Successful ERCP with SpyGlass Laser Lithotripsy in a 37 Y.O. Male with Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis
PACE Hospitals
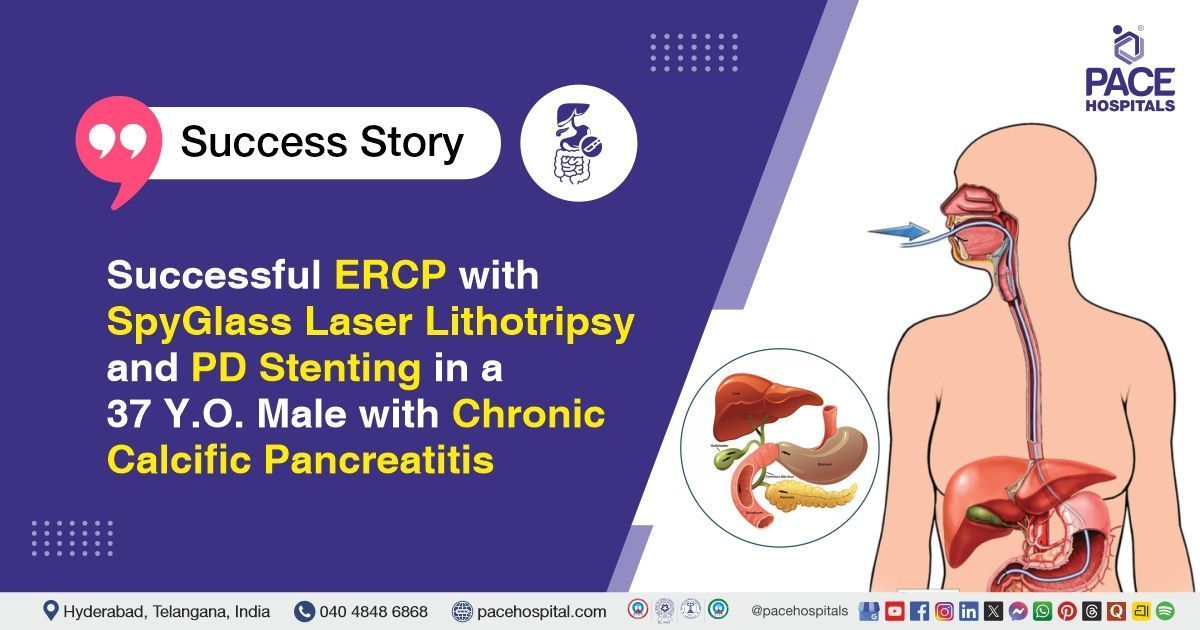
The PACE Hospitals’ expert gastroenterology team successfully performed an Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) combined with SpyGlass-guided laser lithotripsy and pancreatic duct (PD) stenting on a 37-year-old male patient diagnosed with chronic calcific pancreatitis. The aim of the procedure was to relieve ductal obstruction, remove pancreatic duct stones, and restore normal pancreatic drainage to reduce pain and prevent further complications.
Chief Complaints
A 37-year-old male patient with a
body mass index (BMI) of 23 presented to the Gastroenterology Department at
PACE Hospitals, Hitech City, Hyderabad, with a known history of acute-on-chronic pancreatitis of idiopathic etiology, first diagnosed many years ago. He had experienced multiple recurrent episodes of
acute pancreatitis, the most recent having been managed at an outside hospital. During that evaluation, he was diagnosed with
chronic calcific pancreatitis and was advised to undergo
ERCP. He then came to our center for further evaluation and management.
Past Medical History
The patient has a history of Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis, diagnosed in the past with recurrent episodes of acute pancreatitis. He also has diabetes mellitus and hypertension, both managed with regular medications. Despite adherence to therapy and routine follow-up, recent laboratory evaluation indicated suboptimal control of both diabetes and hypertension.
On Examination
On admission, the patient was conscious, coherent, and oriented. General examination was normal with stable vital parameters. Abdominal examination showed mild epigastric tenderness without guarding or rigidity. Cardiovascular and respiratory examinations were normal, with no abnormal findings. No
jaundice, edema, or neurological deficits were noted.
Diagnosis
Upon admission to PACE Hospitals, the patient was thoroughly evaluated by the Gastroenterology team for acute on chronic abdominal pain with a known history of Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis, associated with recurrent episodes of acute pancreatitis.
The patient underwent an extensive diagnostic evaluation. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) demonstrated a moderately atrophic pancreas with irregular dilatation of the main pancreatic duct (MPD) and multiple intraductal calculi in the head, distal body, and tail of the pancreas, with the largest measuring 16.5 mm in the pancreatic head. Multiple areas of branch duct dilatation and minimal peripancreatic fat stranding were also noted. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) confirmed the presence of Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis with multiple pancreatic duct stones causing obstruction. Laboratory evaluation revealed poorly controlled diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
Based on the confirmed diagnosis, the patient was advised to undergo
Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis Treatment in Hyderabad, India, under the expert care of the Gastroenterology Department.
Medical Decision Making
After a detailed consultation with consultant gastroenterologists, Dr. Govind Verma, Dr. M Sudhir, and Dr. Padma Priya, and cross consultation with endocrinologist Dr. Tripti Sharma for diabetes management, a comprehensive evaluation was performed to determine the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Considering the patient’s history of acute on chronic pancreatitis, recurrent abdominal pain, and comorbidities including diabetes mellitus and hypertension, an optimal treatment strategy was formulated.
Based on clinical assessment and imaging findings, including Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) and Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) showing multiple intraductal calculi, irregular main pancreatic duct dilatation, and features of chronic calcific pancreatitis, it was determined that ERCP with Spyglass-assisted laser lithotripsy and pancreatic duct stenting was identified as the most suitable therapeutic intervention to relieve ductal obstruction, remove pancreatic calculi, and minimize the risks associated with major pancreatic surgery.
The patient and his family members were counselled regarding the diagnosis, planned procedure, associated risks, and its potential to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Surgical Procedure
Following the decision, the patient was scheduled to undergo ERCP with Spyglass-assisted Laser Lithotripsy and Pancreatic Duct Stenting Procedure in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals under the expert supervision of the Gastroenterology Department.
The following steps were carried out during the procedure:
- Patient Preparation and Sedation: The patient was positioned appropriately and sedated to ensure comfort and safety. Vital signs were continuously monitored throughout the procedure, and intravenous access was secured for administration of fluids and medications.
- Endoscopic Cannulation of the Pancreatic Duct: A side-viewing duodenoscope was advanced into the duodenum, and the pancreatic duct was cannulated under fluoroscopic guidance. Contrast was injected to delineate the ductal anatomy, confirming multiple intraductal calculi and areas of ductal irregularity.
- SpyGlass System Introduction: The SpyGlass Direct Visualization System was introduced into the pancreatic duct, providing direct endoscopic visualization of the stones and strictures. This allowed precise identification of stone location, size, and ductal anatomy.
- Laser Lithotripsy and Stone Fragmentation: Laser lithotripsy was performed using the SpyGlass system to fragment the intraductal calculi. The fragments were flushed and aspirated from the duct to ensure complete clearance and relieve ductal obstruction.
- Pancreatic Duct Stenting: A pancreatic duct stent was placed to maintain ductal patency, facilitate drainage, and promote healing of the pancreatic duct. Correct stent position was confirmed fluoroscopically, and the procedure was concluded without complications.
Postoperative Care
The patient’s postoperative period was uneventful. An endocrinology consultation was obtained for Diabetes Mellitus, and the recommendations were followed. The patient was managed with intravenous fluids, infection-preventive therapy, gastric-protective measures, pain management, and other supportive care. The patient improved gradually and is being discharged with the following medical advice. The patient is being discharged in a stable condition.
Discharge Medications
Upon discharge, the patient was prescribed medications for the management of infection, acid-related gastrointestinal protection, pancreatic enzyme supplementation, blood sugar control, blood pressure management, and pain relief as required.
Advice on Discharge
The patient was advised to follow a liquid diet for three days, gradually changed to a normal diet, avoid fatty and fried foods, and adhere to a diabetic-friendly diet.
Emergency Care
The patient was informed to contact the emergency ward at PACE Hospitals in case of any emergency or development of symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain and vomiting.
Review and Follow-up Notes
The patient was advised to return for a follow-up visit after four weeks with the Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad at PACE Hospitals to review his condition.
Conclusion
This case highlights a patient with chronic calcific pancreatitis complicated by recurrent acute attacks, poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. He underwent ERCP with SpyGlass laser lithotripsy and pancreatic duct stenting, which was well tolerated. Postoperative recovery was uneventful, and the patient was discharged in stable condition with medical and dietary management. Follow-up and monitoring for glycemic control and pancreatic function were advised.
Complex Management of Chronic Calcific Pancreatitis with Endoscopic Intervention
Chronic calcific pancreatitis is a progressive condition characterized by pancreatic duct obstruction and stone formation, often causing recurrent abdominal pain and impaired pancreatic function. Endoscopic intervention is a key approach to relieve ductal obstruction and improve drainage. Evaluation and planning are guided by advanced imaging techniques. Supportive care, including pain management, pancreatic enzyme supplementation, and dietary modifications, is essential.
A gastroenterologist/gastroenterology doctor plays a central role in coordinating the endoscopic procedure and ongoing management. Long-term follow-up is required to monitor for complications such as diabetes, malabsorption, or recurrent obstruction. Multidisciplinary care improves outcomes and quality of life for these patients.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868