EEG Test - Procedure Indications, Purpose & Cost
Dept. of Neurology and Neurosurgery at Pace Hospitals, is equipped with world-class EEG scan equipment to investigate and diagnose epilepsy (causes of repeated seizures) and other brain conditions such as Sleep apnea, Inflammation of the brain (Encephalitis), Brain tumor, Dementia etc.
Our team of the best neurologist in Hyderabad and top neurosurgeon are having extensive experience in treating all types of brain conditions and performed the complex surgeries.
Request an Appointment for EEG Test
EEG test - appointment
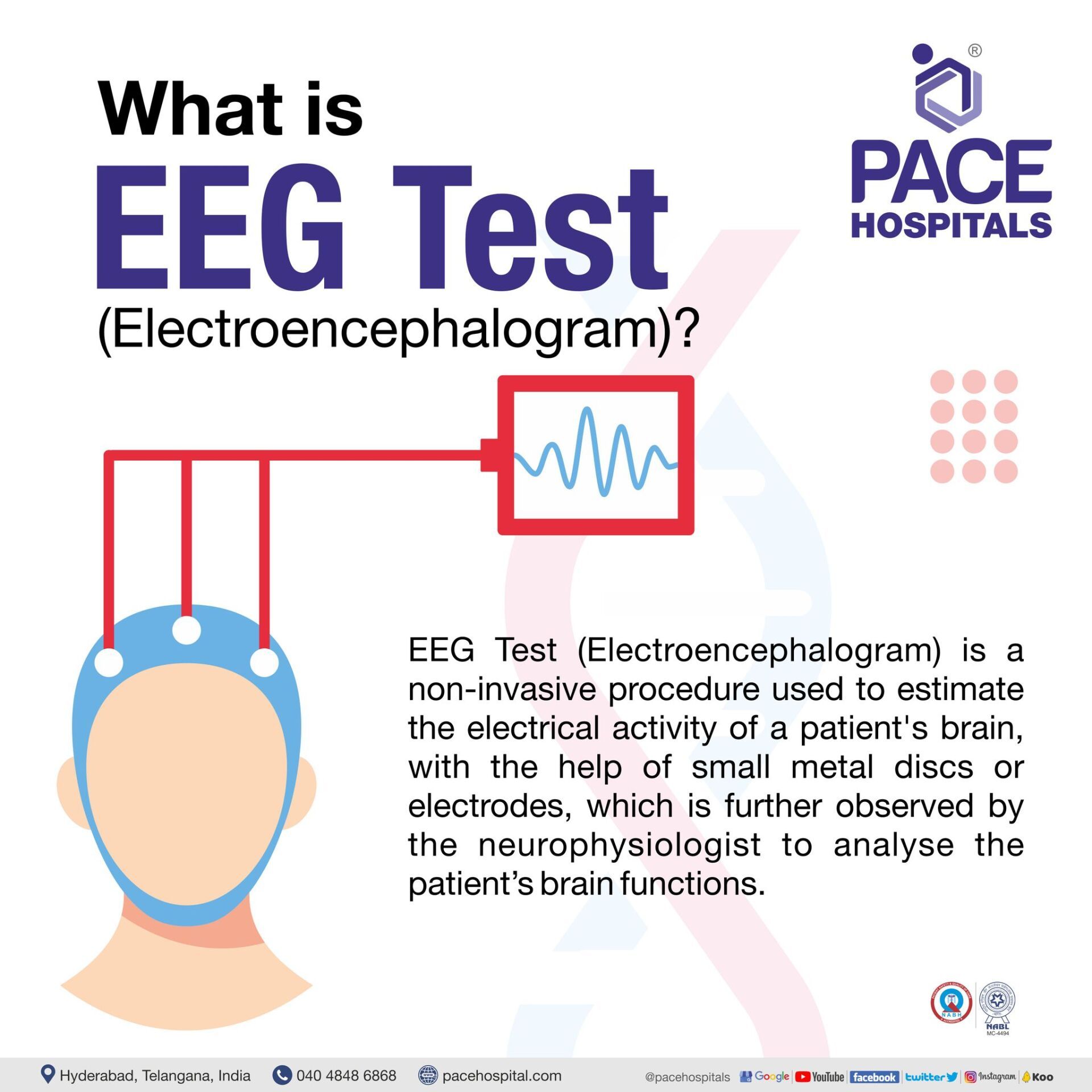
What is EEG test and its purpose?
