Hepatoblastoma - Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, Types & Complications
PACE Hospitals
Overview | Prevalence | Types | Causes | Risk Factors | Symptoms | Complications | Diagnosis | Treatment | FAQs | When to consult a Doctor
Hepatoblastoma Definition
Hepatoblastoma is a type of liver cancer usually seen in paediatric patients. Cancer develops when normally functioning cells undergo mutation and multiply out of control, forming a tumour mass. Cancer can happen in any tissue.
Both malignant and benign forms of tumours exist. If left untreated, a malignant tumour may quickly develop and metastasise (spread) to other organs. When a tumour is considered benign, it might still grow but will not metastasise.
Hepatoblastoma cancer is a very rare but malignant embryonal tumour that occurs in about 1% of all paediatric cancers, commonly seen in children under five years of age (toddler).
Hepatoblastoma meaning
While blastoma is a type of cancer common in children, seen in precursor cells, often called blasts, the prefix "hepato" talks about everything related to the liver; thus, hepatoblastoma demonstrates the origin of cancer in the liver of a child / toddler.
Hepatoblastoma Prevalence
Being a rare tumour, hepatoblastoma comprises approximately 1% of all the prevailing paediatric cancers. Nevertheless, it must be understood that the rate of its incidence is slowly increasing in various parts of the world, especially the North America and Europe. Hepatoblastoma is found to be having a slight male predominance.
What is the liver and its functions?
The liver is one of the crucial and largest parts of the body. It is located towards the upper right-hand portion of the abdominal cavity.
Nearly 1 pint of blood (13% of total volume) is stored in the liver at any time. There are many functions of the liver; few of them include:
- Bile production – necessary for food digestion, especially fats
- Red blood cells apoptosis – The controlled cell death of red blood cells is the source of bilirubin which takes place in the liver. Bilirubin forms the major part of bile juice.
- Metabolism – of various products such as food, medicines, blood etc
- Production of plasma proteins in the blood
- Cholesterol production
- Glycogenesis (excess glucose into glycogen for storage)
- Processing of haemoglobin for the use of its iron content (the liver stores iron)
- Ornithine cycle (conversion of poisonous ammonia to urea)
