Urinary Incontinence - Symptoms, Causes, Types, Prevention & Treatment
Pace Hospitals
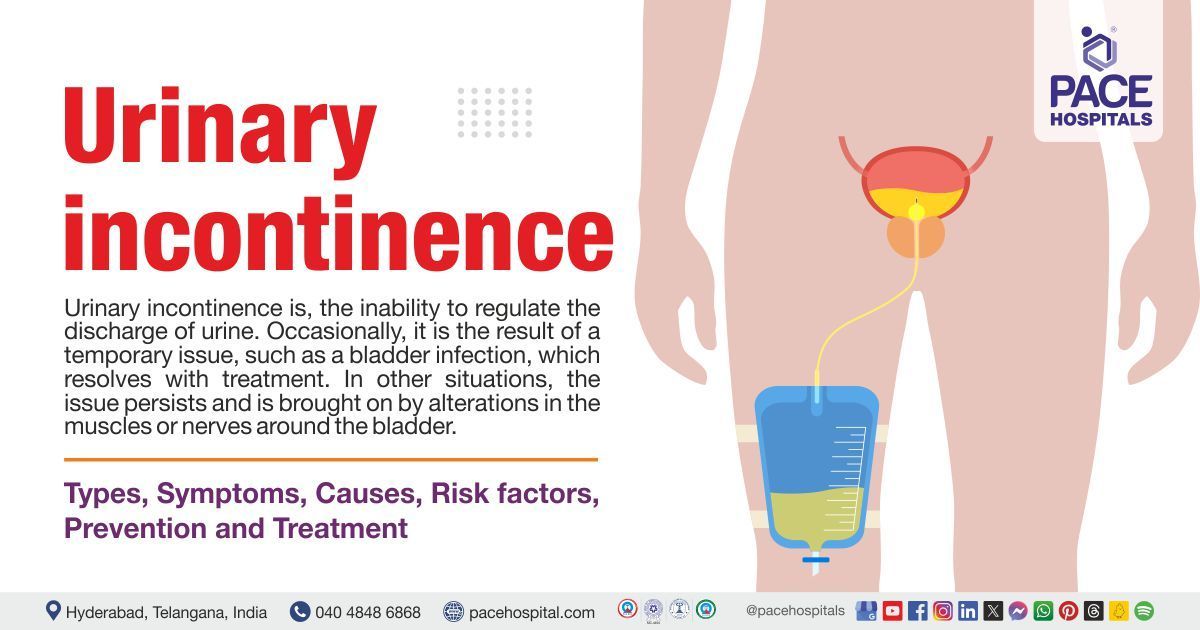
Urinary incontinence is the inability to control one's bladder that causes an involuntary (an action that is not deliberate) flow of urine. It can be brought on by numerous factors, such as weakening of pelvic floor muscles, nerve injury, certain illnesses, or chronic medication use etc.
In medical terminology this condition is also known as enuresis or overactive bladder which is an underdiagnosed and underreported issue that becomes worse with aging. Females are more than twice as likely as males to experience urine incontinence at any age. This condition is said to affect 38–55% of women over 60 and 50–84% of senior citizens.
This condition can be multifactorial which could be a symptom of many underlying diseases and physiological conditions. It is not acceptable to consider incontinence as a side effect of underlying medical issues. With early detection of the underlying problem this condition can be managed effectively by a urologist or a urogynecologist.
If left untreated this condition can cause complications such as sexual dysfunction, urinary tract infections, kidney dysfunction, etc.
Urinary incontinence definition
Urinary incontinence is defined as a condition in which, urine leaks out of the urinary bladder unintentionally making it impossible to carry out daily tasks. People of any age can experience it, although women over 50 are more likely to experience it. World Health Organization has designated this condition as a priority.
Urinary incontinence meaning
Urinary incontinence is the combination of 2 words in which
- ‘Urinary’ is derived from a Latin word ‘urina’ which is used to describe ‘organs involved in the production and secretion of urine’.
- ‘Incontinence’ is taken from the Latin word ‘incontinentia’ which means ‘inability to contain’.
Enuresis meaning
The word ‘enuresis’ is derived from the Greek word ‘enourein’ which means ‘to urinate in’.
Prevalence of urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence is a notable health problem across the globe. It impacts people, both socially and economically. An estimated 42.3 crore adults (20 years of age and older) suffer with some type of urine incontinence world-wide. It is said that up to 7% of children over the age of five, 10-35% of adults, and 50-84% of senior citizens residing in long-term care facilities experience urinary incontinence.
