Successful Cervical Laminectomy for C4-C5 Cervical Myelopathy in a 66-Year-Old Male
PACE Hospitals
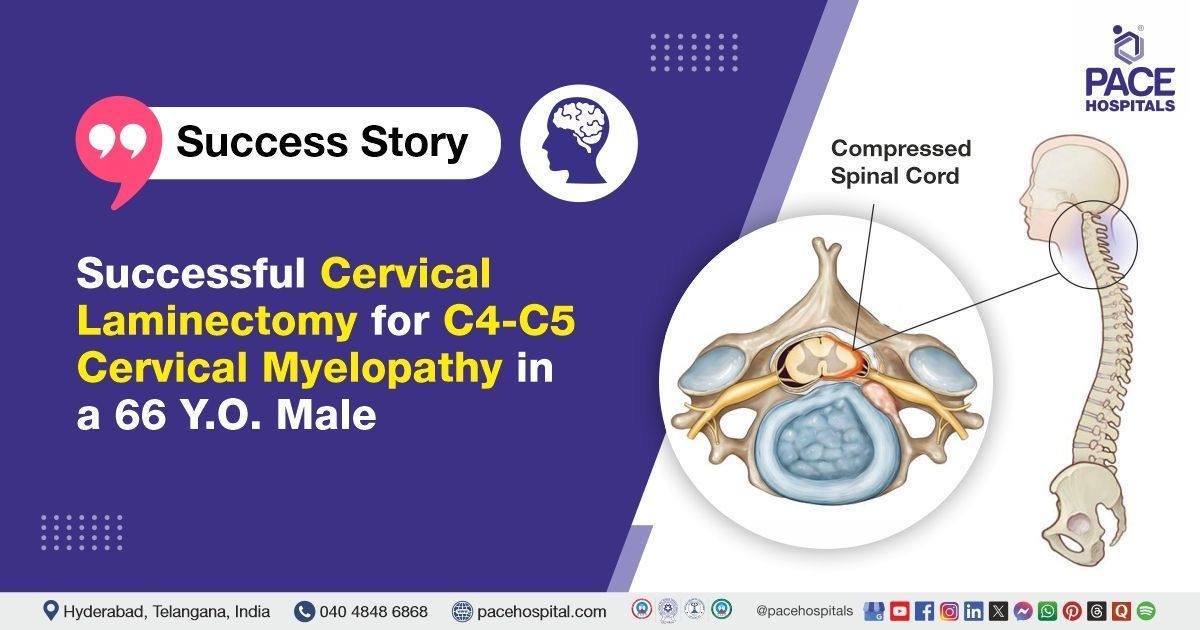
PACE Hospitals’ expert Neurosurgery team successfully performed a cervical laminectomy at the C4-C5 level on a 66-year-old male patient diagnosed with cervical canal stenosis with myelopathy. The procedure was aimed to relieve spinal cord compression, reducing neurological symptoms, and improving the patient’s mobility and quality of life.
Chief Complaints
A 66-year-old male patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 22 presented to the Neurosurgery Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with a two-month history of lower back pain, left lower limb
radiculopathy, gait imbalance, and decreased toe grip, along with difficulty in retaining footwear (slippage of chappals).
Past Medical History
The patient has a history of diabetes mellitus and is on medical management for the condition. There are no known allergies to any foods or medications reported.
On Examination
On general examination, the patient was conscious and coherent with stable vital signs. Neurological assessment revealed normal motor strength in all four limbs, increased muscle tone in both lower limbs, and bilateral extensor plantar reflexes. Knee jerks were brisk, while sensory function was intact. The Romberg test was positive.
Diagnosis
Upon admission, the patient underwent a comprehensive clinical evaluation along with the patient's medical history and detailed diagnostic investigations conducted by the Neurosurgery team.
Laboratory and special investigations were conducted as part of the preoperative assessment. CBC showed mild leukocytosis with neutrophil predominance, but no systemic infection. Liver function tests revealed mild elevation of liver enzymes, with other parameters normal. Renal function tests, serum electrolytes, and coagulation profile were all within normal limits, indicating no bleeding risk or metabolic abnormalities. Chest X-ray showed normal heart size and clear lung fields without acute pathology. Viral screening for HIV, HCV, and HBsAg was negative, and urine examination was unremarkable. Imaging studies included MRI cervical spine, which confirmed cervical canal stenosis with myelopathy.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, the patient was advised to undergo Cervical Canal Stenosis With
Myelopathy Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Neurosurgery Department.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with Dr. U L Sandeep Varma, Neurosurgeon, a comprehensive preoperative neurological risk assessment and overall evaluation were performed to determine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic approach. The patient had presented symptoms suggestive of compressive myelopathy, raising concerns about cervical canal stenosis, neural element compromise, and the risk of progressive neurological deterioration.
Further evaluation confirmed the diagnosis of cervical canal stenosis with myelopathy, evidenced by upper motor neuron signs such as increased tone in the lower limbs, bilateral extensor plantar responses, and a positive Romberg test. Laboratory investigations, including CBC, liver and renal function tests, serum electrolytes, coagulation profile, and viral markers, were all within normal limits except for moderate leukocytosis, which did not indicate any systemic contraindication for surgery.
It was determined that the cervical laminectomy at C4-C5 was identified as the most effective medical approach to decompress neural elements, relieve symptoms, and prevent further neurological decline.
The patient and his family were informed about his condition, the procedure, its associated risks, and its potential to alleviate symptoms and enhance his quality of life.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled to undergo C4-C5 cervical laminectomy surgery in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, under the expert supervision of the Neurosurgery Department.
The procedure involved the following steps:
- Patient Positioning and Preparation: The patient was placed in the prone position under general anaesthesia. The surgical site was cleaned and draped using strict aseptic precautions to maintain sterility throughout the procedure.
- Incision and Exposure: A midline vertical skin incision was made over the cervical spine. The paraspinal muscles were carefully dissected and retracted to expose the spinous processes and laminae of the C4 and C5 vertebrae.
- Decompression: A laminectomy was performed at the C4 and C5 levels. Undercutting of the C6 lamina was also carried out. The ligamentum flavum was removed to ensure complete decompression of the spinal cord.
- Hemostasis and Drain Placement: Hemostasis was meticulously secured using standard surgical techniques. A drain was placed in the surgical field to prevent postoperative collection of fluids.
- Wound Closure and Recovery: The wound was closed in anatomical layers. Following the procedure, the patient was shifted to the recovery room in a hemodynamically stable condition.
Postoperative Care
The postoperative period was uneventful. The patient was initially monitored overnight in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and later shifted to a regular ward. Intravenous antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, analgesics, and other supportive treatments were administered as needed. The Foley catheter was removed on postoperative day one, and the surgical drain was removed on postoperative day two. The patient remained stable throughout the postoperative stay, showing significant symptomatic improvement. He was discharged in a hemodynamically stable condition with detailed instructions for post-discharge care and scheduled follow-up.
Discharge Medications
The patient was discharged with a prescription for antibiotics to prevent postoperative infections and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to manage pain and inflammation. Medications for neuropathic pain were included to alleviate nerve-related symptoms. Proton pump inhibitors were prescribed to protect the gastrointestinal tract, while vitamin supplements were advised to support overall recovery and general health. Immunomodulatory agents were also recommended to promote healing and enhance the immune response. Additionally, the patient was advised to use an antiseptic shampoo to maintain wound hygiene and prevent infection.
Advice on Discharge
The patient was advised to wear the neck collar continuously to ensure cervical stability throughout the recovery period. Diabetic medications were advised to continue as prescribed. Strenuous activities must be avoided to prevent stress on the surgical site. The patient was allowed to perform daily activities and may climb stairs as tolerated. The surgical area needs to be cleaned daily with chlorhexidine shampoo to maintain hygiene and prevent infection. Additionally, the patient needs to follow a diabetic diet to effectively manage blood glucose levels.
Dietary Advice
A soft diet was suggested to ease digestion and promote healing.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms such as fever, wound discharge, neck pain, vomiting, severe headache, or weakness of limbs.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to follow up with the Neurosurgeon in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals after 2 weeks to review his condition.
Conclusion
This case highlights the successful management of cervical canal stenosis with myelopathy through cervical laminectomy. The patient showed significant symptomatic improvement with an uneventful postoperative course. With appropriate medical care and adherence to postoperative instructions, a favourable recovery is anticipated. Regular follow-up will ensure continued progress and timely management of any complications.
Enhancing Neurological Recovery with Timely Surgical Intervention
Prompt diagnosis and early surgical intervention in spinal conditions like cervical stenosis are essential to prevent permanent nerve damage and improve neurological outcomes. Procedures such as laminectomy relieve spinal cord compression, reducing symptoms and halting disease progression. Early surgery, combined with close postoperative monitoring, minimises complications and supports faster recovery.
A neurosurgeon/neurosurgery doctor plays a critical role in ensuring that surgical and postoperative care are tailored to each patient’s needs. Rehabilitation and patient adherence to therapy further enhance functional restoration and mobility. A comprehensive, patient-focused approach ensures better long-term quality of life by maximising neurological restoration and minimising disability.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868