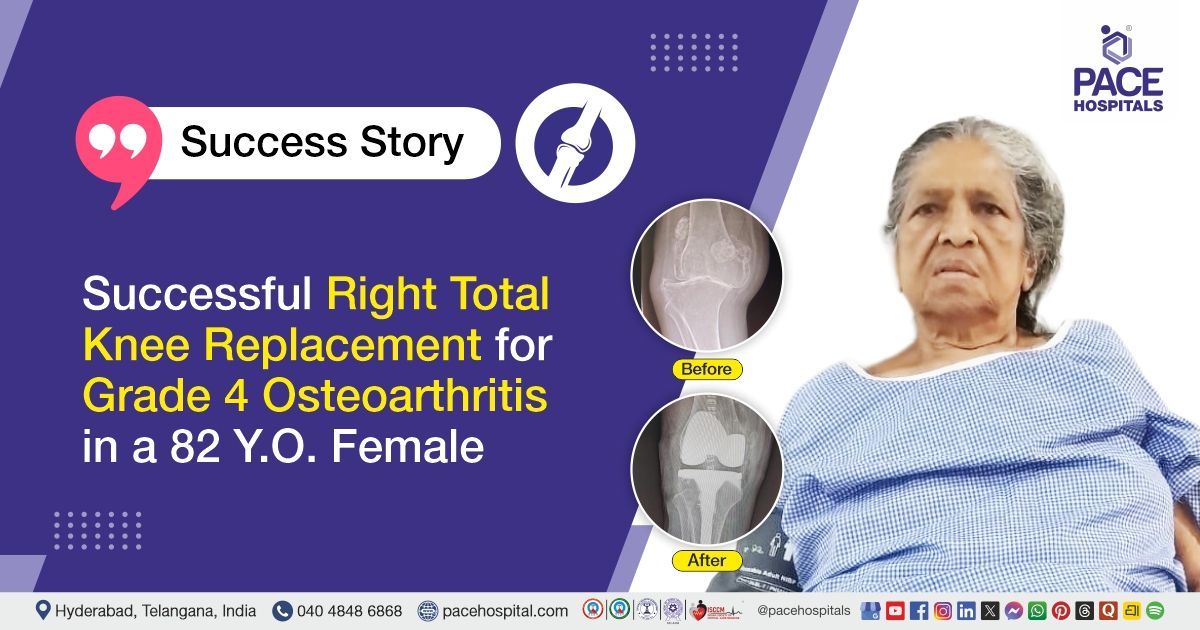
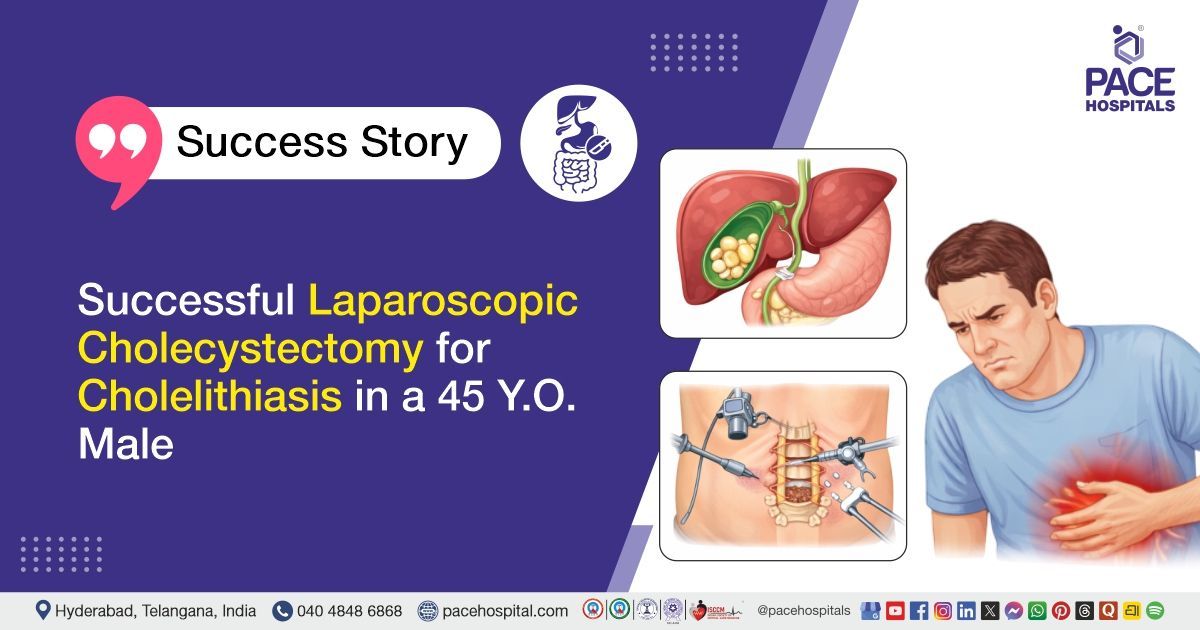
Successful Endoscopic Dilatation for Corrosive Esophageal Stricture in a 4 Y.O. Girl
PACE Hospitals
The PACE Hospitals’ expert gastroenterology team successfully performed an Endoscopic Stricture Dilatation on a 4-year-old girl diagnosed with a corrosive injury–induced esophageal stricture. The procedure was aimed at relieving the esophageal narrowing to restore normal swallowing and improve nutritional intake.
