Liver Failure - Symptoms, Causes, Types, Prevention, Treatment
Pace Hospitals
Liver failure, in other medical term known as hepatic failure, is the damage that causes the liver to lose its ability to function. Liver failure may be presented as acute liver failure that occur fast, sometimes within days or weeks and chronic liver failure which may occur gradually over several months or years and acute on chronic liver failure which is seen in patients who already have chronic liver disease, that is characterized by abrupt hepatic decompensation.
As it is a Life-threatening condition and as well as the last phase of a lot of liver diseases, it requires immediate medical attention. Hepatologist may perform an assessment to determine the history of drug use, exposure to toxins, and evaluate signs of liver cell failure and hepatitis if symptoms such as jaundice (yellowish discoloration of eyes) abdominal pain, fatigue are present.
Liver is the largest organ in the body that is situated in the top right-hand corner of the abdomen which involves many vital functions such as creating the necessary bodily fluids, storing energy, and eliminating dangerous compounds from the blood etc.
Liver failure definition
Liver failure is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the liver is unable to process waste materials and poisons, which builds up in the body. Numerous factors, such as viral infections, binge drinking, drug toxicity, or underlying medical disorders, might cause it.
Liver failure Meaning
Hepatic failure is the combination of 2 words in which
- ‘hepatic’ is a latin word which is used to describe ‘liver’
- ‘failure' is an Anglo-French word which means ‘be lacking’ or ‘not succeed'
Liver failure prevalence
Prevalence of acute liver failure
With a frequency of 1–8 instances per million people, Acute liver failure is a rare disorder that accounts for 6% of liver disease-related deaths and up to 7–8% of liver transplants. Acute liver failure mostly strikes young adults, with a 35–45-year-old peak. About 60% of instances involve women.
Prevalence of chronic liver failure
It is estimated that 1.5 billion cases of chronic liver failure are thought to exist globally, encompassing all stages of the disease's severity. It is demonstrated that age-standardized chronic liver failure and cirrhosis incidence is 20.7/100,000, with an increase of 13% incidence since the year 2000.
Prevalence of acute on chronic liver failure
With a prevalence rate of 20–35% in-risk populations, it is a significant medical issue on a global scale. Globally, 35% of patients with decompensated cirrhosis are found to have acute on chronic liver failure in which South Asia has the highest prevalence, with 65%.
Prevalence of liver failure in India
An estimated 7–12,000 people in India are anticipated to have liver failure annually, of which 1200–2000 have the severity to require liver transplantation. That means that this illness destroys the lives of four to five people every day.
A 2020 World Health Organization (WHO) report states that approximately 3 lakh Indians lose their lives to liver disease annually, accounting for 3.17% of total deaths. India at the moment ranks 83rd in the world with an age-adjusted mortality rate of 22.24 per 1 lakh people. Of the 20 lakhs liver-related deaths worldwide each year, 18.3% occur in India.

Types of liver failure
There are three types of liver failure namely
- Acute liver failure
- Chronic liver failure
- Acute on chronic liver failure
Acute liver failure
Acute liver failure is an uncommon liver disorder that is characterized by sudden and rapid loss of liver function.
Chronic liver failure
Chronic liver failure develops over time due to liver damage that may be caused by various reasons which make liver stop working completely. Chronic liver failure also known as end stage liver disease or decompensated liver cirrhosis.
Acute on chronic liver failure
Patients with pre-existing chronic liver disease may have abrupt hepatic decompensation, a clinical phenomenon known as acute on chronic liver failure. Acute on chronic liver failure is linked to one or more extrahepatic organ failures as well as higher mortality.
Liver failure symptoms
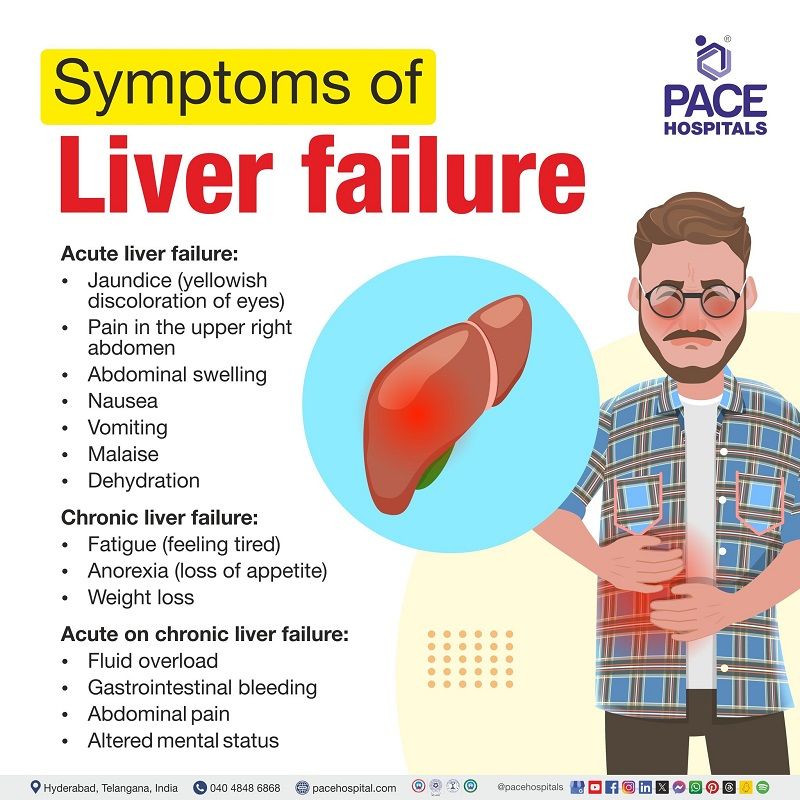
Symptoms related to acute liver failure
The reasons for acute liver failure and the length of time that has passed from the disease's beginning stage will determine the clinical appearance. Acute liver failure symptoms and signs may include the following:
- Jaundice (yellowish discoloration of eyes)
- Pain in the upper right abdomen
- Abdominal swelling
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Malaise
- Dehydration
Symptoms related to chronic liver failure
Depending on the condition the patient has developed, signs and symptoms of chronic liver failure may be non-specific which may include:
- Fatigue (feeling tired)
- Anorexia (loss of appetite)
- Weight loss
Symptoms related to acute on chronic liver failure
- Fluid overload
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Abdominal pain
- Altered mental status
Causes of liver failure
Acute liver failure causes
Although there are several reasons for acute liver failure, The two most frequent causes of acute liver failure globally are:
- Drug-induced hepatitis
- Viral hepatitis
However acute liver failure from hepatitis C is uncommon. Acute liver failure can occur when hepatitis D co-infects or superinfects with the hepatitis B virus.
Metabolic reasons of acute liver failure
- Alpha1-antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency (hereditary disorder brought on by insufficient hepatic synthesis of AAT, a protein that shields the liver and lungs from harm.
- Fructose intolerance (inability of digestive system to absorb fructose)
- Galactosemia (disorder that affects galactose metabolism)
- Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency (disorder that impair cholesterol metabolism)
- Reye syndrome (a condition that affects liver following a viral infection)
- Tyrosinemia (impaired tyrosine metabolism)
- Wilson disease (genetic disorder which that predominantly effects liver due to copper accumulation)
Vascular reasons of acute liver failure
- ischemic hepatitis (inflammation of liver with unknown reason)
- Hepatic vein thrombosis (blockage in the hepatic veins)
- Portal vein thrombosis (blockage in the portal vein that carries blood to liver from intestines)
- Hepatic arterial thrombosis (blood clot in the hepatic arteries)
Cancers
Cancers that lead to liver failure include:
- Primary liver cancers such as hepatocellular carcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma etc
- Secondary cancers such as breast and lung cancer invasion from adenocarcinoma may lead to liver failure.
Toxins induced liver failure
Liver failure may be brought on due to toxins such as:
- Bacillus cereus toxin
- Cyanobacteria toxin
Miscellaneous causes
- Adult-onset Still disease (a rare inflammatory disorder)
- Heatstroke
- Primary graft nonfunction in liver transplant recipients (The need for emergent re-transplant when a graft fails to show initial function after liver transplantation
Chronic liver failure causes
Most frequent causes
- Alcohol-associated liver disease, which is the result of excessive alcohol consumption harming the liver's ability to function
- Chronic infection with hepatitis viruses
- Accumulation of fat in the liver
Not everyone is impacted by these medical issues in the same manner. There may be differences in the amount of liver damage amongst individuals with these disorders. Based on research, the degree of liver damage caused by various disorders may be influenced by specific inherited genes.
Less frequent causes
- Autoimmune hepatitis in which body’s immune system affects liver
- Inherited liver disorders
- Persistent heart failure accompanied by hepatic congestion, a disorder where the liver's blood flow is slowed.
- Abnormalities which cause damage to the bile ducts such as cholangitis etc
- Chronic use of certain medications
- Frequent use of larger amounts of vitamin A
Acute on chronic liver failure causes
The cause of acute on chronic liver failure is thought to have originated from a trigger event in the setting of an underlying liver disease. Alcohol-related injuries, drug-induced liver injuries, viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, and E), hypoxia injuries, and liver procedures, such as the implantation of a trans jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS), are examples of hepatic (liver) causes. The two main extra-hepatic causes are major surgery and bacterial infections. Between 40 and 50 percent of patients are said to have an undiagnosed triggering incident that leads to acute on chronic liver failure.
Liver failure risk factors
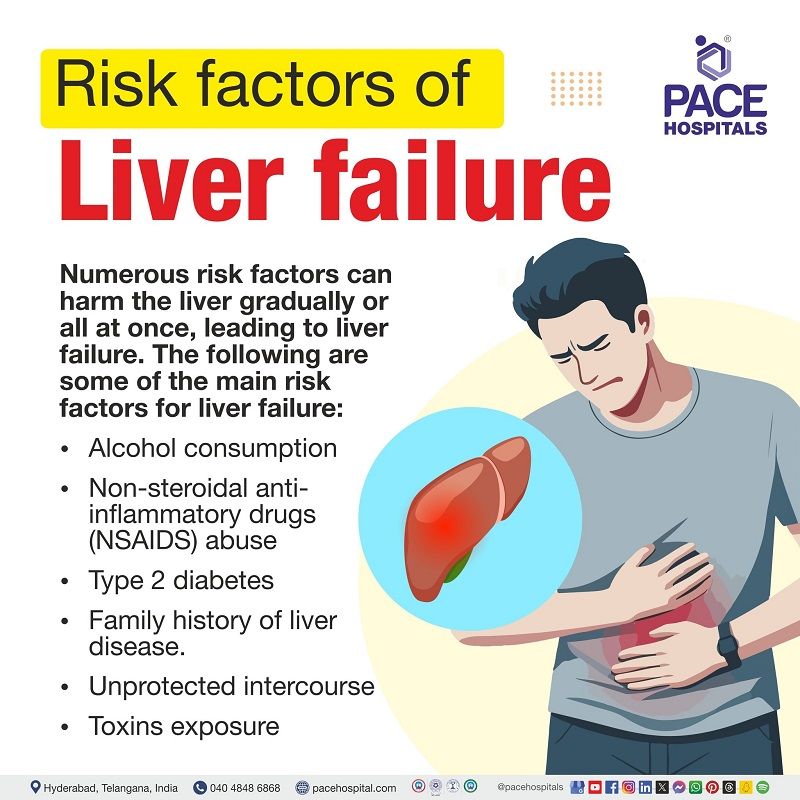
Numerous risk factors can harm the liver gradually or all at once, leading to liver failure. The following are some of the main risk factors for liver failure:
- Alcohol consumption: Chronic alcohol misuse can result in alcoholic liver disease, which can eventually lead to liver failure.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) abuse: Many cases of acute liver failure are caused by excessive NSAIDS use. NSAIDs are painkillers that can be found in a lot of prescription and over-the-counter medications.
- Type 2 diabetes: Numerous liver conditions, such as increased liver enzymes, fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and acute liver failure, are linked to type 2 diabetes.
- Family history of liver disease: There might be more susceptibility to liver issues if a family members has a history of liver disease. Genetic liver illness, such as hemochromatosis, Wilson disease, or alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency has the potential to cause liver failure, so it is highly recommended to check out for symptoms if there is a positive family history.
- Unprotected intercourse: The risk of infectious agent transmission was found to be higher in cases of repeated unprotected intercourse. Sexual transmission is the primary means of transmission for hepatitis B virus among the various forms of infectious hepatitis, which cause immense liver damage.
- Toxins exposure: According to a research, exposure to organic solvents may cause liver damage. Since the liver is the place where most chemical substances are metabolised, it could lead to liver damage due to hepatic toxins produced during the chemical substance breakdown.