- Regulation of blood clotting etc
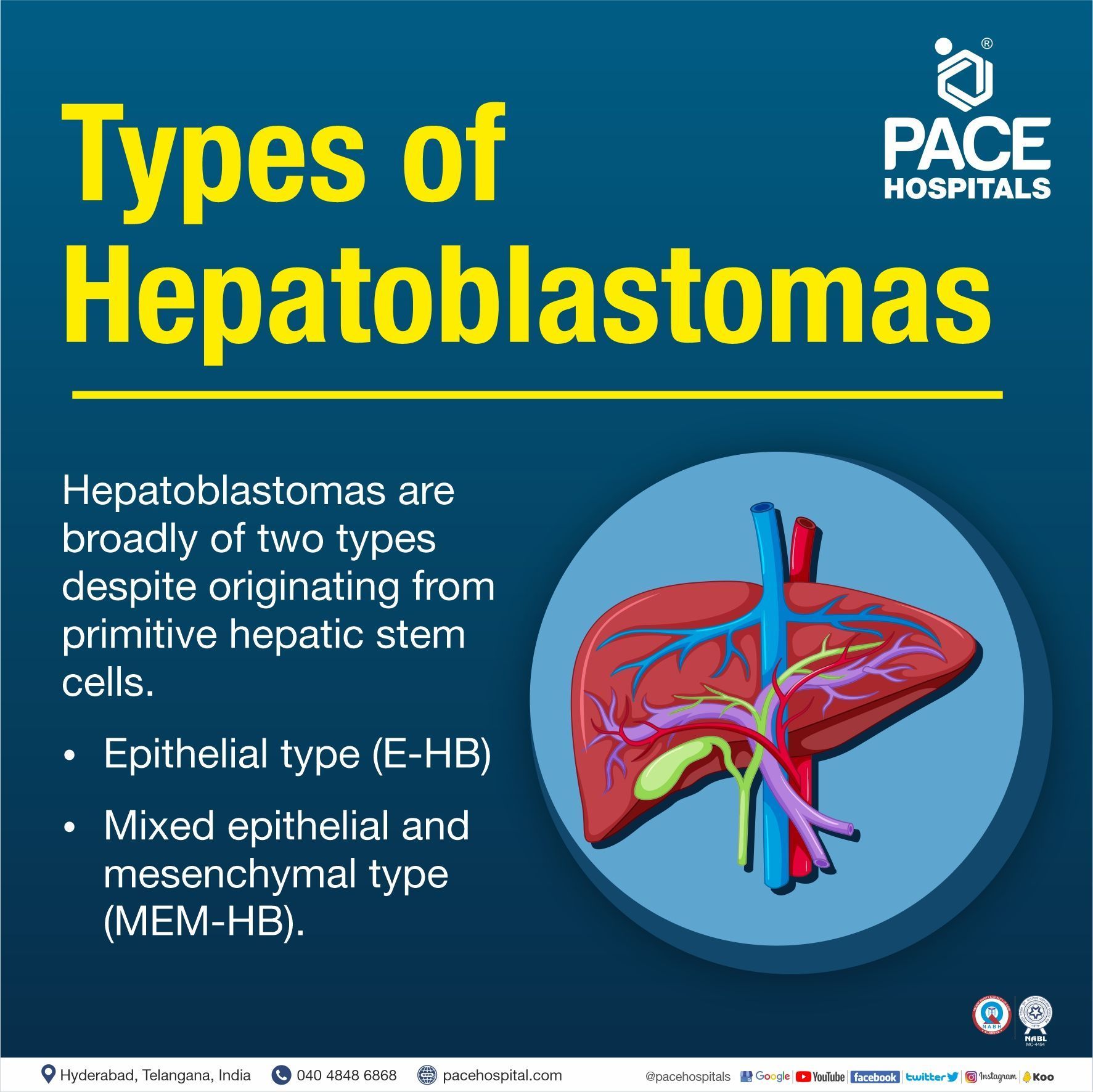
Types of Hepatoblastomas
Hepatoblastomas are broadly of two types, despite originating from primitive hepatic stem cells.
The two types of hepatoblastomas are:
- Epithelial type (E-HB)
- Mixed epithelial and Mesenchymal type (MEM-HB).
While the E-HB includes foetal, embryonal, pleomorphic, macro-trabecular, cholangioblastic, small cell undifferentiated (SCU) and mixed epithelial variants, the MEM-HB is subdivided into tumours with teratoid features (tissues not ordinarily present at the site) and tumours without teratoid features.
Hepatoblastoma Causes
The seeds of hepatoblastoma cancer development are sown in utero, during the gestational period, primarily due to the inactivating mutations of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. Also, very low birth weight (i.e., <1,500 g) is strongly associated with hepatoblastoma cancer. Reports supporting this association come from diverse nations, including the United States, the United Kingdom, the four Nordic countries (Denmark, Norway, Sweden and Finland), Japan, and China.
Hepatoblastoma cancer is closely related to genetic syndromes such as
- Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) - A rare, inherited condition due to a defect in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. While the occurrence is mainly from an inheritance from a parent's gene, spontaneous genetic mutation is seen in 25-30% of people.
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) - Condition of overgrowth syndrome which affects various parts of the body resulting in macrosomia (affected infants are larger than usual), and few may be taller than their peers during childhood.
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards' syndrome) - a rare but serious condition involving the appearance of abnormalities in many parts of the body due to chromosomal abnormality. Most patients with Edwards' syndrome will die before or shortly after birth.
The various other genes which could cause hepatoblastoma are:
- RAS Gene (KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS) is commonly mutated in human cancers
- LncRNA H19 gene, a maternally imprinted gene, is located on chromosome 11p5.5 and is involved in embryonic development.
- LIN28. This gene is located in chromosome 1p36.11 and is involved in human development and metabolism.
