Hypospadias: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Surgery & Recovery Tips
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. Abhik Debnath - Consultant Urologist, Andrologist & Kidney Transplant Surgeon
Hypospadias is one of the most common congenital conditions affecting baby boys, where the urinary opening (meatus) is not located at the tip of the penis but somewhere on the underside. Although the condition may cause understandable worry for new parents, the good news is that hypospadias is highly treatable with modern surgical techniques, especially when done at the right age and by trained paediatric urologists.
Most newborns with hypospadias grow up to have normal urinary, sexual, and reproductive function with early diagnosis and proper treatment.
At PACE Hospitals, our paediatric urologists and reconstructive surgeons use advanced, internationally recommended techniques that ensure excellent cosmetic results, normal urinary function, minimal scarring, and safe recovery for infants and children.
This article explains everything parents need to know, from causes and symptoms to surgery, recovery tips, and long-term outcomes.
What Is Hypospadias?
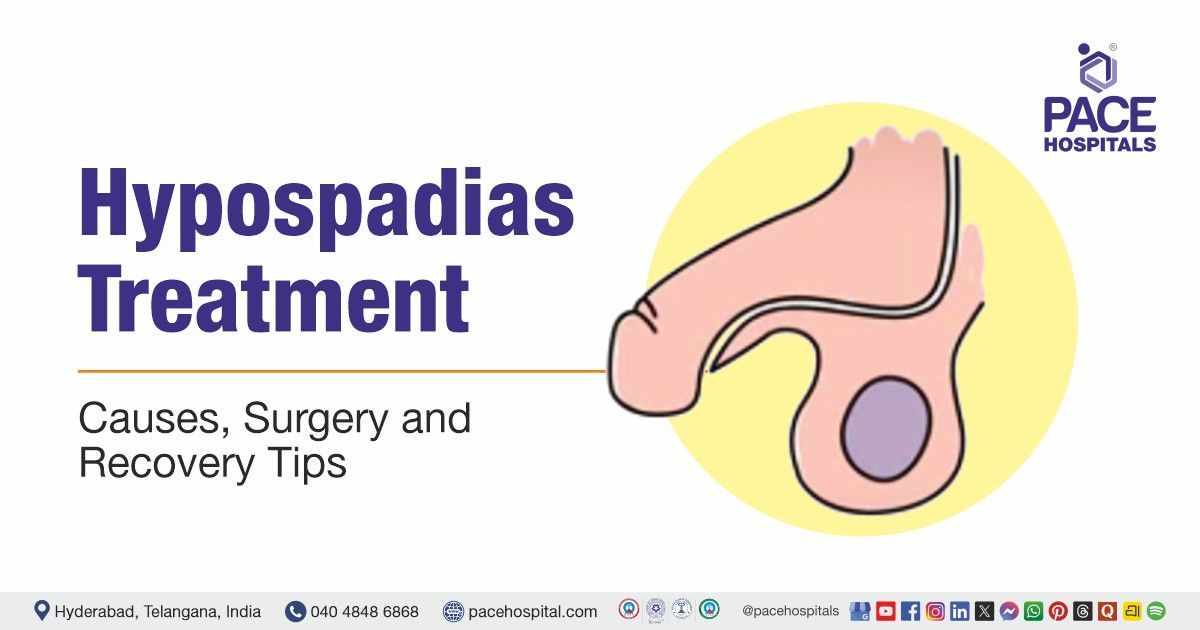
Hypospadias is a birth condition in which the urethral opening does not form at the tip of the penis. Instead, it appears somewhere along the underside.
The opening may be located at:
- Subcoronal – just below the head of the penis
- Mid-shaft – along the shaft
- Penoscrotal – where the penis meets the scrotum
- Scrotal or Perineal – behind the scrotum (rare and severe)
Along with abnormal placement of the urinary opening, hypospadias often includes:
Key Features:
- Chordee – downward curvature of the penis during erection
- Hooded foreskin – excess foreskin on top, lacking on underside
- Abnormal urine stream – spraying or downward dribbling
- Difficulty standing and urinating (in older boys)
Hypospadias is diagnosed at birth and affects nearly 1 in every 150–250 male babies worldwide.