Less men than women globally suffer from urinary incontinence, with 3–11% of males affected compared to 3–17% of women. Men are more likely than women to have urinary incontinence as they age, although the percentage of men who have severe urinary incontinence in their 70s and 80s is still very low.
According to a study conducted by National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2005-2006 found a prevalence of 6.9% for women in the 20–39 age range, 17.2% for women in the 40–59 age range, 23.3% for women in the 60–79 age range, and 31.7% for women over the age of 80.
Prevalence of urinary incontinence in India
Men have often been shown to have a lower frequency of urinary incontinence than women, however, the age-related tendency is similar. According to a comprehensive analysis of 21 research papers, the incidence in young and middle-aged males was 3%–5%, while in elderly men, it was 11%–34%.
Nine population-based door-to-door epidemiological studies conducted in India reveal a prevalence of 10%–42%, with stress urinary incontinence being the most prevalent among Indian women.
Between the third and seventh decades, there was a steady increase in age-adjusted prevalence (5.6%, 14.2%, 27.3%, 34.3%, and 39.0%, respectively).

Types of Urinary incontinence
Based on the description of the urine loss, urinary incontinence is categorized into several types which may include:
- Stress Urinary Incontinence (SUI): This kind of urinary incontinence occurs when there is a physical stressor, including coughing, sneezing, exercising, or engaging in other activities that raise intra-abdominal pressure, and results in urine leakage.
- Urgency incontinence: This is the inability to withhold urine long enough to go to a bathroom. It may be accompanied by a strong, unexpected need to urinate and frequent urination. In addition to being a distinct ailment, it might also be a sign of another illness or condition that needs to be checked out.
- Mixed Urinary Incontinence: This type is the combination of both stress and urgency urinary incontinence.
- Total incontinence: Even throughout the night, total incontinence might result in frequent, large-volume urination. Alternatively, the patient can leak little quantities in between and only pass massive amounts of urine on rare occasions.
- Functional incontinence: This is the result of urine leaking due to physical issues such as arthritis, injuries, or other illnesses that make it difficult to go to the bathroom on time.
- Overflow incontinence: When the amount of urine produced is more than the bladder can contain, leakage happens in this type of urinary incontinence.
- Reflex Urinary Incontinence: leakage resulting from spinal cord injuries or neurological problems that happens suddenly or without the sensation of having to urinate.
- Temporary incontinence: Temporary incontinence, also known as transitory incontinence, is the result of a brief circumstance, such as taking a medication or being unwell and causing leakage.
Urinary incontinence symptoms
Based on the type of urinary incontinence. Each person may, however, experience symptoms in a unique way. Some of the symptoms include:
- Dribbling urine when performing routine tasks like bending, lifting, coughing, or working out
- Having a sudden, intense need to urinate and not being able to hold it inside the bladder
- Urine leakage without warning or urge
- Not being able to get to the toilet in time
- Urine leakage during intercourse
- Nocturnal enuresis (bedwetting during night)
- Sensation of not emptying the bladder completely
- Recurrent infections in the bladder
- Urine leakage that develops or persists after surgery
Urinary incontinence causes
Urinary incontinence can have several causes, each contributing to the illness to a different extent, even in a single patient. Both structural and functional disorders pertaining to the bladder, urethra, ureters, and surrounding connective tissue can contribute to urinary incontinence. Furthermore, in certain instances, a primary causative cause might be an illness affecting the central nervous system (CNS) or spinal cord. Comorbidities related to medicine might also be significant. Lastly, there is a chance that certain instances of urine incontinence are brought on by medication.
Causes of stress incontinence
In case of stress incontinence, the urethra might not be able to remain closed due to damaged urethral sphincter or injured pelvic floor muscles.
These problems could be due to:
- Damage to urethra post vaginal delivery of a baby rather than c-section.
- Increased abdominal pressure due to obesity or pregnancy.
- surgical injury to the bladder or surrounding tissue, such as when the prostate gland or womb are removed.
- neurological diseases including multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease that impact the brain and spinal cord.
- certain diseases of the connective tissue, such Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (a unique set of 13 hereditary diseases that impact the body's connective tissues.)
- chronic use of certain medications
Causes of urge incontinence
In case of urgency continence issues in the detrusor muscles in urinary bladder walls may be the reason for sudden and frequent need to urinate.
The reasons for the issues in the detrusor muscles may include:
- Overconsumption of alcohol and caffeine
- consuming insufficient amounts of fluids which lead to the accumulation of strong, concentrated urine in the bladder, irritating it and producing overactive sensations.
- Constipation
- Urinary tract infections (UTIS)
- Neurological conditions
- Chronic use of certain medications
Causes of overflow incontinence
Overflow incontinence, also known as persistent urine retention, is frequently brought on by bladder blockage or obstruction.
The reasons for bladder obstruction may include:
- Prostate enlargement
- Urinary bladder stones
- Constipation
Causes of total incontinence
Total incontinence is diagnosed when the bladder is completely incapable of holding any urine.
The inability of bladder to hold urine may include:
- Congenital defects in the bladder
- spinal cord damage, which may interfere with the nerve signals that travel from brain to bladder.
- bladder fistula, (tiny, tunnel-like opening that can develop between the bladder and surrounding region, such the vagina)
Causes of functional incontinence
An individual has functional incontinence when they are aware that they need to urinate and are unable to go to the restroom in time. This can be due to different physical or mental disabilities such as
- Mobility issues like arthritis or Parkinson’s disease
- Cognitive impairments like Alzheimer’s disease
- Physiological factors such as anxiety and depression
- Urinary tract infections and chronic usage of certain medicine
Causes of reflex incontinence
This kind of incontinence is linked to neurological issues that impact the brain's communication with the bladder. The kind of incontinence is classified as either supraspinal reflex or spinal reflex incontinence.
This usually happens as a result of a sickness, surgical trauma, or spinal cord damage. Radiation therapy may potentially cause this type of incontinence as a side effect.
Neurological disorders such as Multiple Sclerosis, dementias, stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease are linked to supraspinal reflex incontinence.
Causes of temporary incontinence
- Bacterial infections in the urinary tract
- Medications use
- Temporary bad cough
Urinary incontinence risk factors
Besides, the usual reasons, there are other factors that might raise the chance of having urine incontinence without really causing the problem which include:
- Ageing: Urinary incontinence increases with middle age and is quite frequent in those above the age of 80.
- Family history of urinary incontinence: Urinary incontinence may have a hereditary component, so if other members of a family have the issue, they might be more vulnerable to the disorder.
- Smoking: A 2020 study demonstrated that indulgence in smoking has a correlation with the incidence of urgency and urine incontinence. prevalence is higher in smokers, including present and former smokers, when compared to non-smokers.
- Gender: With a distinct variation in incidence between men and women, gender is in fact a substantial risk factor for urine incontinence.
- Obesity: being overweight may cause a rise in intra-abdominal pressure, which therefore affects pelvic organ function negatively by increasing urethral mobility and bladder pressure as well as chronically straining, stretching, and weakening the muscles, nerves, and other pelvic floor structures. These circumstances may exacerbate the symptoms of overactive bladder, detrusor instability, and urgency urine incontinence, as well as stress urinary incontinence
- Certain diseases: it is demonstrated that health conditions such as diabetes, urinary tract infections, and neurological illnesses etc may increase the risk of developing urinary incontinence.
Urinary incontinence complications
- Altered sexual function (Sexual dysfunction)
- Urinary tract infections (UTI)
- Cellulitis (severe skin infection caused by bacteria)
- Pressure ulcers (skin and underlying tissue damage due to sustained pressure on the skin)
- Catheterization-related trauma and infection
- Worsening of urinary incontinence following surgical treatment
- Reduction in physical activity
- Depression
- Social isolation
- Elevated burden on caregivers

Urinary incontinence prevention
Urinary incontinence and other bladder control issues are not always preventable, however, maintaining the healthiest possible bladder is possible via indulging in excellent practices such as:
- Manage constipation: Constipation can worsen the health of the urinary tract and increase the risk of urinary incontinence. Eat a lot of high-fiber meals, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains; stay hydrated; and engage in physical activity to avoid constipation. Avoid medication that has constipation as an adverse effect.
- Engage in pelvic floor exercises: The muscles of the pelvic floor assist in holding urine in the bladder. Exercises related to the pelvic floor muscles, often known as Kegel exercises, can strengthen those muscles and help prevent the spilling of urine when someone laughs, cough, sneeze, or raise. Exercises targeting the muscles of the pelvic floor are beneficial for both men and women.
- Smoking cessation: Eradication of smoking at any age is beneficial for bladder health as well as general health. Because smoking induces coughing, it increases the risk of developing stress incontinence. Moreover, most occurrences of bladder cancer are caused by smoking. Some claim that smoking exacerbates irritation in the bladder.
- Changing bathroom habits: Urinating when necessary is often recommended because people try to hold urine due to various reasons which cause bladder infections eventually leading to incontinence.
- Healthy weight maintenance: being overweight may cause diabetes (elevated blood glucose). Diabetes may lead to urinary incontinence as a complication
- Getting enough hydration: Not getting enough hydration makes the urine more concentrated, which leads to bladder infections, eventually leading to urinary incontinence. Hence, maintaining good hydration is recommended
- Eating healthy foods: Eating a nutritious diet can help to avoid conditions like diabetes and obesity that increase the risk of urinary incontinence. It is highly recommended to avoid foods that impose risk to develop incontinence.
Urinary incontinence diagnosis
Urinary incontinence itself is a symptom of an underlying disease. To determine the cause of incontinence, the urologist may perform physical examination and inquire past medical history.
To determine what is causing the bladder control issue, the urologist could do a few straightforward tests. If the urologist believes that there might be more than one cause for incontinence patients will probably undergo additional testing that may include:
- Urinalysis and urine culture: These tests help determine the presence of blood or glucose in urine, or the presence of urinary tract infection (UTI). These tests can also reveal the enlarged prostate in males.
- Bladder stress test: It replicates the unintentional discharge of urine that might happen when the patient laughs, sneezes, coughs, or works out. For female patients a test known as Bonney test is performed to determine the unintentional leakage of urine.
- Pad test: to determine the amount of urine leakage
- X-rays or ultrasound: These tests are used to look at how the bladder and urethra move when the patient cough, strain, or pee.
- Electromyogram (EMG): This test captures the electrical activity of the muscles inside the urinary system.
- Cystoscopic exam: During this examination the urologist may use a tiny, illuminated tube to investigate the problems in the urinary tract.
- Cystourethrogram: This test captures the changes in urethra and bladder during urination using x rays
- Urodynamic studies: In case of a failed therapy or if the patient is being considered for surgery, the urologist may prescribe urodynamic studies such as
- Uroflowmetry
- Pressure flow studies
- Post-void residual volume
- Cystometry
Urinary incontinence treatment
There are three types of treatment: conservative, pharmaceutical, and surgical. Depending on the kind of urine incontinence, using the least intrusive techniques first, treatment and care should be escalated as necessary.
Depending on the cause of urinary incontinence the treatment options including the following:
- Behavioral therapy
- Pelvic muscle rehabilitation
- Other treatments
Behavioral therapy
This will assist in regaining control over bladder and may include:
- Bladder training
- Scheduled toileting
Pelvic muscle rehabilitation
This will reduce urine leakage and strengthen the pelvic muscles. This treatment may include:
- Kegel exercises.
- Biofeedback
- Vaginal weight training
- Pelvic floor electrical stimulation
Other treatments
- Pharmacological treatment (treatment using medicine)
- Surgical interventions
Medicine for urinary incontinence may include:
- Alpha-adrenergic agonists
- Selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SSNRIs).
- Antimuscarinics
- Topical vaginal estrogen
- Alpha-adrenergic antagonists
Surgical interventions
Surgical intervention is an option if issues like a blockage or an improperly positioned bladder are the cause of the incontinence. In case of a failed therapy or severe incontinence surgical interventions are considered which may include:
- Intravesical balloons,
- Trans - or periurethral injections of bulking agents
- Sling procedures
- Urethropexy
- Neuromodulation
- Suprapubic catheter
Difference between Urinary incontinence and Urinary retention
Urinary incontinence vs Urinary retention
Urinary incontinence and urinary retention are two opposite conditions that affect the bladder and urination process. Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine, whereas urinary retention is the inability to empty the bladder completely.
