Stroke and Diet: An Indian Perspective | Prevention Guide
PACE Hospitals
Written by: Editorial Team
Medically reviewed by: Dr. S Pramod Kumar - Consultant Neurophysician & Neuromuscular Specialist
Overview
Stroke is one of India’s fastest-growing public-health challenges. While emergency care and medicines matter, everyday diet choices—salt, oil, fruits/vegetables, grains, and proteins—quietly decide risk over years. In a country with diverse cuisines and sharp rural–urban contrasts, a single “Indian diet plan” doesn’t exist; still, the science on what patterns raise or reduce stroke risk is remarkably consistent. This article explains what stroke is, why diet matters, how Indian dietary patterns and migration shape risk, what specialized diets (like Mediterranean and DASH) mean for Indians, and practical meal ideas you can adopt—no matter where you live.
What is a Stroke?
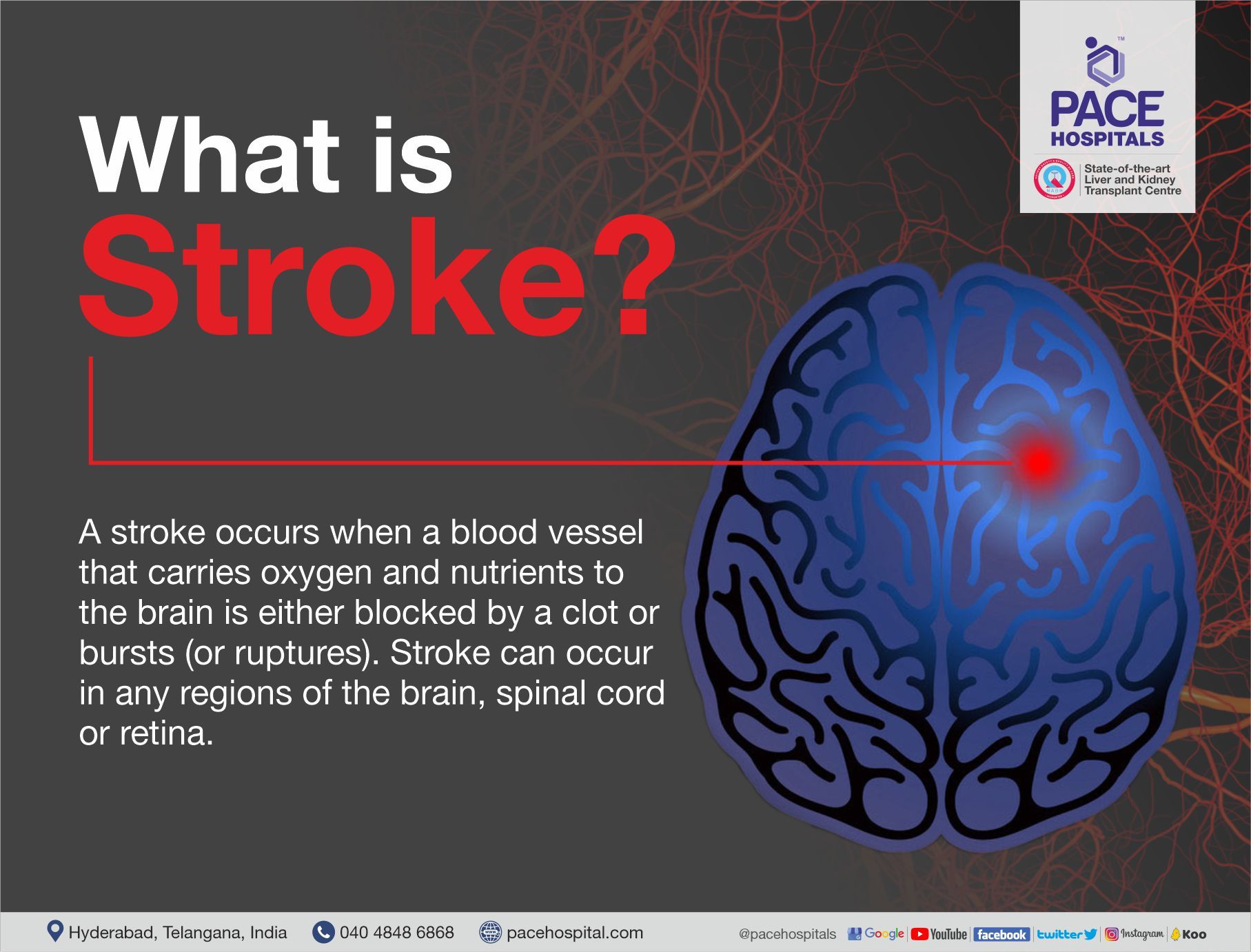
A stroke happens when a brain region doesn’t get enough oxygen and nutrients because a blood vessel is blocked (clot) or bursts (ruptures). Without blood flow, brain cells die. Although we commonly think of stroke as a brain problem, similar events can occur in the spinal cord or retina.
