Prostate Enlargement (BPH): Myths & Facts
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. Abhik Debnath - Consultant Urologist, Endourologist, Andrologist & Kidney Transplant Surgeon
Prostate enlargement or Enlarged Prostate is a common health condition that impacts many men, especially as they grow older. Despite being widespread, it is often surrounded by misinformation, fear, and misconceptions. Many men delay seeking medical help due to myths related to cancer, sexual function, or surgery, which can lead to worsening symptoms and complications.
At PACE Hospitals, we believe that accurate information and early medical guidance are key to maintaining long-term urological health. This comprehensive guide clears common myths, explains medical facts, and outlines modern diagnosis and treatment options for prostate enlargement in a simple, patient-friendly manner.
What Is Prostate Enlargement?
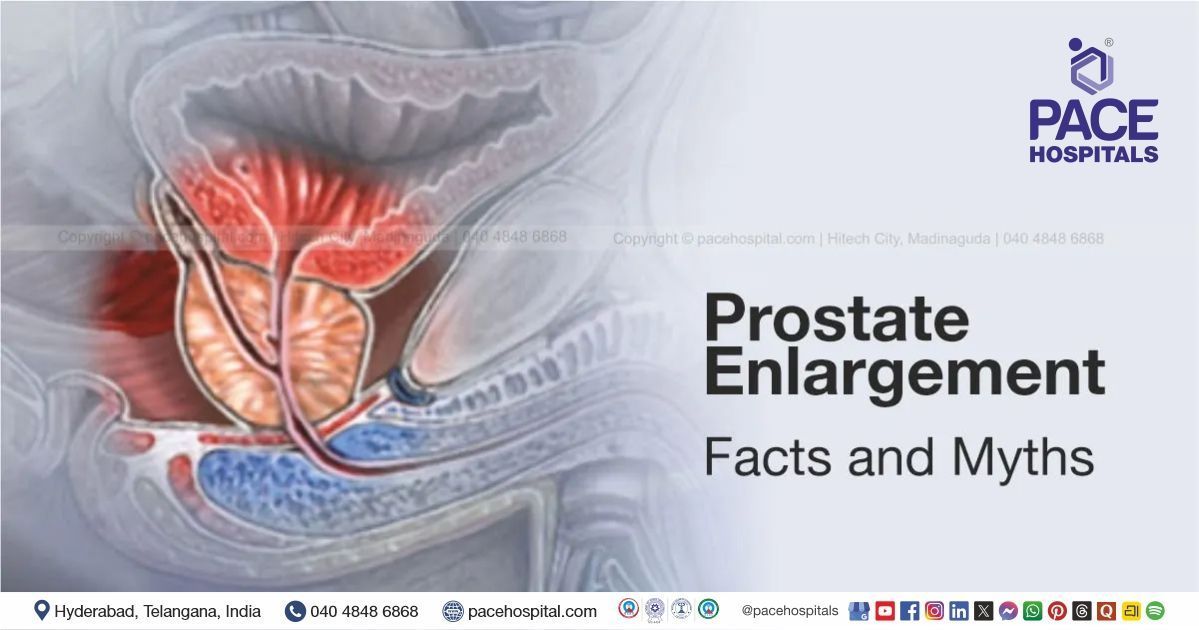
Prostate enlargement, medically referred as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a non-cancerous increase in the size of the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-shaped gland located below the bladder and surrounding the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body.
As the prostate enlarges, it can compress the urethra and interfere with normal urine flow. This leads to urinary symptoms that may range from mild inconvenience to significant discomfort affecting daily life.
Prostate Enlargement and Age: Why It Becomes More Common Over Time?
Prostate enlargement,also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is strongly age-related. It is uncommon in younger men but becomes increasingly prevalent as men grow older due to hormonal changes that occur with aging. Medical studies consistently show that:
- About 40% of men in their 50s show signs of prostate enlargement
- Nearly 50–60% of men in their 60s experience moderate urinary symptoms related to BPH
- Up to 80–90% of men above 70–80 years have some degree of prostate enlargement
Although prostate growth begins slowly after the age of 40, symptoms often become noticeable only later in life. Age-related enlargement is a natural process and does not indicate cancer, but early evaluation helps prevent complications.
Why Does the Prostate Enlarge?
An Enlarged Prostate is closely linked to aging and hormonal changes in men. While the exact cause is not fully understood, factors that contribute include:
- Age-related changes in male hormones such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone
- Increased sensitivity of prostate tissue to hormonal stimulation
- Genetic predisposition and family history
- Lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity
Prostate enlargement is not caused by infection or cancer, and it is considered a natural part of aging for many men.
How Common Is Prostate Enlargement?
Prostate enlargement is one of the most frequently diagnosed urological conditions in aging men worldwide. Population-based studies indicate that:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia accounts for over 70% of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men above 50 years
- Nearly 1 in 3 men over the age of 60 seek medical care for BPH-related symptoms
- The likelihood of requiring treatment increases with age, symptom severity, and prostate size
These statistics highlight why prostate enlargement is considered a major men’s health concern and why timely medical consultation is essential.
Common Symptoms of Prostate Enlargement
Symptoms of an enlarged prostate usually develop gradually and may worsen over time if left untreated. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urge to urinate, mostly at night
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Difficulty starting urination
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Sudden, urgent need to urinate
The severity of symptoms is not usually associated with prostate size. Even a moderately enlarged prostate might produce considerable problems in some individuals.
When Should You See a Doctor for an Enlarged Prostate?
Men should seek specialist care when urinary symptoms begin to interfere with everyday activities, disrupt sleep, or affect overall quality of life. Timely evaluation helps rule out other conditions and reduces the risk of complications such as urinary retention, bladder injury, or kidney problems.
At PACE Hospitals, well-renowned urologists encourage men not to ignore symptoms, even if they seem mild or age-related.
Facts and Myths About Prostate Enlargement
Understanding the truth about prostate enlargement helps reduce anxiety and promotes timely treatment. Below are common myths and the facts behind them.
Myth 1: Prostate Enlargement Means Prostate Cancer
Fact: Prostate enlargement (BPH) is not cancer. It is a benign condition and does not increase the risk of prostate cancer. However, both conditions can coexist, which is why proper evaluation is important.
Myth 2: Only Elderly Men Get Prostate Enlargement
Fact: While prostate enlargement is more common after the age of 50, symptoms can begin earlier. Men in their 40s may also experience early signs of BPH.
Myth 3: Surgery Is the Only Treatment Option
Fact: Prostate enlargement can often be adequately treated with medication and lifestyle changes. Surgical treatment is often considered only when symptoms become severe or problems develop.
Myth 4: Prostate Treatment Affects Sexual Performance
Fact: Modern treatment options are designed to preserve sexual function and are not troublesome. Doctors at PACE Hospitals carefully choose therapies based on individual needs and concerns.
Myth 5: Drinking Less Water Will Improve Symptoms
Fact: Reducing fluid intake excessively can get more bladder irritation and increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Proper hydration is important.
How Is Prostate Enlargement Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a detailed clinical assessment to confirm BPH and rule out other causes of urinary symptoms.
Medical History and Symptom Assessment
Doctors evaluate urinary symptoms, their duration, and their impact on daily life using standardized questionnaires to know how its affecting normal phenomenon.
Physical Examination
A digital rectal examination is performed to assess the size, shape, and firmness of the prostate.
Laboratory Tests
Urine analysis and blood investigations, including the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, may be advised to rule out infections or other prostate-related conditions.
Imaging and Functional Tests
Ultrasound and urine flow studies help assess bladder emptying and urinary flow obstruction.
Treatment Options for Prostate Enlargement
Treatment depends on symptom severity, prostate size, age, and overall health of an individual.
Watchful Waiting
Men with minor symptoms may just need regular monitoring and lifestyle changes.
Medications
Medications help relax prostate muscles or reduce prostate size, improving urine flow and reducing symptoms.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Modern treatments provide symptom relief with a quicker recovery time and less disruption to everyday life.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical intervention is recommended for men with severe symptoms, recurrent urinary retention, bladder stones, repeated urinary tract infections, or kidney-related complications due to prostate enlargement. Some of the best options are:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) – Gold Standard Surgery
- Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) – Advanced Laser Surgery
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP)
One of the most established and effective treatment modalities for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) for several decades is Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP). In this procedure, the enlarged prostate tissue causing urinary obstruction is removed using a specialized wire loop passed through the urethra, without any external incision. TURP is considered the gold standard for moderate to severe prostate enlargement and provides reliable, long-term relief from urinary symptoms.
Laser Surgery for Prostate Enlargement (HoLEP)
The latest and most advanced surgical intervention for prostate enlargement is Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP). This laser-based technique precisely removes the enlarged prostate tissue with excellent safety margins and high efficiency. HoLEP is associated with less blood loss, faster recovery, shorter catheterization times, and long-term outcomes, even in individuals with large prostates.
At PACE Hospitals, treatment decisions are individualized, focusing on safety, effectiveness, and quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes That Help Manage Prostate Enlargement
Certain everyday habits can play an important role in easing urinary symptoms:
- Reducing the intake of caffeine and alcoholic beverages
- Avoiding excess fluid consumption close to bedtime
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Remaining physically active on a regular basis
- Following bladder training and timed voiding techniques
Possible Complications If Left Untreated
Untreated prostate enlargement may lead to:
- Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Acute urinary retention
- Bladder stones
- Bladder or kidney damage
Timely proper treatment helps prevent these complications.
Prostate Enlargement and Quality of Life
Urinary symptoms can affect sleep, work productivity, and emotional well-being. Many men experience embarrassment or frustration. Addressing prostate enlargement improves overall quality of life and confidence level.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Prostate Enlargement
What is prostate enlargement (BPH)?
Prostate enlargement, medically called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a non-cancerous increase in the size of the prostate gland. It is commonly found as men age and can reduce urine flow by compressing the urethra. While not a life-threatening condition, BPH can have a substantial impact on quality of life.
Is prostate enlargement the same as prostate cancer?
No, prostate enlargement (BPH) is a non-cancerous condition. However, these illnesses can elicit similar urine symptoms and may present concurrently. Proper evaluation aids in the differentiation between them.
What are the early symptoms of prostate enlargement?
Early symptoms include frequent urinating, particularly at night, a weak urine stream, and trouble starting to urinate. Symptoms often develop gradually. Early consultation helps to prevent problems.
Does prostate size always correlate with symptom severity?
Not necessarily. Some men with a somewhat enlarged prostate may experience severe symptoms, whereas others with a bigger prostate may experience little symptoms. Symptom severity is determined by the degree of urethral blockage and bladder function.
What happens if prostate enlargement is left untreated?
Untreated BPH can cause recurring urinary tract infections, urine retention, bladder stones, and kidney damage. Early diagnosis and treatment help prevent these complications.
How is prostate enlargement diagnosed?
Symptom assessment, physical examination, urine tests, blood testing (including PSA where necessary), and imaging investigations are all used to make a diagnosis. These help to confirm BPH and rule out other causes.
Can prostate enlargement recur after treatment?
Yes, symptoms can return gradually over time, particularly in patients managed with medications alone. Surgical treatments such as TURP and HoLEP generally offer more durable and long-lasting symptom relief for most individuals.
At what age does prostate enlargement usually begin?
Prostate enlargement typically begins after the age of 40, but symptoms are more common after 50 years. The likelihood of the complexity and severity increase with advancing age. Many men above 60 experience some degree of urinary symptoms related to BPH.
Can prostate enlargement affect daily life?
Yes, untreated BPH can affect normal sleep, reduce work productivity, and create discomfort or humiliation. Timely treatment improves urinary control, overall well-being and quality of life.
Can lifestyle changes help manage BPH symptoms?
Yes, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, staying active, and maintaining a healthy weight can help alleviate symptoms. Lifestyle adjustments are frequently advised in conjunction with medical treatment.
What is HoLEP and how is it different from TURP?
Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) is an advanced laser surgery that removes enlarged prostate tissue with high precision. Compared to Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP), HoLEP offers more advantages such as minimal blood loss, faster recovery, and is effective even for large prostates.
Will prostate surgery affect sexual function?
The majority of current prostate procedures are intended to preserve sexual function. Some males may notice transitory changes, but the long-term results are usually positive. Prior to surgical treatments, doctors thoroughly clarify the potential hazards.
How does PACE Hospitals evaluate prostate enlargement (BPH)?
At PACE Hospitals, prostate enlargement is assessed through a step-by-step clinical approach.
- Detailed discussion of urinary symptoms and their impact on daily life
- Physical examination and appropriate laboratory tests
- Imaging and urine flow studies when required
This thorough evaluation helps doctors confirm BPH and rule out other conditions such as infections or prostate cancer.
What treatment options does PACE Hospitals offer for prostate enlargement?
PACE Hospitals provides a full range of treatment options based on symptom severity.
- Medical management for mild to moderate symptoms
- Established surgical treatment such as TURP
- Advanced laser surgery like HoLEP for larger prostates
- The focus is on choosing the safest and most effective option for each patient.
Is prostate surgery safe at PACE Hospitals?
Prostate surgeries at PACE Hospitals are performed with strict safety protocols.
- Use of modern operation theatres and advanced equipment
- Minimally invasive techniques wherever appropriate
- Careful monitoring before, during, and after surgery
These measures help reduce complications and support faster recovery.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868