Hepatitis - Types, Causes, Symptoms, Risk factors, and Prevention
PACE Hospitals
What is Hepatitis?
Inflammation of the liver is known as hepatitis. It can either resolve on its own or advance to fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. While hepatic viruses are the primary causes worldwide, other factors such as toxic substances and other causes (like autoimmune diseases) can also lead to hepatitis.
Hepatitis may show mild or no symptoms in many cases but can result in serious health complications. Clinical presentations of hepatitis A, B, and C may include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, dark urine, and jaundice. Chronic hepatitis B and C infections could lead to liver cancer and cirrhosis, which can be life-threatening.
Hepatitis D (HDV) affects only those already infected with hepatitis B and can result in more severe outcomes, such as faster development of cirrhosis, although chronic hepatitis D is uncommon.
Hepatitis E (HEV) begins with mild symptoms like fever, reduced appetite, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. It can progress to jaundice, dark urine, pale stools and, in some cases, acute liver failure.
Hepatitis meaning
The term hepatitis is derived from the Greek word ‘hepar’, which means liver and, ‘+itis’ means inflammation.
Prevalence of hepatitis
Hepatitis prevalence worldwide
Viral hepatitis is a significant public health issue of the current decade, as evidenced by data from 187 countries by World Health Organization. New data shows that the estimated deaths due to viral hepatitis have increased from 0.11 crore in 2019 to 0.13 crore in 2022. Of these 0.13 crore, 83% are caused by hepatitis B and 17% by hepatitis C. Every day, more than 6000 people are newly infected and 3500 people die due to hepatitis B and C infections.
The latest World Health Organization estimates show that hepatitis B affects 25.4 crore individuals, while hepatitis C affects 5 crores. In the majority of chronic hepatitis B and C cases, about 50% occur in individuals aged 30–54 and 12% in children under 18. Men make up 58% of all reported cases.
However, the overall number of people infected with hepatitis has increased from 2019 to 2022, but the number of newly infected people has decreased from 0.25 crore in 2019 to 0.22 crore in 2022.
Hepatitis prevalence in India
India has encountered the world’s 2nd highest prevalence of hepatitis, with over 11% of the global burden. In 2022, of the 25.4 crore individuals with hepatitis B, 2.9 crore are Indians and of the 5 crore individuals with hepatitis C, 0.55 crore are Indians.
According to the reports, diagnosis of viral hepatitis is also inadequate in India. Only 2.4% of hepatitis B and 28% of hepatitis C cases were diagnosed.

Types of hepatitis
Hepatitis is categorized into different types based on different considerations. As per the duration of the disease, associated symptoms and treatment approaches, hepatitis is categorized into the following types:
Acute hepatitis
- Acute hepatitis usually lasts for less than six months and often resolves on its own.
- Viral infection, autoimmune disease, or adverse reactions to medication typically cause acute hepatitis.
- It is characterized by significant damage and cell death in the liver.
- Under a microscope, it shows disorganized liver structure and varying degrees of liver cell death.
Chronic hepatitis:
- Elevated liver enzymes persist for more than six months in chronic hepatitis.
- This type involves ongoing, worsening inflammation and damage to liver cells.
- Under a microscope, it shows ongoing inflammation around the portal areas of the liver.
Fulminant hepatitis:
- Fulminant hepatitis is a rare syndrome, combining a massive necrosis (cell death) of hepatic parenchyma and a decrease in liver size.
- It occurs during infection with certain hepatitis viruses, in the case of toxicity or drug.
- The hepatitis B virus is sometimes responsible for fulminant hepatitis. Up to 50% of fulminating hepatitis B implies co-infection with the hepatitis D virus.
Hepatitis causes
Hepatitis is caused by various infectious viruses and non-infectious agents, leading to various lethal complications. Different causes of hepatitis are listed below:
Infectious causes
- Hepatotropic viruses: Hepatitis A Virus (HAV), hepatitis B Virus (HBV), hepatitis C Virus (HCV), hepatitis D Virus (HDV), hepatitis E Virus (HEV).
