Multiple Sclerosis - Symptoms, Types, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
PACE Hospitals
Multiple sclerosis definition
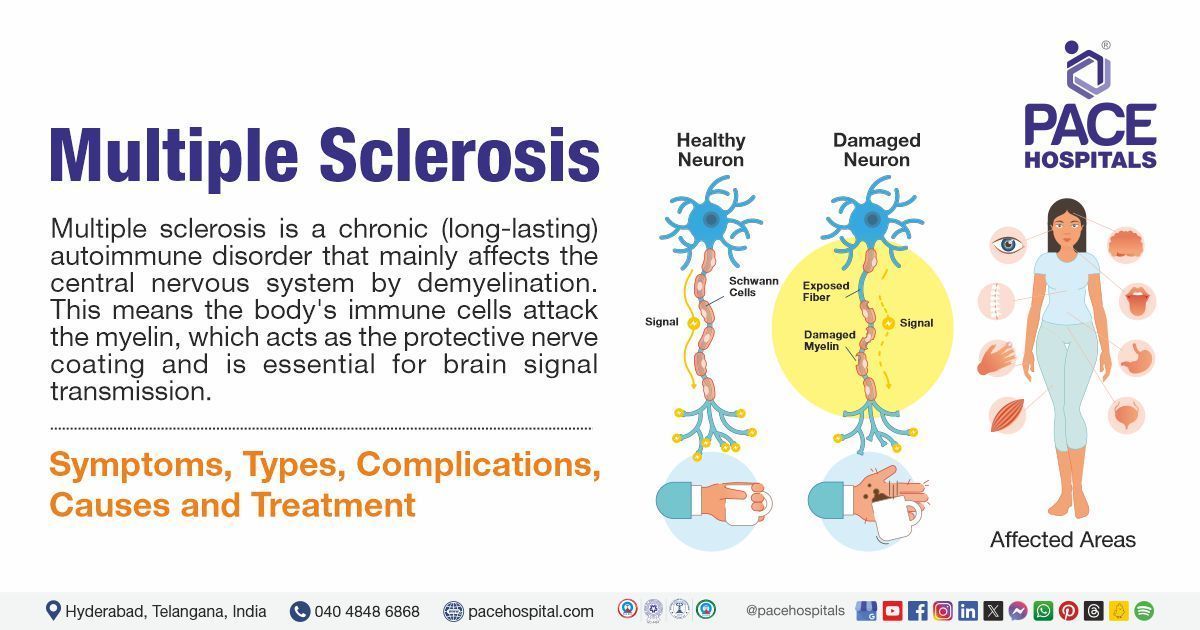
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic(long-lasting) autoimmune disorder that mainly affects the central nervous system by demyelination. This means the body's immune cells attack the myelin, which acts as the protective nerve coating and is essential for brain signal transmission.
Demyelination leads to inflammation and the formation of scars (multiple sclerosis means 'many scars'). These scars, known as plaques or lesions, affect the nerve's ability to transmit messages between the brain and other body parts.
Multiple sclerosis mainly affects the young adults between the ages of 20 and 40. Despite the lack of a cure, researchers are continually making progress and discoveries in understanding and managing the condition. In individuals with MS, neurologists play a key role in diagnosis and treatment.
Multiple sclerosis meaning
Multiple sclerosis is a term coined in 1868 by the French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot
The word "multiple" comes from the Latin word
- "Multi" meaning "many"
- "Plus" meaning "fold."
Means that something that is "multiple" has many parts or made up of more than one thing.
The word "sclerosis" comes from the Greek word
- "Sklēros" meaning "hard "
Describes hardening of tissue or it is used to describe a condition where tissues become hard and inflexible.
Multiple sclerosis prevalence
Global prevalence of multiple sclerosis
In 2020 the global prevalence of MS reached approximately 28 lakh individuals, compared to the 2013 prevalence there is a 30% increase in 2020. The estimated prevalence was 35.9 cases per 1,00,000 persons, with a median multiple sclerosis incidence rate of 2.1 new cases per 100,000 persons per year.