Chief Complaints
A 4-year-old girl presented to the Gastroenterology Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with a 15-day history of vomiting after consuming solid foods, a nocturnal cough for the past 15–20 days, and an unintentional weight loss of 2 kg over the past month.
Past Medical History
The patient had ingested Harpic powder and was subsequently admitted to another facility, where she received injectable antibiotics and was started on a liquid diet. She had no other significant past medical history.
On Examination
On general examination, the patient was conscious, coherent, and oriented to time, place, and person. Vital signs were stable. Cardiovascular examination revealed normal heart sounds with no murmurs, rubs, or gallops. Abdominal examination showed a soft, non-tender abdomen with no organomegaly or palpable masses.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was thoroughly evaluated by the Gastroenterology team following a history of Harpic powder consumption, resulting in vomiting on solid foods, nocturnal cough, and weight loss over 1 month. There was a strong clinical suspicion of esophageal stricture secondary to corrosive injury.
The patient underwent an extensive diagnostic evaluation. Endoscopy revealed a narrowing of the esophagus at 15 cm, and oral gastrograffin study demonstrated an esophageal stricture of approximately 5 cm in length. Laboratory investigations showed microcytic hypochromic anemia with thrombocytosis, raising the possibility of iron deficiency or beta thalassemia trait. Liver and renal function tests were within normal limits.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, the patient was advised to undergo Esophageal stricture Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Gastroenterology Department.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with consultant gastroenterologists, Dr. Govind Verma, Dr. M Sudhir, Dr. Padma Priya, and cross consultation with Pediatrician Dr. Navya Sri Galli, and pulmonologist, Dr. Pradeep Kiran Panchadi, a comprehensive evaluation was performed to determine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Considering the patient’s history of harpic powder ingestion leading to corrosive injury, persistent vomiting on oral feeds, nocturnal cough, weight loss of 2 kg over 1 month, and investigations showing severe microcytic hypochromic anemia with leukocytosis and thrombocytosis, as well as imaging and endoscopy findings of a 5 cm esophageal stricture at 15 cm from the incisors, an optimal management strategy was formulated.
Based on these clinical and diagnostic findings, it was determined that endoscopic stricture dilatation under fluoroscopic guidance with Ryles tube placement was identified as the most suitable therapeutic intervention to relieve obstruction, facilitate enteral nutrition, and reduce the risks associated with more invasive surgical procedures.
The patient and her family members were counselled regarding the diagnosis, planned procedure, associated risks, and its potential to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled to undergo Endoscopic Stricture Dilatation Procedure in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals under the expert supervision of the Gastroenterology Department.
The following steps were carried out during the procedure:
- Anesthesia and Preparation: The patient was placed under sedation/general anesthesia with continuous monitoring of vital signs and oxygen saturation. The patient was positioned for safe endoscopic access.
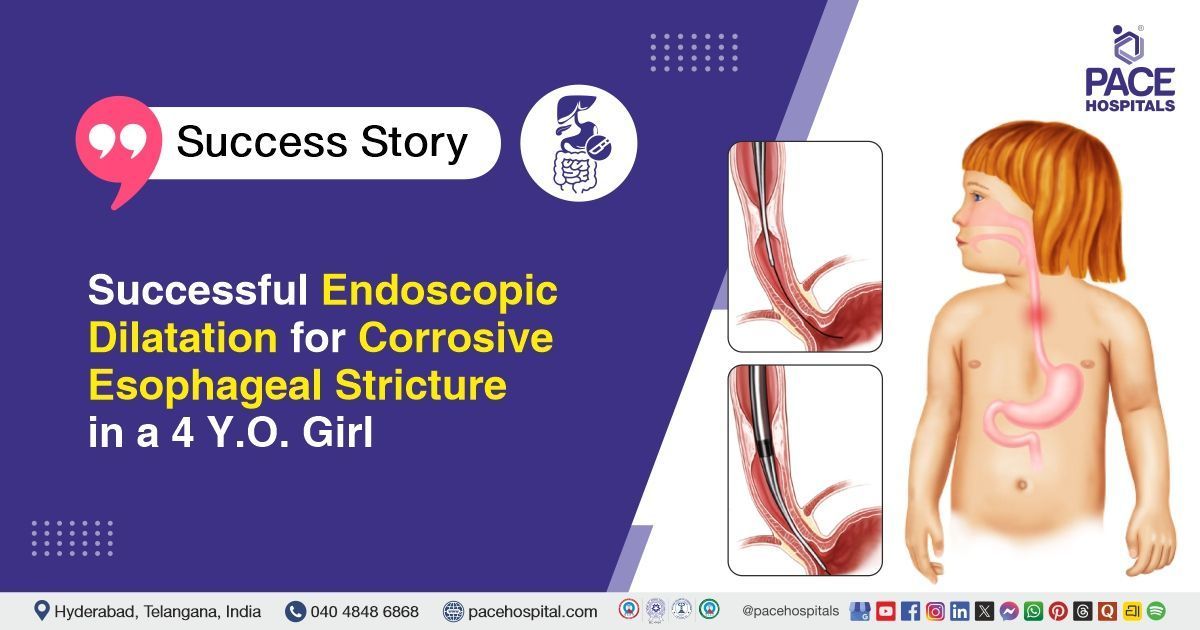
- Diagnostic Endoscopy: A pediatric endoscope was inserted, and the esophageal stricture at 15 cm from the incisors was identified, measuring approximately 5 cm in length. The scope could not initially pass beyond the stricture.
- Endoscopic Stricture Dilatation: Under fluoroscopic guidance, sequential dilators were used to dilate the stricture gradually up to 5 mm and then 7 mm. Care was taken to prevent mucosal injury or perforation.
- Ryle’s Tube Placement: A Ryle’s tube was inserted through the dilated esophagus into the stomach under fluoroscopic guidance to enable enteral feeding. Correct positioning was confirmed.
- Post-Procedure Imaging: Contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) of the abdomen via the Ryle’s tube was performed to verify esophageal patency and normal distal gastrointestinal anatomy, ensuring no perforation or obstruction.
Postoperative Care
The procedure was uneventful, and the patient’s postoperative recovery was satisfactory. During the hospital stay, she received Ryle’s tube (RT) feeds, intravenous antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, and antiemetics. Pulmonology consultation was obtained for cough management, and nebulization therapy was administered. Pediatric consultation was also taken and appropriate management was provided. Nutritional guidance was offered by a dietician, and caregivers were counseled on balanced feeding through the Ryle’s tube. The patient tolerated feeds well and was discharged in stable hemodynamic condition with appropriate postoperative instructions and follow-up advice.
Discharge Medications
At discharge, the patient was advised to continue treatment to prevent infection, improve anaemia, and protect the stomach. Medicines were also provided to control nausea and address any respiratory or allergy-related symptoms. Additional support included medication for fever or general discomfort.
Advice on Discharge
The patient was advised on discharge to take proper care of the Ryle's tube (RT) and to avoid oral feeding. They were instructed to undergo an iron profile and hemoglobin electrophoresis. Dietary guidance included following the prescribed diet chart and administering RT feeds at 50 ml/h in a propped-up position, while withholding feeds from 10 PM to 6 AM. Additionally, the patient was advised to continue chest physiotherapy as recommended.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, vomiting, cough, chest pain, intolerance or resistance to Ryle’s tube feeds, or rapid or labored breathing.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up visit after one week with the Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals and also with the pediatrician, to review her condition.
Conclusion
This case highlights the effective endoscopic management of a corrosive-induced esophageal stricture in a young child. Timely stricture dilatation with Ryle’s tube placement restored safe enteral feeding and improved symptoms. Multidisciplinary care supported recovery, and the child was discharged in stable condition with appropriate follow-up planned.
Healing Beyond the Stricture: A Minimally Invasive Success in Pediatric Care
Minimally invasive techniques in pediatric healthcare have transformed the management of complex conditions. These approaches reduce surgical trauma, lower complication risks, and promote faster recovery in children. They allow precise treatment of gastrointestinal and other internal disorders with minimal disruption to normal anatomy and function. Comprehensive care, including nutritional support and careful monitoring, is essential for optimal recovery.
Collaboration among specialists, including a gastroenterologist / gastroenterology doctor, enhances treatment outcomes. These methods also contribute to shorter hospital stays and less emotional and physical stress for both children and their families. Overall, such advanced interventions improve pediatric patient health, safety, and quality of life.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868