Successful EUS-Guided Cystogastrostomy for Walled-Off Pancreatic Necrosis in a 38 Y.O. Female
PACE Hospitals
The PACE Hospitals’ expert gastroenterology team successfully performed an EUS-Guided Cystogastrostomy on a 38-year-old female patient diagnosed with Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis on Chronic Idiopathic Pancreatitis with Walled-Off Pancreatic Necrosis (WOPN). The aim of the procedure was to drain the walled-off necrotic collection, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications such as infection or obstruction.
Chief Complaints
A 38-year-old female patient with a body mass index (BMI) of 22 presented to the Gastroenterology Department at PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with chief complaints of acute epigastric and left hypochondriac pain radiating to the back lasting for one day.
Past Medical History
The patient had a known history of Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis, systemic
hypertension and
fissure in ano, for which she was on regular medication.
On Examination
On general examination, the patient was conscious, coherent and oriented, with pallor present. Vital signs were abnormal, indicating tachycardia and fever, while oxygen saturation was normal. On systemic examination, the abdomen was soft, but tenderness was noted in the epigastrium and left hypochondrium, with a palpable mass in the same regions.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was evaluated by the Gastroenterology team for a 1-day history of severe epigastric and left hypochondrial pain radiating to the back, with fever and reduced oral intake. Her history included idiopathic chronic pancreatitis, systemic hypertension, and a known fissure in ano. Examination showed pallor, fever, tachycardia, and a palpable epigastric mass, raising suspicion of acute necrotising pancreatitis with fluid collection.
The patient underwent an extensive diagnostic evaluation. Ultrasound of the abdomen showed necrotizing pancreatitis with a large walled-off pancreatic necrosis (WOPN) and minimal bilateral pleural effusion. Contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) of the abdomen confirmed a well-defined walled-off necrotic collection measuring 18.3 × 12.3 × 9.2 cm in the peripancreatic region with chronic calcific pancreatitis changes and intraductal calculi. Laboratory investigations revealed iron deficiency anemia, hypoalbuminemia, elevated inflammatory markers (CRP, Procalcitonin), transient acute kidney injury, hyponatremia, and urine culture positive for Candida species suggestive of fungal urinary tract infection (UTI). Pus culture from the collection showed multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sensitive to specific antibiotics.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, the patient was advised to undergo Walled-off Pancreatic Necrosis Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Gastroenterology Department.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with consultant gastroenterologists, Dr. Govind Verma, Dr. M Sudhir, Dr. Padma Priya, and cross-consultation with the anaesthesia and critical care team including, Dr. Manasa Gaddam, Dr. Renuka Seshamamba K , a comprehensive evaluation was performed to determine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Considering the patient’s history of acute necrotising pancreatitis on chronic calcific pancreatitis, severe epigastric and left hypochondrial pain with a palpable mass, recurrent fever spikes, and systemic comorbidities, an optimal minimally invasive treatment strategy was planned.
Based on the clinical and imaging findings, it was determined that EUS-guided cystogastrostomy with metallic stent placement was identified as the most suitable intervention to achieve effective internal drainage, reduce infection and inflammation, relieve pain, and minimize surgical risks in a patient with anemia and systemic compromise.
The patient and her family members were counselled regarding the diagnosis, the planned procedure, associated risks, expected benefits, and the potential for significant improvement in quality of life, after which informed consent was obtained.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled to undergo an EUS Guided Cystogastrostomy Procedure in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, under the expert supervision of the Gastroenterology Department.
The following steps were carried out during the procedure:
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Assessment: Under sedation, an
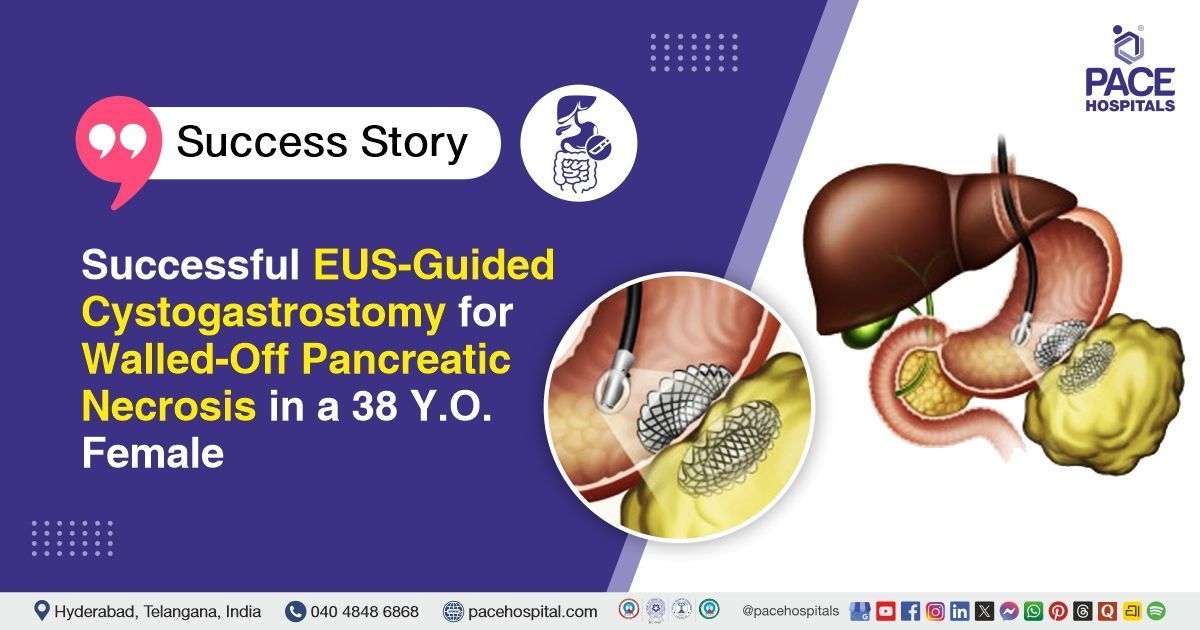
endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) scope was advanced into the stomach to visualize the walled-off pancreatic necrosis (WOPN). The collection measured approximately 14 × 6.6 cm, with evidence of pus and necrotic debris. Critical anatomical structures, including surrounding vessels, were identified to avoid complications during puncture.
- Site Selection and Puncture: The optimal puncture site on the gastric wall was identified based on proximity to the WOPN and absence of interposing vessels. The collection was accessed through the gastric wall using a dedicated puncture needle, ensuring safe entry into the necrotic cavity.
- Guidewire Placement: A guidewire was carefully passed into the necrotic collection through the puncture needle. The position of the guidewire was confirmed under EUS and fluoroscopic guidance to secure access and facilitate stent deployment.
- Tract Dilation: The puncture tract was dilated over the guidewire to allow placement of the metallic stent, creating a secure pathway for drainage from the WOPN into the stomach.
- Stent Deployment: An axiom metallic stent was deployed across the cystogastric tract. Successful placement was confirmed as pus and necrotic material drained through the stent, establishing effective internal drainage.
Postoperative Care
The procedure was uneventful. The patient was kept Nil by mouth (NBM) for 24 hours, and a follow-up CT abdomen showed the stent in situ with a reduction in the size of the collection compared to prior imaging. During the hospital stay, the patient was treated with IV fluids, IV sensitive antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and other supportive medications. The patient improved symptomatically and was discharged with the prescribed medications.
Discharge Medications
The patient was discharged with medications for infection control, digestive support, cholesterol management, and cardiac stabilization. Nutritional supplements were advised, along with medicines for fever,
constipation, local anorectal care, pain relief, and nausea as needed.
Advice on Discharge
Upon discharge, the patient was advised to follow a high-protein diet to support tissue repair, recovery, and overall healing.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain and vomiting.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up visit after 10 days with the Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, to review her condition.
Conclusion
This case highlights the effective endoscopic management of acute necrotising pancreatitis with a large walled-off pancreatic necrosis. EUS-guided cystogastrostomy achieved successful drainage with clear radiological improvement. Associated complications like anemia, hypoalbuminemia, acute kidney injury (AKI) and fungal urinary tract infection (UTI) were managed appropriately. The patient improved clinically and was discharged in stable condition.
Minimally Invasive Management of Pancreatic Fluid Collections
Minimally invasive endoscopic techniques, such as EUS-guided cystogastrostomy, have transformed the management of pancreatic fluid collections and necrosis. These procedures provide effective internal drainage while minimizing surgical risks and hospital stay. Early intervention, combined with supportive care including antibiotics, nutritional support, and monitoring for systemic complications, enhances recovery.
Multidisciplinary collaboration between gastroenterologist/gastroenterology doctor, radiologists, and critical care specialists is critical for optimizing outcomes. Careful imaging evaluation, procedural planning, and post-procedure follow-up are essential to ensure safety and efficacy. This approach highlights the importance of precision and individualized care in complex pancreatic disorders.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868
Appointment request - health articles
Recent Articles