Types of Stroke
- Ischemic stroke (≈80%): A clot obstructs blood flow to a part of the brain.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: A blood vessel ruptures, spilling blood into/around the brain.
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): A “mini-stroke” where a temporary clot causes brief symptoms; warning sign for future stroke.
The burden in India
- Stroke is the second leading cause of death and disability worldwide.
- Indian incidence data show higher rates in rural areas (≈194–215/100,000) than the national average (≈119–145/100,000).
- Estimates suggest ~18 lakh new strokes annually in India; the lifetime burden is rising with urbanization, nutrition transitions, and longer life expectancy.
Critically, beyond medicines (antiplatelets, statins for secondary prevention), dietary and lifestyle modification can lower stroke risk by up to ~60%. Given India’s cultural and culinary diversity, prevention must be region-aware and habit-based, not one-size-fits-all.
Diet and stroke: why what we eat matters
Your long-term stroke risk tracks with your blood pressure, blood sugar, lipids, body weight, inflammation, and vascular health—all strongly influenced by diet.
- Salt → Blood pressure → Stroke
- Refined carbs + sugars → Weight gain/diabetes → Stroke
- Saturated/trans fats & processed meats → Atherosclerosis → Stroke
- Low potassium/fiber (few fruits/vegetables/whole grains) → Higher BP & lipids
- Protective patterns: More green/yellow vegetables, fruits, whole grains, pulses/legumes, nuts/seeds, and fish lower risk.
Key takeaway: Diet quality doesn’t just follow calories; it follows food patterns—how often you eat salt-heavy snacks, refined rice, fried foods, sweets, pickles, and red/organ meats, versus how often you eat dal–sabzi–salad–fruit–millets–fish.
Rural vs urban: the Indian nutrition transition
- Urbanization increases calorie intake, processed foods, and animal products; it can raise obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and stroke risk.
- Rural diets often rely on staples (rice/wheat) but may be low in fruits/vegetables/fiber, increasing risk via hypertension and nutrient gaps.
- Migration can bring both benefits and harms: better access to diverse foods but also more fried snacks, sugary drinks, and red meat.
Diet is also shaped by income, market access, infrastructure, women’s workforce participation, and local norms.
What do Indians actually eat? (Dietary pattern snapshots)
Systematic reviews identify ~41 dietary patterns across India. Most frequent food groups: vegetables, cereals, fruits, meat, pulses, dairy.
- East & South: More sweets/snacks characterize some patterns; fish/meat more common.
- North & West: More fruits/vegetables noted in certain patterns.
- Men vs women: Largely similar patterns.
- Gap to close: India consumes more whole grains but significantly fewer fruits/vegetables/legumes/meat/fish/eggs than global recommendations.
Body size and metabolic health
Patterns high in fat–sugar snacks and animal products → larger waist/BMI and unhealthy lipids.
Patterns rich in vegetables, fruits, pulses, nuts → lower cholesterol and healthier profiles.
Snacks (often deep-fried, salty) predict a worse risk-factor profile.
Modifiable risk factors that connect diet to stroke
- Hypertension (top driver of ischemic & hemorrhagic stroke in India)
- High LDL / low HDL (dyslipidemia)
- Diabetes and insulin resistance
- Smoking & alcohol excess
- Sedentary lifestyle and central obesity
Salt reduction and potassium-rich foods (fruits/vegetables, pulses) help lower blood pressure. Excess salt, refined carbs, snacks, red/organ meat, and sugary drinks elevate risk.