Liver failure complications
Whether acute, or chronic, or acute on chronic liver failure can result in several hazardous complications. The following are a few of the most typical complications of liver failure:
- Variceal bleeding (bleeding from enlarged veins predominantly in oesophagus)
- Ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen)
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (bacterial infection in the membrane that lines abdominal cavity)
- Hepatic encephalopathy (brain disorder that occur due to liver failure)
- Hepatorenal syndrome (kidney failure due to liver failure)
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome (dilated blood vessels in the lungs due to liver failure)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
- Cerebral oedema (brain swelling)
- Hepatitis-associated aplastic anaemia (bone marrow failure due to hepatitis)
- Electrolytes and acid-base imbalance
- Pulmonary oedema (fluid accumulation in the lungs)
- Concomitant bacterial and fungal infections
Liver failure prevention
Choosing a healthier way of living
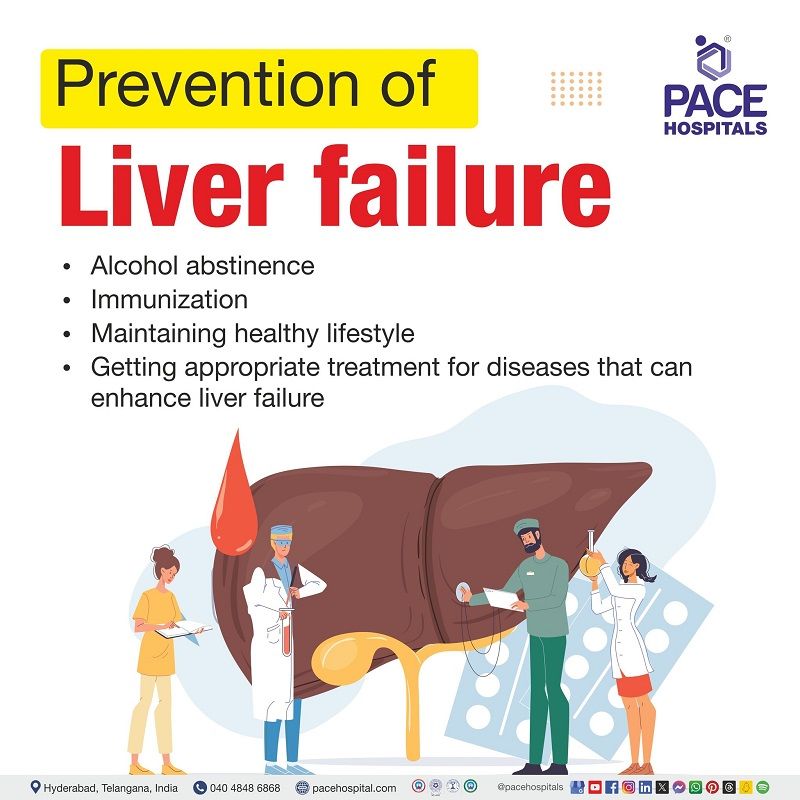
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle reduces risk of liver disease and maximizes the function of liver. Suggestions for leading a healthy lifestyle may include:
- Keeping a healthy weight
- Maintaining a nutritious diet
- Regular exercise and staying away from alcohol, which causes liver to work harder to function
- Taking only the necessary amount of medication and closely adhering to dosage guidelines
Enhancing Treatment for Diseases That May Cause Liver Disease
In case of any underlying medical condition or liver disease it's critical to adhere to care guidelines and do regular follow-up with a hepatologist. Ensuring the best possible care is particularly crucial against conditions like:
- Diabetes (increased blood glucose)
- Hepatitis B (viral infection of liver by Hepatitis B virus)
- Hepatitis C (viral infection of liver by Hepatitis C virus)
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Cystic fibrosis (genetic disorder that damages lungs and digestive system)
Risk factors management
- Alcohol abstinence: More than four drinks (48 g) of alcohol per day are linked to a higher risk of liver cancer, cirrhosis, and early mortality. Strict abstinence of alcohol may help prevent occurrence of liver diseases.
- Immunization:
when severe, acute liver may lead to liver failure, so it is highly recommended that all the infants and adults should vaccinate against hepatitis viruses especially against hepatitis b.
Diagnosis of liver failure
Acute liver failure
Acute liver failure diagnosis involves history, physical examination, laboratory tests, abdominal imaging, prior jaundice episodes, medication, alcohol use, family liver disease history, and risk factors for viral hepatitis.
Laboratory tests: To determine the cause and assess the severity, below mentioned laboratory tests are necessary.
- Prothrombin time test
- Liver function test
- Kidney function test
- Metabolic panel test
- Complete blood picture
- Viral hepatitis serology
- HIV (human immune deficiency virus) serology
- Autoimmune markers
- Arterial blood gas
- Level of NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) in the blood
Abdominal imaging
- Ultrasonography
Other tests
- Ceruloplasmin test in patients with suspected Wilson’s disease
- Hepatologist may advice hepatitis b virus anti-hepatitis D virus antibodies from individuals who have either acute or chronic hepatitis. Antibodies against the hepatitis E virus are also tested if there is a history of travel to endemic regions.