- Non hepatotropic virus: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), herpes simplex virus (HSV), coxsackievirus, adenovirus, dengue virus, coronavirus-19(COVID-19)
- Bacteria, fungi, and parasites
Toxin causes include:
- Alcohol-related: Fatty liver disease, acute alcoholic hepatitis, or alcoholic cirrhosis.
- Drugs and toxins
- Dose-dependent
- Non-dose-dependent
- Other toxins (mushroom, herbal and dietary supplements, carbon tetrachloride, sea anemone sting).
Immunologic or inflammatory conditions: Autoimmune hepatitis, biliary disease such as primary biliary cholangitis or primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Other conditions causing hepatitis
- Metabolic or hereditary: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease.
- Pregnancy-related: Preeclampsia, acute fatty liver of pregnancy.
- Ischemic and vascular: Cardiogenic shock, hypotension, heatstroke, cocaine, methamphetamine, ephedrine, Budd-Chiari syndrome, sinusoidal obstruction syndrome.
- Miscellaneous: Acute fatty liver of pregnancy, malignancy, eclampsia, HELLP syndrome, Reye' syndrome, primary graft non-function after liver transplantation.
Infectious hepatitis causes
Viral hepatitis is a condition caused by a virus that affects the liver (hepatotropic viruses). There are five main viruses causing viral hepatitis: A, B, C, D, and E, this sometimes causes liver cirrhosis or cancer.
| TYPES | VIRUS | TRANSMISSION | INCUBATION PERIOD | VACCINE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis A | Hepatitis A virus (HAV) | Contaminated food and water | 14 to 49 days (avg. 28 days) | Hepatitis A vaccine (after 1 year) |
| Hepatitis B | Hepatitis B virus (HBV) | From human to humans during sex, contact with blood or contaminated objects | 30-180 days (avg. 75days) | Hepatitis B vaccine (within 24 hours) |
| Hepatitis C | Hepatitis C virus (HCV) | On contamination with infected blood | 15-150 days | No vaccine |
| Hepatitis D | Hepatitis D virus (HDV) | There can be no hepatitis D if there has been no infection with hepatitis B before. | 21 to 49 days (app. 35 days) | No vaccine. |
| Hepatitis E | Hepatitis E virus (HEV) | From animals to humans, mainly by eating raw or uncooked pork. | 14 to 70 days (avg. 45 days) | Vaccine available only in China |
Toxin causes
The liver processes everything entering the bloodstream, breaking down chemicals and drugs to remove them from your body. The liver processes substances from food and medications, transforming them for elimination. Occasionally, this process generates harmful byproducts that can harm the liver.
Medications: Many medications can cause liver toxicity, which is often detected through blood tests. Most issues are mild and can be resolved by adjusting or stopping the medication. Rarely, some people have a severe reaction where liver cells are rapidly destroyed, leading to liver failure. These patients must stop the medication immediately and may need liver transplantation as a life-saving treatment.
Herbs and nutrient supplements: Certain herbs and supplements are not exposed to regulatory testing like conventional drugs. These may contain certain impurities like steroids or antibiotics, which can cause liver damage. Individuals with liver diseases must consider avoiding these without a doctor’s approval.
Alcohol abuse: Alcohol abuse is widely known and proven to cause liver injury, but the extent of damage depends on the amount of the alcohol consumption and genetic factors. People prone to liver damage because of genetics are more likely to develop acute liver injury, which is fatal and needs hospitalization. Others may develop progressive damage on heavy use.
Occupational hazard: Occupational activities can cause abnormalities in liver function tests without any symptoms suggestive of liver disease. Taking this into account, collecting complete history is essential. The History collection needs to include the time of exposure, duration of exposure and other chronic diseases associated with liver damage.
Immunological causes
Autoimmune hepatitis is a non-contagious, progressive and chronic inflammatory liver disease where one’s immune system attacks the liver cells with an unclear cause. Failure in the immune system, genetic predisposition, and environmental triggers are known to cause autoimmune hepatitis.
Other autoimmune diseases are frequently linked to the illness, but chronic viral infection, alcohol consumption, or exposure to hepatotoxic medications or chemicals do not account for autoimmune hepatitis.