EEG full form in medical - Electroencephalogram
EEG Test (Electroencephalogram) is a non-invasive procedure used to estimate the electrical activity of a patient's brain, with the help of small metal discs or electrodes, which is further observed by the neurophysiologist to analyse the patient’s brain functions.
It helps diagnose and monitors several conditions affecting the brain, such as epilepsy (a condition that causes repeated seizures), memory loss, etc. In addition, an EEG Test will assist the neurophysiologist in determining the type of epilepsy the patient might have, any potential causes of seizures, and the best course of treatment.

Indications for EEG test
EEG Test used to diagnose and monitor the following conditions:
- Epilepsy and seizures
- Presence of internal bleeding and tumours of the brain
- Damage caused by a traumatic brain injury
- Alzheimer’s disease and dementia
- Infections, such as encephalitis
- Sleep disorders such as narcolepsy
- Stroke
- Metabolic and hormonal conditions that affect brain tissue
Types of EEG Test
Based on the patient’s requirements, they are categorised as follows:
- Routine EEG
- Prolonged EEG
- Ambulatory EEG
- Video EEG
- Sleep EEG
- Invasive EEG
Routine EEG: In this test, the patient could be asked to rest quietly, close and open their eyes from time to time, or in some cases, the technician might request the patient to look at flashing lights or breathe quickly during the test. It lasts for about 30 to 40 minutes.
Prolonged EEG: The neurologist might use prolonged EEG scan to diagnose and manage seizure disorders. This examination typically lasts one to two hours, but it can go on for several days if the neurologist wants additional data on the patient's brain waves. A video might be used with prolonged EEG.
Ambulatory EEG: In this EEG scan, the patient could wear a small, portable device (EEG recorder) connected to electrodes on their scalp for one to three days. It captures all the electrical activity of the patient's brain throughout the day and night when they are on daily activities, either awake or asleep.
It also helps capture the data at specific times; for instance, if a patient experiences a seizure or any incident that the doctor wants to capture, the patient’s assistant can press a button on the device to capture the brain's activity. An ambulatory EEG can help patients to avoid a diagnostic hospital stay and provide more information about their daily brain activity.
Video EEG: It is a unique kind of EEG scan where it is used in patients admitted to the hospital. It is also called Video telemetry, during which an EEG procedure is filmed. This type of EEG can provide more details about the functioning of the patient’s brain, plan for potential treatment options, confirm the intensity of seizure activity and locate the brain region where it begins. The computer receives the EEG signals wirelessly. Additionally, the computer records the video, which is continually monitored by skilled professionals.
Sleep EEG: As the name defines, it will be performed by the technician while the patient sleeps for several hours. This type of EEG scan is used mainly to evaluate symptoms for sleep disorders, or it might be preferred when the information provided through routine EEG is insufficient.
Invasive EEG:
This type of EEG scan is rare, and it may be used to check whether surgery is an option for a patient with more complex epilepsy. In this method, the electrodes are surgically implanted in the patient's brain to pinpoint the precise location of the seizures.
Preparing patient for EEG (electroencephalogram)
The patient needs to inform the surgeon about the intake of daily medications, and the patient should stop taking any medicines before the test that might affect the test as per the physician’s advice.
- The patient should not wash the hair with conditioner and should not use any gels or hair sprays on the day of the procedure or the night before the test. This will help sensors (electrodes) stick to the patient’s scalp more easily.
- The patient should avoid foods or drinks that contain caffeine at least 8 to 12 hours before the test.
- The patient should have enough food before the day of the test, as low blood sugar might influence the result.
- For a sleep EEG, adults should not sleep more than 4 to 5 hours; for children, it is 5 to 7 hours the night before the procedure.
- The patient might be asked to remove any jewellery or other metal objects that might interfere with the EEG recordings.
- The neuro physician will select the type of EEG test based on the patient's needs.
- The neuro physician will explain the complete procedure to the patient and could ask the patient to make other special preparations depending on the patient's medical condition.
