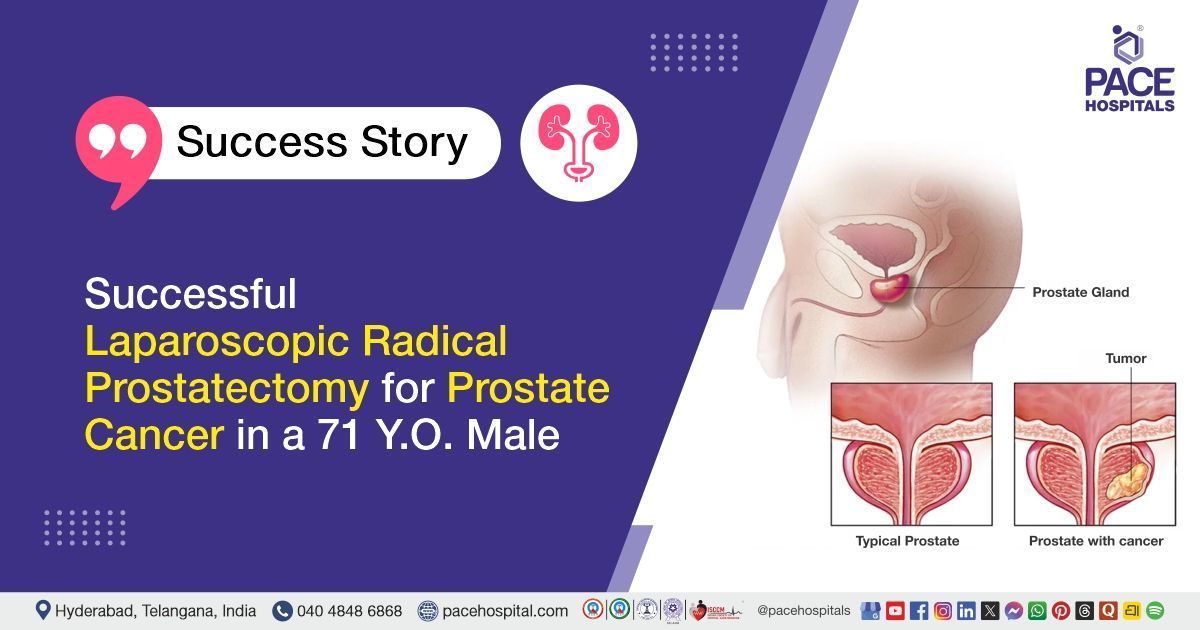
Gallbladder Cancer: Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment & Cost
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. Suresh Kumar S - Surgical Gastroenterologist and Advance Laparoscopic Surgeon
Overview
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is a rare but highly aggressive gastrointestinal (GI) malignancy that often goes undiagnosed until it reaches an advanced stage. The disease begins in the gallbladder — a small, pear-shaped organ beneath the liver that stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver.
Because the gallbladder lies deep within the abdomen and has thin walls, cancer in this organ can easily spread to nearby organs, especially the liver, bile ducts, and lymph nodes.
In India, gallbladder cancer is particularly common in the northern and eastern regions — Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Bengal, and Assam, collectively known as the “Gallbladder Cancer Belt.” However, the incidence is now rising in other parts of the country, including southern and western states.
At PACE Hospitals, Hyderabad, our Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Oncology team specializes in early detection, surgical management, and targeted therapy for gallbladder and biliary tract cancers. The focus is on personalized care, using advanced laparoscopic and robotic techniques to improve outcomes and survival rates.
What Causes Gallbladder Cancer?
Gallbladder cancer usually develops when mutations occur in the DNA of the cells lining the gallbladder, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation. Over time, these cancerous cells can invade the liver, bile ducts, and nearby lymph nodes.
While the exact cause of these genetic changes remains unclear, chronic inflammation of the gallbladder — most often due to gallstones or infections — plays a major role in triggering this disease.
Common Risk Factors for Gallbladder Cancer
A risk factor is anything that increases or the likelihood of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors does not necessarily mean that you will get cancer, but understanding them helps in early detection and prevention.