Public-health nuance: Cutting ~3 g/day of salt could meaningfully lower BP and stroke risk. But since iodized salt prevents iodine deficiency, reduce total salt while maintaining iodized salt in cooking.
Indian evidence: diet patterns in stroke patients
Northwest India (Ludhiana)
Stroke patients consumed more milk/milk products; fruits/juices were low. Conclusion: Increase fruits/juices; reduce high-fat milk products to lower risk there.
South India (Hyderabad; urban)
Stroke patients ate high-carbohydrate traditional diets (rice in ~99%, pulses ~41%) with lower intake of green leafy vegetables, roots/tubers, fruits, and water; red/organ meat, chicken, and alcohol were higher than controls. Younger patients reported more fruit juices and junk foods; tender coconut water was low.
Regional advice (Telangana/Hyderabad):
- Increase green leafy veg, seasonal fruits, fish, and water intake.
- Decrease red/organ meat, fried snacks, pickles, and excess refined rice.
India needs more local studies to tailor state-wise and cuisine-wise guidelines. Until then, apply the universal principles below and localize intelligently.
Specialized diets and how to “Indianize” them
Mediterranean Diet (MedDiet)
- High: fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts/seeds, olive oil (primary fat)
- Moderate: fish, poultry, fermented dairy
- Low: red/processed meat, sweets
- Indianize it:
- Use mustard/groundnut/til (sesame) oils if olive is expensive; keep total oil 3–4 tsp/day/person.
- Swap refined rice with millets (jowar/bajra/ragi) or unpolished rice; add dal–chana–rajma–lobia.
- Handful of nuts (badam/akhrot) most days.
- Fish 2–3x/week where culturally acceptable.
DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)
- High: fruits/vegetables, low-fat dairy, pulses, whole grains
- Low: salt, red/processed meats, sweets
- Typical BP drop: ≈5–6 mmHg systolic, ≈3 mmHg diastolic.
- Indianize it:
- Half plate sabzi + salad; 1–2 bowls low-fat dahi/chaas (if tolerant).
