Lymphocyte Count: Normal Range, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. Mounika Jetti - General Physician and Diabetologist
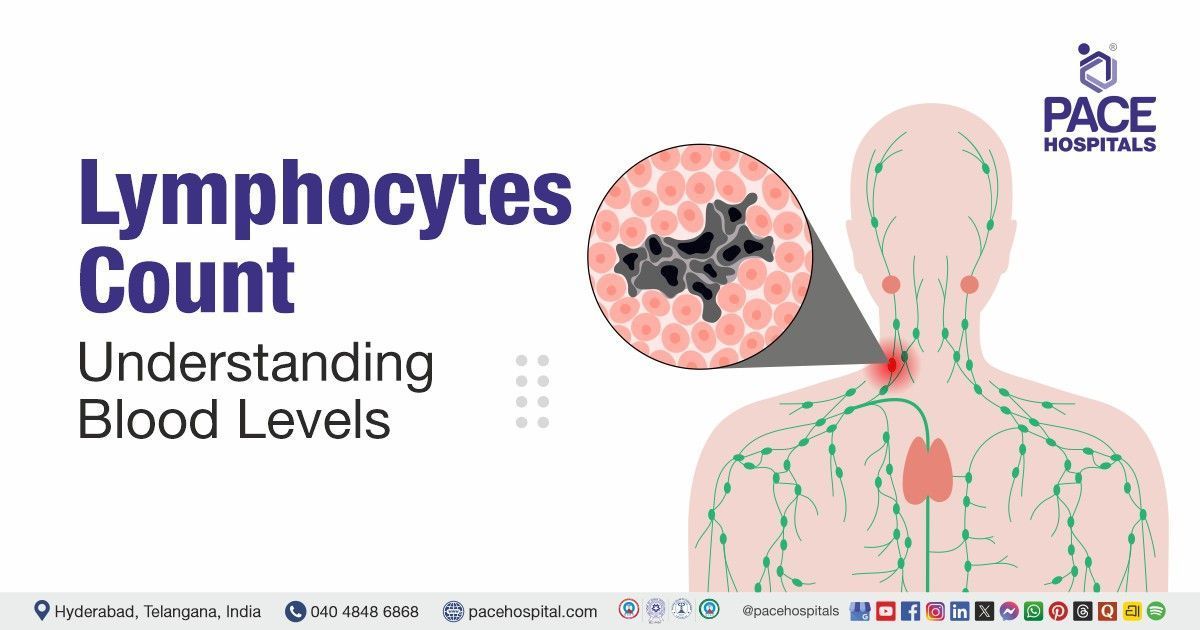
Lymphocytes Count in Blood
Lymphocytes are a vital part of our immune system. They are a type of white blood cell. These cells aid in the body's defense against illnesses and infections.
Understanding lymphocytes count in blood is quite important. It provides insights into our immune health. A normal lymphocyte count indicates a balanced immune system.
However, changes in lymphocyte levels can signal health issues and what level of lymphocytes is dangerous for a human being. A lymphocyte increase might suggest an infection or inflammation. Conversely, a lymphocyte decrease could indicate a weakened immune system.
Different factors can affect lymphocyte levels. Age, stress, and overall health play a role. Regular monitoring of lymphocyte count is important for maintaining proper health.
This article will explore the role of lymphocytes. It will also discuss the implications of abnormal lymphocyte counts. Understanding these concepts is key to managing health effectively.
Summary
Lymphocytes are key white blood cells, and measuring their blood levels—by differential percentage or absolute count—helps assess immune status. Typically lymphocytes normal range are 20–40% of white blood cells and 1,000–4,800 per microlite; increased lymphocytes levels often rise with infections, inflammation, some cancers, or autoimmunity, and fall with viral illness, malnutrition, immune-suppressing therapies, or aging.
This article covers lymphocyte types and functions, how normal lymphocyte count are measured, what abnormal high lymphocyte count results mean (including for children and older adults), and strategies for diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle support. Regular monitoring lymphocytes in blood and context-specific interpretation of lymphocytes high causes with healthcare guidance are important for accurate care.
What Are Lymphocytes?
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell essential to our immune system. They originate in the bone marrow and circulate throughout the blood and lymphatic system. Their primary role is to recognize and eliminate foreign invaders.