It is categorized into two types, Type1 and Type2 based on the type of antibodies present.
Hepatitis risk factors
Risk factors vary for different causes of hepatitis. Various health, environmental, and behavioral factors increase the risk of hepatitis. The risk of alcoholic hepatitis increases in people consuming alcohol for a long time.
Risk factors raising the chance of hepatitis include:
- Genetics: Patients having a family history of hepatitis are more susceptible.
- Gender: Females are more prone than males.
- Infections:
- Linked to having hepatic infections
- Unhygienic lifestyle habits
- Sexual relation with someone having hepatitis
- Sharing used injectables
- Travelling to endemic countries
- Having diseases like sexually transmitted diseases and liver diseases.
- Other autoimmune diseases: Thyroiditis, grave's disease, type 1 diabetes, hemolytic anemia, immune thrombocytopenia, celiac disease, and ulcerative colitis.
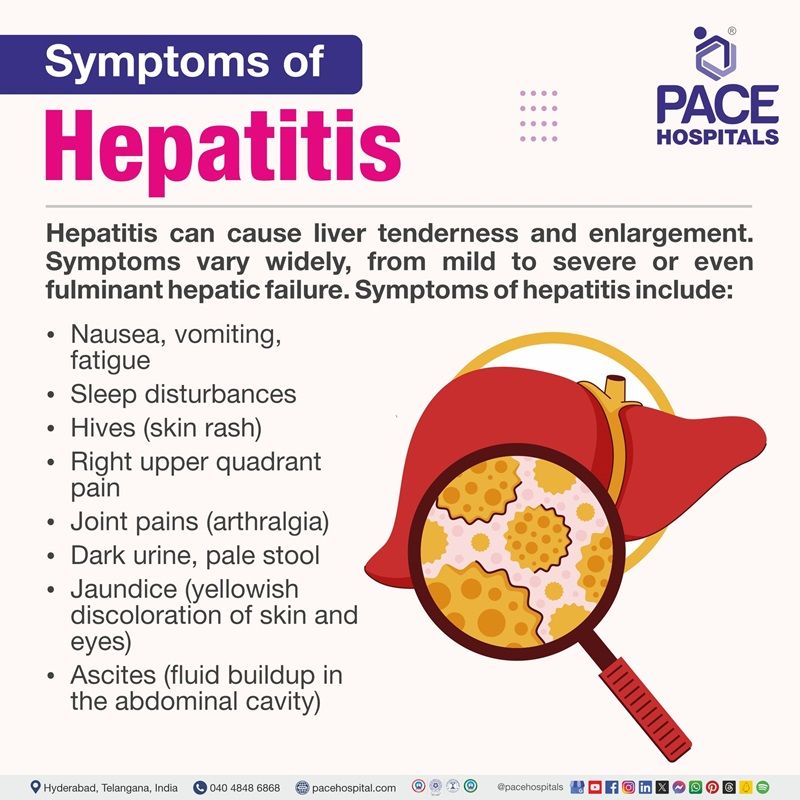
Hepatitis symptoms
The liver may be tender and enlarged in hepatitis. Signs and symptoms of infectious hepatitis vary from person to person and virus-causing infection. Upon presentation, some patients may exhibit no or only mild symptoms. In contrast, others may rapidly develop fulminant hepatic failure (FHF). Symptoms of hepatitis include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dysgeusia (changes in taste)
- Symptoms of dehydration
- Sleep disturbances
- Hives (skin rash)
- Itching
- Right upper quadrant pain
- Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
- Extreme tiredness (fatigue)
- Malaise (feeling of discomfort)
- Joint pains (arthralgia)
- Dark urine
- Anorexia (loss of appetite)
- Pale stools
- Rectal bleeding
- Jaundice (yellowish discoloration of skin and eyes)
- Ascites (fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity)
- Hepatic encephalopathy (brain dysfunction caused by liver dysfunction)
- Variceal hemorrhage (bleeding from abnormally dilated veins)
- Splenomegaly (inflammation of the spleen)
- Spider angioma (spider blood vessels in the skin)
Complication of hepatitis
The consequences of acute hepatitis are typically not persistent. However, chronic hepatitis can lead to more severe complications. Certain supplements and medications can also complicate hepatitis. Consulting a general physician before taking medicine is beneficial. Below are the complications of hepatitis:
- Chronic liver diseases (like liver abscess)
- Acute or subacute hepatic necrosis (cell death)
- Liver cirrhosis (scarring of liver tissue)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (cancer in the liver cells)
- Liver failure
- Bleeding disorders
- Ascites (buildup of fluid in the abdomen)
- Portal hypertension (increased blood pressure in the portal veins)
- Kidney failure
- Esophageal varices (enlarged veins in the esophagus)
- Liver cancer
Hepatitis diagnosis
The initial presentation of symptoms of hepatitis varies based on the individual and the stage of the disease. On suspicion of hepatitis based on presentation, a hepatologist or gastroenterologist suggests further tests. All the parameters considered for diagnosis of hepatitis are listed below:
- Physical examination: It may vary depending on the patient and the stage of disease. The severity of the disease can be assessed depending on the symptoms.