- Limit salt to ≤5 g/day (≈1 tsp total in all meals). Continue iodized salt, not rock salt (which often isn’t iodized).
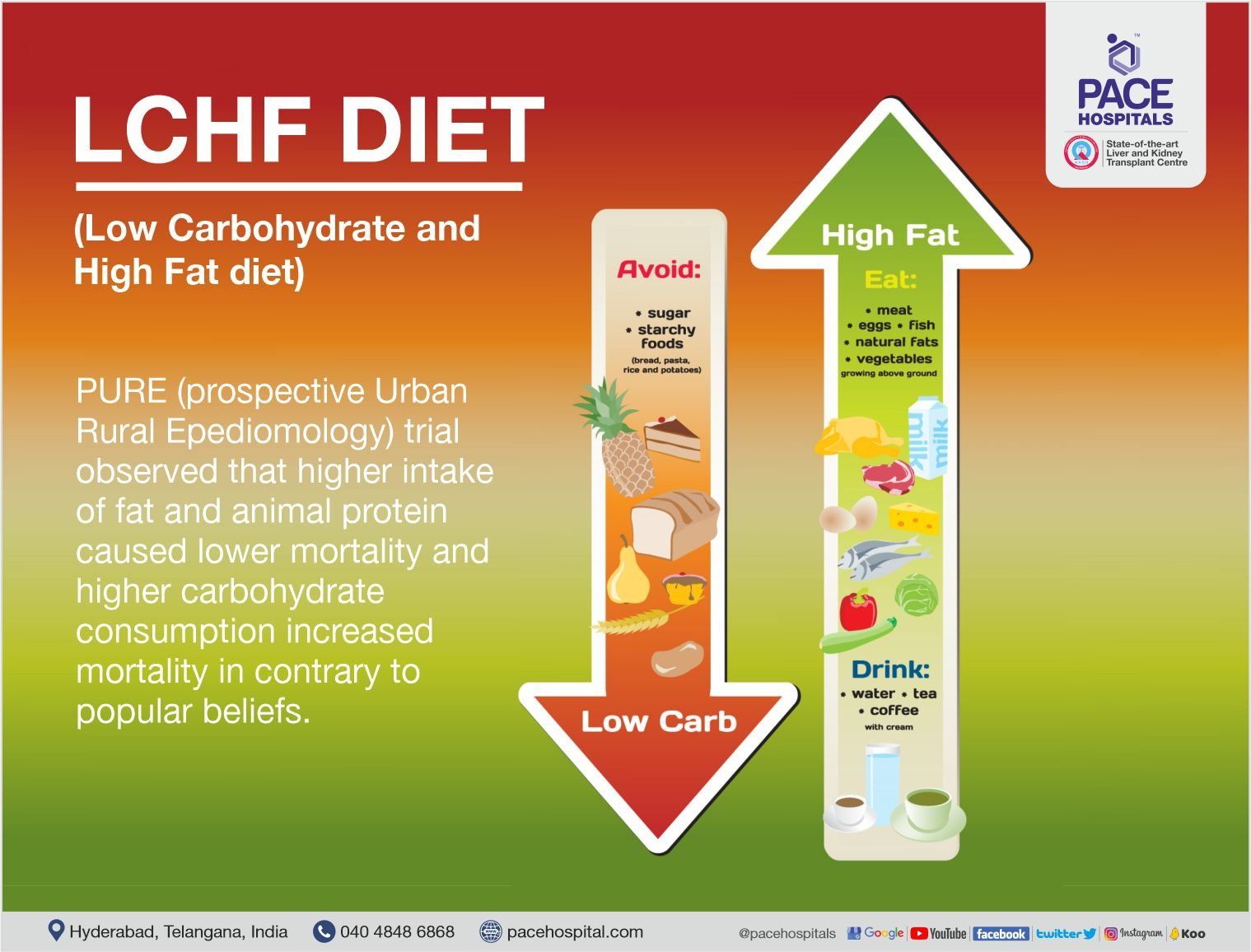
LCHF (Low-Carb, High-Fat) – PURE trial context
- Observed: higher fat/animal protein → lower mortality; very high carbs → higher mortality in some settings.
- Indianize with caution:
- Aim for controlled carbs (swap refined rice with millets/unpolished rice; smaller rotis), quality fats (nuts, seeds, plant oils), ample non-starchy vegetables, adequate protein (dal, paneer, eggs, fish, lean chicken).
- Avoid ghee/oil excess, processed meats, and deep-fried snacks.
Practical, region-aware recommendations
Universal moves (work across India)
- Salt: Cap ≤5 g/day (all sources). Use iodized salt; flavor with lime, jeera, dhania, adrak, lehsun, and fresh herbs instead of salt-heavy masalas/pickles.
- Vegetables & fruits: ≥400–500 g/day combined. Prioritize green leafy, yellow/orange veg, guava, amla, citrus, banana (potassium-rich).
- Carbs: Swap polished rice for parboiled/unpolished or millets; limit refined flour.
- Protein: Dal-chawal or dal-roti daily; add curd/chaas, paneer/tofu, or eggs/fish/chicken depending on preference.
- Fats: 3–4 tsp oil/day/person; rotate mustard/groundnut/sesame. Avoid vanaspati, repeated frying, and packaged fried snacks.
- Beverages: Unsweetened tea/coffee; target ≥8–10 glasses water/day (individualize in heart/kidney disease).
- Alcohol: If you drink, do so sparingly; consider abstinence post-TIA/stroke.
- Tea bonus: 3+ cups/day of black/green tea correlates with ~21% lower stroke risk vs <1 cup/day (watch added sugar).
- Weight & activity: 150–300 min/week moderate activity + 2–3 strength sessions; aim for waist <90 cm (men), <80 cm (women) for South Asians.
Regional nudges
- South/East: Scale back refined rice, pickles, fried snacks; scale up greens, raw salads, fish (where acceptable), buttermilk, fresh fruit, tender coconut water.
- North/East: Moderate full-cream dairy and ghee; increase fruits/veg and fish (Bengal/Assam).