There are three primary types of lymphocytes:
- T cells (T lymphocytes): These cells help manage and direct immune responses.
- B cells (B lymphocytes): They produce antibodies to target specific pathogens.
- Natural Killer (NK) cells: NK cells attack and destroy infected or cancerous cells.
B and T lymphocytes form a crucial part of the adaptive immune system. This system provides long-term immunity and remembers past infections. Thanks to B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes, the body can mount stronger and faster responses to repeat invaders.
These cells are vital for maintaining health. They protect against bacteria, viruses, and other harmful organisms. A well-functioning lymphocyte population is key to a robust immune defense and fighting against infections.
Types of Lymphocytes and Different Lymphocytes Function in Immune System
Lymphocytes are divided into three main types: T cells, B cells, and Natural Killer (NK) cells. Each type has unique roles that contribute to immune defense.
Different types of T lymphocytes (T cells) are further classified into helper, cytotoxic, and regulatory subtypes. Helper T lymphocytes (Helper T cells) assist other immune cells by releasing signaling molecules. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (Cytotoxic T cells) target and kill infected or cancerous cells.
Activation of B lymphocytes (B cells) have a crucial function in producing antibodies. These antibodies specifically bind to antigens, marking them for destruction by other immune cells. B cells can also form memory cells for quicker response to future exposures.
Natural Killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that belong to the innate immune system, the body's first line of defense against infections. They circulate throughout the body, identifying and destroying abnormal or infected cells without needing prior exposure. This swift action helps control early threats before they spread.
Different types of T lymphocytes function, B lymphocytes function, and Natural Killer (NK) cells function are mentioned below:
- Helper T cells - Coordinate immune responses.
- Cytotoxic T cells - Destroy infected cells.
- Regulatory T cells - Maintain immune balance.
- B cells - Produce antibodies.
- NK cells - Capable of attacking infected or damaged cancerous cells.
Each lymphocyte type is vital for maintaining the immune system's adaptability and strength. By acting together, they help the body defend itself effectively against different kinds of threats.
NK cells produce quick responses, whereas T and B cells give long-term immunity. This coordination allows the body to effectively combat both unfamiliar problems and novel challenges effectively.
The Role of Lymphocytes in the Immune System
Lymphocytes are pivotal in orchestrating the body's defense mechanisms. They identify and neutralize pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and abnormal cells.
T cells play an important part in the adaptive immune response. They identify certain antigens and assist to activate other immune cells, improving the body's ability to fight off intruders.
B cells contribute by producing antibodies that target pathogens directly. These antibodies are crucial in marking invaders for destruction by other immune components.
Natural Killer (NK) cells provide a rapid response to infected cells. They scan for irregularities and execute damaged cells, preventing the spread of infection.
Some of the key roles of lymphocytes include:
- Identifying and neutralizing pathogens.
- Producing antibodies through B cells.
- Directly attacking infected cells via NK cells.
In summary, lymphocytes form the backbone of both the innate and adaptive immune responses. They ensure that once a pathogen is encountered, it is handled swiftly and efficiently.
A visual representation can highlight how lymphocytes interact with other immune components to maintain health.
How Lymphocytes Are Produced and Regulated
Lymphocytes originate from stem cells in the bone marrow. These cells differentiate into various types based on signals received from the body.
Once formed, they migrate to lymphoid organs where they mature. The thymus is where T cells mature and T lymphocytes are produced in, while B cells or B lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow.
Regulation of lymphocyte production is a complex process. The body maintains a balance according to requirement, boosting production during infections or illnesses. Key body parts involved in lymphocyte regulation include:
- Bone Marrow: Site of initial production.
- Thymus: Essential for T cell maturation.
- Lymphoid Organs: Facilitate further development and activation.
Hormones and cytokines play crucial roles in this regulation. They ensure an adequate but not excessive response to pathogens.
Understanding Lymphocytes Count
Understanding lymphocyte counts involves two main types: differential and absolute. Both provide insights into immune health.
The differential lymphocytes count measures the percentage of lymphocytes within the total white blood cell count. This helps to relate the proportion of lymphocytes compared to other white blood cells present.
