Tight Underwear Is Not Healthy – Here’s Why
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. Abhik Debnath - Consultant Urologist, Andrologist & Kidney Transplant Surgeon
Overview
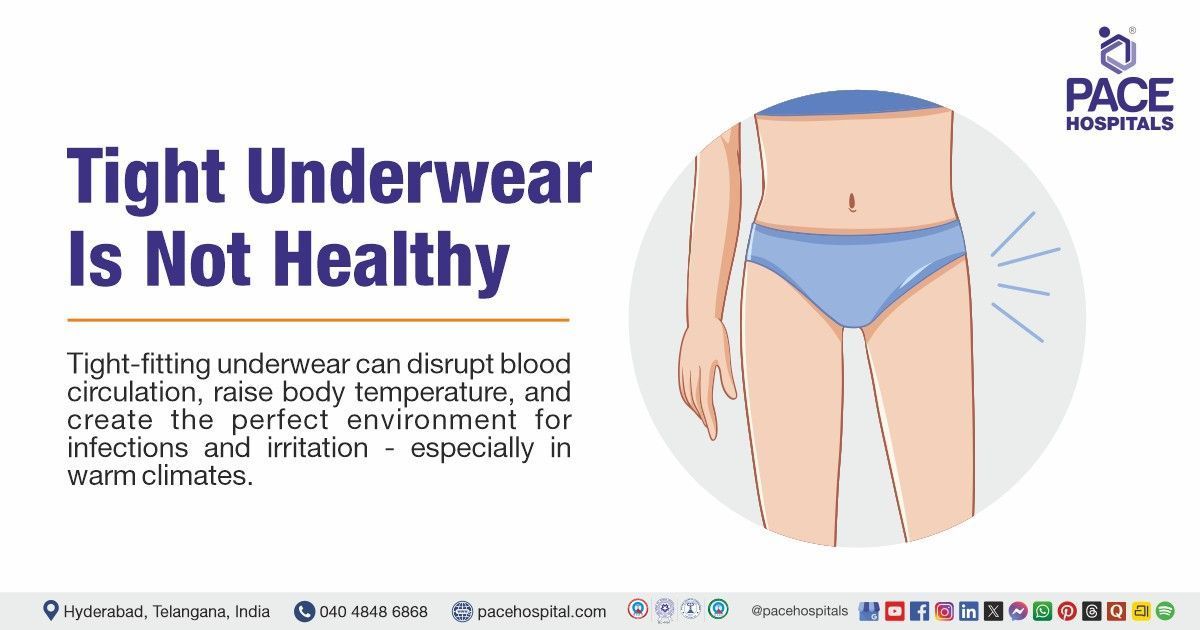
Underwear is a small part of our wardrobe but has a surprisingly large effect on health. Tight-fitting underwear can disrupt blood circulation, raise body temperature, and create the perfect environment for infections and irritation — especially in warm climates.
This guide explores in depth how tight underwear affects both men and women, the science behind airflow and temperature regulation, and what experts recommend for better reproductive and skin health.

Health Problems Caused by Tight Underwear
The skin around the pelvic and groin region is thin, sensitive, and prone to moisture accumulation. When underwear is too tight, it compresses this region and limits airflow, creating a warm, moist environment — ideal for bacterial and fungal growth.
Moreover, tight-fitting underwear exerts continuous pressure on blood vessels, lymphatic drainage, and nerves, which can affect both circulation and sensation.
For men: This can lead to reduced sperm quality and testicular overheating.
For women: Wearing tight underwear can increase the risk of infections, inflammation, and pain in the pelvis.
Reduced Blood Circulation
Wearing tight waistbands and thigh bands may restrict major blood arteries and lymph systems, resulting in decreased circulation. Over time, this might result in numbness, tingling, or discomfort in the thighs and pelvis region.
Testicular Overheating and Fertility Concerns (Men)
The testicles are designed to stay slightly cooler than the rest of the body to support healthy sperm production. wearing tight underwear traps heat and elevates scrotal temperature, which can result in:
- Lower sperm count and motility
- Increased sperm DNA damage
- Hormonal imbalance
- Long-term fertility decline
Research indicates that wearing tight underwear is a stronger inhibitor of sperm motility than other lifestyle habits such as alcohol consumption or smoking.
For Men:
It is not advised for men who want to have children to wear tight underwear. Constrictive briefs elevate scrotal temperature and interfere with sperm viability. Body heat stability is crucial for sperm health — and choosing looser underwear, such as cotton boxers, helps maintain it.
Vaginal Infections and Irritation (Women)
Tight underwear in women increases moisture retention and friction, which can disrupt the vaginal microbiome — the balance of beneficial bacteria that protect against infection.
This imbalance can cause:
- Vaginal itching and irritation
- Yeast (Candida) infections
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Ingrown hairs or folliculitis due to friction
Synthetic fabrics like nylon and polyester worsen this problem as they do not allow skin to breathe.
Increased Risk of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
For both men and women, the warm and moist environment caused by tight undergarments is a breeding ground for bacteria such as E. coli, which can travel to the urinary tract.
This is especially true for people who wear tight underwear after exercise, where sweat and friction further irritate the skin.
Skin Chafing, Rashes, and Fungal Infections
- Skin friction from tight clothing can lead to chafing (especially between the thighs and groin).
- Sweat accumulation promotes fungal infections like tinea cruris (commonly known as “jock itch”), which causes red, itchy, ring-shaped rashes around the groin area.
PACE Hospitals’ dermatologists often treat recurrent fungal infections that are linked directly to poor fabric hygiene or tight undergarments.
Hormonal and Lymphatic Imbalance
Chronic compression of the pelvic area can restrict lymph flow — the body's system for removing toxins and waste. This stagnation can cause mild swelling, discomfort, and even subtle hormonal imbalances over time.
In women, this constant pressure can also increase pelvic floor tension, worsening menstrual cramps and contributing to discomfort during the cycle.
Poor Hygiene and Odour
Restricts airflow and retains sweat, providing a perfect environment for bacteria to grow. Bacteria cause unpleasant odour by feeding on dead skin cells and perspiration. In addition, bacteria feed on dead skin cells and trapped sweat, making it difficult to maintain hygiene even with regular washing.
Ingrown Hairs and Folliculitis
Tight fabric can cause friction that pushes hair back into the follicle, leading to painful ingrown hairs, bumps, and folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles) — especially after shaving or waxing.
Nerve Compression and Pain
In some cases, tight garments can compress nerves around the thighs and pelvic area, causing numbness or tingling. Prolonged compression may even lead to Meralgia Paresthetica — a nerve entrapment condition causing burning pain or tingling in the outer thigh.
Gender-Specific Effects
For Men
- Increased scrotal heat reduces sperm count.
- Pressure may cause varicocele (enlarged scrotal veins).
- Restricted circulation increases the risk of erectile issues over time.
For Women
- Constant pressure and poor ventilation raise the risk of bacterial vaginosis, UTIs, and yeast infections.
- Synthetic underwear can worsen eczema or dermatitis in the groin.
Fabric Matters: Cotton vs Synthetic
Cotton Underwear
- Naturally breathable and soft
- Allows proper air circulation and keeps the skin dry.
- Hypoallergenic is a material that is less likely to cause an allergic reaction, which is suitable for sensitive and allergy-prone skins.
Synthetic Underwear (Polyester, Nylon, Spandex)
- Synthetic fabrics may look stylish, but they trap heat and moisture, provides a perfect environment for bacteria and fungi
- Increases the likelihood of irritation, rashes, and infections.
- Can trigger allergic reactions or worsen existing skin conditions.
PACE Hospitals’ urology, gynaecology and dermatology teams recommend cotton or bamboo fabric underwear for daily wear, especially in humid climates like Hyderabad.
When to Replace Underwear?
Even with good hygiene, underwear should be replaced every 6 to 12 months. Elastic degradation, fabric thinning, and bacterial buildup can occur over time — even after washing.
Signs you need to replace them:
- Persistent odour despite washing
- Fraying or stretched-out fabric
- Itchiness or irritation after wearing
Tips for Choosing Healthy Underwear
- Choose 100% cotton or breathable fabrics.
- Avoid tight waistbands or leg elastics.
- Change underwear daily — and after workouts.
- Wash with mild detergents and dry thoroughly.
- Avoid wearing underwear to bed if possible (to allow ventilation).
- Women should prefer cotton-lined panties and avoid thongs for long periods.
The Science Behind “Breathability”
When your skin breathes freely, sweat evaporates, bacteria stay in check, and temperature remains balanced. Tight underwear disrupts this natural homeostasis.
Over time, your body’s microbiome and temperature regulation in sensitive regions become imbalanced, leading to chronic irritation or inflammation.
Thus, the concept of “breathable fabric” is medically justified — it helps preserve the natural defense barrier of the skin and reproductive organs.
Why tight underwear is considered unhealthy?
Tight underwear traps heat, restricts airflow, and increases moisture — causing infections, irritation, and fertility issues in both men and women.
How does tight underwear affect male fertility?
It raises scrotal temperature, impairing sperm production and motility. Long-term use can contribute to infertility and testicular discomfort.
Can tight-fitting underwear lead to urinary infections (UTIs)?
Yes. Tight, non-breathable underwear can trap heat and moisture, creating a perfect environment for bacterial growth. This increases the risk of urinary tract infection (UTI), particularly in women, where restricted airflow can allow bacteria to spread more easily.
What are the skin problems caused by tight underwear?
Skin chafing, fungal infections, rashes, and folliculitis (inflamed hair follicles) are common. Cotton fabric helps prevent these issues.
Does wearing tight underwear at night affect health?
Yes. Wearing tight underwear to bed restricts airflow and increases temperature, which can cause sweating and irritation. Sleeping without underwear helps skin breathe.
What type of underwear is best for men?
Loose, breathable cotton boxers or briefs are ideal. They maintain proper testicular temperature and improve comfort, circulation, and sperm health.
What type of underwear is best for women?
Cotton panties or those with cotton lining are safest. Avoid synthetic thongs and tight elastic bands that can cause friction or infections.
Can tight underwear cause nerve or circulation problems?
Yes. Prolonged compression can lead to nerve entrapment (Meralgia Paresthetica), poor circulation, and numbness in the thighs or groin.
How often should underwear be replaced?
Every 6–12 months. Replace sooner if there’s persistent odour, fabric thinning, or discomfort even after washing.
Why choose PACE Hospitals for urology and skin health in Hyderabad?
PACE Hospitals provides expert urology, dermatology, and reproductive care, helping patients prevent infections, infertility, and skin problems through advanced diagnosis and counseling.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868