- West: Mind farsan/namkeen; switch to roasted chana/makhana/nuts.
- Northwest: If dairy-heavy, shift to toned/low-fat and increase fruit/vegetable variety.
One-day sample plate (vegetarian)
- Breakfast: Vegetable upma with peas + unsweetened chai; or moong chilla with mint chutney.
- Mid-morning: Guava or amla; water.
- Lunch: Roti (2 small) + rajma (1 bowl) + mixed sabzi (½–1 plate) + salad (kheera–gajar–tamatar) + chaas (little salt/jeera).
- Evening: Roasted chana/makhana + green tea.
- Dinner: Millet khichdi (moong + veg) + curd + sautéed greens.
- Extras: Handful of nuts (almonds/walnuts) 4–5×/week.
One-day sample plate (non-vegetarian)
- Swap one protein to fish (2–3×/week) or skinless chicken; keep red/organ meat occasional.
- Example lunch add-on: Grilled fish (150 g) with lemon–pepper instead of fried.
Diet, BP, lipids, and stroke mechanics—connecting the dots
- Hypertension is India’s dominant stroke driver. Each 5 g extra salt/day can raise BP, increasing ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke risk.
- Refined carbs and sugary beverages push weight, triglycerides, insulin resistance.
- Fruits/vegetables/pulses/nuts add potassium, fiber, antioxidants—all BP- and vessel-friendly.
- Fish (omega-3) may improve lipids and endothelial function.
- Tea polyphenols provide modest vascular benefits (again, go easy on sugar).
Key message for families
Household change beats individual willpower:
- Cook with measured oil and iodized salt.
- Serve a ½-plate of vegetables at lunch and dinner.
- Keep cut fruit visible and salted namkeen invisible.
- Hydrate with water/chaas/nimbu pani (little salt) instead of soft drinks.
- Make walking or cycling a shared routine.
FAQs on Stroke & Diet - an Indian Perspective
How does diet influence stroke risk in Indians?
High salt, refined carbs, fried snacks, and red/organ meat raise BP, weight, and atherosclerosis—key stroke drivers. Fruits/vegetables/pulses/millets/fish and less salt lower risk.
Is salt reduction really that important?
Yes. Indians average 8.5–15 g/day salt. Bringing this toward ≤5 g/day (while retaining iodized salt) reduces BP and both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke risk.
Do tea and coffee help or harm?
3+ cups/day of unsweetened black/green tea associates with lower stroke risk. Limit sugar and creamers. Coffee is fine in moderation if BP is controlled.
What about stroke survivors—any special diet?
Yes: strict salt control, BP/glucose/lipid management, high-veg, high-fiber meals, adequate protein, and limited alcohol. Meet a dietitian for tailored plans (texture needs may change after stroke).
Can diet alone prevent stroke?
Diet is a major lever but works best with BP/diabetes control, exercise, not smoking, limited alcohol, healthy weight, and regular check-ups.
Are traditional Indian diets safe?
They can be—dal–sabzi–roti/rice is protective if vegetable/legume-rich and light on salt, ghee, fried snacks, and pickles. Trouble begins with deep-fried namkeen, refined rice, and oversalted gravies.
Which oil is best for stroke prevention?
Use any one regional oil (mustard/groundnut/til) in small amounts; rotate if you like. Avoid vanaspati/trans fats and reheated oil. Total oil ≈3–4 tsp/day/person.
How do Mediterranean/DASH diets fit Indian meals?
Adopt principles: more veg/fruit/legumes/nuts, whole grains/millets, fish (where acceptable), less salt and red meat. Keep spices; cut the oil and salt.
Is LCHF safe for Indians?
A moderate-carb, quality-fat approach can help some, but avoid excess ghee/fried foods. Prioritize veg, pulses, nuts, fish/eggs, tofu/paneer; work with a clinician if you have diabetes/CVD.
Are pickles, papad, and namkeen okay if baked?
They’re still high in salt and often refined carbs. Keep portions small and occasional; prefer salads, roasted chana, nuts, makhana.
Share on
Request an appointment
Fill in the appointment form or call us instantly to book a confirmed appointment with our super specialist at 04048486868