- Gallstones: The most common association with gallbladder cancer. Nearly 75% of patients with GBC have gallstones at diagnosis. However, gallstones alone rarely cause cancer — most people with stones never develop malignancy. Surgery for gallstones should not be performed solely to prevent cancer unless symptoms or complications exist.
- Porcelain Gallbladder: A rare condition in which the gallbladder wall becomes calcified after long-standing inflammation (chronic cholecystitis). It significantly increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
- Gender: Women are two to three times more likely than men to develop gallbladder cancer — mainly due to higher rates of gallstones and hormonal factors.
- Obesity: Obesity is a well-documented risk factor for GBC, possibly due to altered bile composition and increased gallstone formation.
- Older Age: Gallbladder cancer primarily affects older adults, though it can occur at any age of human being.
- Choledochal Cysts: These are congenital bile duct dilations that can grow over time and harbor precancerous changes. Early surgical removal of these so called cysts is recommended.
- Abnormal Pancreaticobiliary Junction: An anatomical defect where pancreatic juices reflux into the bile ducts, causing chronic irritation that increases cancer risk.
- Gallbladder Polyps: Polyps larger than 1 cm are more likely to be malignant. Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is often recommended and advised in such cases.
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC): An autoimmune disease that causes bile duct scarring and inflammation. PSC patients have a significantly higher risk of gallbladder and bile duct cancers.
- Industrial and Environmental Exposure: Prolonged exposure to substances like nitrosamines, rubber, or textile industry chemicals may increase gallbladder cancer (GBC) risk.
- Chronic Typhoid Infection: Chronic carriers of Salmonella typhi (the bacterium that causes typhoid disease) have a greater chance of developing gallbladder cancer due to long-term inflammation.
- Family History: Though rare, a family history of gallbladder cancer slightly increases the individual risk of getting affected by the disease.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Gallbladder cancer often remains silent until it reaches an advanced stage. However, some common symptoms include:
- Persistent pain in the upper right abdomen
- Jaundice (yellowing of eyes and skin)
- Loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss
- Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal bloating
- Fever and general malaise
- Dark urine and pale stools
- A palpable lump in the upper abdomen (in advanced cases)
Because these symptoms are nonspecific and often mimic gallstone disease or hepatitis, early diagnosis is frequently delayed.
Diagnosis of Gallbladder Cancer
At PACE Hospitals, diagnosis of gallbladder cancer involves a comprehensive and multi-modality approach with various tests, imaging tests, including:
- Blood Tests
- Liver function tests (LFT) - To detect bile duct obstruction
- Tumor markers such as CA 19-9 and CEA
- Imaging Studies
- Ultrasound (Abdomen): First-line investigation for gallbladder wall thickening or masses like abnormal gallbladder contour.
- Computed tomography (CT) / Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Scans: Assess local invasion, lymph node involvement, and if any metastasis.
- MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography): Provides complete and detailed bile duct visualization.
- PET-CT Scan: It helps to detect the spread or invasion of cancer to distant organs or located adjacent to gallbladder.
- Biopsy or Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC): When feasible, a tissue sample is obtained for pathological confirmation from the abnormal area of gallbladder with suspicious growth.
Staging and Spread
Gallbladder cancer is staged according to the TNM classification (Tumor size, Node involvement, Metastasis):
- Stage I: It is the stage observed when cancer is confined to the gallbladder wall.
- Stage II: Tumor invades surrounding muscle or connective tissue.
- Stage III: Involvement of nearby organs such as the liver or bile ducts.
- Stage IV: Distant organ spread (lungs, peritoneum, bones).
Early-stage detection of Gallbladder cancer significantly improves the survival rates. Unfortunately, most patients in India present in Stage III or IV - a critical stage, when curative surgery may no longer be possible or difficult.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage, extent of spread, and overall health of the patient.
- Surgery (Curative Option for Early Stage)
- Radical Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder, part of the liver (segments IVb and V), and nearby lymph nodes.
- Extended Hepatectomy: This procedure is performed if cancer has spread into the liver.
- Bile Duct Resection: If the tumor involves the bile duct junction.
