Successful Total Abdominal Hysterectomy for Multiple Uterine Fibroids in a 39 Y.O. Female
PACE Hospitals
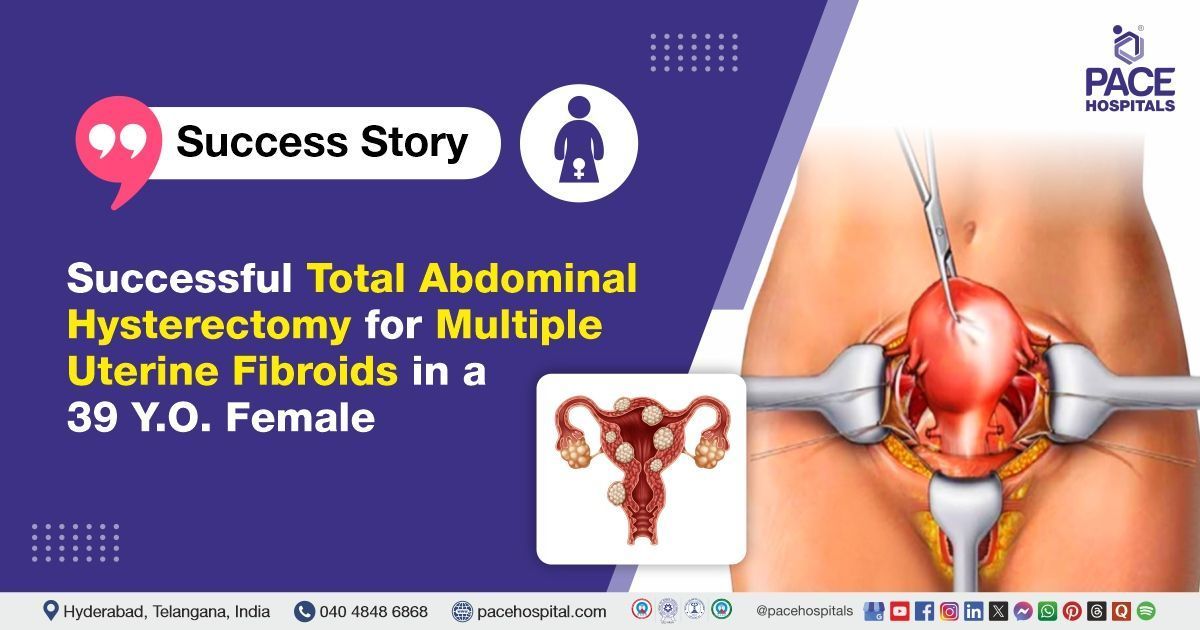
PACE Hospitals’ Expert Gynaecology team successfully performed a Total Abdominal Hysterectomy with Bilateral Salpingectomy and Bilateral Ureteric Catheterization on a 39-year-old female diagnosed with multiple uterine fibroids causing abnormal uterine bleeding. The procedure was performed to relieve her symptoms of pain in the left iliac region, recurrent urinary tract infections, pressure symptoms, dysmenorrhoea, and menorrhagia. The surgery aimed to improve her overall quality of life and prevent further complications.
Chief Complaints
A 39-year-old female patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 23 presented to the Gynaecology Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with complaints of pain in the left iliac region, on-and-off
urinary tract infections (UTI), pressure symptoms,
dysmenorrhoea (painful menstruation), and menorrhagia (heavy menstrual bleeding). These symptoms had a significant impact on her quality of life and prompted further evaluation and surgical intervention.
Past Medical History
The patient had an obstetric history of two full-term normal vaginal deliveries and a tubectomy (P2L2 - NVD Tubectomised). She had no known drug allergies.
On Examination
On examination, the patient was conscious, coherent, and cooperative, with stable vital signs, slightly elevated borderline blood pressure, but not an immediate concern. General physical examination revealed no pallor, icterus, cyanosis, clubbing, lymphadenopathy, or pedal edema. Abdominal examination showed a non-mobile mass corresponding to approximately 24 weeks’ size of the uterus, with no tenderness. Per speculum and per vaginal examination revealed a bulky cervix positioned high up, with no tenderness in the fornices. A systemic examination of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems was within normal limits, with equal air entry and normal heart sounds.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was evaluated by the Gynaecology team, which included a detailed review of her medical history and a comprehensive clinical examination revealing a significantly enlarged, non-mobile, non-tender uterus corresponding to approximately 24 weeks’ size.
Ultrasound imaging showed a predominantly anechoic pelvic collection with internal septae beneath the abdominal wall incision, and Mild bilateral hydronephrosis was present with no internal echoes in the pelvicalyceal system. The right and left renal pelvis measured 10.8 mm and 13.7 mm, respectively, due to ureteral compression by the fibroid. No abnormal echoes were seen in the pelvicalyceal system. Preoperative blood investigations revealed mild anemia with microcytic hypochromic red blood cells, neutrophilic leukocytosis, and adequate platelet count, indicating chronic blood loss and possible inflammation. Serum electrolytes, blood urea, and serum creatinine were within normal limits. There were no signs of acute infection or systemic compromise.
Based on the confirmed findings, the patient was advised to undergo
Uterine Fibroid Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Gynaecology Department, ensuring comprehensive evaluation and management tailored to the patient's needs.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with Dr. Mugdha Bandawar, a Gynaecologist, in collaboration with Urology consultants Dr. Abhik Debnath and Dr. K. Ravichandra, a multidisciplinary approach was taken to determine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic strategy for the patient. Considering her history of previous normal vaginal deliveries, alongside the clinical findings of a significantly enlarged uterus and ultrasound evidence of a huge fibroid, the team assessed the extent of the pathology and potential complications.
Further evaluation, including physical examination and laboratory investigations, confirmed the need for surgical intervention. It was determined that a Total Abdominal Hysterectomy with Bilateral Salpingectomy and Bilateral Ureteric Catheterisation was identified as the most effective medical approach to relieve symptoms and prevent further gynaecological or urological complications.
The patient and her family were counselled in detail regarding the diagnosis, the planned procedure, associated risks, expected benefits, and the potential for improvement in quality of life, after which informed consent was obtained.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled to undergo a Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Surgery in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals along with Bilateral Salpingectomy and Bilateral Ureteric Catheterisation under the supervision of the expert Gynaecology Department.
The following steps were carried out during the procedure:
- Preoperative Preparation and Access: The patient was positioned supine and administered general anesthesia. Prophylactic antibiotics were given, and the abdominal area was prepped and draped in a sterile manner.
- Incision and Exploration: A lower abdominal incision, typically a Pfannenstiel incision, was made to gain access to the pelvic cavity. Upon entering, a large uterus with multiple fibroids was identified and assessed.
- Bilateral Ureteric Catheterisation: Due to anticipated ureteral compression from the fibroids, bilateral ureteric catheterisation was performed to help identify and protect the ureters during surgery.
- Dissection and Mobilisation: The bladder was carefully dissected off the lower uterine segment to create a bladder flap. Both uterine vessels and the round ligaments were ligated and divided bilaterally to mobilise the uterus.
- Bilateral Salpingectomy: Both fallopian tubes were identified and removed as part of the procedure.
- Uterus Removal: The uterus, along with the fibroids, was fully mobilised and detached from surrounding tissues. The specimen was then removed through the abdominal incision.
- Hemostasis and Closure: Hemostasis was meticulously achieved, and the pelvic cavity was irrigated. Depending on intraoperative conditions, ureteric catheters were either removed or left in place. The abdominal incision was then closed in layers.
- Intraoperative Management: One unit of packed red blood cells was transfused intraoperatively to manage blood loss.
Postoperative Care
The postoperative period was uneventful. During the hospital stay, the patient was closely monitored in the surgical intensive care unit (SICU) for 48 hours before being shifted to the ward once hemodynamically stable. Ultrasound screening was within normal limits. A Foley catheter was kept for 72 hours to aid healing and was removed along with the ureteric catheter. The patient received intravenous antibiotics, pain relief medications, stomach protection therapy, and supportive treatments. Additionally, she was administered intravenous Iron (Hematologic Agent) before discharge. Pain was well controlled with appropriate analgesics. The patient was discharged in stable condition with follow-up instructions.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed an antibiotic to prevent postoperative infection, a pain relief medication to manage discomfort, a medication to reduce stomach acid, an enzyme supplement to aid tissue healing, vitamin D, multivitamins to support overall nutrition, and a laxative to maintain bowel regularity. She was also advised to use a topical ointment for local wound care.
Advice on Discharge
The patient was advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise during the recovery period.
Dietary Advice
A soft diet was suggested to ease digestion and promote healing.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms like heavy bleeding, fever, abdominal pain, or vomiting.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up appointment with the Gynaecologist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals after 10 days.
Conclusion
The patient underwent a successful total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingectomy and bilateral ureteric catheterisation for multiple uterine fibroids with abnormal uterine bleeding. The postoperative period was uneventful, and the patient showed steady recovery with appropriate care. Follow-up appointments have been scheduled to monitor continued recovery and ensure long-term well-being.
Timely Surgical Intervention Prevented Further Complications
The patient was experiencing persistent symptoms such as pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, and pressure on nearby organs due to large uterine fibroids. After evaluation by the gynaecologist, it was determined that delaying treatment could result in worsening symptoms and potential long-term complications.
A gynaecologist / Gynaecology doctor recommended surgical intervention as the most effective approach to relieve these issues. By proceeding with surgery at the right time, the medical team successfully prevented further health risks and significantly improved the patient’s quality of life. Timely decision-making by the gynaecology team played a crucial role in the positive outcome. This case underscores the importance of early consultation with a gynaecologist when chronic symptoms arise.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868