The absolute lymphocytes count refers to the actual number of lymphocytes in a specific blood volume. It provides a specific measure of immune function by quantifying the cells. Key Differences:
- Differential Count of Lymphocytes:
- Expressed as a percentage.
- Indicates balance among white blood cells.
- Absolute Lymphocyte Count Range:
- Provides actual count per volume.
- More accurate for diagnosing disorders.
The normal range for these counts can vary slightly between different labs. Generally, the normal range for absolute lymphocyte count varies in between 1,000 to 4,800 lymphocytes per microliter of blood.
Benefits of Each Count:
- Differential Count:
- Easier to compare proportions.
- Useful for spotting imbalances.
- Absolute Count:
- More reliable for specific conditions.
- Better for tracking treatment effects.
Lymphocytes Differential Count Normal Range
The lymphocytes differential count expresses the percentage of lymphocytes out of the total white blood cells. Understanding this range helps assess immune function balance.
Typically, the normal range for lymphocytes as part of the total white blood cell count fluctuates in between 20% and 40%. This percentage ensures and reflects an idea about adequate immune response without overactivity. Key Points:
- Lymphocytes normal range percentage: 20% to 40% of of total white blood cells.
- Indicates immune cell balance.
- Slight variations exist between labs.
This range helps healthcare providers detect conditions affecting immune health. Deviations from the norm may signal potential health concerns. Regular monitoring of differential counts of lymphocytes can be crucial for managing chronic conditions. Visual aids can clarify normal range significance and variation.
Causes of Lymphocyte Increase (Lymphocytosis)
Lymphocytosis refers to a higher than normal lymphocyte count. This condition often indicates an active response of the immune system.
Common causes of lymphocyte increase include infections. Viral infections such as mononucleosis or the flu are frequent triggers. Some cancers, like leukemia (acute lymphocytic leukemia), can also lead to elevated lymphocyte levels. Chronic conditions may provoke similar increases.
In addition, autoimmune disorders can cause lymphocyte numbers to surge. Diseases where the body mistakenly attacks itself often show this pattern. Increased Lymphocytes Causes Include:
- Viral infections (e.g., Mono (Epstein-Barr Virus), flu)
- Certain cancers (e.g., leukemia)
- Autoimmune diseases
- Chronic inflammatory conditions
- Stress-related responses
For some, temporary elevation is simply a natural immune response. Others may require further investigation to determine the exact cause. A comprehensive lymphocytes blood test helps confirm the presence and cause of lymphocytosis, guiding proper and appropriate treatment.
High Lymphocytes Count Meaning: What Does It Indicate?
An elevated lymphocyte count can signal various health conditions. Often, it reflects an immune system actively fighting an infection. It is value is more than 4,000/µL in adults. Viral infections typically result in high lymphocytes in blood. This surge is the body's way of countering invading pathogens and reasons for high lymphocytes.
Beyond infections, certain cancers like lymphoma might lead to high lymphocyte levels. Malignant cells can cause the bone marrow to produce excess lymphocytes. Autoimmune disorders are another possible explanation. In these cases, the immune response is heightened even without an outside threat.
Lymphocytes Count High 45: What will happen if lymphocytes count is high?
A lymphocytes count high 45% means the level is above the normal range. Usually, lymphocytes should be around 20% to 40% of total white blood cells. When the count goes up to 45%, it may mean the body is fighting a viral infection, inflammation, or another mild health issue. Sometimes this rise is temporary and settles on its own, but if it stays high for many days, a doctor or health professional may suggest a check-up to find the exact reason. Lymphocytes Increased Conditions include the following:
- Viral infections
- Certain types of cancer
- Autoimmune diseases
- Chronic inflammatory states
Though high lymphocyte counts can indicate serious issues, they can also be temporary. Factors such as stress and recent infections might cause a short-lived increase. Consultation with a healthcare provider is very important to interpret these results accurately.
Causes of Lymphocyte Decrease (Lymphocytopenia)
A low lymphocyte count, known as lymphocytopenia, signals potential issues in immune health. It suggests that the body may struggle to fight against infections. Its value is less than 1,000/µL in adults.
Viral infections are common causes of decreased lymphocytes. Viruses such as HIV can directly impact lymphocyte production or function. Malnutrition also plays a critical role in lowering lymphocyte levels. Lack of essential nutrients can impair the body's ability to produce immune cells.
Medical treatment, particularly chemotherapy and radiation, have the potential to lower lymphocyte numbers. These treatments use medicines that work by suppressing the immune system and targeting cancer cells.
Autoimmune diseases and genetic disorders can further lead to lymphocytopenia. For example, in conditions like lupus, lymphocyte levels can drop because the immune system does not function properly.
Common Causes of Lymphocyte Decrease:
- Viral infections (e.g., HIV)
- Malnutrition
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Autoimmune diseases
- Genetic conditions
Identifying what causes low lymphocyte levels is an important factor. It helps guide treatment strategies and supports restoring immune function. Consulting an experienced healthcare provider ensures appropriate evaluation, diagnosis and management.
Reduced Lymphocytes Count: Health Implications
A reduced lymphocyte count can have several health implications. It may indicate an underlying condition that compromises immune defenses. This makes individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Increased vulnerability due to low lymphocyte levels can result in frequent, severe infections. Chronic lymphopenia may also impede recovery from illnesses and reduce overall quality of life.
Additionally, a low lymphocyte count can exacerbate existing health conditions. It may interfere with effective response to vaccines and other treatments. Health Implications of Low Lymphocyte Count:
- Increased chance of infection risk
- Delayed illness recovery
- Compromised vaccine efficacy
Addressing a reduced lymphocyte count involves identifying and treating the underlying cause. Prompt medical attention can help mitigate the associated risks.
Lymphocyte Levels in Special Populations (Children and Elderly)
Lymphocyte levels can vary significantly across different populations. Understanding these variations is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Children
Children typically have higher lymphocyte counts compared to adults. This is due to their developing immune systems. This difference necessitates pediatric-specific reference ranges in blood tests.
Elderly
In the elderly population, a decline in lymphocyte count is common phenomenon noticed. This decrease can contribute to increased vulnerability to infections and a slower response to vaccines. Monitoring lymphocytes count in older adults is important for preventing health complications.
Special Considerations:
- Pediatric immune development
- Age-related immune decline
Understanding age difference ensures better health outcomes and proper treatment.
How Lymphocyte Levels Are Measured: Tests and Analysis
Lymphocyte levels in the blood offer vital insights and outline into the immune system's health. Measuring these lymphocyte count levels involves specific tests and detailed analysis investigation.
Blood Tests
A complete blood count (CBC) is the primary test used to assess lymphocyte levels. It quantifies various blood components, including lymphocytes range. This test is simple, requiring just a blood sample and provides a comprehensive overview of one's blood health.
Types of Lymphocyte Counts
- Absolute Lymphocyte Count (ALC): Measures the total number of lymphocytes per microliter of blood. It gives a precise measure of the immune system's capacity to respond to pathogens.
- Differential Count: Provides the percentage of lymphocytes compared to other white blood cells. It helps identify shifts in the immune response pattern and any alterations.
Additional Analysis
In some cases, a lymphocyte subset panel is ordered. This panel analyzes the proportion of T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells within total lymphocytes.
- T Cells: Integral for cell-mediated immunity.
- B Cells: Responsible for antibody production.
- NK Cells: Crucial for identifying and killing infected cells.
Understanding these metrics provides healthcare providers with the required knowledge for diagnosing and monitoring immune-related disorders. Accurate lymphocyte count analysis is essential for developing effective medical interventions, diagnostic approaches and treatment plans.
Factors Affecting Lymphocyte Levels and its Count
Lymphocyte levels are also affected due to a range of factors, each influencing the immune response uniquely. Understanding these factors helps in interpreting blood test results and lymphocyte count accurately.
Physiological Influences
Age and stress are significant physiological factors. As we age, our immune systems naturally varies, affecting lymphocyte level and its production. Stress, whether physical or mental, can produce transient changes in lymphocyte levels due to hormonal changes that influence lymphocyte count.
Environmental and Lifestyle Impacts
Environmental influences, such as exposure to pathogens or toxic substances, can also impact lymphocyte levels. Lifestyle choices also impacts as well.