- Laboratory findings
- Complete blood picture (CBP): Checks for an increase in the number of white blood cells and a decrease in the number of red blood cells.
- Liver function test: Checks for increased alkaline phosphate, bilirubin, creatinine, PT, INR, and changes in liver enzymes.
- Autoimmune antibodies test: It includes detecting anti-liver kidney microsome type 1 antibody (anti- LKM-1), anti-nuclear antibody (ANA), anti-smooth muscle antibody (SMA) and serum IgG.
- Imaging tests
- Computed tomography: It can show detailed images of body parts.
- Ultrasound: Create a picture of organs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging: Detailed picture of organ and its structure.
- Liver biopsy: Tissue sample of the organ is tested.
Hepatitis treatment
The treatment for hepatitis is determined by the type of hepatitis. Acute hepatitis may resolve on its own, and adequate rest and fluids can help you feel better. Various medications are available to treat different chronic types of hepatitis. Surgery and other medical procedures may also be considered as potential treatments.
Infectious hepatitis treatment
General management of viral hepatitis is a supportive treatment. Efforts must be made to prevent the spread of infection and to avoid potentially hepatotoxic substances. Symptomatic treatment is recommended based on the individual symptoms and their severity. Treatment is performed based on the infection causing organism includes:
- Hepatitis A: Supportive therapy, no antiviral therapy is present.
- Hepatitis B: Acute- supportive therapy, nucleoside or nucleotide analogs, Chronic- nucleoside or nucleotide analogs, pegylated interferon.
- Hepatitis C: Acute and chronic-nucleoside or nucleotide analogs, pegylated interferon, the second generation of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agents.
- Hepatitis D: Pegylated interferon.
- Hepatitis E: Pegylated interferon.
Treatment of hepatitis caused by toxins
Identifying and removing the substance (medications, herbs, alcohol) causing toxic hepatitis is the first and most crucial step in treatment. For alcohol-related liver damage, it is strongly advised and may be necessary to participate in programs like Alcoholics Anonymous and seek treatment and rehabilitation. Alcoholism is a severe addiction, and without proper treatment and support systems, individuals often face recurrence and resume drinking.
Treatment for autoimmune cause of hepatitis
Timely detection and treatment are essential for controlling autoimmune hepatitis and achieving a state where symptoms are reduced or absent, known as remission. The duration of remission may vary from months to years, and some individuals may need lifelong treatment.
- Symptoms and liver damage can be managed with corticosteroids and immune suppressors.
- Liver transplantation is necessary in severe cases of liver failure.
- Getting vaccinated is important for preventing complications of liver disease.
Hepatitis prevention
Prevention of viral hepatitis contributes to a wide range of health outcomes, and it includes the following measures:
- Vaccination should be prioritized.
- Precautions must be taken to ensure the safety of injections, blood transfusions, and surgical procedures.
- Take measures to prevent HBV transmission from mother to child.
- It is also essential to maintain high standards of sanitation and ensure access to safe food and water to prevent and manage epidemics.