At PACE Hospitals, advanced laparoscopic and latest techniques enable precise tumor removal with minimal blood loss and faster recovery.
- Chemotherapy
- Used for advanced or metastatic disease. Common drugs are antineoplastic (anticancer) chemotherapy drugs.
- Radiation Therapy
- It is an important mode of cancer treatment as it helps to control local disease progression or relieve symptoms.
- Targeted and Immunotherapy
- For selected patients, targeted therapy or immunotherapy agents may be utilized to attack cancer cells more precisely.
Cost of Gallbladder Cancer Treatment in India
The cost of gallbladder cancer treatment varies depending on the stage, treatment type, hospital infrastructure and facilities provided.
- The Diagnostic Workup, which includes blood tests, CT, MRI, and PET-CT scans, generally costs around ₹25,000 to ₹70,000 (approximately $300 to $850) and covers all necessary imaging tests and tumor marker evaluations.
- The Surgical Management, such as radical cholecystectomy (performed through either laparoscopic or open surgery), is estimated to cost between ₹2,50,000 and ₹4,00,000 (around $3,000 to $4,800).
- Each chemotherapy cycle costs about ₹30,000 to ₹70,000 (approximately $350 to $850), and most patients typically require 6 to 8 cycles as part of their treatment plan.
- Radiation therapy is priced between ₹1,20,000 and ₹2,50,000 (roughly $1,400 to $3,000) and usually involves 20 to 25 treatment sessions.
- If targeted therapy or immunotherapy is advised based on genetic profiling, the cost may range from ₹2,50,000 to ₹5,00,000 (approximately $3,000 to $6,000) per course.
- The total treatment cost for gallbladder or bile duct cancer generally falls between ₹4,00,000 and ₹12,00,000 (around $4,800 to $14,000), depending on the stage of the disease, type of procedure, and combination of therapies used.
At PACE Hospitals, gallbladder cancer treatment is available with cashless insurance facilities and multidisciplinary team care including surgical oncologists, hepatobiliary surgeons, radiologists, and cancer nutritionists.
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Gallbladder Cancer Treatment
- Expert Team: Experienced Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary (HPB) surgeons and medical oncologists.
- Advanced Imaging & Diagnostics: 128-slice CT, MRI, PET-CT for accurate staging.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Laparoscopic techniques for faster recovery.
- Comprehensive Care: Surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and nutrition under one roof.
- Postoperative Rehabilitation: Dedicated physiotherapy and follow-up care.
- Affordable & Transparent Costs: Cashless insurance tie-ups with major providers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Gallbladder Cancer
What is gallbladder cancer?
Gallbladder cancer is a rare but aggressive malignancy that starts in the gallbladder and can quickly spread to the liver and bile ducts.
What are the early symptoms of gallbladder cancer?
Symptoms include abdominal pain, jaundice, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. Early diagnosis is challenging as symptoms mimic gallstones.
What causes gallbladder cancer?
Chronic gallbladder inflammation due to gallstones, infections, or structural abnormalities in bile ducts are key causes.
Who is most at risk of developing gallbladder cancer?
Women, people over 50, those with gallstones, obesity, porcelain gallbladder, or a history of typhoid are at higher risk.
How is gallbladder cancer diagnosed?
Through imaging (Ultrasound, CT, MRI, PET-CT), blood tests for tumor markers (CA 19-9), and biopsy for confirmation.
Is gallbladder cancer curable?
Yes, when detected early and surgically removed. Advanced stages can be managed with chemotherapy and targeted therapy to improve survival.
What are the treatment options available?
Surgery (radical cholecystectomy), chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy depending on the stage and spread.
How much does gallbladder cancer treatment cost in India?
At PACE Hospitals, costs range between ₹4 to ₹12 lakhs depending on diagnosis, surgery type, and treatment plan.
Can gallbladder cancer be prevented?
There is no sure prevention, but maintaining a healthy weight, treating gallstones, and avoiding chronic infections help reduce risk.
Why choose PACE Hospitals for gallbladder cancer treatment?
PACE Hospitals offers advanced surgical oncology care with experienced HPB surgeons, modern diagnostics, and personalized, affordable treatment plans.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868