Prevalence of multiple sclerosis in India
MS prevalence is changing all over the world. India has shifted from being a low MS risk zone to a moderate one. The prevalence rate of MS in India is low but slowly growing. In India, MS prevalence has increased from 1.33 per 1,00,000 to 8.35 per 1,00,000 (8-9 people per 1, 00,000).

Types of multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is classified based on its progression and symptoms pattern. There are 4 types of multiple sclerosis, as follows:
- Relapsing-remitting MS: This type of MS involves episodes of worsening symptoms called attacks or relapses. These are followed by periods of recovery called remission, where symptoms improve or disappear. These attacks can last days or weeks, while remissions can last for months or even years.
- Secondary-progressive MS: It is the disease that starts after relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Symptoms get worse slowly over time, even without new attacks. It is different from individuals and people who have relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis always will not develop secondary progressive MS.
- Primary-progressive MS: It is a type of multiple sclerosis that causes symptoms to gradually worsen and also causes disability. In this type, the episodes of remission are less.
- Progressive-relapsing MS: It is the rare form of MS involving worsening of disability and attack or relapses.
There are some rare types of multiple sclerosis they include:
- Clinically isolated syndrome: This type of MS shows the first episode of symptoms. It is caused when the nerve tissue in central nervous system gets demyelinated or inflammated.
- Marburg MS: It is also known as malignant multiple sclerosis; this type is very extensive fulminant (aggressive) and it also leads to death.
- Balo's concentric sclerosis: It is another rare type of multiple sclerosis which mainly effects the white matter of brain.

Multiple sclerosis symptoms
The signs and symptoms of multiple sclerosis can vary widely among individuals and may change over time, here is a list of the symptoms:
Multiple sclerosis early symptoms
These are also considered as early symptoms of multiple sclerosis in adults which include:
- Vision problems
- Balance problems especially during walking
- Muscle weakness
- Bladder control problems
- Irregular or continuous dizziness
- Numbness, Tingling
Common physical symptoms of MS
- Muscle spasticity (stiffness)
- Sexual dysfunction (difficulties or problems with sexual performance)
- Bowel problems
- Swallowing disorders
- Speech difficulties
- Tremor
The psychological symptoms of MS
- Anxiety
- Changes in cognition
- Depression
- Pseudobulbar Affect (PBA), which is a neurologic effect manifested by sudden and uncontrollable episodes of laughter or crying without an apparent trigger.
Common “Invisible” Symptoms of MS
- Dizziness/vertigo
- Fatigue
- Numbness
- Pain
- Sleep issues
- Uhthoff’s syndrome (the temporary appearance of symptoms resulting from heat stress)
- Visual disorders
- Weakness
Multiple sclerosis symptoms in females
- Vaginal dryness
- Sexual dysfunction
- Amenorrhea—the absence of a period.
Multiple sclerosis symptoms in males
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased libido
- Anorgasmia—orgasms (climax of sexual arousal) that become absent, less frequent & less intense.

Multiple sclerosis causes
The exact cause of multiple sclerosis disease remains unknown. However, a combination of factors contributes to its development. These factors are categorized into three main types:
- Immune System
- Environmental factors
- Genetic factors
Immune System: The primary theory is multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease. This means the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its tissues. In MS, it attacks the myelin, a protective coating around nerve fibers.
Environmental factors: Several environmental factors such as latitude gradient (changes that occur along different latitudes including climate etc), and vitamin D deficiency might contribute to the development of the disease.
Genetic factors: Genetics also plays a role in the development of multiple sclerosis (MS).
These genetic factors and environmental factors contribute to the risk and progression of the disease but are not direct causes.