- Provide treatment for chronic HBV and HCV infections as part of efforts in secondary and tertiary prevention.
Identifying and eliminating the use of hepatotoxic substances is key preventive measure for toxic hepatitis. Alcoholic hepatitis can be prevented by avoiding the consumption of alcohol. Autoimmune hepatitis can be prevented by monitoring and treating the risk factors leading to hepatitis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Hepatitis
Which hepatitis is more dangerous?
Both hepatitis B and C are more dangerous and most frequently seen. A vaccine can prevent the Hepatitis B virus, whereas a vaccine is not available for hepatitis C. Transmission of hepatitis B is more accessible than that of hepatitis C.
Is hepatitis contagious?
Transmission of hepatitis depends on the type of hepatitis. Viral hepatitis is contagious, whereas toxic and autoimmune hepatitis are not. In viral hepatitis, the scale of transmission also depends on the type of hepatitis virus.
Can hepatitis B be transmitted through saliva and sweat?
Yes, the hepatitis B virus can spread through saliva, sweat and body fluids. Thus, HBV vaccination is recommended for sports players and people working in direct patient care sector.
Can hepatitis be cured?
Hepatitis A and E typically result in recovery without the need for treatment. In contrast, hepatitis B, C, and D can lead to chronic infection, potentially resulting in liver cancer or cirrhosis. However, early detection allows for effective treatment.
Is jaundice and hepatitis the same?
No, hepatitis and jaundice are not the same. Jaundice is a symptom of hepatitis, which is inflammation of the liver. In contrast, jaundice is an increase in bilirubin levels in the blood, which shows yellowing of the skin and eyes.
How is hepatitis transmitted?
The virus is mainly transmitted when a person who is not infected (and has not been vaccinated) consumes food or water that has been contaminated. The illness is strongly linked to unsafe food or water, insufficient sanitation, inadequate personal hygiene, oral-anal intercourse and mother to child during pregnancy.
What is the best food for hepatitis patients?
Whole foods such as fresh vegetables, fruits, whole grains, plant-based proteins (such as tofu, legumes, and peanuts), fish, and lean meats are best for hepatitis. Staying away from processed foods and restricting the intake of foods containing added sugar can help.
What is the HBsAg test?
If the HBsAg test result is "positive" or "reactive", it indicates that the individual has hepatitis B infection. This test can be used to identify the existence of HBV in the bloodstream.
Does sleep help repair the liver?
During sleep, our bodies are actively engaged in cell repair and eliminating toxins, with the liver being a crucial player in this process. Insufficient sleep can disrupt these functions, resulting in elevated toxin levels and placing additional strain on the liver.
Is hepatitis a waterborne disease?
Yes, Hepatitis A virus and Hepatitis E virus are transmitted through the fecal-oral route. These are spread by water and food as media for the transmission of virus.
Which hepatitis is lifelong?
After being diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B, the virus will likely remain in your blood and liver indefinitely. It's crucial to understand that an infected person can transmit the virus to others, even if the person does not experience any symptoms.
How long does hepatitis immunity last?
People who have received all three vaccine doses do not need booster shots. The hepatitis B vaccine provides protection for a minimum of 20 years and likely for a lifetime.
Which hepatitis is mostly asymptomatic?
Chronic hepatitis B poses a risk because it often goes undetected with no symptoms, and liver enzyme blood tests may show expected results. When symptoms like abdominal pain or abdominal swelling arise, it is frequently too late for effective treatment.
Can hepatitis affect the brain?
The nervous system can be impacted by hepatitis viruses, which can affect the brain, spinal cord, motor neurons, peripheral nerves, and muscles. Peripheral neuropathy is the primary neurological effect of hepatitis C virus and hepatitis B virus. Many individuals with chronic hepatitis C virus may undergo cognitive impairment even without advanced liver disease.
When was hepatitis b vaccine introduced in India?
Hepatitis B vaccine was introduced as a part of immunization program in 2002-03 on pilot basis and expanded in entire country by 2010 to protect children from liver diseases. It is now given as pentavalent vaccine to children.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles