What Is the First Sign of Kidney Problems?
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. A Kishore Kumar - Consultant Nephrologist and Kidney Transplant Physician
Your kidneys play an important role in keeping your body healthy. They act as natural filters, removing waste products, excess fluids, and toxins from your bloodstream. They also help in regulating blood pressure, red blood cell production, and electrolyte balance.
But when kidneys begin to malfunction, the early signs are often subtle — and easily ignored. Because kidney disease progresses silently, many people don’t realize they have a problem until 70–80% of kidney function is already lost.
Understanding how to know if you have kidney problems early can help you get treatment before lasting damage occurs.
Quick Kidney Health Check
If you checked 2+ boxes, continue reading to understand your symptoms and consider scheduling a kidney screening.
Understanding Kidney Functions
Each person has two kidneys located on either side of the spine, just beneath the rib cage. These bean-shaped organs perform several essential tasks:
- Filtering toxins, waste, and excess fluid from the blood.
- Maintaining electrolyte balance (sodium, potassium, calcium).
- Regulating blood pressure through hormone control.
- Supporting bone and red blood cell health.
When kidneys are damaged — due to infection,
diabetes,
hypertension, or lifestyle factors — these functions become impaired, leading to fluid retention, metabolic imbalance, and systemic symptoms.
How to Know You Have Kidney Problems?
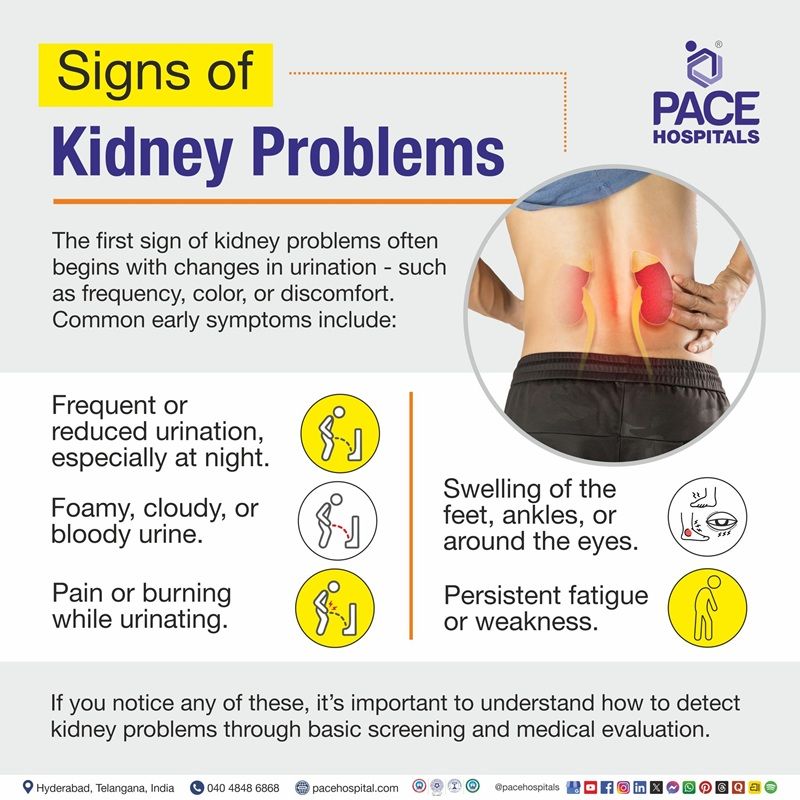
The first sign of kidney problems often begins with changes in urination, for a detailed explanation of urinary changes, see the Early Warning Signs section below.
Common early symptoms of kidney problems include:
- Frequent or reduced urination, especially at night.
- Foamy, cloudy, or bloody urine.
- Pain or burning while urinating.
- Swelling of the feet, ankles, or around the eyes.
- Persistent fatigue or weakness.
If you notice any of these, it’s important to understand how to detect kidney problems through basic screening and medical evaluation.
Early Warning Signs of Kidney Problems
Kidney issues can begin silently and progress gradually. However, there are some early warning symptoms that may indicate trouble.
1. Changes in Urination
This is often the first and most obvious sign of kidney problems.
You may notice:
- Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Reduced urine output
- Foamy or bubbly urine (sign of protein leakage)
- Dark-colored, bloody, or cloudy urine
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating
Changes in urine frequency, color, or consistency should never be ignored. They often indicate that your kidneys are struggling to filter waste effectively.
2. Swelling (Edema)
Healthy kidneys balance sodium and fluid levels in your body. When they fail, fluid builds up, causing swelling in the ankles, feet, face, or hands. In severe cases, swelling may extend to the abdomen or around the eyes.
3. Fatigue and Weakness
One of the earliest non-specific symptoms of kidney dysfunction is unusual tiredness. Damaged kidneys produce less erythropoietin (EPO) — a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. Fewer red blood cells mean less oxygen delivery to tissues, leading to anaemia, fatigue, and breathlessness.
4. High Blood Pressure
The kidneys aid in regulating blood pressure by controlling fluid and sodium levels. Damaged kidneys trigger hormonal imbalances that can cause or worsen hypertension, creating a dangerous feedback loop.
5. Loss of Appetite and Nausea
As toxins build up in the bloodstream (a condition called uremia), it can cause loss of appetite, metallic taste in the mouth and nausea. Some people also experience unintentional weight loss or vomiting.
6. Puffiness Around the Eyes
Persistent puffiness around the eyes, especially in the morning, can indicate protein leakage in the urine — a classic early sign of kidney damage.
7. Dry and Itchy Skin
When the kidneys fail to maintain proper mineral balance, phosphorus and urea levels rise, causing itchy, dry or scaly skin. This is often seen in moderate-to-severe kidney disease.
8. Muscle Cramps
Electrolyte imbalance, especially low calcium and high potassium levels, can lead to twitching, muscle cramps, or spasms. These are often overlooked as signs of dehydration but can be early indicators of kidney dysfunction.
9. Shortness of Breath
Accumulation of fluid in the lungs because of poor kidney filtration can cause difficulty in breathing. Additionally, anemia caused by kidney disease reduces oxygen levels, worsening shortness of breath.
10. Trouble Concentrating and Dizziness
Improper kidney function results in decreased oxygen and toxin buildup in the brain, causing dizziness, difficulty concentrating, and also confusion in advanced stages.
What Causes Kidney Problems?
Many people wonder, “What causes kidney problems?” The truth is, kidney diseases can stem from multiple reasons:
- Diabetes (Type 1 and Type 2): High blood sugar damages the delicate filtering units of the kidneys (nephrons), causing diabetic nephropathy — the leading cause of kidney failure worldwide.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Uncontrolled hypertension puts extra pressure on the kidney blood vessels, impairing their filtering ability.
- Dehydration: Inadequate water intake over long periods can lead to crystal formation and kidney stones, which can cause damage to the kidney tissue.
- Prolonged Use of Painkillers (NSAIDs): Excessive use of painkillers can reduce blood flow to the kidneys, leading to analgesic nephropathy.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Repeated or untreated infections can spread to the kidneys (pyelonephritis) and cause long-term scarring.
- Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle: Obesity may increase the risk of both diabetes and hypertension, which are major causes of kidney damage.
- Excessive Alcohol and Smoking: Both alcohol and nicotine harm blood vessels and increase the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
So if you’re asking, “Can smoking cause kidney problems?” — the answer is yes. Nicotine damages blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the kidneys.
Similarly, “Can multivitamins cause kidney problems?” Excess supplements (high vitamin C or calcium) can lead to kidney stones.
Even “Can tea cause kidney problems?” — drinking very large amounts of black tea (high in oxalates) may increase the risk of stones if hydration is poor.
How to Detect Kidney Problems?
Early detection saves lives. Here’s how to find out if your kidneys are healthy:
- Blood Tests
- Serum Creatinine & GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate): These indicate how effectively your kidneys filter waste.
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): Waste accumulation in blood is measured by blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
- Electrolyte Levels: These Look for abnormalities connected to renal failure.
- Urine Tests
- Urinalysis: Checks for protein, blood, or infection.
- Microalbumin Test: Detects tiny protein leakage — the earliest sign of kidney damage.
- Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound, CT or MRI Scan – These detect structural changes or obstructions like cysts or kidney stones.
- Kidney Biopsy
- In selected cases, a small tissue sample may be analyzed to find out the exact cause of kidney damage.
- Specialist Consultation (Nephrologist or Urologist)
At PACE Hospitals, both the nephrology and urology departments work together to diagnose and manage early renal disorders through advanced testing and screening.
Who is at Risk of Kidney Disease?
High Risk Alert
If you have diabetes OR high blood pressure, you have a significantly higher risk of kidney disease. Schedule kidney function tests every 6 months, even without symptoms. These two conditions account for nearly 70% of all kidney disease cases.
People with below mentioned conditions are at high risk of kidney problems:
- Diabetes or High BP
- Family History of Kidney Disease
- Obesity or Sedentary Lifestyle
- Recurrent Urinary tract infections (UTIs) or Stones
- Chronic Painkiller usage
- Smoking Habit
How to Prevent Kidney Problems?