- HMGA2, a type of high mobility group (HMG) proteins
- Base Excision Repair Pathway Genes
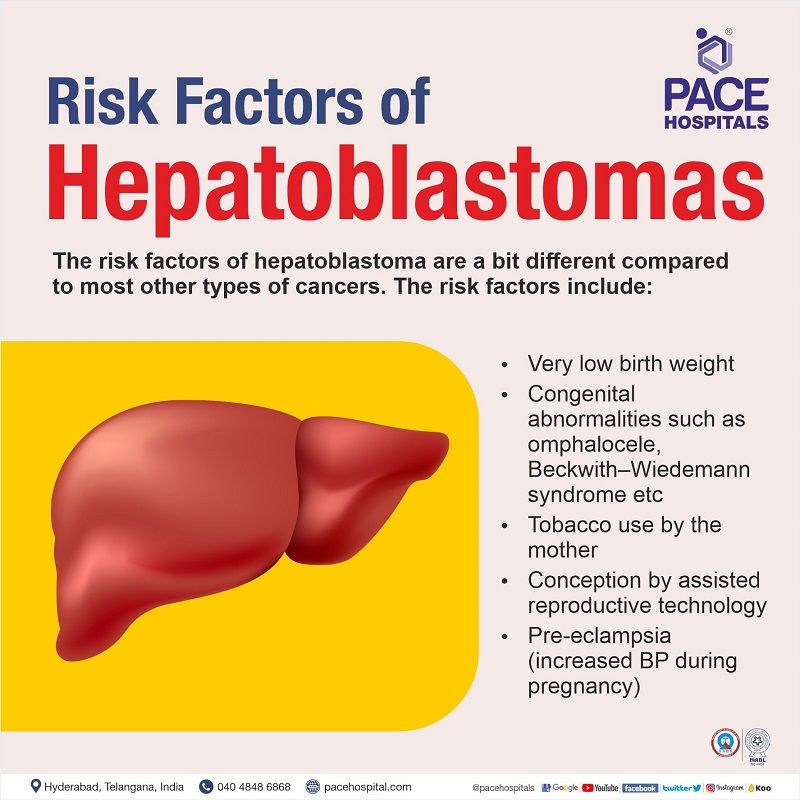
Hepatoblastoma Risk factors
The risk factors of hepatoblastoma are similar to most other types of cancers, including avoidable and non-avoidable risk factors. The various types of liver cancer risk factors include:
- Very low birth weight
- Congenital abnormalities such as omphalocele, Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome etc
- Asian race
- Pre-eclampsia (hypertension during the gestational period)
- Tobacco use by the mother
- Conception by assisted reproductive technology
Pre-eclampsia, also called maternal hypertension, usually occurs during the gestational period and is one of the risk factors for many congenital disorders. Indulgence of tobacco and pre-eclampsia are known to reduce the birth weight of the newborn in the womb.
Assisted reproductive technology uses various procedures in infertile couples. The risk of prenatal hepatoblastoma is increased by nine times if the couple opts for any assisted reproductive technology, such as:
- In vitro fertilisation
- Gamete intra fallopian transfer
- Zygote intra fallopian transfer
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
- Artificial insemination
- Intrauterine insemination
- Intra cervical insemination
- Intra tubal insemination

Hepatoblastoma Symptoms
Being sporadic and mostly appearing in neonates and children, who cannot express their disease state as coherently or as articulately as adults, the presentation of hepatoblastoma symptoms in toddlers could be pretty tricky.
It is the parents' and caretakers' duty to contemplate and understand the abnormalities expressed in the child. The possible hepatoblastoma symptoms (if the tumour is intact) could include the following:
- Abdominal distension or abdominal mass
- Abdominal discomfort
- Generalised fatigue
- Loss of appetite due to tumour distension
- Anaemia
If the tumour is ruptured, the following symptoms can be seen along with the above:
- Vomiting
- Symptoms of peritoneal irritation and severe anaemia
In rare cases, precocious puberty (the changes of a child's body into that of an adult too soon) can also be seen due to the secretion of β-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) by the tumour.
Complications of Hepatoblastoma
Untreated hepatoblastoma cancers usually results in death but both the disease and the treatment could also lead to few complications such as
- Intraperitoneal tumour rupture
- Chemotherapeutic Complications
- Post-transplant complications
- Psychosocial effects of treatment and painful procedures
Hepatoblastoma Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Hepatoblastoma is performed by hepatologist (liver specialist) by doing the following:
- Physical examination
- Blood tests
- Contrast-enhanced sonography
- Doppler's ultrasound (hepatoblastoma ultrasound)
- Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan of the abdomen
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen
- Liver scintigraphy
- Liver biopsy
Hepatoblastoma Treatment
To treat Hepatoblastoma in children or adult, a team of hepatologists, liver transplant surgeons and oncologists may decide the treatment approach based on the condition of the patient, such as:
- Hepatoblastoma surgical resection
- Liver Transplant
- Ablation
- Embolisation
- Chemotherapy
Why Choose PACE Hospitals?
Expert Super Specialist Doctors
Advanced Diagnostics & Treatment
Affordable & Transparent Care
24x7 Emergency & ICU Support
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Hepatoblastoma
When to consult a doctor for Hepatoblastoma?
Consult a doctor for Hepatoblastoma when symptoms such as abdominal swelling, loss of appetite, or unexplained weight loss last for more than a few days or interfere with normal eating and daily activities. Hepatoblastoma can worsen without timely treatment and may lead to serious complications if ignored.
Warning signs that require medical attention include:
- A lump or swelling in the abdomen
- Persistent nausea, vomiting, or fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
If these symptoms persist, a hepatoblastoma specialist or a hepatologist can confirm the diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment to promote recovery and prevent complications.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles











