Successful Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy and IPOM Plus Repair for Umbilical Hernia with Gallstones in a 44-Y.O Male
PACE Hospitals
PACE Hospitals’ expert Surgical Gastroenterology team successfully performed a Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy combined with an Intraperitoneal Onlay Mesh (IPOM) PLUS on a 44-year-old male patient who had presented with umbilical hernia and cholelithiasis. The procedure aimed to remove the gallbladder to treat gallstones and reinforce the abdominal wall to repair the hernia, preventing recurrence and improving overall abdominal function.
Chief Complaints
A 44-year-old male patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 21 presented to the Surgical Gastroenterology Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with the complaints of a reducible swelling and pain near the umbilicus (Navel).
Past Medical History
The patient had no known history of hypertension or diabetes. The absence of these comorbid conditions was considered clinically favourable, as it minimized the risk of intraoperative and postoperative complications and supported a smoother, more stable recovery.
On Examination
On examination, the patient was conscious, oriented, and cooperative. He appeared clinically stable with no signs of pallor, icterus, cyanosis, clubbing, or pedal edema. Abdominal examination revealed a soft and non-distended abdomen with tenderness near the umbilicus. A reducible swelling was noted in the umbilical region, consistent with an
umbilical hernia, and omentum was palpable within the hernial sac. There were no signs of guarding or rigidity. Bowel sounds were present and normal. Systemic examination of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and central nervous systems showed no abnormalities.
Diagnosis
Upon admission, the patient underwent a comprehensive clinical evaluation, along with a detailed review of his prior medical records and diagnostic reports by the surgical Gastroenterology team.
To support clinical findings, Laboratory and special investigations were carried out as part of the preoperative assessment. Complete blood count (CBC) was within normal limits, with no evidence of leukocytosis or anemia. Liver function tests (LFTs) were normal, indicating no signs of cholestasis or hepatic dysfunction despite the presence of gallstones. Renal function tests (RFTs) and serum electrolytes were also within normal limits, confirming adequate renal function and electrolyte balance. Coagulation profile, including PT, INR, and APTT, was normal, indicating no bleeding risk. Electrocardiogram (ECG) and chest X-ray, done as part of the pre-anesthetic check-up, were unremarkable with no abnormalities detected. Abdominal ultrasound was abnormal, revealing cholelithiasis with multiple gallstones and a 2 cm umbilical hernia with omentum. These findings supported the diagnosis and guided the decision for appropriate management.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, the patient was advised to undergo
Umbilical Hernia and
Gallstones Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the surgical Gastroenterology Department.
Medical Decision Making
After consulting with Dr. Suresh Kumar S, a surgical gastroenterologist, a comprehensive evaluation was carried out to determine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic approach for the patient.
It was determined that the patient had umbilical hernia and cholelithiasis responsible for his reducible swelling and pain near the umbilicus. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy combined with Intraperitoneal Onlay Mesh (IPOM) PLUS was identified as the most effective intervention to relieve his symptoms and improve his overall condition.
The patient and his family were informed about his condition, the procedure, its associated risks, and its potential to alleviate symptoms and enhance his quality of life.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled to undergo Laparoscopic Intraperitoneal Onlay Mesh (IPOM) Plus and Cholecystectomy Surgery in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, under the supervision of an expert in the Surgical Gastroenterology Department.
The following steps were carried out during the procedure:
- Anesthesia and Port Placement: The patient was administered general anesthesia and positioned supine. Pneumoperitoneum was created, and four laparoscopic ports were placed—one at the umbilicus (also used for mesh placement), one in the epigastrium, and two on the right side for instrumentation.
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: The gallbladder was visualized and retracted. Dissection was performed to identify the cystic duct and artery, achieving the Critical View of Safety (CVS). Both structures were clipped and divided, and the gallbladder was removed from the liver bed and extracted through the umbilical port.
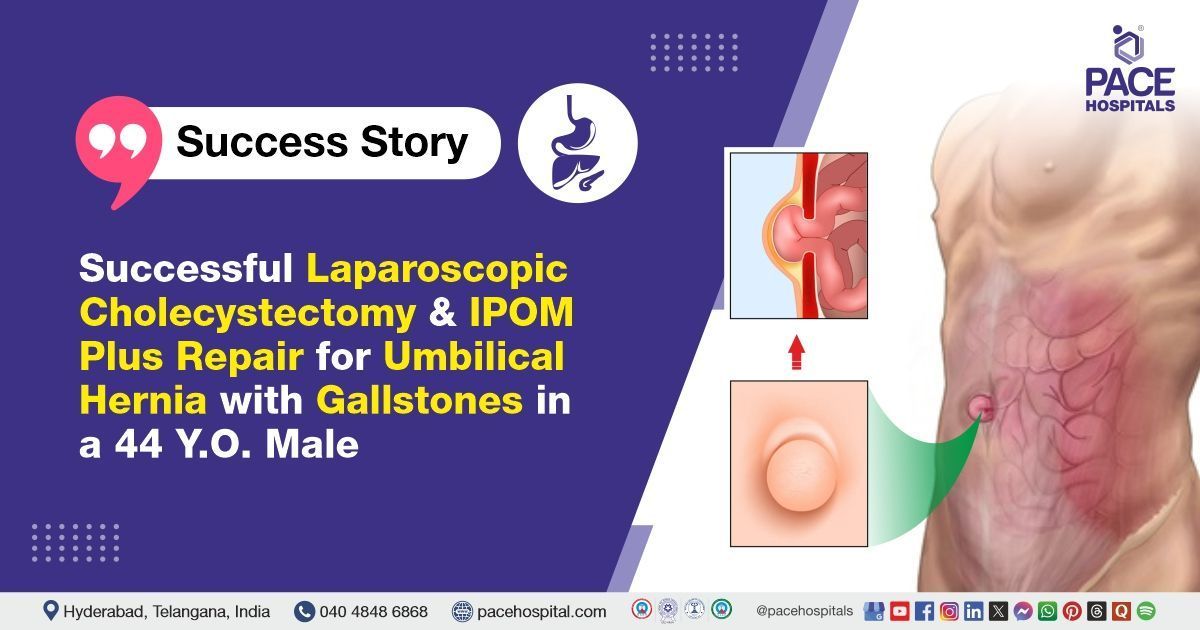
- Umbilical Hernia Identification and Reduction: The umbilical hernia defect was identified (approximately 2 cm), and the herniated omentum was carefully reduced back into the abdominal cavity. The surrounding tissue was inspected to ensure no ischemia or adhesions.
- IPOM Plus Repair: The hernia defect was closed primarily with non-absorbable sutures (1-0 Prolene). A 15 x 15 cm dual-layer mesh was inserted through the port and placed intraperitoneally over the defect with at least a 3–5 cm overlap. The mesh was fixed with tackers to the abdominal wall.
- Completion and Closure: The peritoneal cavity was inspected for bleeding or bile leak, then irrigated and suctioned. Trocars were removed under vision, the fascia at the 10 mm ports was closed, and the skin was sutured. Sterile dressings were applied, and the patient was shifted to recovery in stable condition.
Intraoperative Findings:
- The gallbladder was found to be well distended. The Critical View of Safety (CVS) was achieved.
- A single cystic duct and single cystic artery were clearly identified. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy was completed without complications.
- An umbilical hernia with a defect measuring approximately 2 cm was noted, containing omentum as its content.
- The hernial defect was closed primarily using 1-0 Prolene sutures. A 15 x 15 cm dual-layer mesh was placed intraperitoneally over the defect and fixed securely with tackers.
Postoperative Care
The procedure was uneventful, and the patient’s postoperative recovery was satisfactory. During the hospital stay, he was managed with intravenous fluids, IV antibiotics, laxatives, and other supportive medications. The patient showed progressive symptomatic improvement and tolerated oral intake well. He remained hemodynamically stable throughout and was discharged with prescribed medications and detailed follow-up instructions.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed medications tailored to his postoperative condition. This included an antibiotic to prevent infection, a proton pump inhibitor to reduce gastric acidity and protect the gastrointestinal tract, a prokinetic agent to enhance gastrointestinal motility, an analgesic for pain control, and a laxative to maintain regular bowel movements. Additionally, supportive treatment was advised to aid in recovery.
Advice on Discharge
The patient was advised to use an abdominal binder for 8 weeks and to avoid straining and heavy exercises during the recovery period. He was also instructed to follow a soft diet.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain and vomiting.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up visit with the Surgical Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals, after 5 days for further evaluation.
Conclusion
This case highlights the surgical management of a symptomatic umbilical hernia with coexisting cholelithiasis. The patient underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy with IPOM Plus repair without complications. Postoperative recovery was uneventful, and the patient was discharged in stable condition with appropriate medications and follow-up advice.
Integrated Laparoscopic Management of Gallbladder Disease and Abdominal Wall Hernias
The combined laparoscopic treatment of gallbladder disease and abdominal wall hernias represents a major advancement in minimally invasive surgery. When performed by a skilled
surgical gastroenterologist / surgical gastroenterology doctor, this approach allows for the simultaneous management of both conditions in a single procedure. This reduces overall surgical trauma, decreases hospital stay, and promotes faster postoperative recovery. Additionally, addressing both issues together lowers the risk of complications that can arise from multiple surgeries. The use of mesh reinforcement in hernia repair further enhances long-term outcomes by reducing recurrence rates. Overall, this integrated technique offers an efficient, safe, and patient-centred solution for managing complex abdominal pathologies.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868