Electroencephalogram EEG Procedure
The EEG procedure may be done in several methods. In general, it is a painless test where small metal sensors called electrodes (depending on the disease being investigated, the number of electrodes used is between 8 and 23) are affixed to the patient’s scalp using washable glue or a cap with embedded electrodes to collect the electrical signals generated by the brain.
This process is carried out by a highly skilled professional (neurophysiologist). In some cases, a neurosurgeon could place electrodes in or on the brain through a surgery process to record electrical activity for a longer period of time.
The patient will be requested to lie on a bed or reclining chair. The neurophysiologist attaches the electrodes with the help of adhesive or conductive paste post cleaning the patient’s scalp.
On initiating the procedure, the electrodes that are attached to the patient’s scalp detect the electrical impulses that move between brain cells. The EEG equipment is connected to the electrodes by wires that transmit the patient’s electrical impulses data to the EEG equipment. The equipment records the information as lines (waves) that show the patient's brain wave patterns.
The neurophysiologist will examine the recorded brain activity post-EEG procedure, looking for abnormal patterns or changes. The EEG can help rule out or confirm the presence of certain neurological disorders, such as brain injuries, sleep disorders etc. In addition to that, it also aids the physician in taking an appropriate therapy decision.
Post- EEG Test
- The electrodes will be taken off after the EEG brain test, and the electrode paste attached to the scalp will be cleaned using warm water and acetone. In some cases, the patient may need to wash their hair once more at their home post-procedure.
- If the patient is on sedative during the test, the patient might need to rest until the sedative effects wear off.
- The patient can have some skin redness or irritation where the electrodes are inserted, but this will go away in a few hours.
- The neuro-physician will let the patient know when to resume their old medications that have stopped before the test.
- Post-procedure, depending on the patient’s health situation, the doctor may provide the patient with alternative or additional instructions.
Complications of EEG Test
- EEG scan is a painless and comfortable procedure with no side effects. However, an episode of seizures might occur due to the usage of various stimuli in the procedures, including flashing lights or deep breathing. On the other side, technicians believe the occurrence of a seizures' episode during the EEG scan process might help diagnose
- Apart from that, the patient might feel lightheaded and have a tingling sensation in their lips and fingers. To reduce this effect, the patient will be asked to breathe in and out deeply during the EEG procedure. This effect usually stays for a few minutes.
- The patient might develop a mild rash at the point where electrodes are attached.
Factors that may interfere with the EEG test reading
- EEG scan is a painless and comfortable procedure with no side effects. However, an episode of seizures might occur due to the usage of various stimuli in the procedures, including flashing lights or deep breathing. On the other side, technicians believe the occurrence of a seizures' episode during the EEG scan process might help diagnose
- Apart from that, the patient might feel lightheaded and have a tingling sensation in their lips and fingers. To reduce this effect, the patient will be asked to breathe in and out deeply during the EEG procedure. This effect usually stays for a few minutes.
- The patient might develop a mild rash at the point where electrodes are attached.
Contraindications of EEG Test
- An EEG brain test is contraindicated in patients with acute or recent stroke, cerebrovascular disease, severe cardiovascular or respiratory disease, and sickle cell anaemia, who might be performing hyperventilation (rapid or deep breathing) during the EEG procedure.
EEG Test Price in Hyderabad, India
The
cost of an EEG test in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹1,200 to ₹5,500 (approximately US $14 – US $66).
The exact EEG test cost varies depending on factors such as the type of EEG performed (routine EEG, sleep-deprived EEG, ambulatory EEG, long-duration EEG), duration of monitoring, whether video EEG is required, neurologist interpretation charges, and the hospital or diagnostic facilities chosen — including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance approvals wherever applicable.
Cost Breakdown According to Type of EEG Test
- Routine EEG (20–30 minutes) – ₹1,200 – ₹2,000 (US $14 – US $24)
- Sleep-Deprived EEG – ₹1,500 – ₹2,500 (US $18 – US $30)
- Video EEG (1–2 hours) – ₹2,500 – ₹4,000 (US $30 – US $48)
- Long-Duration / Prolonged Video EEG (4–6 hours) – ₹3,500 – ₹5,000 (US $42 – US $60)
- Ambulatory EEG (24 hours monitoring) – ₹4,000 – ₹5,500 (US $48 – US $66)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on EEG Test
What can an EEG show that an MRI cannot?
