HPV Vaccination in Hyderabad, India
At PACE Hospitals, embark on your journey to peace of mind with our comprehensive HPV vaccination services. Trust our expert HPV doctors to safeguard your health confidently. Prioritize your well-being today by scheduling your appointment for HPV vaccine (Gardasil / Gardasil 9 / Cervavac) and embracing a healthier tomorrow with us.
Safeguarding Your Health: A Step-by-Step Guide to Booking HPV Vaccination for Yourself!
People residing in Hyderabad who are seeking 'HPV Vaccination near me' can schedule an appointment online at PACE Hospitals by completing the form above titled 'Request an Appointment for HPV Vaccination (Gardasil / Gardasil 9 / Cervavac)' or can call our appointment desk at 04048486868.
These are some additional things to keep in mind when visiting center for Vaccination:
- Know your vaccination schedule: You can find the recommended vaccine dose schedule by age, here 👉 HPV Vaccination Schedule.
- Please remember to bring your previous vaccination records. This will assist the healthcare provider in determining which HPV or any other vaccinations you have already received.
What is HPV Vaccination?
HPV vaccine full form - Human Papillomavirus vaccine
HPV vaccination involves administering HPV vaccines containing virus-like particles to boost immunity against HPV infection. It significantly reduces the risk of HPV-related cancers like cervical, vaginal, vulvar, penile, anal, and oropharyngeal cancer. This vaccine marks a breakthrough in prophylactic vaccination, contributing to declining cervical cancer rates in many countries.
Notably, HPV vaccines offer long-term protection, generating stable antibody responses for over a decade without requiring frequent boosters. They're among the earliest and most accessible vaccines, providing infection prevention without triggering specific mucosal immunity. Overall, HPV vaccination demonstrates efficacy in providing durable protection against HPV infection and associated cancers.
HPV vaccine and cervical cancer
The huge burden of cervical cancer mortality, especially in the low- and middle-income countries, can be greatly attributed to decades of neglect by the global health community. Nevertheless, with the recent increase in global advocacy for women’s health, the World Health Organization (WHO) devised as strategy to achieve its goal for 2030. By 2030 the WHO strives to achieve the following:
- 90% of girls (15 years of age) are to be fully vaccinated with HPV vaccine.
- 70% of women must be screened using a high-performance test by 35 years of age and again by 45 years of age.
- 90% of women suffering from cervical disease are treated, which should include:
- 90% of women with precancer treated.
- 90% of women with invasive cancer managed.
Through these goals, WHO anticipates for a global elimination of cervical cancer, which can be defined as an incidence of cases < 4 per 1,00,000 women per year globally.
The WHO aims to achieve the goal through:
- Low-cost approaches to screening and treating cervical cancer precursors
- Development of resource-appropriate management guidelines
- Novel approaches to surgical training
- Initiatives to increase global access to anti-cancer drugs
Along with the above factors, the WHO also ensures a constant and steady flow of commercial availability of prophylactic HPV vaccines which also plays an important role in the eradication of cervical cancers.
Among various other factors which prompted the initiation of the aforementioned campaign, the prime reason included is the slow roll-out of HPV vaccination. The other factors could include low levels of screening as well as limited access to cervical cancer treatment.

Necessity of HPV vaccines
Fortunately, protection from HPV-related sexually transmitted diseases and infection also with its associated cancers can be obtained through immunization by HPV vaccine. HPV vaccination, in general, has demonstrated superior efficacy and tolerability (safety).
Since among 50% of adolescents become sexually active at some point during high school the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) – an American organization governing the health related aspects recommended the administration of HPV vaccination to be initiated of between the ages of 11 and 12 to, so adolescents get enough time to develop adequate immunity prior to HPV exposure. The endorsement of advisory committee on immunization practices (ACIP) supported CDC’s recommendation encouraging the incorporation of HPV vaccine into the routine immunization schedule aimed at adolescent girls.
HPV vaccine prevents cervical cancer
A 2021 Danish study demonstrated that a nationwide cohort study in which the result of HPV vaccinations is reported:
- A reduction of 86% in cervical cancer among 16-year-old and younger people
- A 68% decrease is seen among older teens
Similarly, a Swedish study also demonstrated a reduction of 62% in cervical cancer among young women who were vaccinated between 20 and 30 years of age.
While there is an overwhelming evidence of HPV vaccination in the reduction of cervical cancer cases worldwide, the availability of HPV vaccine is constrained owing to its slow roll-out rate (which may continue until 2022/25) due to which an alternative scheduling of doses and/or reduction of doses are under discussion.
While the initial recommendation of three-dosing schedule, priming doses at 0 and 1/2 months followed by a boost at 6 months, was altered in 2014 by WHO SAGE for adolescents at <15 years of age to two doses, at 0 and 6 or 12 months.
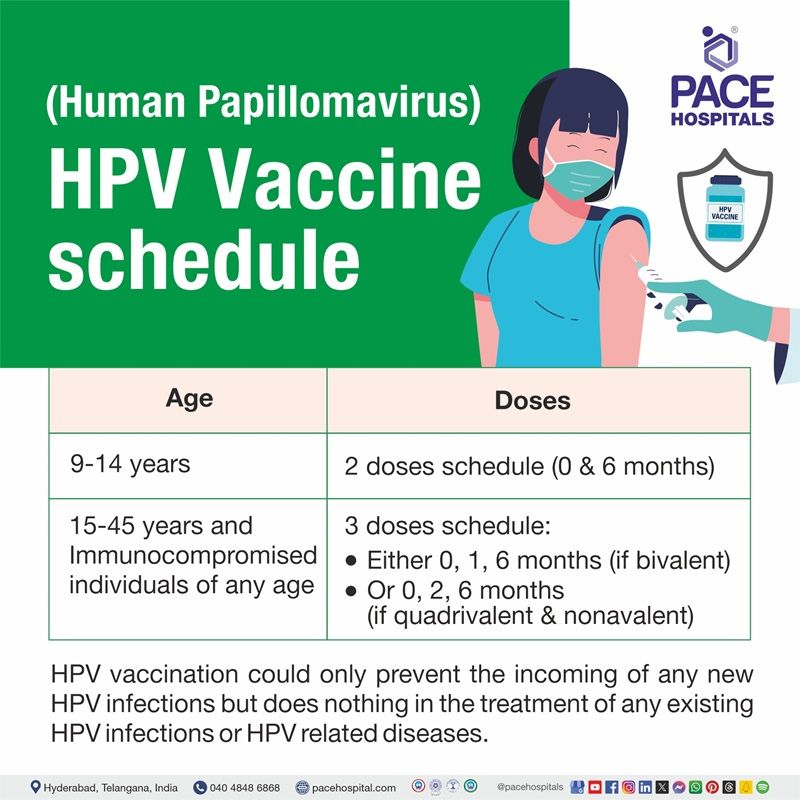
HPV vaccine schedule by age
| Age | Doses |
|---|---|
| 9 to 14 years | 2 doses schedule (0 & 6 months) |
| 15 to 45 years and Immunocompromised individuals of any age | 3 doses schedule: Either 0, 1, 6 months (if bivalent) Or 0, 2, 6 months (if quadrivalent & nonavalent) |
- Women more than 26 years with active sexual history would require discussion and medical counselling with the doctor, as the HPV vaccination could provide only minimal efficacy.
- It must be understood that HPV vaccination could only prevent the incoming of any new HPV infections but does nothing in the treatment of any existing HPV infections or HPV related diseases.
- Individuals practicing mutually monogamous relationship in the long-term are not likely to get a new HPV infection.
HPV vaccine mechanism of action
HPV vaccines administrated through intramuscular injection induce immunity by triggering B-cell and T-cell responses. These are components of the immune system. The mechanism of HPV vaccines lies in the formation of antibodies.
- They induce formation of antibodies which bind the virions, preventing initial infections.
- These antibodies (mostly immunoglobulin G (Ig)) can reach the cervicovaginal infection sites either by
- transudation of antibodies across the epithelial barrier into mucosal secretions at the cervix or
- direct exudation of serum and interstitial antibodies at the site.
HPV vaccine side effects / risks
The risks include both local and systemic adverse effects. The overall local side effects mainly include the possibility of infection at the injection site, which contains no statistical significance when compared with the serious side effects events.
A WHO-commissioned 2018 Cochrane study demonstrated no difference in the terms of a few selected serious side events when compared in those who were vaccinated with the HPV vaccine against the those were unvaccinated.
The data from the vaccine adverse event reporting system (VAERS) from data with over 60 million doses administered demonstrated no identified association between HPV vaccine and the following:
- Guillain–Barré syndrome (rare autoimmune disorder affecting the nerves)
- Complex regional pain syndrome (chronic pain in the limbs which develops after injury, surgery, stroke or heart attack)
- Bell’s palsy (sudden onset of muscular weakness on one half of the face)
- Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (sudden syncope due to reduced blood volume seen during getting up)
- Premature ovarian insufficiency (loss of ovarian function before the age of 40)
- Venous thromboembolism (condition of blood clot in a vein)
While HPV vaccine demonstrated no connection in pregnancy outcome, it is recommended to not get vaccinated during pregnancy.
Benefits of HPV vaccine
A 2013 European study demonstrated the benefits of HPV vaccine. It brought:
- 90% reduction in HPV infection related cancers in females
- 86% reduction in HPV infection related cancers in males
- 58% of reduction in HPV of infection related genital warts in females
- 71% of reduction in HPV of infection related genital warts in males
The study concluded that the vaccinations of both boys and girls against HPV was associated with substantial reduction of not only HPV infection related cancers and warts but also other anticipated additional clinical benefits such as reduced incidence of head/neck cancers, cervical, vaginal & vulvar diseases etc.
The scenario of HPV vaccine in India
Bivalent and quadrivalent HPV vaccines were licensed for prescription use by Indian authorities in 2008. The first large-scale introduction of HPV vaccination in the public health setting in India was in demonstration projects in 2009 that aimed to establish how best to deliver the vaccine. These projects were implemented by the state governments of Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Programme for Appropriate Technology in Health (PATH), a US-based not-for-profit nongovernmental organization, in 2009.
- The bivalent vaccine (against HPV subtypes 16 and 18) was used in Vadodara district.
- The quadrivalent vaccine (against HPV subtypes 6, 11, 16, and 18) was used in Khammam district. The last couple of strains, HPV-16 and HPV-18, are responsible for causing at least 80-85% of all the cases of cervical cancers in India, while HPV-6 and -11 are responsible for at least 90% of genital warts. Vaccination against these subtypes can result in the increased chances of prevention of these cancers and warts.
- A nonvalent vaccine had been licensed for use in India since 2018 which prevents infection arising from the nine HPV subtypes (6,11,16,18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58). Vaccination with this nonvalent vaccine can help in the prevention of the additional about 10% of cervical cancers.
Recently, India has indigenously rolled out its own vaccine against HPV. This quadrivalent vaccine - Cervavac was launched in the eve of India’s entry into the list of the global Cervical Cancer Elimination Initiative which aims at the acceleration of cervical cancer elimination.
It was a joint venture of the Indian Government’s Department of Biotechnology and the Serum Institute of India, Pune. It was approved for marketing on the 12th of July 2022 by Drug Controller General of India after reviewing a positive data from a large-scale phase 2/3 clinical trial.
HPV vaccine types and names
Therapeutic vaccination is the most obvious strategy, as host immunity plays an important role in viral clearance. The names and efficacy of various HPV vaccines is as follows:
| Name | Type | Protection against | Prevents the risk of |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gardasil | Quadrivalent | HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18 | Cervical, vulvar, vaginal, anal cancer, genital warts and precancerous or dysplastic lesions |
| Gardasil 9 | Nonavalent | HPV 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52 and 58 | Cervical, vulvar, vaginal, oropharyngeal, anal cancer, precancerous or dysplastic lesions and genital warts |
| Cervavac | Quadrivalent | HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18 | Cervical, vulvar, vaginal, anal cancer, genital warts and precancerous or dysplastic lesions |
HPV vaccine cost in Hyderabad
HPV vaccine cost in Hyderabad, India can vary from ₹ 1,000 to ₹ 10,850 (Rs one thousand to ten thousand eight hundred fifty only) per dose
for child or adults that totally depends on the HPV vaccine brand a person choose. There are 4 types of HPV vaccines which are marketed in India. The below table includes HPV vaccine price in India along with their target HPV strains:
| Brand name | Manufacturer | HPV vaccine cost |
|---|---|---|
| Gardasil | Merck | ₹ 3927 per dose |
| Gardasil 9 | Merck | ₹ 10850 per dose |
| Cervavac | Serum Institute of India | ₹ 2000 for two dose |
Frequently asked questions on HPV vaccine:
Is HPV vaccine mandatory?
Yes. HPV vaccine is mandatory. HPV infection is the most common risk factor for cervical cancer. Apart from reducing the risk of cervical cancer, the vaccines have demonstrated significant efficacy against high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), anal intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN), vaginal intraepithelial cancer (VaIN) in women, vulvar intraepithelial cancer (VIN) in women and genital warts.
Who should get HPV vaccine?
HPV vaccination can be given to anyone aged 9–45 years of age. Depending on age, it can be given in 2 or 3 doses.
- Two doses of HPV vaccines are recommended for those who initiate vaccination at ages 9–14 years, with a minimum interval of 6 months.
- A three-dose schedule is required for those who initiate at age 15–26 and for immunocompromised persons. The maximum interval between HPV vaccine doses is not specified, but the attempt should be to complete the vaccination schedule in 15–18 months.
While the vaccines are licensed up to the age of 45, the WHO recommends targeting 9–14-year-old girls.
Can HPV vaccine cause warts?
No. HPV vaccine does not cause warts. On the contrary, vaccination with HPV vaccine reduces the risk of warts. The other benefits apart from reduced risk of genital warts include reduced risk of cervical cancer, high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), anal intraepithelial neoplasia (AIN), vaginal intraepithelial cancer (VaIN) in women, vulvar intraepithelial cancer (VIN) in women.
How often do you have to get the HPV vaccine?
The frequency of HPV vaccine depends upon the age of the individual. If the vaccination is initiated in the individual ranging between 9-14 years, a minimum interval of 6 months is necessary. In case of vaccine initiation within the ages of 15-26 years the vaccination schedule could range from 15 to 18 months. Currently trials are underway to assess if even one-dose of HPV vaccine may be effective (single-dose vaccination strategy).
What is HPV vaccine?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination is the administration of HPV vaccine which contain virus-like particles to help the immune system in the body to develop immunity from HPV infection. The individuals who were vaccinated were rarely tested positive for HPV infection. It shows that HPV vaccines provide “sterilizing” immunity in most cases.
Can you get the HPV vaccine after 26?
Yes, HPV vaccine can be taken even after 26 to 45 years of age but no statistically significant efficacy has been demonstrated for various cancers such as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), anal intraepithelial neoplasia or cervical cancer. This is why the WHO recommended the administration of HPV vaccine to 9–14 yeas old girls, despite being licensed up to the age of 45 years.
Can you get the HPV vaccine after being sexually active?
Although HPV vaccination is most effective in the prevention of genital cancers if administered before the onset of sexual activity, HPV vaccines can also be administered after being sexually active. Nevertheless, the individuals with active sexual history who are vaccinated can receive few benefits as exposure to all HPV types prevented by the vaccines is relatively unlikely in persons aged 13 years through 26 years
Should men get HPV vaccine?
Yes. In males, 92%, 63% and 89% of the anal, penile, oral or oropharyngeal cancer cases respectively can be attributed to HPV. A 2011 study demonstrated that the administration of quadrivalent HPV vaccine for men decreased the incidence of HPV infection related genital lesions by 90% in 16-26-year-old males.
What is the HPV vaccine age limit?
According to WHO, the recommended the administration of HPV vaccine to 9–14 years old girls. Nevertheless, HPV vaccine can be licensed up to the age of 45 years.
Which doctors are specialize in giving HPV vaccine?
Both gynecologists and medical oncologists administer the HPV vaccine.
- Gynecologist: Specialize in women's reproductive health and commonly suggest the HPV vaccine during routine visits.
- Medical Oncologist: Generally, focus on cancer diagnosis and treatment but also emphasize preventive measures like HPV vaccination to reduce cancer risk.
Both plays a vital role in promoting HPV vaccination for preventing HPV-related diseases, including cervical cancer.