Chronic liver failure
- Liver function test
- Bilirubin testSerum albumin
- Ultrasound abdomen
- Computed tomography
- Transient elastography
- Wedge hepatic venous pressure
- Doppler scan
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- An upper endoscopy
- A liver biopsy
Acute on chronic liver failure
Since acute on chronic liver failure is often associated with extra hepatic organ damage, imaging tests may be necessary to confirm infection, organ involvement, or organ failure, as well as to support the findings of the clinical examination.
This type of liver failure may require diagnostic tests such as:
- Abdominal, chest, and brain imaging
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans of various organs
- Abdominal sonogram with Doppler
Liver failure treatment
Liver failure is a complex syndrome requiring intensive care, liver transplant facilities, and prompt treatment, along with diagnostic workup, to prevent complications. Depending on the cause, liver failure can be treated by:
Medications
- Antidote for NSAIDS overdose
- Antivirals for hepatitis viruses induced liver failure
- Steroids for autoimmune induced liver failure
- Antibiotics for mushroom poisoning
Surgical interventions
- Liver transplant
- Endoscopic band ligation and injection sclerotherapy
- Trans jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
Difference between liver failure and liver cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis vs liver failure
Although both liver cirrhosis and liver failure are significant liver diseases, they differ in their aetiology, symptoms, and prognosis etc.
| Parameter | Liver failure | Liver cirrhosis |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | collapse or shutdown of the liver. | late stage of liver disease associated with significant scarring |
| Causes | Numerous factors, such as poisons, infections, acute injury, or long-term illnesses | chronic fibrosis, nodules, and inflammation-related liver damage. |
| Symptoms | Organ failure, haemorrhage, disorientation, and jaundice with a rapid onset. | gradual onset of ascites, exhaustion, weight loss, and portal hypertension |
| Liver function | Liver is drastically weakened and is unable to carry out necessary functions. | The liver is scarred yet may be able to perform some functions. |
| Prognosis | This is often life threatening | Patients with cirrhosis can live to some extent |
| Treatment | Liver transplant | Symptomatic treatment, Managing complications and Life style modifications |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Liver Failure
What are the warning symptoms of liver failure?
The warning symptoms of liver failure are:
- Confusion
- Feeling of sleepiness
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Hematemesis (vomiting blood)
- Ascites (build up of fluid in the abdomen)
Can someone really survive liver failure?
Despite injury or even if a part of the liver is removed, it can continue to function. Nevertheless patients won't be able to survive more than a day or two days without emergency treatment, if the liver starts to fully shut down.
How does liver failure affect the body?
In case of liver failure, the body may experience complications such as bacterial infections, low blood sugar. Another serious consequence of acute liver failure is brain swelling. Additionally frequent complications are disorientation, edema in the abdomen, and irregular bleeding.
Can liver failure cause sudden death?
Yes, liver failure can cause sudden death. Advanced cirrhosis patients often experience infections, hepatic failure, and variceal hemorrhage and even the rate of unexpected deaths is much higher
What is liver failure?
Liver failure is a deadly condition that requires emergency medical treatment or interventions. Liver failure typically develops slowly over a long period of time. It is the final phase of a lot of liver conditions.
Liver failure occurs when significant portions of the liver are irreparably damaged and no longer functional.
What are the phases of liver failure?
Liver failure progress through four stages they are inflammation of the liver, fibrosis or scarring, cirrhosis and end stage liver disease, eventually leading to liver failure.
What is fulminant liver failure?
Fulminant hepatic (liver) failure is also known as acute liver failure. It is a hazardous clinical illness that, in individuals without a history of chronic liver disease, is defined by a substantial reduction in hepatic synthetic function within 28 days after the onset of symptoms and a rapid development of hepatic encephalopathy.
How is liver failure slowed down?
Liver failure can be slowed down by appropriate treatment along with:
- Alcohol abstinence
- Avoiding excess use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
- Getting vaccinated against hepatitis viruses that cause inflammation of liver
- Lifestyle modifications such as, avoiding excess dietary fat and indulging in regular exercise
How quickly can liver failure happen?
Acute hepatic (liver) failure may occur within 48 hours. It's critical to get medical attention as soon as something seems wrong. Fatigue, nausea, diarrhoea, and pain in the area directly behind the ribcage and right side are some possible symptoms.
Does liver failure affect blood sugar?
Yes. Liver failure may cause high blood sugar. It is necessary for the pancreas to release more insulin when liver impairment reduces the liver's ability to respond to insulin. Insulin production by pancreatic cells may eventually become insufficient, resulting in type-2 diabetes.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868