| Parameters | Urinary incontinence | Urinary retention |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Urinary incontinence is uncontrolled leakage of urine | This condition is the inability to empty the bladder completely |
| Cause | This condition occurs mainly as a symptom to many underlying diseases such as urinary tract infections, bladder fistula etc. | This condition can also present as a symptom which may be caused by other illnesses such as enlarged prostate, urethral strictures, urethral stones etc. |
| Symptoms | Leaking urine before using a toilet | Inability to completely empty the bladder and persistent urge to urinate without relief |
| Treatment | Age, menopause, childbirth, and other medical conditions can all result in or exacerbate bladder control issues in women. Urinary incontinence in males may be brought on by ageing and prostate issues. The type of urine incontinence will determine the treatment for this condition. Teaching the patient behavioural therapy, such as training their bladder and toileting habits, changing their food, avoiding bladder irritants, and changing their lifestyle are all part of the first-line treatment. | Depending on the retention whether it is acute or chronic urine retention, as well as its underlying cause, the treatment options will vary. This condition may be treated by draining the bladder, medicines, medical procedures or devices, surgery, and self-care treatments. |
| prevention | Although bladder control issues are not always preventable, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough fluids all contribute to a healthy bladder. | This condition may be prevented by Changing bathroom habits, Staying in tune with the body, Medication adherence (taking medicines according to prescription) Making changes in diet. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Urinary incontinence
Can urinary incontinence be cured?
Yes. Urinary incontinence can be cured. Since it is a symptom of many underlying diseases, the condition that is responsible for urinary incontinence should be treated appropriately with available treatment options in order to cure the urinary incontinence.
How to control urinary incontinence naturally?
Urinary incontinence can be naturally controlled to some extent by
- Doing Kegel exercises.
- Bladder training
- Weight loss
- Smoking cessation
- Eating healthy diet
- Managing constipation
Why urinary incontinence in women is more than men?
Because women experience distinctive health events such as pregnancy, delivery, and menopause that affect women specifically and may have an impact on the urinary system and surrounding muscles. Due to this there is a possibility that the pelvic floor muscles that support the uterus (womb), bladder, urethra, and intestines could weaken or get damaged.
In addition, the urethras of women are shorter than men. Urinary incontinence in women is more likely to occur in cases when there is urethral weakness or injury.
Which vitamins help prevent overflowing bladders?
According to some research, vitamin D may assist both men and women who experience urine incontinence. Prostate cells have the ability to synthesize the active form of vitamin D, and both the bladder and the pelvic floor muscles have vitamin D receptors. Men with moderate to severe urinary incontinence and women with pelvic floor issues have been related to low vitamin D levels.
Is it necessary to consume less water or liquids in case of urinary incontinence?
No. Many people who have pee leakage falsely believe that drinking less may lessen their urine leakage. However, fluids, especially water are essential for optimal health.
Consuming enough water not only keeps kidneys healthy but also helps to prevent urinary tract infections, constipation etc. That make urinary incontinence severe.
What is urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is unintentional spilling of urine. Though this condition can affect both the genders, females and elderly are frequently affected. The health and quality of life of patients might be negatively impacted by urinary incontinence. The prevalence of this condition could be underestimated due to concealment of urine incontinence problems to medical professionals for a variety of reasons.
How can urine incontinence result from childbirth?
The pelvic floor muscles might become weaker and the nerves controlling the bladder can be damaged by issues encountered during labor and delivery, particularly vaginal birth. Most bladder control issues resulting from labor and delivery resolve on their own when the muscles receive sufficient time to repair.
Can colon cancer cause urinary incontinence?
Yes. Following colon cancer treatment, urinary impairment is frequently seen, especially if radiation is part of the treatment regimen. Before beginning cancer therapy, all patients must be made aware of the danger, and during follow-up, functional results should be regularly evaluated.
How quickly will urine incontinence improve after beginning Kegel exercises?
It might take four to six weeks for the symptoms to start getting better. Everybody's experience with Kegel exercises varies. There are three possible outcomes for the symptoms: they could completely disappear, they might get better and still leak, or they might not get better at all. Kegel exercises, however, can help stop the worsening of incontinence even if symptoms do not improve.
What type of medications can cause urinary incontinence?
Medications that may lead to urinary incontinence include:
- Cholinergic and anticholinergic drugs
- Alpha-blockers
- Antihistamines
- Estrogen replacement
- Tocolytic agents
- Sedatives
- Muscle relaxants
- Diuretics
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Which fruits help to reduce urinary incontinence?
A 2022 study demonstrated that regular intake of cranberry has significant effects in reducing daily urination and urgency of urine.
Moreover, cranberries contain a substance known as proanthocyanidins (PACs) that prevent bacteria from adhering to the urothelial cells that line the bladder. For many years, cranberry products have been used extensively as a preventative measure against urinary tract infections.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868