Hepatitis - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
PACE Hospitals
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can be caused by a virus in most cases, but also by the consumption of toxic (alcohol, drugs, etc.).
What is hepatitis?
Viral hepatitis is an infection with a liver tissue virus. There are five main viruses of main hepatitis: A, B, C, D and E. The severity of the disease and treatment to follow depend on the type of hepatitis and the individual, this sometimes causes cirrhosis or a Cancer. Hepatitis manifests itself by a yellow skin (jaundice or jaundice), dark urine, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain.
Hepatitis A: acute viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis A virus. It is often caused by contaminated food or water.
Hepatitis A: Symptoms, vaccine, how long does it last?
Hepatitis A is a viral disease of the liver that is mainly transmitted by ingestion of infected food or water in fecal materials. Fortunately, a vaccine exists to prevent contagion. What are the symptoms and are there treatments to treat it?
Hepatitis B: acute viral hepatitis caused by the HBV virus. It is transmitted from human to humans during sex, contact with blood or contaminated objects.
Hepatitis C: Acute or chronic hepatitis caused by the VHC virus or by the consumption of toxic (alcohol, drugs, etc.)
Hepatitis C: Symptoms, Treatments, Contagion: This viral liver disease remains silent for a long time, which is why one in three people does not know they are infected. Update on symptoms, contagion mode, treatments and chances of recovery.
Hepatitis D: Acute or chronic hepatitis caused by the HDV virus that needs hepatitis B virus to reproduce. There can be no hepatitis D if there has been no infection with hepatitis B before.
Hepatitis E: viral hepatitis transmitted animals to humans. It is mainly transmitted by eating raw or insufficient pork.
Hepatitis E: symptoms, treatment, how is it transmitted?
Less known than hepatitis B and C, hepatitis E is also a liver disease. WHO estimates that hepatitis E provokes just over 44,000 deaths per year around the world. How is the transmission? Is it contagious ? What are the symptoms of warning and what dangers? Update on this liver disease.
Acute viral hepatitis: This can be acute, that is to say occurring at a given moment and disappear spontaneously as for hepatitis A, or become chronic after an infection, such as hepatitis C or hepatitis C more rarely from hepatitis B . "Viral symptoms of viral hepatitis usually occur as flu syndrome with fever, fatigue, joint pain and pains, headaches and digestive signs sometimes, followed by yellow discoloration Skin and mucous membranes called jaundice.
Chronic hepatitis: It is a chronic inflammation of the liver that most often follows acute hepatitis. Chronic hepatitis is more serious, with possible progression of cirrhosis or liver cancer. Note that other viruses such as cytomegalovirus (CMV) or herpes virus can give hepatitis.
Fulminant hepatitis: Fulminant hepatitis is a rare syndrome combining a massive necrosis of hepatic parenchyma and a decrease in liver size (acute atrophy) that occurs during infection with certain hepatitis viruses or in case of toxicity or drug. The hepatitis B virus is sometimes responsible for the fulminant hepatitis and up to 50% of the fulminating hepatitis B implies co-infection with the hepatitis D virus.
Causes:
Viral hepatitis is caused by infection with a virus. In developed countries, hepatitis A, B and C viruses cause about 90% of acute hepatitis cases. Hepatitis D and E viruses are also responsible for hepatitis.
Non-viral hepatitis is mainly caused by the ingestion of products toxic to the liver (alcohol, drugs, toxic chemicals, etc.). They can also be the result of diseases affecting the liver, such as fatty liver (NASH or "fatty liver").
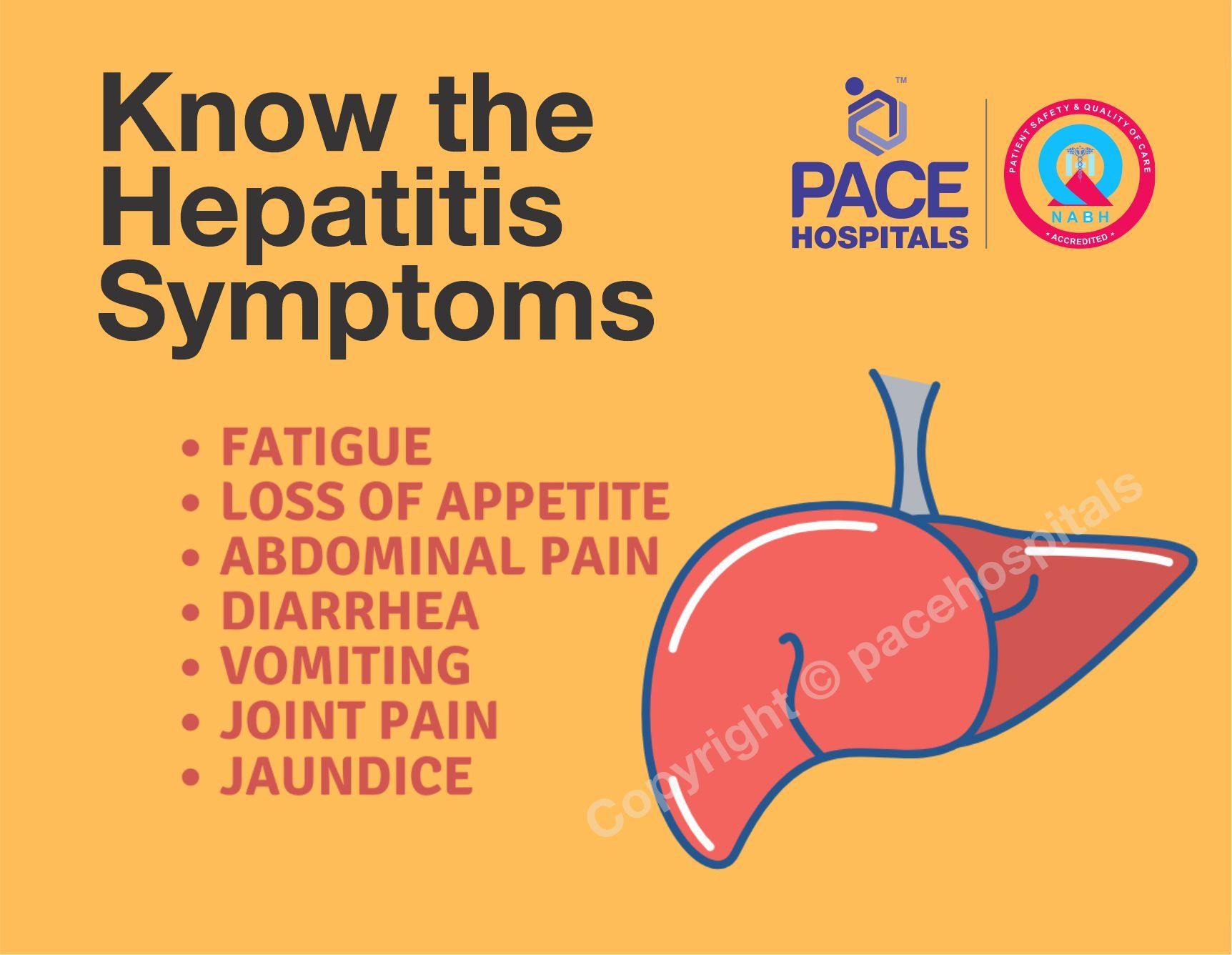
Symptoms:
- Intense fatigue similar to that of flu syndrome
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea
- Jaundice
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Coloring of urine (dark urine)
- Nausea and vomiting
Transmission:
Hepatitis is transmitted differently according to the virus involved, by accidental ingestion of feces for hepatitis A, bodily secretions such as saliva, sexual secretions or by blood contamination for another hepatitis.
Treatments
Treatments vary depending on the type of hepatitis:
- Hepatitis A: "Normally, the body is able to fight against the hepatitis A virus. So this disease does not require special medical treatment, but the rest and a good diet are indicated. The symptoms disappear after 4 to 6 weeks "Remember our interlocutor.
- Hepatitis B: In the vast majority of cases (90%), infection with hepatitis B virus resolves spontaneously and no pharmacological treatment is necessary. The recommendations are then the same as for hepatitis A: rest and healthy food. When infection persists beyond 6 months, it means that the body can not eliminate the virus. He then needs help. In this case, several drugs can be used.
Evolution and risks
Hepatitis healed in a few weeks without treatment. We observe prolonged forms over several weeks healing. Hepatitis never advance with a chronic infection (unlike hepatitis B or hepatitis C). Hepatitis A is cured and induces immunity of life (a second infection with the HAV virus is impossible).
Acute hepatitis B progresses healing in the majority of cases (more than 90%). When acute infection does not recover, the evolution is towards chronic hepatitis B, defined by the persistence of the virus in the body for more than six months. Chronic hepatitis B takes place in 2 to 10% of cases and requires long-term follow-up and sometimes treatment.
In 90% of cases, hepatitis C goes unnoticed; Its diagnosis can then be performed when screening for hepatitis C. Acute hepatitis C can progress in two different ways:
to recovery in 15 to 30% of cases; towards the passage to chronicity (chronic hepatitis C) in 70 to 85% of cases. Chronic hepatitis C is defined by the persistence of the virus in the body for more than six months.
Prevention:
There are vaccines for hepatitis A and B. Hepatitis A vaccination only concerns people exposed to this virus. It has the effect of significantly reducing the risk of contracting this infection.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868