- Drink 2–3 liters of water daily unless restricted by the doctor.
- Avoid smoking habit and alcohol consumption.
- Limit salt and processed foods.
- Control diabetes and blood pressure.
- Get moderate sun exposure and stay active.
- Avoid excess multivitamins and high-oxalate drinks like strong tea in large quantities.
At PACE Hospitals, the nephrology team educates patients on personalized diet, hydration, and lifestyle plans to prevent recurrence of renal complications.
When to Consult a Doctor?
If you experience persistent swelling in your feet or face, fatigue, blood in your urine, or changes in urination patterns, it’s important to consult the right specialist.
- A nephrologist (kidney specialist) treats kidney conditions such as chronic kidney disease, high creatinine levels, and hypertension-related kidney damage.
- A urologist manages surgical or structural problems such as kidney stones, urinary obstruction, or prostate-related issues.
When to seek immediate medical attention?
Urgent (go to emergency room)
- Blood in urine with severe pain
- Complete inability to urinate
- Severe swelling with breathing difficulty
Schedule appointment within 24-48 hours
- Persistent foamy urine
- Sudden swelling in face/feet
- Unexplained fatigue with other symptoms
Treatment of Early Kidney Problems
Treatment of kidney problems is based on the cause and severity.
Lifestyle Modifications
1. Manage Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar
- Maintain blood pressure below 130/80 mm Hg.
- Maintain optimal blood sugar levels if diabetic.
2. Dietary Modifications
- Reduce salt, sugar, and processed foods.
- Consume foods which are rich in fiber, lean proteins and antioxidants.
- Limit red meat and high-phosphorus foods, including processed meats, cheese or soft drinks.
3. Stay Hydrated
- Consume 2–3 liters of water everyday unless restricted by the doctor. Sufficient hydration helps in flushing toxins and preventing kidney stones.
4. Avoid Overuse of Painkillers
Avoid long-term NSAID usage or any such medication without medical advice.
Habit Changes
5. Quit Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking reduces blood flow to kidneys, and alcohol strains kidney function.
Medical Management
6. Medications and Monitoring
- Doctor may prescribe medications for controlling blood pressure, anemia management, vitamin D supplements, if needed
7. Regular Check-ups
- If you already have hypertension, diabetes, or a family history of kidney disease, get kidney function tests every 6–12 months.
Natural Ways to Keep Kidneys Healthy
- Add more amounts of fruits and vegetables to your diet.
- Need to exercise for at least 30 minutes daily.
- Avoid high-protein crash diets.
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Manage stress with yoga or meditation.
- Sleep 7–8 hours regularly.
Even small, consistent lifestyle changes can significantly improve kidney health over time.
FAQs – Early Signs and Detection of Kidney Problems
What is usually the first sign of kidney disease?
The first sign of kidney disease is usually a change in urination pattern. This can include:
- Urinating more or less frequently than usual
- Dark, foamy, or cloudy urine
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Difficulty passing urine or a weak stream
These changes occur because the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste and balance fluids effectively. As the condition progresses, symptoms like fatigue, swelling around the eyes or in the ankles, legs, nausea, and itching may develop due to toxin buildup and fluid retention.
Since early kidney disease is often silent and painless, noticing subtle urinary changes early can be life-saving. Routine blood (creatinine, GFR) and urine (protein, albumin) tests help detect kidney issues before irreversible damage occurs.
How to detect kidney problems early?
Do routine blood (GFR, creatinine) and urine (albumin) tests every 6–12 months if you’re at risk.
Can kidney disease be reversed?
In the early stages, kidney disease can often be slowed — and sometimes partially reversed — with proper management.
When detected early, addressing underlying causes such as diabetes, hypertension, and dehydration, along with a healthy diet, controlled salt intake, weight management, and quitting smoking, can help stabilise or even improve kidney function.
However, in advanced stages (Stage 4 or 5 CKD) where permanent scarring occurs, the damage is usually irreversible, and treatment focuses on slowing progression and managing symptoms.
What causes kidney problems?
Major causes include diabetes, hypertension, infections, smoking, and drug toxicity.
Can kidney problems cause high blood pressure?
Yes. Kidney problems can cause high blood pressure (hypertension) because damaged kidneys can’t effectively filter sodium and water, leading to fluid buildup in the body.
The kidneys also release hormones such as renin, which help regulate blood pressure. When filtration is impaired, excess renin production and salt retention increase blood volume and pressure.
Over time, high blood pressure can further damage kidney blood vessels, creating a harmful cycle between kidney disease and hypertension.
Can a blood test detect kidney problems?
Yes. A simple blood test can effectively detect kidney problems.
The most common tests are:
- Serum Creatinine Test: This particular test measures the level of creatinine (a waste product) in the blood. Higher levels may indicate reduced kidney function.
- Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR): Calculated from creatinine and age, it estimates how well your kidneys are filtering waste.
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): Helps assess how well your kidneys remove urea, another waste product.
These tests are often combined with urine analysis to check for blood or protein in the urine, providing a complete picture of kidney health.
What foods are harmful to the kidneys?
Foods high in salt, unhealthy fats, processed foods, red meats, fried snacks, soft drinks and preservatives can harm your kidneys and accelerate kidney disease progression.
The worst offenders include:
- Excess salt and processed foods: Increase blood pressure and cause fluid retention, putting strain on the kidneys.
- Red and processed meats: These contain high levels of protein, sodium, and phosphorus that overwork the kidneys and raise uric acid.
- Fried snacks and fast food: Loaded with unhealthy trans fats and refined carbs, which promote obesity and hypertension.
- Soft drinks and colas: Rich in phosphoric acid and sugar, linked to kidney stones, insulin resistance, and faster kidney decline.
Patients with kidney disease should limit sodium intake (< 2 g/day), control phosphorus and potassium levels, and maintain hydration with water rather than sugary or caffeinated beverages.
Does high blood pressure affect the kidneys?
Yes. High blood pressure (hypertension) can directly damage the kidneys.
Over time, elevated blood pressure weakens and scars the small blood vessels (glomeruli) in the kidneys, which filter waste and excess fluid from the blood. When these vessels are damaged, filtration efficiency drops, leading to fluid retention, toxin buildup, and further rise in blood pressure — creating a dangerous cycle between hypertension and kidney disease.
Hypertension is the second leading cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and kidney failure, following diabetes. Managing blood pressure through medication, salt restriction, exercise, and regular monitoring is vital for kidney protection.
Are early kidney problems painful?
No, early kidney problems are usually not painful.
The kidneys have very few pain receptors, so early stages of kidney disease — even when function begins to decline — rarely cause noticeable pain or discomfort. This is why chronic kidney disease (CKD) is often called a “silent disease.”
Pain usually appears only in advanced stages or when there’s a secondary condition such as a kidney stone, infection (pyelonephritis), or swelling (hydronephrosis).
Because early kidney damage shows no pain or visible symptoms, routine screening with urine tests, blood creatinine, and GFR estimation is essential, especially for people with hypertension, diabetes or who are having a family history of kidney problem.
Can smoking cause kidney problems?
Yes. Smoking can cause and worsen kidney problems.
It damages the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste efficiently. Over time, this poor blood flow can accelerate chronic kidney disease (CKD) and increase the risk of kidney failure.
Smoking also raises blood pressure and blood sugar levels, both of which are major contributors to kidney damage. In people with diabetes or hypertension, smoking multiplies the risk of kidney complications.
Quitting smoking can significantly slow CKD progression, improve circulation, and enhance the effectiveness of kidney medications.
Can kidney problems affect your eyes or cause dry mouth?
Yes. Fluid imbalance and toxin build-up can lead to eye swelling and dry mouth.
Can kidney problems cause erectile dysfunction or vomiting?
Yes. Hormonal changes and uremic toxins can affect sexual and digestive health.
What color urine indicates kidney issues?
Dark, foamy, cloudy, or reddish urine can be a sign of dehydration, infection, or protein leakage due to kidney dysfunction.
Can multivitamins or tea cause kidney problems?
Excess use of certain supplements or oxalate-rich tea can increase the risk of stones in susceptible people.
Is back pain a sign of kidney problems?
Yes, especially if it’s deep, persistent, and accompanied by urinary changes or fever.
How can I keep my kidneys healthy naturally?
Drink enough water, maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking and painkillers.
Can dehydration damage the kidneys?
Yes. Chronic dehydration increases the risk of kidney stones and reduces filtration efficiency over time.
Final Takeaway
Kidney problems start quietly but can lead to serious consequences if neglected. The first signs are usually seen in your urine patterns, energy levels, and blood pressure.
By understanding how to know and detect kidney problems early, you can prevent chronic damage and maintain a healthy life.
For complete evaluation and advanced care, consult the nephrologist experts at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad — specializing in early diagnosis and treatment of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Take Action Today
If you've noticed any warning signs mentioned in this article:
- Document your symptoms (when, how often, severity)
- Schedule a kidney function tests (GFR, creatinine, urinalysis)
- Consult a nephrologist at PACE Hospitals for expert evaluation
Early detection can prevent 90% of kidney damage progression.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles