Cystitis - Types, Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, Treatment
PACE Hospitals
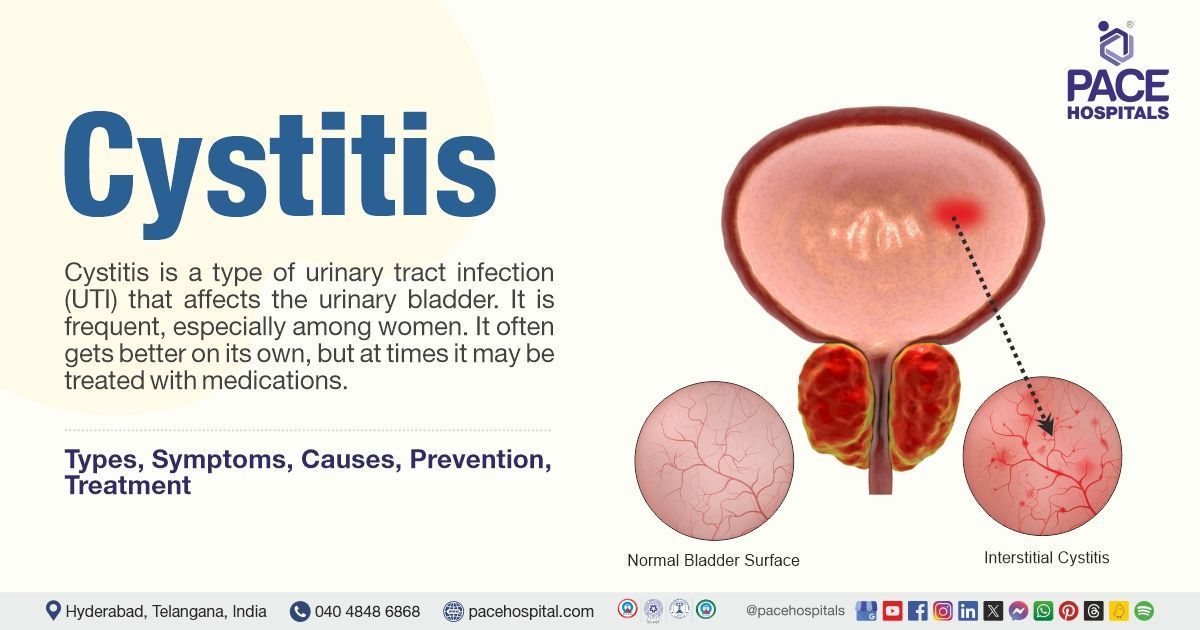
Cystitis refers to the inflammation of the urinary bladder. There are several causes, with bacteria being the most prevalent. Cystitis, often known as a lower urinary tract infection (UTI), when it is caused by bacteria. It's a common ailment that heals easily with appropriate care and infrequently causes complications.
The urethra is a narrow tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body. Urine travels through it. It is possible for bacteria to enter the body through the urethra.
Perhaps the regular flow of urine flushes out harmful germs from the body before an illness arises, but occasionally the bacteria find their way up to the urethra and into the bladder, where they cause cystitis.
Although cystitis can occur in both men and women it is more common in women than men due to shorter urethra, moist environment in the urethra, and close proximity of urethra to anus (where bacteria may reside) than men’s urethra.
Cystitis can frequently be cured with a course of antibiotics. Nevertheless, further therapies could be recommended to reduce symptoms if cystitis is severe and problematic.
Cystitis definition
Cystitis is defined as inflammation of the bladder that is frequently brought on by a bacterial infection. It may cause pain, discomfort, and frequent urine urges. Though cystitis is more common in women, it can also affect men. Antibiotics are usually used as part of treatment to eradicate the infection and reduce symptoms.
Cystitis meaning
The term ‘cystitis’ has a prefix ‘cyst’ and a suffix ‘itis’.
- ‘Cyst’ is derived from a Greek word ‘kustis’ which is used to refer the ‘bladder’
- ‘Itis’ is a Greek word which is used to describe ‘inflammation of an organ, tissue’ etc.
Prevalence of cystitis
It is asserted that by the age of 24, about one-third of women will have experienced a urinary tract infection, and by the age of 32, almost half of the women will have experienced it. According to self-reported annual incidence, women experience urinary tract infection at a rate of 12%.
According to university cohort research, the annual incidence of urinary tract infections in sexually active women is between 0.5 and 0.7 per person-year.
Men rarely get diagnosed with simple cystitis. Less than 10 cases are estimated to happen annually for every 10,000 men under the age of 65.
Prevalence of cystitis in India
According to a 2023 study, 37% of Indians suffer from urinary tract infections on a regular basis; however, other investigations have indicated lower percentages. The study additionally found that many antibiotics cannot kill the bacterium that causes urinary tract infections, and females are more likely than males to get the infection.
In India, 5–10% of pregnant women experience urinary tract infections at some point throughout their pregnancy.
Types of cystitis
Cystitis can manifest in a variety of ways, each with unique causes and characteristics. For accurate diagnosis and therapy, it's critical to understand the type of cystitis. Types of cystitis may include:
- Infectious or bacterial cystitis
- Interstitial cystitis
- Radiation cystitis
- Chemical cystitis
- Haemorrhagic cystitis
- Foreign body cystitis
Infectious or bacterial cystitis
This is the most common kind of cystitis, typically brought on by an infection with Escherichia coli (E. coli). Through the urethra, bacteria can enter the bladder, causing inflammation and infection. As women's urethras are shorter than men's, bacteria can more easily enter the bladder, leading to an increased risk of this kind of cystitis in women. It also occurs more frequently in people with weak immune systems and in people with urinary tract abnormalities.
Interstitial cystitis
This form of cystitis is also referred to as painful bladder syndrome. This is distinguished by persistent inflammation of the bladder lining. Although the precise origin of interstitial cystitis is unknown. Several factors, including nerve dysfunction, autoimmune reactions, and bladder lining damage are thought to be involved. Severe pain, frequent urination, and a strong desire to urinate all these could be the symptoms of interstitial cystitis. It can have a major impact on a person's quality of life and frequently require continuous care.
Radiation cystitis
Radiation cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder caused by radiation therapy used to treat specific diseases such as cervical or prostate cancer. Urinary symptoms include blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pain during urination are caused by damage to the cells lining the bladder caused by radiation. Radiation cystitis may need specific care and can develop weeks to months after radiation therapy is completed.
Chemical cystitis
The bladder lining can become inflamed and irritated when exposed to specific chemicals, such as those in douches, soaps, or spermicides. Like infectious cystitis, this type of cystitis can cause symptoms including pain and frequent urination. It is more common in those with sensitive bladder linings. Chemical cystitis can be prevented by avoiding irritating exposure and by using moderate, fragrance-free products.
Haemorrhagic cystitis
Haematuria (the presence of blood in the urine) is a defining feature of this type of cystitis, which is frequently brought on by viral infections like adenovirus or cytomegalovirus. Some drugs used in chemotherapy can potentially cause haemorrhagic cystitis. It can be extremely uncomfortable, and managing symptoms could need supportive care.
Foreign body cystitis
Prolonged insertion of an external object, like a catheter or contraceptive device, into the bladder can irritate and inflame the lining of the bladder. Cystitis symptoms, including pain and frequent urination, may result from this. To alleviate symptoms, the external object inserted must be removed and any underlying infection must be treated appropriately, if it exists.
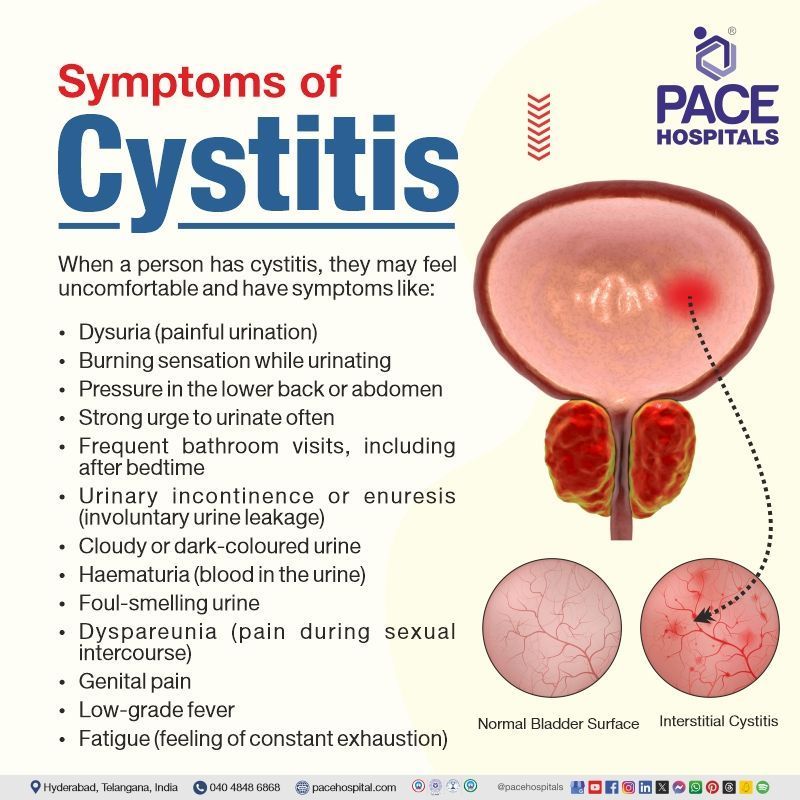
Cystitis symptoms
When a person has cystitis, they may feel uncomfortable and have symptoms like:
- Dysuria (painful urination)
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Pressure in the lower back or abdomen
- Strong urge to urinate often
- Frequent bathroom visits, including after bedtime
- Urinary incontinence or enuresis (involuntary urine leakage)
- Cloudy or dark-coloured urine
- Haematuria (blood in the urine)
- Foul-smelling urine
- Dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse)
- Genital pain
- Low-grade fever
- Fatigue (feeling of constant exhaustion)

Cystitis causes
Bacteria in the lower urinary tract are typically the cause of cystitis. The bacteria Escherichia coli is usually the cause, accounting for 95% of cases. At times, bacteria may enter the bladder through the urethra and cause cystitis in the bladder. Instances that raise the possibility of bacteria entering the bladder include:
- When intercourse happens in vagina and anus
- When people have weak urinary bladder
- When people don't completely clean themselves after a bowel movement or those who have faecal incontinence (loss of faeces or stool that is not intentional because of inadequate bowel control).
- When inserted a catheter into the someone’s urethra
- Among males whose penises are not circumcised (surgical removal of foreskin of the penis).
Causes of cystitis other than bacteria include:
- Medications
- Chemicals
- Radiation
- Foreign bodies
- Other medical conditions
Cystitis risk factors
Risk factors associated with cystitis may differ in both men and women.
Women who possess a higher chance of developing cystitis include:
- Those who recently have had an sexual intercourse
- Who had used contraceptive methods such as insertion of diaphragms or spermicide
- Who had a history of urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Post menopausal women
- Who are pregnant
- Those who diagnosed with diabetes (high blood glucose)
- Women who Experience urinary or faecal incontinence
- Women who had a history of kidney stones
- Who have had a prolapsed bladder wall (cystocele)
- Women suffering from urinary retention (difficulty in fully emptying the bladder)
- Women who had a catheter inserted into the urethra
- Women who are afflicted with Insufficient bladder control as a result of brain, nerve, or spinal cord disorders, such as diabetes, Parkinson's disease, or multiple sclerosis
Men who are at more risk of developing cystitis include:
- Men whose penis is uncircumcised
- Those who actively participate in insertive anal intercourse
- Those who had enlarged prostate and has a bladder blockage
- Men who have urinary retention
- Men with diabetes mellitus (increased blood glucose)
- Those who have had inserted catheter into the urethra
- Men who are afflicted with Insufficient bladder control due to brain, nerve, or spinal cord disorders, such as diabetes, Parkinson's disease, or multiple sclerosis.
Complications of Cystitis
Untreated cystitis can lead to complications such as:
- Pyelonephritis (inflammation of kidney due to bacteria or virus)
- Renal or perinephric abscess formation (accumulation of pus in the kidney)
- Renal vein thrombosis (blood clot in the vein that carries blood from the kidney and ureter to the inferior vena cava).
- Sepsis (When an infection triggers an excessive immune response in the body, organ malfunction results in sepsis, a potentially fatal condition).
- Acute renal failure (sudden decline in kidney function)
- Emphysematous pyelonephritis (necrotizing infection of the kidney and surrounding tissues that causes gas to accumulate in the renal parenchyma, collecting system, or perinephric tissue).
- Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland)
Prevention of Cystitis
To avoid the occurrence of cystitis frequently, it is necessary to indulge in things such as:
- When using a bathroom, cleanse from front to back
- Urinating immediately after intercourse
- Drinking a lot of liquids, especially water, to prevent thirst and ensure frequent urination during the day
- Taking a shower instead of a bath to avoid overexposing the genitalia to cleaning agents.
- Washing the area outside the vagina with water both before and after intercourse
- Replacing used incontinence pads or nappies as quickly as possible
- Maintaining a clean, dry genital area
Things that may stop prevention of cystitis include:
- Using fragrant soaps, bubble baths and talcum powder
- Holding urine even during urgency to urinate
- Not emptying the bladder fully
- Consuming excess sugar containing foods that has the potential to encourage bacterial growth
- Using spermicide along with condoms and diaphragm
Other strategies to stop the recurrence of cystitis include:
- Consuming minimal amounts of D-mannose and cranberry products may help preventing recurrence of cystitis
Cystitis diagnosis
To diagnose cystitis the urologist may perform tests such as:
- Urine analysis
- Urine culture
- Cystoscopy
- Ultrasound
- Computed tomography
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Intravenous urogram (IVU)
- Voiding cystourethrography
- Retrograde urethrography
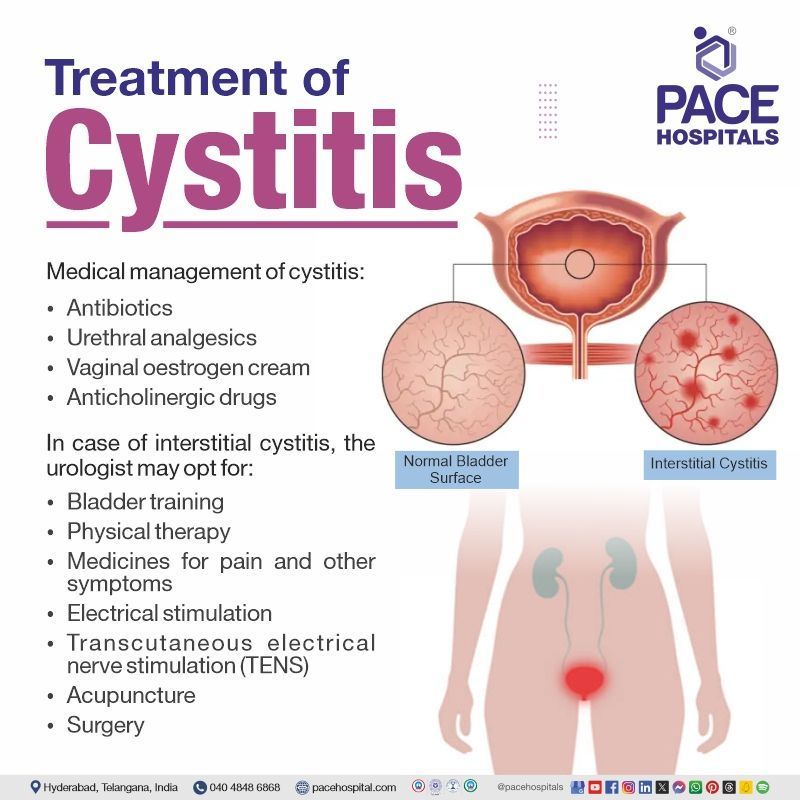
Cystitis treatment
To treat cystitis caused by bacterial infection, suitable Antibiotics are prescribed for one week.
If symptoms cause discomfort, other drugs may be used in addition to antibiotics. Which may include:
- Urethral analgesics
- Vaginal oestrogen cream
- Anticholinergic drugs
- Warm/hot sitz baths
Surgical intervention can be required to increase urine flow in case of any physical restriction to the bladder or urethra, which is extremely uncommon and is shown to be the cause of persistent cystitis.
- In case of interstitial cystitis, the urologist may opt for:
- Bladder training
- Physical therapy
- Medicines for pain and other symptoms
- Electrical stimulation
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
- Acupuncture
- Surgery
In case of cystitis due to soaps, bubble baths, and similar things, it is highly recommended to stay away from them.
Difference between cystitis and urinary tract infection
Cystitis vs Urinary tract infection (UTI)
| Aspect | Cystitis | Urinary tract infections |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Inflammation only confined to the urinary bladder | Any urinary tract infection that affects the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra. |
| Intensity of infection | Limited to the urinary bladder. | Can affect any area of the urinary system. |
| Symptoms | Pelvic pain, unclear or bloody urine, burning when urinating, and frequent urination. | Similar symptoms like cystitis and additional symptoms may include: Fever, Nausea and Vomiting especially if kidney infection is present |
| Treatment | Severe instances require antibiotics whereas mild cases may heal on their own. | Antibiotics recommended for a period of 7–14 days. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Cystitis
What is chronic cystitis?
Chronic cystitis is also known as bladder pain syndrome (BPS) or interstitial cystitis (IC), is a chronic bladder health problem. It is a sensation of pressure and pain in the bladder region. Besides pain in the bladder, symptoms of lower urinary tract may persist for longer than six weeks without an infection or other obvious causes.
What is acute cystitis?
Acute cystitis refers to the sudden development of inflammation of the bladder or the lower urinary tract, which is characterized by symptoms such as haematuria (bloody urine), foul-smelling urine, low grade fever, Pain or burning while urinating etc.
How long can cystitis last?
This kind of Infection is frequent, especially in women, and normally only causes little discomfort rather than significant concern. A few days is usually enough time for mild cases to resolve on their own. But some people have cystitis episodes often, and they may require ongoing or frequent therapy.
Can cystitis cause lower back pain?
Yes, cystitis can cause lower back pain, or cramps and pressure in the lower back or abdomen.
A cross-sectional study demonstrated that regardless of the location, most patients described their pain as intermittent. Overall, many patients reported moderate pain intensity. Urinary symptoms were significantly correlated with lower back, lower abdominal, and urethral pain.
How much water someone drink to flush out cystitis?
It is recommended to encourage premenopausal women who experience recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) and low fluid consumption to drink 1.5 litres or more of water per day to help lower their UTI frequency.
What is cystitis?
An infection of the lower urinary system, more especially the bladder, is referred to as cystitis. It can be generically classified as complicated or uncomplicated. Lower urinary tract infections (UTIs) in healthy men and women who are not pregnant are referred to as "uncomplicated cystitis.
What is honeymoon cystitis?
Honeymoon cystitis, sometimes referred to as honeymoon syndrome or honeymoon bladder infection, is a frequent ailment that typically strikes people soon after they have had intercourse. Due to the entry of microorganisms into the urinary tract during sexual activity, it is characterized by inflammation and infection of the bladder.
What is the Pathophysiology of cystitis?
The pathology of cystitis involves the colonization of the periurethral mucosa by bacteria from the vaginal or faecal flora, which then spreads to the bladder. Uropathogens may possess microbial virulence factors that enable them to penetrate urinary tract tissues and evade host defences.
What is mild cystitis?
Mild cystitis is one common form of urinary tract infection (UTI) that is not extremely severe or deadly and causes bladder irritation. It affects more women than males and is typically brought on by a bacterial infection. Mild instances frequently resolve on their own in a matter of days.
What is emphysematous cystitis?
Emphysematous cystitis (EC) is one of the rarest types of complex urinary tract infections (UTIs) that is characterized by gas in the bladder lumen and wall. Patients with emphysematous cystitis might have a wide range of clinical symptoms, from severe sepsis to no symptoms at all. Elderly ladies with severe diabetes mellitus are usually the ones who get emphysematous cystitis. Urine cultures frequently yield Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Computed tomography and plain conventional abdomen radiography are two essential imaging techniques for making a conclusive diagnosis of emphysematous cystitis.
What is bad for cystitis?
Some individuals with interstitial cystitis, however, find that specific foods or beverages exacerbate or cause their symptoms. Caffeinated beverages, citrus juices and drinks, chocolate, coffee, soda, alcohol, tomatoes, hot and spicy foods, and high-acid foods can all cause or exacerbate interstitial cystitis symptoms.
What vitamins help prevent lower urinary tract infections?
Infections, particularly urinary tract infections, are minimized by vitamin D, which may play a part in immunological modulation. As a result, it plays a beneficial regulating role in both acute and recurring infections, particularly in women who are fertile.
Can cystitis affect bowel movements?
Yes, bowel movements may be impacted by cystitis. However, there is an indirect rather than a direct link between bowel movements and cystitis. Because the intestines and bladder are so close together, inflammation in one might occasionally cause symptoms in the other.
Since there is a closer proximity between bladder and the rectum, irritation or inflammation in one organ may potentially extend to the other. In addition to potentially impairing bowel movements this may result in widespread pelvic pain or discomfort.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868