Multiple sclerosis risk factors
By identifying and monitoring potential risk factors, individuals can take active steps to manage their health and reduce their chances of developing MS. Some of the risk factors of multiple sclerosis are listed below:
- Viral infections: Particularly the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is associated with increased risk of developing MS. However, it is important to understand that infections do not directly cause MS. Instead, researchers believe that in people who are predisposed to multiple sclerosis, these infections act as a trigger. They can stimulate an abnormal immune response, leading to the development or progression of the disease.
- Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of developing multiple sclerosis (MS) and can cause severe types of multiple sclerosis. It contributes to inflammation and immune system alterations, which can worsen MS symptoms and its progression. Hence, it is strongly advised for individuals with MS to stop smoking and improve their health.
- Age: Age is a risk factor for multiple sclerosis (MS) as it typically appears between the age of 20 and 40 years, high in early adulthood. This indicates the risk of multiple sclerosis rises with age.
- Gender: Multiple sclerosis is mostly common in women compared to men because of hormonal factors, like oestrogen, influence immune function and raise the risk for autoimmune diseases like MS. Genetic factors and environmental factors also plays a key role.
- Vitamin D deficiency: It is associated with lower risk of developing multiple sclerosis (MS) and less disease progression. Sufficient levels of vitamin D is required to modulating immune function and reducing inflammation, potentially offering protective effects against MS. It's recommended to ensure adequate vitamin D intake to prevent and manage MS, empowering individuals to take control of their health.
- Early obesity: It can increase the risk of multiple sclerosis (MS) through increased serum levels of inflammatory markers in the blood like C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) which can promote autoimmune responses. Additionally, obesity often leads to lower serum vitamin D levels, which important for immune function, and lower levels are linked to higher MS risk. It also leads to changes in immune function, and all these contribute to the likelihood of developing MS.
- Geographic location: The latitude gradient indicates that people living away from the equator have a higher risk of developing MS. This suggests that environmental factors, such as lower sunlight exposure and vitamin D deficiency lead to the risk of developing multiple sclerosis.
- Family history: Having a first-degree relative like parent, sibling, or child with MS increases the hereditary risk of developing the disease, indicates a genetic factor.
- Identical twins: These are the multiple sclerosis genetic risk. Twins have a higher chance of developing MS compared to non-identical twins, suggesting a vital genetic component. Identical twins, who share 100 percent of their genetic material, do not always both develop MS.

Multiple sclerosis complications
The unpredictable nature of multiple sclerosis (MS) leads to a wide range of complications, and managing the complications effectively is essential for maintaining quality of life. Some of the complications of multiple sclerosis include:
- Pneumonia: Individuals with multiple sclerosis are at an increased risk of pulmonary infections due to muscle weakness, a decreased ability to clear secretions, and swallowing problems. These issues reduce lung function and increase the risk of aspiration pneumonia.
- Urinary problems: People with MS experience urinary issues like incontinence or difficulty emptying the bladder (neurogenic bladder). This can lead to UTIs due to factors like urine retention, bladder stones, and catheter use. As UTI symptoms mimic (copy) those of neurogenic bladder, they're often overlooked, potentially causing kidney damage, systemic infections, sepsis, and even death.
- Pressure ulcers: Those with MS are at higher risk of developing pressure ulcers due to limited mobility, decreased sensation, and cognitive challenges. These sores can significantly impact the quality of life by causing pain, affecting mobility, and leading to social isolation due to odour. In severe cases, pressure ulcers can infect and lead to systemic infections or sepsis.
- Depression: Depression is significantly more common in people with MS compared to the general population. The exact reasons for this are complex but involve a combination of factors. Neurological changes associated with MS, such as the buildup of lesions and brain tissue loss, may contribute. Additionally, the psychological impact of living with a chronic, progressive disease can also play a significant role. Severe depression in MS patients increases the risk of suicide.
- Accidents: MS often leads to neurodegeneration, affecting balance, coordination, and muscle strength. These issues arise early in the disease and significantly impact mobility, increasing the risk of falls and accidents.
- Osteoporosis: Reduced physical activity due to MS, linked with lower bone density (osteopenia), significantly increases the risk of osteoporosis. This condition weakens bones, making falls more dangerous and increasing the likelihood of severe injuries.
Multiple sclerosis diagnosis
It's important to note that there is no single multiple sclerosis test for diagnosing MS. The general physician initially conducts physical examinations and based on the findings patient is referred to a neurologist where they recommend several tests to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. These may include:
- Complete medical history
- Physical examination
- Detailed neurological examination
- Blood Tests: These are essential to the MS diagnostic process, but they primarily rule out other potential causes of the symptoms. Conditions like vitamin deficiencies or severe neuromyelitis Optica are rare but can mimic MS symptoms, so blood tests help to differentiate between these conditions.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans: These images can reveal brain and spinal cord lesions (area of damage) characteristic of MS.
- Lumbar puncture (spinal tap): A sample of cerebrospinal fluid is collected and analysed for signs of inflammation, or other abnormalities associated with MS.
- Evoked potential tests: This measures how the brain responds to stimuli, such as light or sound, and can help identify nerve damage.
Multiple sclerosis treatment
Treatments for multiple sclerosis (MS) concentrate on managing symptoms, modifying the course of the disease, and improving quality of life. Here’s an overview of current multiple sclerosis treatments:
- Disease-Modifying Therapies in multiple sclerosis (DMTs)
- Acute relapsing multiple sclerosis
- Multiple sclerosis Symptomatic treatment
- Multiple sclerosis Alternative treatment
Disease-Modifying Therapies multiple sclerosis (DMTs)
These multiple sclerosis disease-modifying drugs aim to reduce the occurrence, severity of relapses and also slowdowns the disease progression.
- Biological Response Modifiers: Reduce inflammation and immune activity.
- Immunomodulators: Modulate immune responses to protect myelin.
- Monoclonal antibodies: These prevent immune cells from entering the brain, and Target B cells, which are a type of immune cell involved in MS.
Acute relapsing multiple sclerosis
- Corticosteroids: Used to reduce inflammation and speed recovery from acute exacerbations. These drugs help people recover faster from MS flare-ups, but they don't stop the disease from getting worse over time.
Multiple sclerosis symptomatic treatment
Acute relapses Treatment: Corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation and manage acute relapses..
- Spasticity Treatments: Medications such as muscle relaxants and physical therapy help manage muscle spasticity.
- Pain Management: Analgesics and neuropathic pain medications addresses MS-related pain.
- Fatigue Management: Medications such as wakefulness-promoting agents and lifestyle adjustments help alleviate MS-related fatigue.
Multiple sclerosis alternative treatments
- Diet and Nutritional Supplements for MS: The connection between MS and vitamins, minerals, and supplements is complex.
- Vitamin D: Lack of vitamin D is linked to MS progression. Sun exposure and dietary sources like milk, eggs, fish, and vegetables contribute to vitamin D, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Vitamin B12: Inadequate levels of Vitamin B12 can harm the spinal cord and optic nerve. Those with a deficiency may benefit from supplementation.
- Low-fat diet: Adopting a low-fat diet could lessen the severity of the disease and the frequency of MS.
- Acupuncture: It can reduce pain, muscle spasticity, numbness, and tingling in MS patients. It might take 6-10 weeks to see if it works. Therefore, it is recommended to get it done by a certified professional in a sterile environment to avoid infections.
- Reflexology: It is CAM (Complementary and Alternative Medicine) therapy that involves stimulating foot reflex points, which is relaxing and benefits the entire body.
- Massage and bodywork: It is also an alternative treatment that reduces pain, improves circulation, and relieves muscle spasticity, but it might be unsafe for those with heart disease, cancer, osteoporosis, arthritis, oedema, ulcers, or pregnancy.
- Magnet therapy: Especially Pulse Electromagnetic Fields (PEMF), increases circulation and oxygenation, stimulates ions and electrolytes, boosts energy, and reduces pain and inflammation.
- Aromatherapy: Uses essential oils for health and wellness. It's often used for pain relief. For MS patients, it might help with sleep, relaxation, joint and muscle mobility, and overall well-being.
Multiple sclerosis prevention
Multiple sclerosis disease prevention involves managing known risk factors to improve the quality of life. Some of the MS prevention measures are listed below:
- Vitamin D: This nutrient is necessary for immune function. While the body can generate vitamin D through sunlight exposure, supplements may be required in areas with limited sunlight.
- Healthy eating: A well-rounded diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help overall health and potentially reduce inflammation, a factor in MS.
- Regular physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise not only supports overall health but also benefits the immune system.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking is linked to a higher risk of MS and can exacerbate the condition.
- Stress Management: While stress isn't a direct cause of MS, managing it can contribute to overall well-being.
Difference between Multiple sclerosis (MS) and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Multiple sclerosis vs ALS
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are both neurological illnesses that affect the central nervous system (CNS), although they have distinct causes, symptoms, and prognosis. Below are some of the parameters that help in differentiating multiple sclerosis and ALS:
| Elements | Multiple sclerosis | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that mainly affects the central nervous system by demyelination | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis also called Lou Gehrig's disease is one of the prevalent motor neuron diseases which involves both upper and lower motor neurons |
| Causes | The exact cause of MS is unknown but some of the causes include the immune System, environmental factors, and genetic factors | The cause of ALS is idiopathic, but a few possible causes such as oxidative stress, genetic changes, and environmental poisons |
| Symptoms | Vision problems, balance problems especially during walking, muscle weakness, bladder control problems, irregular or continuous dizziness, numbness, tingling | Stiffness, weakness, difficulty in swallowing, slurred speech and cramps |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Multiple sclerosis (MS)
What is the difference between multiple sclerosis and transverse myelitis?
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic, progressive disease that disturbs the central nervous system. At the same time, transverse myelitis is a sudden inflammation of the spinal cord that can be a separate condition or part of MS. MS often involves multiple lesions over time. In contrast, transverse myelitis typically affects a specific spinal cord area.
Is multiple sclerosis curable?
No, MS has no cure, but several treatments can help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. These include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Is multiple sclerosis fatal?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) itself is generally not considered fatal but in rare cases it may become fatal, However, it is a severe and chronic condition that can impact quality of life. While MS can lead to severe disability and complications, most people with the disease have a near-normal life expectancy.
How to prevent multiple sclerosis naturally?
Natural preventive measures include maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Ensuring adequate vitamin D levels through sunlight or supplements, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, and managing stress are important factors that support overall health and help lower the risk of MS.
What is multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a long-term condition in which the body's immune system targets the central nervous system, causing damage to the protective sheath around nerve fibres known as myelin. This damage results in various neurological symptoms.
How does MS progress?
MS can have different courses: relapsing-remitting (with episodes of worsening symptoms developed by periods of improvement), primary progressive (gradual worsening without distinct relapses), and secondary progressive (initially relapsing-remitting that gradually worsens).
How is MS diagnosed?
The Diagnosis of MS includes a combination of medical history, neurological exams, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and sometimes lumbar punctures to analyse cerebrospinal fluid.
How do doctors test for multiple sclerosis?
Neurologists diagnose MS using a combination of tests: neurological exams, MRI scans to detect lesions, and lumbar punctures to analyse cerebrospinal fluid. Evoked potentials may also be used to assess nerve function.
How does multiple sclerosis affect nerve conduction?
Multiple sclerosis (MS) harms the myelin sheath and impairs electrical signals' conduction along nerve fibres in the central nervous system. This interruption leads to various symptoms, including muscle weakness, balance problems, and sensory changes.
Can multiple sclerosis cause tinnitus?
Yes, MS can cause tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, as a result of nerve damage affecting auditory pathways. Tinnitus may be a symptom of MS-related neurological issues, though it's less common than other symptoms.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868