infection or pus that disrupts the liver function and causes pain and discomfort. When the liver abscess bursts, it spreads infection wherever it goes.
What not to eat in a liver abscess?
Normally, proteins help in tissue repair in the body. They also protect the liver cells from harm and lipid accumulation. Proteins are not effectively digested in those whose livers are severely damaged. The brain may be affected by waste materials that accumulate. So, a high intake of protein needs to be avoided. Instead, carbohydrates and fats can be taken.
How to avoid liver abscesses?
Treating stomach infections as soon as possible is the best defense against liver abscesses. Most issues can be avoided with careful follow-up with the doctor and adherence to the recommended antibiotic prescription.
Is fasting good for liver repair?
Yes, according to several studies, fasting may enhance liver function and indicate a decrease in inflammation or fat deposition in the liver. Furthermore, during this fasting period, total cholesterol levels may also improve.
How big can a liver abscess be?
A large maximal diameter of the liver abscess upon admission indicated a severe condition, which ultimately prolonged hospitalization and complicated recovery. The average maximal diameter of the liver abscess was 5.4 ± 2.6 cm. For individuals with large liver abscesses, more intensive treatment approaches along with close monitoring are necessary.
Can a liver abscess reoccur?
Yes, but it doesn't happen often. Additionally, it depends on the organism causing infection. Failure to adhere to antibiotic medication and to drain when necessary are risk factors for recurrence. Liver abscesses can manifest as sepsis or as an asymptomatic illness.
What is the incubation period of a liver abscess?
The incubation period depends on the type of organism. For Entamoeba histolytic, within 2 to 4 weeks of exposure, 80% of individuals will experience symptoms, which include fever, coughing, and dull, painful right upper quadrant or epigastric stomach pain.
How long after liver abscess can I consume alcohol?
Healthcare professionals’ advise liver abscess patients to not consume alcohol. Based on a study, alcohol consumption significantly increases the risk of developing both amoebic liver abscess and pyogenic liver abscess, mainly due to the toxic effects of alcohol on the liver.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868