- Diet: Nutrient-rich foods support optimal lymphocyte function.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can enhance immune response.
- Sleep: Adequate rest is essential for maintaining immune balance.
Recognizing these influences helps in managing lymphocyte levels through lifestyle modifications. It also prioritizes the importance of a holistic approach to maintaining a healthy immune system.
Symptoms and Signs of Abnormal Lymphocyte Counts
Recognizing abnormal lymphocyte counts can be challenging, as symptoms often overlap with other conditions. However, certain signs may suggest an underlying issue and any harmful indications.
Physical Symptoms
Physical manifestations can include frequent infections or late wound healing. These could indicate a weakened immune response due to low lymphocytes count.
Common Signs
Abnormal lymphocyte levels might also present with other common signs:
- Fever and fatigue: Continuous tiredness or unexplained fevers.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Particularly marked around the neck or armpits.
- Night sweats: A frequent occurrence with lymphocyte fluctuations.
Understanding these symptoms aids in early detection and timely intervention. It highlights the requirement for regular health check-ups to monitor lymphocyte levels and its counts effectively.
Diagnosing and Monitoring Lymphocyte Disorders
Diagnosing lymphocyte disorders starts with a detailed analysis of blood samples. A Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is typically the first step to know if any problem is indicated.
Diagnostic Tests
Several tests can help in the diagnosis and monitoring of lymphocyte disorders are mentioned:
- CBC Test: Measures overall white blood cells, including lymphocytes.
- Flow Cytometry: Helps identify specific lymphocyte types.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: Provides insights into cell production issues or any abrupt changes.
These tests offer vital information about the immune system's status.
Monitoring Over Time
Regular monitoring is crucial for patients with chronic lymphocyte disorders. This involves repeat blood testing for lymphocyte count to assess any changes. Monitoring helps in evaluating the effectiveness of treatments and understanding disease progression.
Treatment and Management of Abnormal Lymphocyte Counts
Managing abnormal lymphocyte counts involves addressing the underlying cause. Treatment plans vary depending on whether the count is high or low.
Approaches for High Lymphocytes Count
When dealing with lymphocytosis, understanding the cause is key. Infections may require antibiotics or antivirals. Chronic conditions like leukemia need more intensive treatments such as chemotherapy.
Strategies for Low Lymphocytes Count
For lymphocytopenia, boosting the immune system is often required. This might involve nutritional support or medication. In some cases, immune globulin therapy is used to enhance immune function.
General Management Tips
General management focuses on maintaining immune balance. Here are mentioned some strategies and workout plan of action:
- Regular Monitoring Check-up: Keeps track of changes in lymphocyte levels.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Supports immune function through healthy diet and exercise.
- Stress Management: Helps prevent lymphocyte fluctuations.
Proactive treatment and precautionary management can help restore normal lymphocyte count. Regular proper in time consultations with experienced healthcare providers are crucial for effective monitoring.
Lifestyle and Natural Ways to Support Healthy Lymphocyte Levels
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is highly recommended for optimal lymphocyte function. Simple changes can have a significant impact on the immune health.
Dietary Influences
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support lymphocyte production. Foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids are particularly beneficial and highly needed by the body.
Physical Activity and Stress Reduction
Regular and routine exercise improves immune health, contributing to normal lymphocyte levels. Meanwhile, stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can prevent immune suppression to a better extent.
Natural Methods to Enhance Lymphocytes
Consider incorporating these daily routine habits:
- Eat a Variety of Fruits and Vegetables
- Practice Mindful Relaxation Techniques
- Engage in Consistent Physical Activity
These lifestyle choices promote not only lymphocyte health but also overall well-being. Small, consistent changes make a significant difference.
Quick Facts
- Lymphocytes Normal Range (Adults): Typically 20% to 40% of total white blood cells (WBCs).
- Common Causes of High Counts (Lymphocytes high): Infections, stress
- Common Causes of Low Counts (Lymphocytes low): Viral infections, malnutrition
These questions help to determine and give an impression upon the significance of lymphocyte levels. Understanding your blood test results is vital for effective healthcare decisions.
