An Overview of Low Back Pain - Causes, Risk Factors and Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Low back pain or Lumbago (medical term of low back pain) is one of the most frequent health issues worldwide. It affects more than 80% of adults at some time in their life, making it a common reason for people to consult a doctor.
Lower back pain is also a leading cause of disability, according to the Global Burden of Disease study published in the Lancet medical journal. Low back pain is categorized as acute, subacute, or chronic. Acute episodes of lower back pain last a few days to four weeks, whereas subacute episodes last for four to twelve weeks. About 20 percent of people with acute back pain go on to develop chronic back pain defined as pain that lasts 12 weeks or longer. The good thing is that most of the time back pain improves or resolves with proper care and treatment.
Anatomy of the Spine and Its function
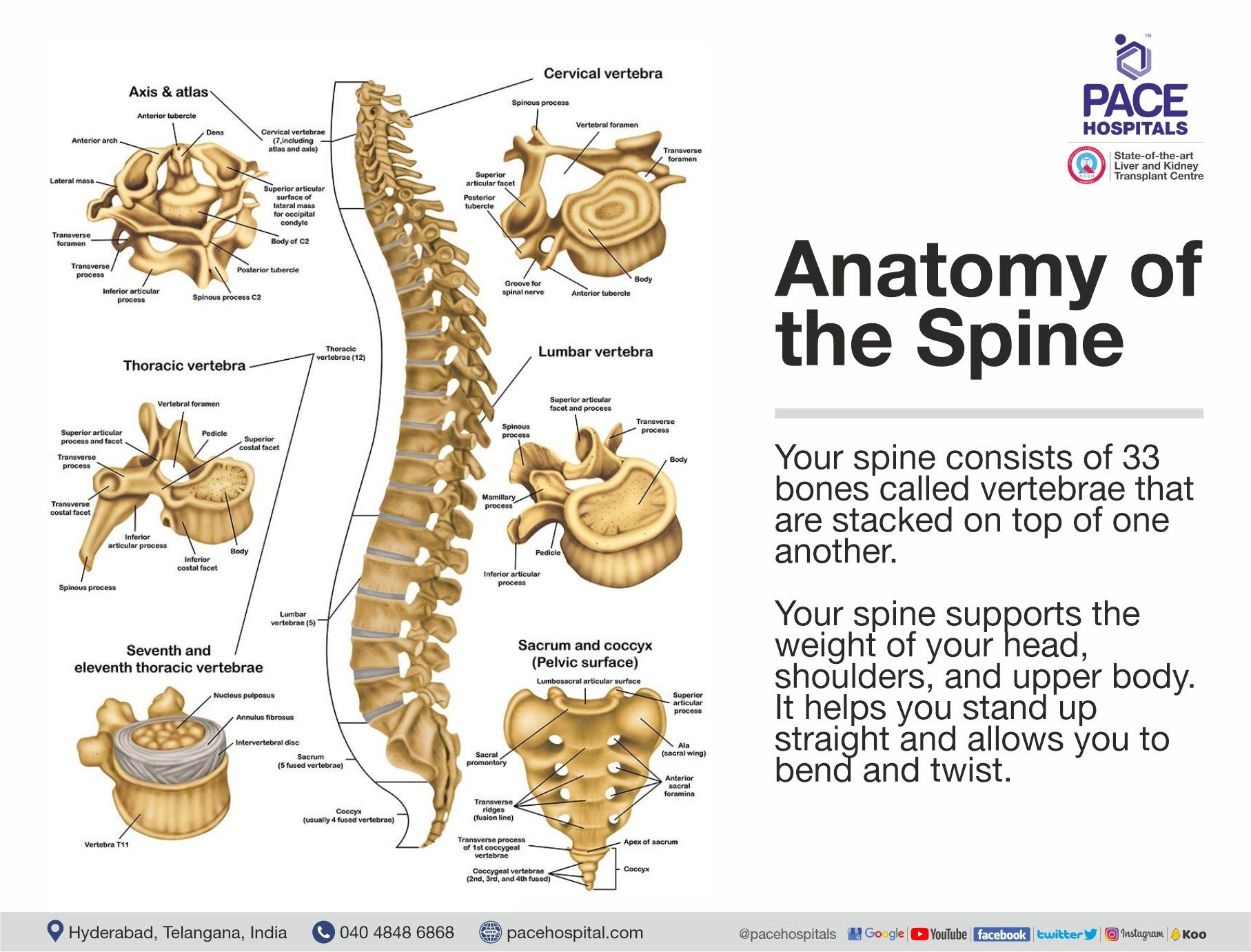
The spine is a remarkable and complex structure that plays several essential roles in your body. It supports the weight of your head, shoulders, and upper body, helps you stand upright, and enables you to bend and twist. With constant demands placed on it, understanding how your spine functions can provide insights into the causes of back pain, particularly in the lower back, also known as the lumbar region.
Anatomy of the Spine
Your spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae, stacked on top of one another. The lumbar spine, located in the lower back, is made up of five vertebrae. Together, these bones form a spinal canal that houses and protects the spinal cord.
Spinal nerves, resembling electrical cables, travel through the spinal canal, transmitting signals between the brain and muscles. These nerves exit the spinal canal through openings in the vertebrae known as foramina.
Facet joints, located between each vertebra, facilitate spinal movement. Between the vertebrae are intervertebral discs, which serve as shock absorbers and prevent the bones from rubbing against each other during activities like walking or running.
The Role of Intervertebral Discs
Intervertebral discs are flat, round, and about half an inch thick. Each disc has two main components:
- Annulus Fibrosus: The tough, flexible outer layer that provides structural integrity.
- Nucleus Pulposus: The soft, jelly-like center responsible for absorbing shocks.
The discs and facet joints work together to enable smooth spinal movements like twisting and bending.
Ageing and Back Pain
In children and young adults, intervertebral discs are rich in water, which helps maintain their cushioning ability. However, as we age, these discs gradually lose water, shrink, and become less effective at cushioning the vertebrae. This degeneration is a common cause of back pain.
Supporting Structures of the Spine
Muscles and ligaments play a crucial role in providing support and stability to the spine. Strong ligaments connect the vertebrae, keeping the spinal column aligned and functional.
Causes of Back Pain
Issues with any component of the spine—be it the vertebrae, facet joints, intervertebral discs, nerves, muscles, or ligaments—can lead to back pain. Understanding these structures and their functions is key to identifying and addressing the root causes of discomfort.
By taking steps to maintain a healthy spine, such as staying active, maintaining proper posture, and seeking timely medical advice, you can reduce the risk of back pain and support overall spinal health.
Most common causes of low back pain
Strains and sprains
Any injury to the muscles and ligaments that support your spine will cause back pain. Injury can occur while lifting a heavy weight improperly, poor posture or being overweight.
Herniated Discs
Intervertebral discs' protective outer layer might break away over time. The soft inner disc tissue may push through the outer layer. A disc that bulges or slips out of place is known as a herniated disc, bulging disc, or slipped disc and may press on nerve roots, leading to symptoms such as pain, tingling, numbness or weakness in the area that the nerve root supplies. Sciatica is a type of pain caused by a pinched or irritated sciatic nerve. This nerve runs down your lower back through your hips and buttocks and down each leg. Sciatica is how common people refer to pain that travels down the leg from the lower back, although your doctor may use the term lumbar radiculopathy.
Disc Degeneration
While the word may sound frightening, it just implies you have a damaged disc that is giving you discomfort. The discs begin to wear away and shrink as we age. In some cases, they may entirely collapse, causing the facet joints to rub against one other. Pain and stiffness result. This wear and tear on the facet joints are known as osteoarthritis. The pain gets worse with movement. When the disc collapse and osteoarthritis develops, your body may respond by growing new bone in your facet joints to help support the vertebrae. This bone overgrowth called spurs can lead to narrowing of the spinal canal (Spinal Stenosis). Osteoarthritis can also cause the ligaments that connect the vertebrae to thicken, which can also narrow the spinal canal. Spinal stenosis can occur in both upper (cervical) spine and the lumbar spine, but lumbar spinal stenosis is more common
Spondylolisthesis
It is a condition where your vertebra can slide forward on the top of another. If too much slippage occurs, the bones begin to press on the spinal nerves, resulting in weakness of muscles and bowel and bladder disturbances.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can cause low back pain, this is a condition that makes your bones brittle and porous. Compression fractures occur when too much pressure is placed on the weakened vertebra. The thinned bone may even break with everyday activity. In severe osteoporosis, the vertebral bone completely collapses. Multiple fractures cause a severely rounded back.
Infections of the spine
Infections of the spine like TB and non-Tb infections can cause back pain. Infections of discs (discitis) and bone (osteomyelitis) can cause severe pain and require prompt medical attention.
Abnormal shape of the spine
Some conditions make your spine to develop abnormal shapes like kyphosis (Increased forward bending of the spine), scoliosis (side bending of the spine) and excessive lordosis.
Inflammatory back pain
They are usually associated with multiple joint pains and morning stiffness. Ankylosing spondylitis is a rare arthritic condition that causes pain and stiffness.
Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis, are some examples.
Sacroiliac joint pain
Your spine is connected to your pelvis on both the sides by the sacroiliac joints. Inflammation and infections of the sacroiliac joints produces back pain.
Other conditions that can cause low back pain
Cancer of the spine, Bladder infections, kidney stones, kidney infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, sleeping disorders
Posture related
Some daily activities and poor posture can cause back pain. These include awkward bending movements involving the spine, forward bending and lifting heavy weights, Standing or sitting for a longer time, Improper sleeping postures, Improper sitting posture while driving or using a computer
Who all are at risk to get low back pain?
People with sedentary life style, poor physical activity, Obesity, Smoking and drinking, pregnant women. Women are at more risk than men due to hormonal factors.
When is Lower Back Pain an Emergency?
Although most episodes of lower back pain subside on their own, there are occasions when you should seek medical attention immediately, these conditions include:
- Accident, injury, other trauma
- Fever, unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite
- Weakness develop in the legs and/or feet
- Inability to control urine and stools or urinary retention
- Previous history of cancer
- Pain is severe, constant, suddenly or progressively worsens, and/or doesn’t go away
- Pain interrupts sleep
Cauda Equina Syndrome
It occurs due to the compression of bundle of nerves below the spinal cord in the lumbar spine. Patients will have inability to control urine and stools or urinary retention and numbness around the genital and anal region. It is a serious disorder that requires immediate medical attention and emergency surgery.
Treatment of low back pain
Most of the time, back pain resolves on its own. You may begin by practising home care techniques such as taking rest, ice, and heat packs, however, in some cases, it requires medical or surgical treatment. The treatment is cause specific.
Medications: Based on the severity, your doctor might prescribe you pain relievers, muscle relaxants, topical pain relievers and antidepressants in chronic pain. These medications are to be taken under the guidance of your doctor. Otherwise, they will result in serious side effects.
Physiotherapy: It involves passive and active therapies to build core muscle strength, improve spine flexibility, range of motion and correct the posture. Various modalities of physical therapy like massage, exercises, Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy and ultrasound are in use.
Surgery: Surgery is rarely required for back pain. Your doctor suggests surgery if the patient suffers from disc problems, spinal instability, nerve compression that lead to muscle weakness, loss of bowel and bladder control.
Commonly performed spine surgeries include:
- Discectomy (Microdiscectomy (MLD) / Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy)
- Laminectomy
- Spinal fusion procedures
Tips to Prevent Lower Back Pain
You can't stop ageing, but you can adopt lifestyle adjustments to help manage and avoid lower back pain.
Improve your physical fitness: Physical fitness will improve core muscles strength that support your spine. Regular exercises such as walking, swimming, yoga are excellent ways of preventing back pain
Stay active: People who maintain a sedentary life may harm themselves more when they exercise. It is advised to do a smaller amount of physical activity most days of the week than to sit all week and over-exercise yourself on the weekends.
Maintain proper body weight: Proper food habits-Have food rich in calcium and vitamin D and vitamin K, as they are important in making bones strong. Milk, leafy green vegetables, broccoli etc.
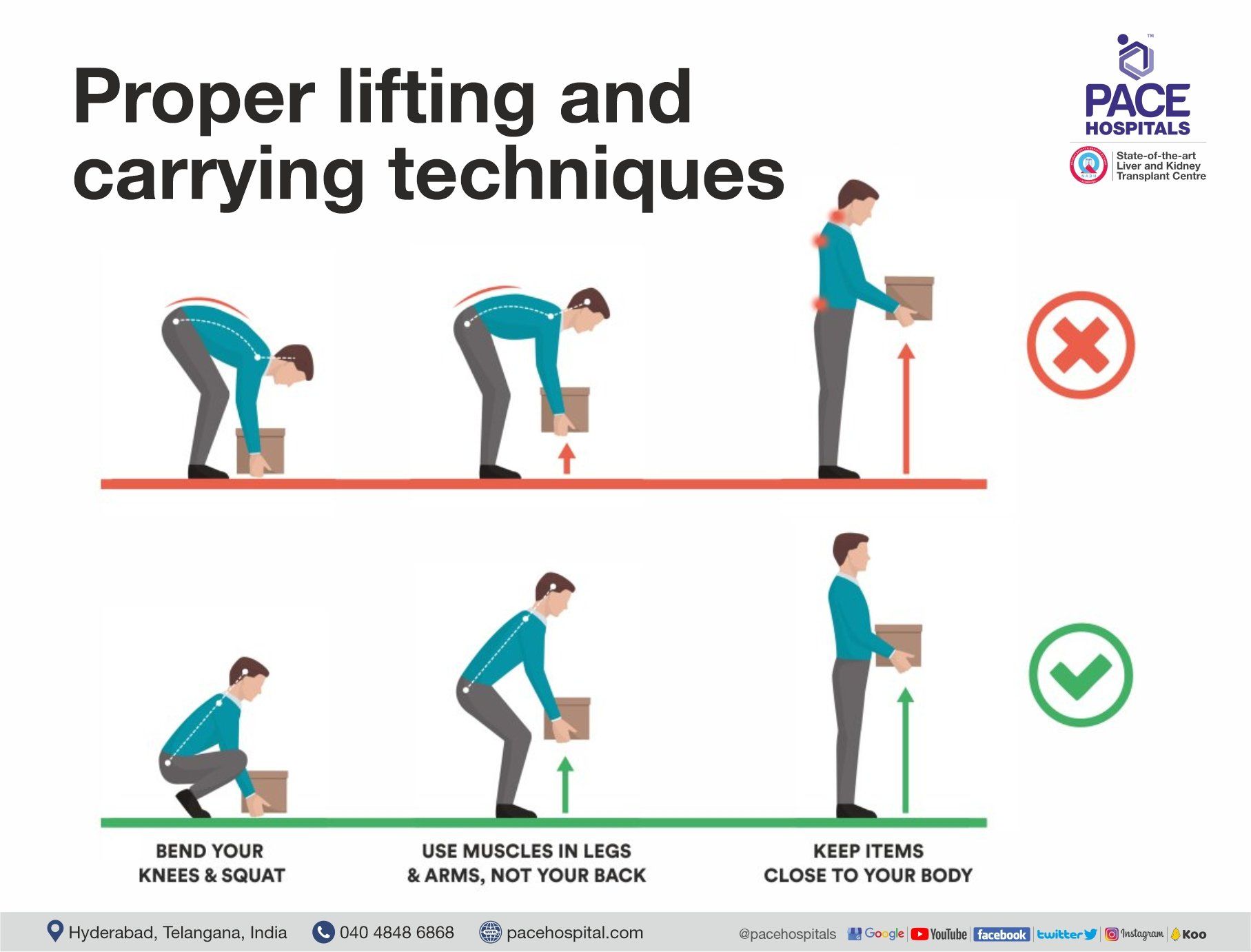
Proper lifting and carrying techniques
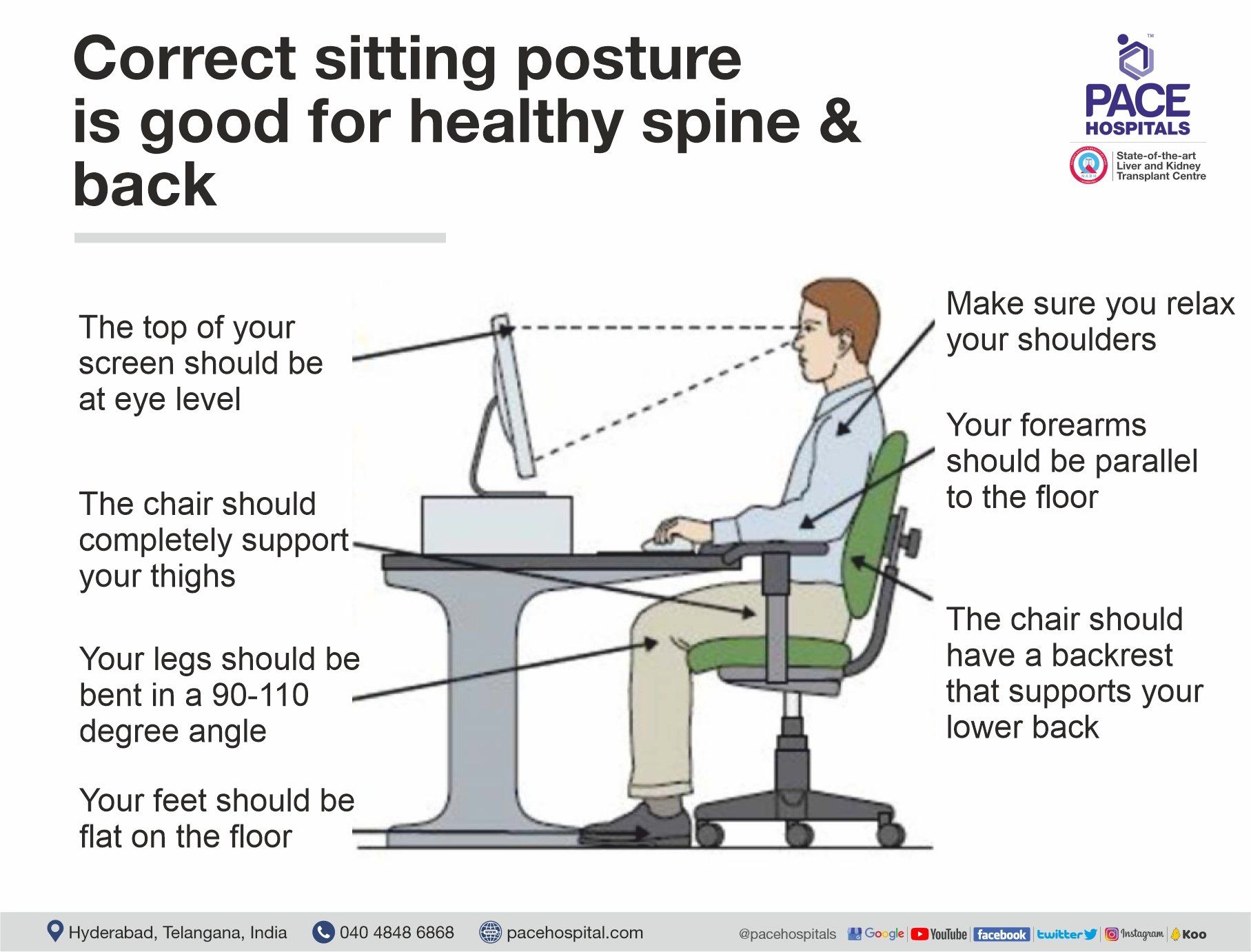
Make your workspace as ergonomic as possible. If you sit at a desk, make sure your chair has plenty of low-back support and your hips are at a right angle to the floor. Correct sitting posture is good for healthy spine and back.
Manage your mental health. People who have anxiety and depression, or face excessive stress, are more likely to experience back pain over time. Making your mental health a priority can help reduce your risk of lower back pain.
Avoid alcohol and smoking
Wear your seatbelt at all times while in a moving vehicle.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868