An EEG brain test simply provides data about the patient’s brain electrical activity with a high temporal resolution. In contrast, MRI, with the help of radio waves and the magnetic field, provides the structures of the brain tissue, cannot measure brain activity and also produce a low temporal resolution.
What are the possible causes of an abnormal EEG report?
The possible causes of an abnormal EEG report are due to the presence of the following:
- Haemorrhage
- Brain tumour
- Cerebral infarction (a result of disrupted blood flow to the brain)
- Drug or alcohol abuse
- Injury in head
- Migraines
- Seizure disorder
- Sleep disorder
- Oedema (swelling of the brain)
- Liver or kidney disease
- Infections in brain
What is an EEG signal?
Electroencephalography (EEG) signals are the neural activity signatures and integrals of active potentials that the brain produces with different latencies at each instant. They serve as the markers of neural activity. Based on signal frequencies ranging from 0.1 Hz to more than 100 Hz, these signals are generally categorised as delta, theta, alpha, beta and gamma.
Can EEG send signals back to the brain?
No, the EEG test can’t send the signals back to the brain. It transmits the patient’s electrical impulses data from the electrodes attached on the patient’s skull to the computer device and represents it in the form of waves.
What is the difference between EEG and EMG?
The electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive technology that measures the voltage variations caused by the electrical activity of neuronal mass through electrodes which will be fixed on the patient's scalp at the time of the procedure. Whereas Electromyography (EMG) is a technique that records the electrical impulses generated by muscle activity or skeletal muscles.
Can an abnormal EEG be wrong?
Yes, the chances of having a wrong interpretation of abnormal EEG report or being misdiagnosed with epilepsy are obvious and severe. The most fundamental causes for this are a lack of neurophysician's training and experience (not exposed to enough normal reading and the range of normal fluctuations), which leads to over-read normal tracings as abnormal. The lesser the experience, the more the chances of misinterpretation.
Can you smoke before an EEG?
No, the patient should not smoke before an EEG procedure since hazardous substances, including nicotine, drugs, and alcohol, impair brain signal activity. As a result, smoking before an EEG procedure may cause the EEG data to be misinterpreted. According to a study, there was a significant difference in EEG performance between smokers and non-smokers before and after the smoking task, as smoking caused a modest rise in theta and delta frequency.
Is EEG test indicated for psychiatry?
Yes, an EEG test is indicated in patients with new-onset psychosis, associated with rapid changes in mood or behaviour or conditions characterised by fluctuating or increasing cognitive impairment. The goal of using EEG is to see if the patient has epileptic or slow EEG activity.
How some drugs affect the electroencephalogram?
Drugs have varying and generally dose-dependent effects on the electroencephalogram (EEG). Drugs can have a wide range of effects on the electroencephalogram, from having no effect to emphasising beta activity, which includes slowing the background with reduced alpha amplitude and/or frequency, a mixture of theta and delta activity, reducing seizure activity and lowering the seizure threshold with increased spike and wave discharges.
What is a major disadvantage of EEG brain test?
The major disadvantage of EEG brain test is the limited spatial resolution. During the EEG procedure, the electrodes monitor electrical activity at the brain's surface, but it is difficult to locate whether the signal was created near the surface of the cortex or from a deeper location.
Should you eat before EEG scan?
The patient can consume a normal diet on the day of surgery. However, the patient should not eat anything (foods or drinks) that contain caffeine for at least 8 to 12 hours before the tests, which might affect the EEG reading.
What is the EEG cost in India?
EEG scan cost in India, ranges vary from Rs. 1,100 to Rs. 3,800 (Rupees one thousand one hundred to three thousand eight hundred). However, EEG cost / price / charges in India vary in different private hospitals in different cities.
What is the EEG scan cost in Hyderabad?
EEG cost in Hyderabad ranges vary from Rs. 1,200 to Rs. 3,600 (Rupees one thousand two hundred to three thousand six hundred). However, cost of EEG test in Hyderabad depends upon the multiple factors such as patient condition, age, hospital and insurance or corporate approvals for cashless facility.