Key Takeaways and Summary
Understanding lymphocyte count is crucial for determining and assessing the immune health. These white blood cells play an important role in defending the body against infections and diseases. So, regular lymphocytes blood tests help to check these levels is an effective way to monitor it and get valuable information about your overall health condition.
Essential Points to Remember
- Key Function: Defense against infections.
- Normal Range: 20% to 40% of white blood cells.
- Impact of Abnormal Levels: Can indicate infections, cancers, or immune disorders.
Keeping track of lymphocyte counts aids in the diagnosis and management of a variety of health issues, as well as the proper functioning of your immune system.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lymphocytes Count
What Do high lymphocyte counts mean?
High lymphocyte counts, or lymphocytosis, can signal an immune response to infection or inflammation. Lymphocytes high means it indicate certain cancers or autoimmune disorders.
Are Low lymphocyte counts dangerous?
Low lymphocyte counts, known as lymphocytopenia, can reduce the body's ability to fight infections. Lymphocytes low means it can lead to viral infections, malnutrition, and medical treatments.
What level of lymphocytes count is dangerous?
- A normal lymphocyte percentage is 20%–40% of total white blood cells, or 1,000–4,000 cells/µL.
- A level below 1,000 cells/µL is considered low and may weaken immunity.
- A count above 4,000 cells/µL is considered high and may point to infections or, rarely, blood-related conditions.
However, the danger depends on symptoms, how long it stays abnormal, and the underlying cause.
How to increase lymphocytes count?
If lymphocytes fall below 1,000 cells/µL, treatment focuses on correcting the cause.
- Doctors may treat infections, improve nutrition, or manage chronic illnesses that lower immunity.
- Balanced diet, vitamins (B6, B12, folate), proper sleep, and managing stress can support recovery.
- Monitoring is needed if levels stay low for weeks.
Does reactive lymphocytes mean cancer?
Reactive lymphocytes often appear when lymphocyte levels rise above 40% due to viral infections.
- They are usually a sign of strong immune activity — not cancer.
- Most cases return to normal once the infection improves.
- Only persistent high counts (over 4,000/µL for a long period) need further evaluation.
How to increase lymphocytes count naturally?
If your count is slightly low (just under 1,000/µL), lifestyle support helps.
Eating fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, and protein-rich foods improves immune function.
Proper sleep (7–8 hours), hydration, sunlight for vitamin D, and reducing stress naturally support lymphocyte production.
What does lymphocytes mean in a blood test?
- A blood test measures lymphocytes as a percentage (20%–40%) and absolute count (1,000–4,000/µL).
- It helps show how well your immune system is functioning.
- Low or high levels can suggest infections, inflammation, or immune-related conditions.
Are lymphocytes high or low in HIV?
- In HIV, lymphocyte levels—especially CD4 cells—gradually fall below 500 cells/µL, and severe drop is under 200 cells/µL.
- This decline weakens immunity over time.
- Regular monitoring helps track disease progression and treatment response.
Is chronic lymphocytic leukemia hereditary?
- A family history of CLL slightly increases risk, but there is no fixed hereditary pattern. Most cases can occur without any genetic link.
- Having a close relative with CLL raises risk about 3–7 times, but it still remains uncommon.
What is CD4 lymphocytes?
CD4 lymphocytes are T-cells that guide immune responses. Normal CD4 count is 500–1,500 cells/µL. Levels below 200 cells/µL indicate severe immune weakness, especially in HIV.
What is lymphocytes and monocytes?
Lymphocytes (20%–40%) fight viruses and support long-term immunity. Monocytes (2%–8%) remove dead cells, fight bacteria, and help tissue healing. Their balance helps doctors understand immune health.
What is lymphocytes test?
A lymphocytes test measures both percentage and actual count. Normal lymphocyte count is 1,000–4,000 cells/µL. Doctors use this test to detect infections, immune disorders, or blood-related conditions.
What is the function of lymphocytes in blood?
Lymphocytes help the body fight infections and remember past germs for faster future responses. They identify viruses, bacteria, and abnormal cells. Their normal functioning keeps the immune system strong and balanced.
Can chronic lymphocytic leukemia be cured?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) currently has no complete cure, but treatments can keep it under control for many years. Some people remain stable without treatment for long periods. Modern therapies help reduce symptoms and improve survival.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868