Successful Endoscopic Ampullectomy & CBD Stenting for Periampullary Adenoma in a 60 Y.O. Male
PACE Hospitals
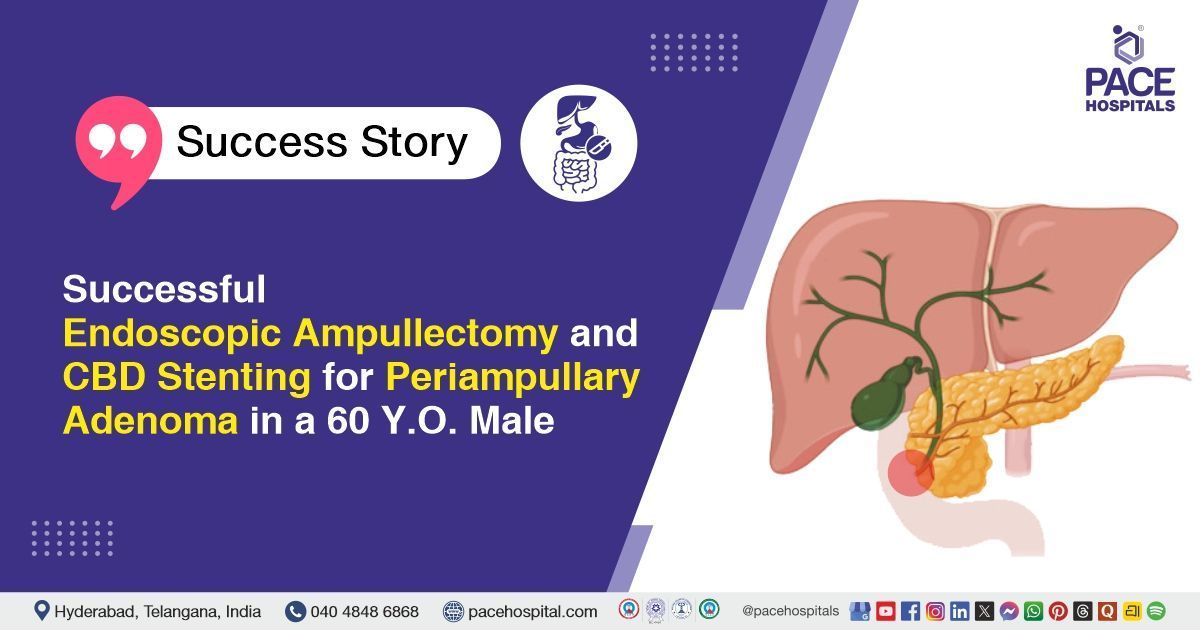
The PACE Hospitals’ expert gastroenterology team successfully performed an Endoscopic Ampullectomy, Precut Sphincterotomy, and Common Bile Duct (CBD) Stenting on a 60-year-old male patient diagnosed with a periampullary mass lesion. The aim of the procedure was to safely remove the ampullary lesion, relieve biliary obstruction, and ensure adequate bile drainage while preventing complications.
Chief Complaints
A 60-year-old male patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 22.4 presented to the Gastroenterology Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with chief complaints of burning pain in the chest and abdomen for the past one month, persistent hiccups for one month, and loss of appetite for one month.
Past Medical History
The patient had a known history of
diabetes mellitus and
heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) secondary to dilated cardiomyopathy. No other significant chronic illnesses or prior major surgeries were reported.
On Examination
On admission, the patient was conscious, coherent, and oriented. General examination was normal with stable vital parameters. Systemic examination revealed a soft, non-tender abdomen with no organomegaly or guarding. Respiratory system examination showed normal breath sounds bilaterally without added sounds. Cardiovascular examination demonstrated normal heart sounds without murmurs. No peripheral edema, cyanosis, or signs of dehydration were noted. Neurological examination was normal with no focal deficits.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was thoroughly evaluated by the Gastroenterology team following a 1-month history of burning pain in the chest and abdominal pain, persistent hiccups, and loss of appetite. There was a strong clinical suspicion of a periampullary mass causing distal common bile duct (CBD) obstruction.
The patient underwent an extensive diagnostic evaluation. Triphasic CT Abdomen demonstrated a well-defined minimally enhancing periampullary mass lesion (15 × 13 mm) with external compression of the terminal CBD and bilobar intrahepatic biliary radicle dilatation (IHBRD). Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) confirmed the presence of an ampullary lesion. Laboratory markers, including CEA and CA-19-9, were within normal limits. Echocardiography showed heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 50%.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, the patient was advised to undergo Periampullary Mass Lesion Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Gastroenterology Department.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with consultant gastroenterologists, Dr. Govind Verma, Dr. M Sudhir, Dr. Padma Priya, and cross consultation with cardiologist, Dr. Seshi Vardhan Janjirala, a comprehensive evaluation was performed to determine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Considering the patient’s history of burning chest and abdominal pain, persistent hiccups, and loss of appetite, along with significant comorbidities such as Diabetes Mellitus, Dilated Cardiomyopathy, and HFrEF (EF 50%), an optimal treatment strategy was formulated.
Based on these clinical and imaging findings, it was determined that Endoscopic Ampullectomy with precut sphincterotomy and CBD stenting was identified as the most suitable therapeutic intervention to relieve obstruction, obtain definitive tissue diagnosis, and avoid the risks associated with major surgery.
The patient and his family members were clearly counselled about the periampullary lesion, the need for endoscopic ampullectomy with common bile duct (CBD) stenting, and the associated risks.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled to undergo Endoscopic Ampullectomy with Precut Sphincterotomy and Common Bile Duct (CBD) Stenting Surgery in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals under the expert supervision of the Gastroenterology Department.
The following steps were carried out during the procedure:
- Pre-procedure Evaluation: Before the procedure, the patient was thoroughly evaluated for comorbidities including diabetes and heart failure. Anesthetic and cardiology clearances were obtained due to cardiac risk. The patient was kept nil per oral to prevent aspiration and was started on intravenous fluids and monitoring. Prophylactic antibiotics were administered as needed, and sedation was planned based on patient stability.
- Anesthesia and Endoscopic Access: The procedure was performed under short general anesthesia with cardiology and anesthesia monitoring. A side-viewing endoscope was advanced to the second part of the duodenum to locate the ampullary lesion.
- Visualization and Assessment: The ampullary mass, measuring 15 x 13 mm, was carefully examined using the side-viewing scope. The anatomy of the bile and pancreatic ducts was assessed to plan safe removal.
- Ampullectomy and Tissue Removal: The lesion was excised using a hot snare technique. Any bleeding encountered during removal was controlled immediately with hemoclips. The excised tissue was sent for histopathological examination.
- Sphincterotomy and Stenting: A precut sphincterotomy was performed to ensure bile drainage. A 7 Fr x 7 cm single pigtail biliary stent was placed to maintain duct patency and prevent obstruction.
Postoperative Care
The patient’s postoperative period was uneventful. The patient was shifted to the Medical Intensive Care Unit (MICU) post-procedure and was monitored with serial hemoglobin checks. He developed fever spikes, with blood cultures growing Staphylococcus haemolyticus and sputum cultures growing multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. He was kept NPO (nil per os) initially and was gradually shifted to a solid diet. He was treated with IV fluids, proton pump inhibitors, culture-sensitive antibiotics, and cardiac medications. A follow-up endoscopy showed the stent in situ with no bleeding, and the patient improved gradually and was discharged in stable condition.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed a course of antibiotics for infection control, a proton pump inhibitor for gastric protection, and a combination of heart failure medications for cardiac management. He was also continued on a statin for lipid control and an oral hypoglycemic agent for diabetes management. Additionally, he was given a medication for gastrointestinal motility and a laxative for constipation as needed.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain and vomiting.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up visit after one month with the Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, to review his condition.
Conclusion
This case highlights a patient with a periampullary tubular adenoma causing mild biliary obstruction, successfully managed with endoscopic ampullectomy and stenting. The patient experienced transient post-procedure infections, treated with antibiotics. He was discharged hemodynamically stable with follow-up advised for GI and cardiac care.
Comprehensive Endoscopic and Multidisciplinary Approach in Managing Periampullary Lesions
Endoscopic evaluation plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing periampullary lesions, allowing gastroenterologist / gastroenterology doctor to accurately assess mass characteristics and biliary obstruction. Procedures such as EUS and ERCP offer detailed visualization, enabling targeted interventions like endoscopic ampullectomy and CBD stent placement. When complications arise, such as septicemia from organisms like Staphylococcus haemolyticus or MDRO Klebsiella - culture-guided antibiotics are essential for effective control.
Concurrent management of comorbidities, including HFrEF and coronary artery disease (CAD), ensures patient stability throughout treatment. This coordinated, evidence-based approach supports timely recovery and optimizes outcomes in complex hepatobiliary disorders.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868