Who is at Risk for Hypospadias?
Hypospadias can occur in any newborn boy, but certain factors increase the likelihood:
Higher Risk in:
- Babies with family history of hypospadias
- Babies conceived through IVF or fertility treatments
- Mothers with:
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Hormonal disorders
- Premature, low-birth-weight infants
- Mothers taking certain hormonal medicines during pregnancy
What Causes Hypospadias?
The exact cause is still under research, but experts believe hypospadias results from incomplete development of the urethra during the early pregnancy period (8–14 weeks).
Possible contributing factors include:
Genetic Factors
- If the father or siblings have hypospadias, the risk increases significantly.
- Certain genetic mutations affect penile development.
Hormonal Influences
- Low levels of testosterone or androgen activity in the fetus
- Problems with hormone receptors
Maternal Factors
- Poorly controlled diabetes
- Smoking during pregnancy
- Obesity
- Older maternal age
- Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals
Environmental Factors
- Pesticides
- Plastic-related chemicals
- Hormonal medications
At PACE Hospitals, our paediatric urology team frequently evaluates newborns and infants to determine the type and severity of hypospadias, helping guide the best treatment plan.
Hypospadias Symptoms
While hypospadias is usually diagnosed at birth, some milder cases may be picked up later.
Common Signs:
- Opening of urethra not at the tip
- Curved penis (chordee)
- Dorsal hooded foreskin
- Abnormal urine stream (spraying or downward)
- Difficulty pointing urine stream straight (in toddlers)
- Penis appears twisted or rotated
Associated Conditions:
- Undescended testicles
- Inguinal hernia
- Abnormal scrotal development (rare)
Early diagnosis avoids complications later in life.
Diagnosis of Hypospadias
Hypospadias is diagnosed shortly after birth. If you notice abnormalities, consult a paediatric urologist immediately.
Important: Do NOT circumcise the baby before evaluation, as the foreskin may be needed for repair.
Hypospadias Treatment
Surgery is the only effective treatment for hypospadias. No medicines, exercises, or home methods can correct the urinary opening.
The goal of surgery is to:
- Move the opening to the tip of the penis
- Straighten the penis (correct chordee)
- Reconstruct the urethra
- Create a normal appearance
- Ensure normal urinary & sexual function in adulthood
Hypospadias Surgery (Urethroplasty)
Hypospadias surgery is best performed between 6 and 18 months, as healing is faster, tissues are more adaptable, and the child does not remember the procedure.
Surgical Techniques Used at PACE Hospitals:
TIP Urethroplasty (Snodgrass Procedure)
Most commonly used for distal and mid-shaft cases.
- Makes the opening straight
- Creates a natural-looking meatus
- Minimal scarring
- Excellent long-term results
Onlay Flap Repair
Used for moderate cases.
- Uses foreskin tissue to reconstruct the urethra
- Avoids tension on the repair
Two-Stage Repair
Recommended for severe or penoscrotal hypospadias.
- First stage: Straightening and creating new urethral plate
- Second stage: Urethral reconstruction
Chordee Correction
Straightens the penis to ensure normal adult sexual function.
Foreskin Reconstruction
Optional, based on parent preference (if not circumcising).
Benefits of Modern Surgical Approaches:
- Safe general anaesthesia
- Minimal blood loss
- Quick recovery
- High cosmetic satisfaction
- Natural urinary flow
- Good long-term functional results
Do’s and Don’ts for Parents Before and After Surgery
Do’s
- Follow surgeon’s instructions carefully
- Give medicines exactly as prescribed by the doctor
- Keep the child well-hydrated and drinking normal water
- Use double diapers to protect the catheter
- Maintain hygiene around the dressing
- Attend all follow-up appointments
- Watch for changes in urine flow
Don’ts
- Don't remove or disturb the catheter by self
- Don’t bathe the child until allowed
- Don’t apply powders, oils, or home remedies
- Don’t allow the child to sit on hard or straddle toys for some days
- Don't ignore redness, discharge, or fever post-operation
- Don't skip follow-ups and keep a note of schedule
Proper care ensures faster healing and avoids complications.
Recovery Timeline After Hypospadias Surgery
Recovery may vary by severity, surgical technique, and child's health.
Typical Recovery Milestones:
- Day 1–3: Swelling and mild discomfort (normal)
- Day 5–10: Catheter removal
- 2 weeks: Wound largely healed
- 4–6 weeks: Normal activity can resume
- 3 months: Final healing and complete tissue recovery
- 6–12 months: Cosmetic result stabilizes
At PACE Hospitals, our success rates for primary hypospadias surgery range between 95%–98%, with excellent long-term outcomes.
Home Care Tips for Parents After Surgery
- Keep diaper area clean, dry and maintain hygiene
- Use double-diaper method:
- Inner diaper for stool
- Outer diaper for urine (catheter output)
- Give pain-relief medicines as advised
- Use antibiotic ointments if prescribed
- Avoid pressure over the groin area
- Protect the stitch line from infections
- Encourage calm and normal activities only
For older children:
- Avoid rigorous work such as cycling, jumping, and rough play for 4–6 weeks
- Encourage hydration to maintain urine flow
When to See a Doctor for Hypospadias?
Contact the paediatric urologist if:
- Baby develops fever and rise in body temperature
- Redness or pus appears around the surgical area
- Blood in urine beyond expected
- Excessive swelling
- Catheter stops draining
- Child seems uncomfortable or in pain
Quick response prevents complications.
Hypospadias Diagnostic Tests
Although hypospadias is visually diagnosed, additional tests may be recommended in certain cases to have proper evaluation:
Physical Examination
Primary tool for identifying location of meatus, curvature, and foreskin abnormality.
Ultrasound (if needed)
To check:
- Kidney abnormalities
- Undescended testicles
- Internal genital structures
Hormonal Assessment ( in rare cases)
For severe proximal hypospadias or ambiguous genitalia.
Imaging for Chordee
To evaluate severity of penile curvature.
Genetic Testing
Only in complex cases with disorders of sexual development (DSD).
These diagnostics ensure precise planning for surgery and long-term management
Long-Term Outlook After Hypospadias Surgery
Most children treated early achieve:
- Normal urine stream
- Straight penis
- Normal sexual function in adulthood
- Normal fertility
- Minimal visible scarring
Routine follow-up during:
- Infancy
- Early childhood
- Puberty
is recommended to ensure ideal function and penile growth.
Hypospadias Prevention
Though hypospadias cannot always be prevented, certain steps may reduce risk:
Maternal Precautions:
- Control diabetes during pregnancy
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Avoid hormone-containing medications unless prescribed
- Maintain healthy weight during pregnancy
- Ensure early prenatal checkups
- Avoid exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals
Healthy pregnancy practices support normal fetal development.
Hypospadias Care at PACE Hospitals – Why Parents Trust Us
PACE Hospitals is one of the leading centres in Hyderabad for paediatric urology and hypospadias surgery. Our strengths include:
- Experienced paediatric urologists & reconstructive surgeons
- High success rate in primary repair
- Advanced surgical approaches (TIP, Onlay, Two-Stage)
- Ultra-precise anaesthesia for infants
- Dedicated postoperative nursing care
- Child-friendly environment
- Complete monitoring from birth to puberty
- Focus on cosmetic, urinary, and sexual outcomes
We ensure your child receives the safest and most advanced care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Frozen Shoulder
What is hypospadias why does it occur?
Hypospadias is a birth condition where the urinary opening lies on the underside of the penis instead of the tip. It occurs due to incomplete development of the urethra during early pregnancy, often caused and influenced by hereditary (genetic), hormonal, or maternal factors.
How can parents identify hypospadias in a newborn?
Parents may notice an abnormal urinary opening, downward curvature of the penis (chordee), a hooded foreskin, or a spraying/deflected urine stream. Most cases are diagnosed immediately after birth during newborn examination.
What surgical techniques are used at PACE Hospitals for hypospadias repair?
Our experienced surgeons perform:
- TIP (Snodgrass) Urethroplasty
- Onlay Flap Repair
- Two-Stage Urethroplasty
- Chordee correction
Techniques are selected based on hypospadias severity, ensuring functional and cosmetic excellence.
Can hypospadias be treated without surgery?
No. Surgery is the only effective treatment. Medicines, creams, or stretching exercises cannot correct the abnormal opening or urinary pathway.
What is the best age for hypospadias repair?
Most hypospadias experts (pediatric urologists or hypospadias surgeons) recommend surgery between 6 to 18 months of age. At this age, healing is faster, discomfort is minimal, and long-term functional and cosmetic results are optimal.
Can hypospadias affect fertility or sexual function later in life?
Untreated severe hypospadias may affect penile curvature and ejaculation pathways. However, children treated early at PACE Hospitals achieve normal sexual function, normal erections, and normal fertility as adults.
What makes PACE Hospitals a top centre for hypospadias treatment?
- We have dedicated paediatric urology team with expertise:
- High success rates (95–98%)
- Latest reconstructive techniques (TIP, Onlay, Two-Stage)
- Advanced paediatric anaesthesia and ICU care
- Child-friendly environment and compassionate staff
- Full support from newborn stage to puberty
These factors ensure superior outcomes for both mild and complex hypospadias.
Why should hypospadias be treated early and how do PACE Hospitals help?
Early treatment (between 6–18 months) ensures better healing, minimal scarring, and normal urinary/sexual function. PACE Hospitals follows internationally accepted surgical timelines, regulations and offers comprehensive pre-operative assessments for safe early correction.
How long does recovery take after surgery?
Initial healing takes about 2–3 weeks, but complete tissue recovery may take 2–3 months. Most children resume normal activities after catheter removal and early healing.
What is recovery like after hypospadias surgery at PACE Hospitals?
Parents can expect:
- Catheter for 5–10 days
- Wound healing in 2–3 weeks
- Full recovery in 3 months
PACE Hospitals provides detailed postoperative guidance, daily reviews (if needed), and dedicated nursing support to ensure smooth recovery.
Is hypospadias surgery a one-time procedure?
Mild and moderate cases usually need only one surgery. Severe or proximal types may require a two-stage repair. Follow-up helps ensure the best outcome.
Why shouldn’t parents circumcise a child before visiting PACE Hospitals?
Because the foreskin is often essential for reconstructive repair. At PACE Hospitals, we advise parents not to circumcise until a paediatric urologist evaluates the child.
Does PACE Hospitals offer treatment for severe hypospadias cases?
Yes. We specialise in managing complex, proximal, penoscrotal, reoperative, and failed hypospadias repairs using multi-stage reconstructive surgeries.
Can hypospadias return after successful surgery?
Recurrence is rare in some cases. However, it is advised to have consistent follow-up without negligence, proper wound care, and early detection ensure excellent long-term outcomes and can avoid confusion.
How does PACE Hospitals ensure minimal scarring and natural cosmetic results?
Our of team of paediatric surgeons, paediatric urologists, adult reconstructive urologists, and plastic surgeons use ultra-fine sutures, tissue-sparing techniques, and high-precision magnification tools. This results in:
- Natural appearance
- Symmetrical shape
- Minimal visible scarring
- Normal foreskin or circumcised look based on parent preference
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles