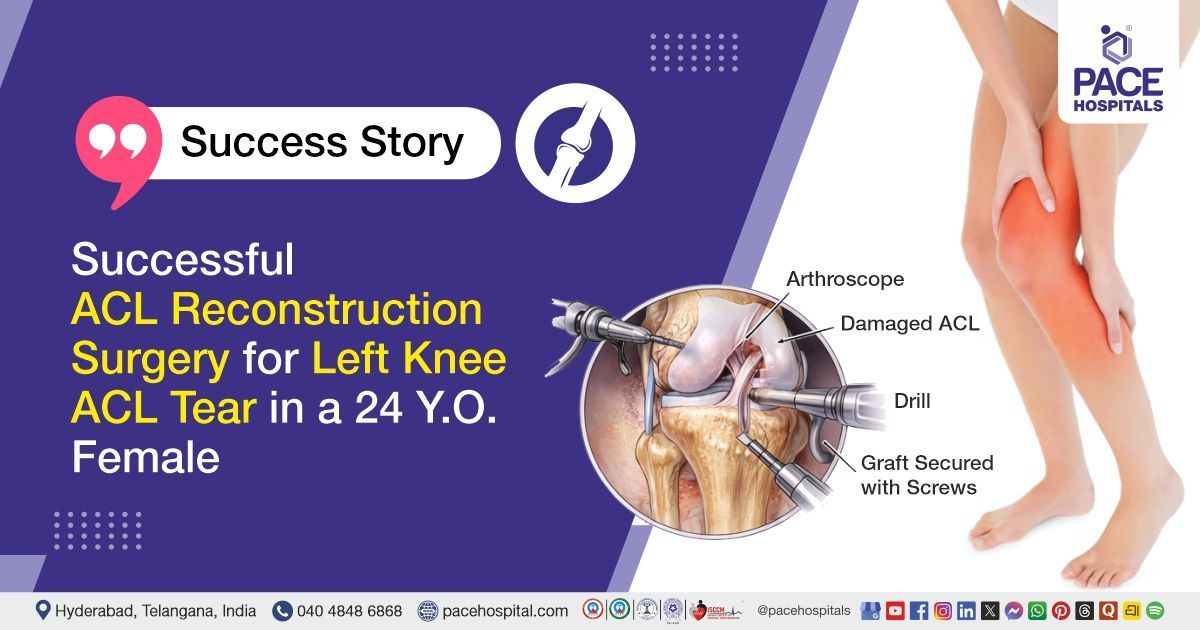
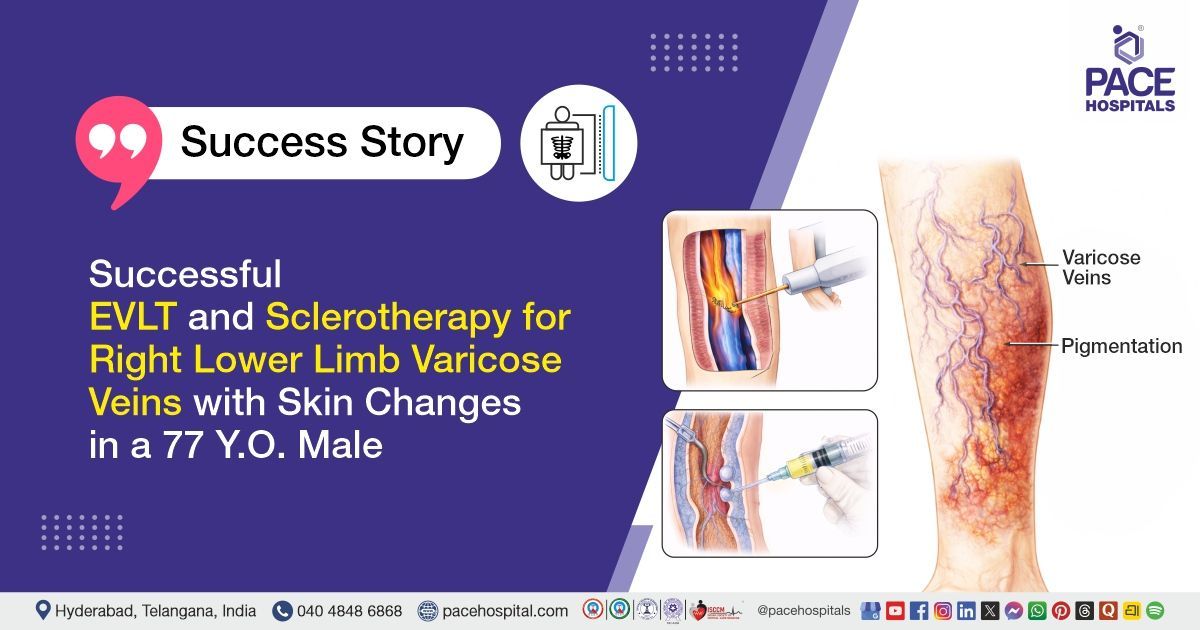
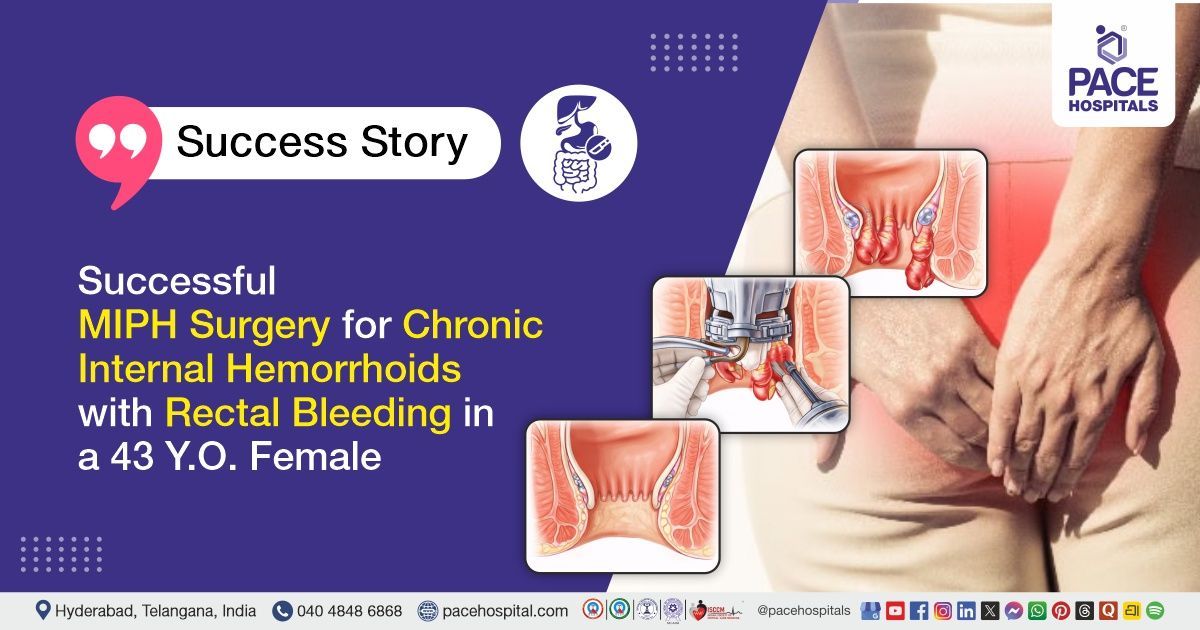
Successful Bilateral FESS and Septoplasty Restored Nasal Function in a 57-Y.O Woman with Chronic Sinus Issues
PACE Hospitals
PACE Hospitals’ expert ENT team successfully performed Bilateral Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS), Septoplasty, and Right Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation
on a 57-year-old female patient who presented with complaints of persistent right nasal blockage and intermittent right ear blockage, occurring on and off for the past three years. The aim of the procedure was to restore normal sinus drainage, correct the deviated nasal septum, and relieve nasal and ear symptoms. The procedure significantly improved the patient's nasal air flow and quality of life.
Chief Complaints
A 57-year-old female patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 21 presented to the ENT Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with complaints of persistent right nasal obstruction and intermittent right ear blockage, occurring on and off for the past three years.
Past Medical History
The patient had no significant history of drug allergies or chronic illnesses. The absence of comorbid conditions was considered favorable in her case, as it reduced the risk of complications during and after surgery and contributed to the expectation of a smoother and more stable postoperative recovery.
On Examination
On general examination, the patient was conscious, coherent, and oriented to time, place, and person, with no signs of acute distress. Systemic examination revealed a deviated nasal septum towards the right side (DNS to right), with no tenderness over the frontal or maxillary sinuses, suggesting absence of acute sinusitis. Bilateral tympanic membranes were intact, with no signs of perforation, discharge, or fluid accumulation, indicating preserved middle ear integrity. The oral cavity appeared normal, with healthy mucosa, intact dentition, and no visible ulcers or lesions. The uvula and soft palate were midline and showed symmetrical movement.
Diagnosis
Following the clinical examination, the ENT team conducted a comprehensive assessment, which included a detailed review of the patient’s medical history and a focused evaluation of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, ears, and oral cavity.
The patient underwent a detailed diagnostic workup including diagnostic nasal endoscopy, which revealed right-sided mucosal hypertrophy and a deviated nasal septum. A non-contrast CT scan of the paranasal sinuses showed polypoidal changes in the bilateral maxillary and anterior ethmoid sinuses, along with a right-sided deviated nasal septum and left concha bullosa. Pure tone audiometry and tympanometry confirmed right-sided Eustachian tube dysfunction without significant hearing loss. Routine blood tests, including inflammatory markers, were normal.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, she was advised to undergo of
Chronic Rhinosinusitis, Deviated Nasal Septum, and Right Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the care of the expert ENT department, ensuring comprehensive management.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with Dr. Mohana Jambula, ENT Surgeon & Allergy Specialist, and cross-consultation with Dr. Mounika Jetti, Consultant General Physician and Diabetologist, in view of patient’s blood pressure (Denovo hypertension) and overall medical condition were optimized prior to surgery to ensure safety. A comprehensive evaluation was then conducted, focusing on the patient’s persistent right nasal and ear blockage. Clinical examination and radiological investigations confirmed chronic rhinosinusitis with a right-sided deviated nasal septum, bilateral mucosal hypertrophy, and right Eustachian tube dysfunction.
It was determined that the patient had chronic rhinosinusitis, a deviated nasal septum, and right Eustachian tube dysfunction. Bilateral Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS), septoplasty, and right Eustachian tube balloon dilation were identified as the most appropriate interventions to restore sinus drainage, correct the septal deviation, and improve Eustachian tube function
The patient and her family were informed about her condition, the procedure, its associated risks, and its potential to alleviate symptoms and enhance her quality of life.
Surgical Procedure
Following the diagnosis, the patient was scheduled to undergo Bilateral Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS), Right Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation, and Septoplasty Surgery in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, under the expert care of the ENT Department.
- Patient Preparation and Anesthesia: The patient was placed in the reverse Trendelenburg position. General anesthesia was administered. Surgical sites were painted and draped under strict aseptic precautions.
- Nasal Cavity Preparation: Bilateral nasal cavity decongestion was achieved with local infiltration of 2% local anesthetic with catecholamine. Nasal packing was done using 4% local anesthetic for additional topical anesthesia.
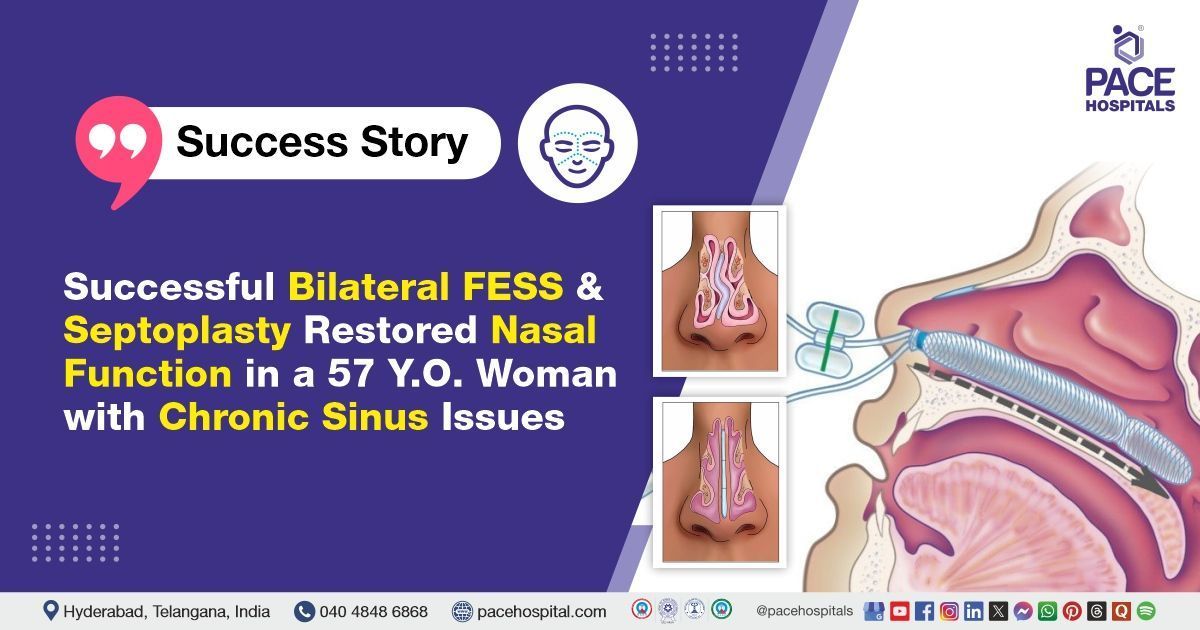
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: Bilateral uncinectomy and middle meatal antrostomy were performed to open the maxillary sinuses. Left conchotomy was done to reduce hypertrophy of the middle turbinate. Bilateral anterior ethmoidectomy was completed to clear ethmoidal sinus disease.
- Septoplasty and Eustachian Tube Procedure: Right-sided deviated nasal septum was corrected via Killian’s incision endoscopic septoplasty on the left side. Right Eustachian tube balloon dilation was performed to improve middle ear ventilation.
- Mucosal Flap Management: Bilateral mucoperichondrial and periosteal flaps were repositioned and sutured with Vicryl to restore nasal mucosa integrity.
- Final Steps and Hemostasis: Bilateral nasal cavities were packed with Ivalon nasal packs (1+1). Dressing was applied, and hemostasis was achieved throughout all stages of the procedure. The immediate postoperative period was uneventful.
Operative Findings:
- Deviated nasal septum (DNS) to the right
- Mucosal hypertrophy in the right maxillary sinus
- Mucosal hypertrophy in the right anterior and posterior ethmoidal sinuses
- Left concha bullosa (pneumatized middle turbinate)
- Polypoidal changes in bilateral maxillary sinuses
- Polypoidal changes in bilateral anterior ethmoidal sinuses
Postoperative Care
The patient postoperative period was uneventful. Postoperatively, the patient was managed with antibiotics, analgesics, antacids, and antihypertensives. Nasal packing was removed prior to discharge, and the patient was discharged in a stable condition with specific post-operative instructions.
Discharge Medications
The patient was prescribed a broad-spectrum antibiotic to prevent postoperative infection. A proton pump inhibitor was given to reduce gastric acidity and prevent gastrointestinal side effects from other medications. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with a muscle relaxant was prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. An antihistamine with a leukotriene receptor antagonist was given to minimize allergic symptoms and nasal mucosal swelling. Additionally, a topical nasal antihistamine spray was advised for bilateral nasal use to control local nasal allergy symptoms and support mucosal healing. An antihypertensive medication was continued to maintain optimal blood pressure during recovery.
Advice on Discharge
The patient was advised to avoid excessive nose blowing and refrain from lifting heavy weights to prevent postoperative complications and promote proper healing.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms such as fever, nose bleeding, abdominal pain, and vomiting.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return to the ENT specialist at PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, for a follow-up appointment for further evaluation of the surgical site and overall progress. Additionally, a review with a general physician was recommended, along with a one-week home blood pressure monitoring chart.
Conclusion
This case highlights the effective multidisciplinary management of chronic rhinosinusitis with a deviated nasal septum and Eustachian tube dysfunction. Surgical intervention led to significant improvement in symptoms, ensuring optimal recovery and long-term patient well-being through recommended follow-up care.
Comprehensive Surgical Intervention for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Structural Nasal Issues
Chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by structural nasal abnormalities requires a well-planned, multidisciplinary surgical approach to achieve lasting symptom relief. Correcting septal deviation alongside addressing mucosal hypertrophy and Eustachian tube dysfunction simultaneously helps restore normal nasal airflow and sinus drainage, significantly improving patient comfort and function. Close collaboration with an
Otolaryngologist / ENT specialist ensures precise diagnosis and tailored treatment, minimising the risk of recurrence and postoperative complications. This integrated strategy highlights the value of addressing both anatomical and inflammatory factors to enhance patient outcomes and quality of life.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868