Angioplasty Procedure - Uses, Indications, Surgery & Cost
PACE Hospitals is one of the best hospitals for angioplasty in Hyderabad, India. The Department of Cardiology consists of some of the best cardiologists in Hyderabad, with vast experience in performing a wide range of cardiac procedures, including angioplasty. The hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and the next-generation image-guided therapy platform — the Philips Azurion Cath Lab — enabling outstanding interventional cardiac, electrophysiology, neuro, and vascular performance.
Request an Appointment for Angioplasty Procedure
Angioplasty surgery - appointment
Why Choose PACE Hospitals for Angioplasty Procedure?
State-of-the-art facility with Philips Azurion Cath Lab
Team of the best cardiologist with 15+ years of expertise
Cost-effective treatment with 99.9% success rate
All insurance accepted with No-cost EMI option
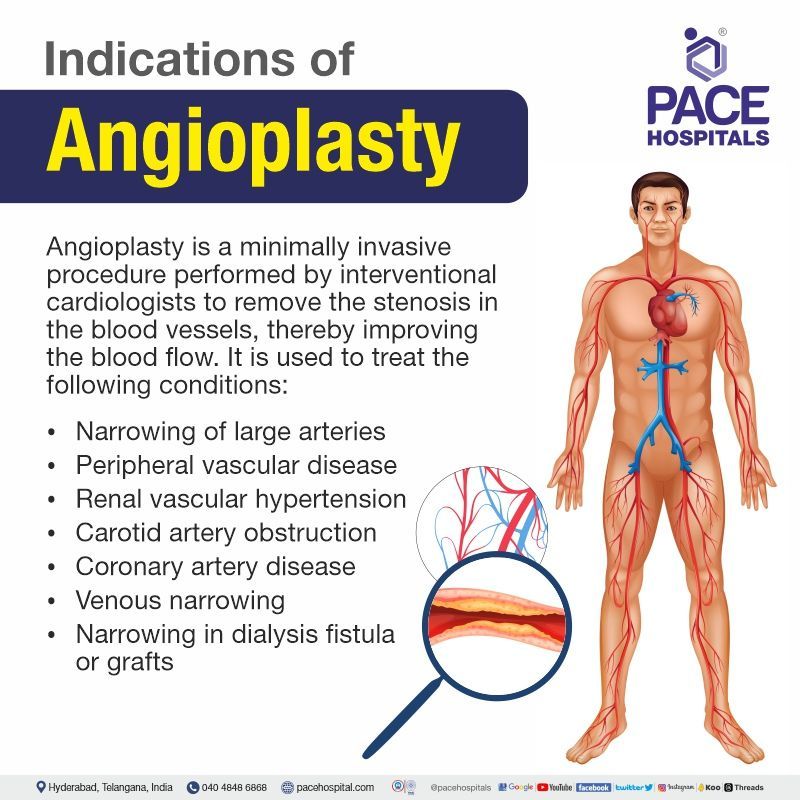
What is an Angioplasty Procedure?
Angioplasty meaning
Angioplasty procedure, also called balloon angioplasty or percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure, either with or without placing an angioplasty stent, used to widen the blocked or narrowed blood vessels (stenosis), as a result of underlying atherosclerosis (blockage due to formation of plaque in the arteries). These blockages can occur at any place in the arteries of the pelvis, neck, arms, legs, and kidneys.
During the angioplasty surgery, a catheter with an inflatable balloon tip is inserted through the access site, and the balloon is inflated once the catheter has passed through the stenosed artery site. It restores the luminal diameter, forces the atherosclerotic intraluminal plaque toward the artery wall, and normalises blood flow. In order to prevent the reformation of obstruction, the interventional cardiologist places an angioplasty stent between the walls of the blood vessels.
Types of Angioplasty Procedure
The following are the different types of angioplasty procedures based on the anatomical location or area of the body being treated with the help of the balloon technique, with or without the placement of a stent.
- Coronary Angioplasty
- Cerebral Angioplasty
- Peripheral Angioplasty or Peripheral Artery Disease Angioplasty
- Renal Artery Angioplasty
- Pulmonary Angioplasty
- Carotid Angioplasty
- Aroto Angioplasty
- Coronary Angioplasty: It is the procedure used to widen the blocked narrowed coronary arteries (that supply oxygenated blood to heart muscles). It is used to treat coronary heart disease, emergency heart attack and angina.
- Cerebral Angioplasty: It is used to dilate or open partially blocked carotid blood vessels (that supply oxygenated blood to the brain), vertebral arteries and blood vessels inside the brain.
- Peripheral Angioplasty or Peripheral Artery Disease Angioplasty: It is used to treat narrowing or blockage of major blood vessels supplying blood to the lower extremities of the body such as hip, knee, ankle, thigh, leg and toes.
- Renal Artery Angioplasty: It is used to treat obstructed blood vessels that supply blood to the kidneys.
- Pulmonary Angioplasty: It is used to clear multiple blood clots that appear on the pulmonary arteries that supply blood to the heart.
- Carotid Angioplasty: It is used to treat blockages in the blood vessels of the carotid artery that supply blood to the brain.
- Aroto angioplasty:
It is used to treat the stenosis or blockages that appear in the aorta (main artery) that carry oxygenated blood to the lower body.
Angioplasty Methods
Depending on the method used to dilate the blood vessel or remove the stenosis (obstruction), they are two different methods of angioplasty.
- Balloon angioplasty with or without stent placement:
- Laser Angioplasty
Balloon angioplasty with or without stent placement:
Balloon angioplasty (BA) involves removing the blocked plaque by applying pressure through an inflated balloon. In some patients, the angioplasty stent (made up of wire mesh) exists around the balloon, placed between the walls of the blood vessel, with the help of the inflated balloon technique, to prevent the recurrence of plaque formation.
Laser Angioplasty:
A laser (ultraviolet cool beam) will be used that works on a principle of photochemical action, breaks the carbon bonds in the blood clots, and creates a local heat (photothermal). This heat forms bubbles that vaporise the blockage or stenosis in the blood vessels.
The goal of angioplasty treatment:
The goal of the angioplasty procedure is as follows:
- To widen the damaged blood vessel in order to restore normal blood flow.
- To prevent the expanded artery from collapsing or recurrence of narrowing by placing stents, a metal-mesh tube.
Angioplasty Preparations
The angioplasty patient preparation includes the following.
- A hospital visit may be required for an angioplasty surgery eligibility check. Depending on the patient’s condition, the interventional cardiologist assesses the patient’s chances of having the following course of treatment, such as
- Plain angioplasty (balloon angioplasty)
- Stent placement and its type
- During the initial assessment, the interventional cardiologist assesses more about the patient's medical, pregnancy, and medication history, including the use of over-the-counter and herbal supplements.
- People on oral hypoglycaemic agents for diabetes, antiplatelet or anticoagulant medicines, and patients with a history of hypersensitivity to iodinated contrast dye would be carefully examined before the angioplasty procedure to prevent complications.
- The physician prescribes a renal examination, as the angioplasty procedure requires considerable contrast material for clear visibility. Appropriate renal function plays a vital role in the excretion of contrast dye.
- The patient should not consume anything orally for 8 to 12 hours before the angioplasty procedure.
- The entire angioplasty procedure and the risk (if any) involved will be explained clearly to the patient, and the patient will be provided with a consent form to sign, which permits the interventional cardiologists to do the angioplasty procedure. It is important for the patient to read the consent document carefully and ask any questions they may have before signing.
- Nephrotoxic drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, loop diuretics, and anti-oral hypoglycaemics may be stopped before the angioplasty procedure.
- The patient will be provided with a surgical gown, and their vitals, such as blood pressure, blood sugar levels (if diabetic), and electrocardiogram, will be checked before inserting the intravenous line. The blood pressure and heart rate will be continuously monitored throughout the angioplasty procedure.
- The target area will be shaved, an antiseptic will be put on it, and drapes will be put around the target access site to prepare it for the angioplasty procedure.
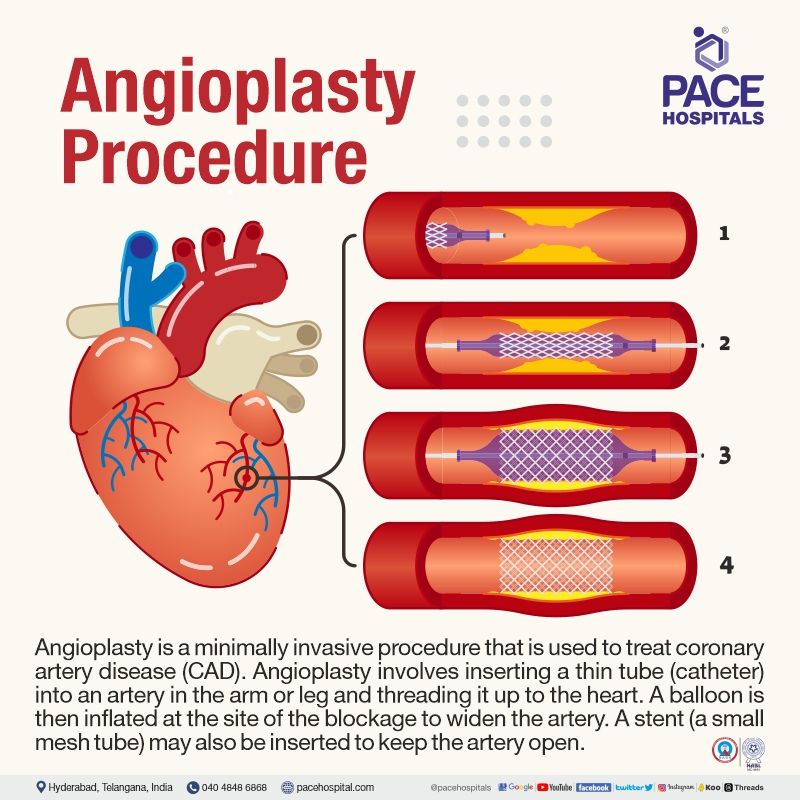
During Angioplasty Procedure
The angioplasty procedure steps are as follows:
- The patient will be given general anaesthesia, and a small incision will be created to have access site in order to administer the catheter. A local anaesthetic is given to numb the area before making an incision in the skin over one of the arteries (radial or femoral).
- Radial artery access will be avoided in patients with chronic kidney disease who might need haemodialysis for End-Stage Renal Disease condition, where a potential future fistula will be installed.
- The cardiologist will insert a guide wire into the patient's blood vessel through the wrist or groin.
- A flexible balloon-tipped catheter (tube) is threaded by an interventional cardiologist into the patient’s arteries and guided by X-rays to the blocked or restricted artery. The guide wire will be removed, and contrast dye or angioplasty dye will be released through the catheter to improve blood vessel visibility; the patient might feel warm during this period.
- Once the blockage area has been identified, the balloon-tipped catheter will be advanced to the area of stenosis (blockage).
- Inflation and deflation of the small balloon re-establish blood flow in the artery by pushing the vessel walls out. The deflated balloon will be withdrawn once the blocked vessel is reopened, and the same procedure is repeated in case of multiple blockages.
- In many instances, the patients might receive a stent (a small tube made of wired mesh). The stent will be placed over the deflated catheter; when inserted into the position (blockage site) and the balloon is inflated, the stent expands and locks itself at the site. The balloon will be deflated and withdrawn, leaving the stent behind to hold the artery open and prevent further blockage.
Precautions After Angioplasty (Post Angioplasty Care)
- After the angioplasty procedure or as a part of precautions after angioplasty, the patient may be shifted to the recovery room and kept under observation. The health care staff would monitor for any bleeding at the access site and vital signs such as blood pressure and heart rate.
- Once the patient seems normal, he/she would be shifted to the general room. The patient needs to inform the health care staff if they experience any discomfort, such as chest tightness, or any pain in the leg or at the access site.
- Depending on the patient’s condition, the doctor may suggest bed rest for a few hours. In some instances, due to clinical demand, the sheath or introducer will be left at the insertion site; in such cases, the bed rest duration would increase until it is removed.
- The patient might urinate frequently due to an increased intake of water or fluids before the angioplasty procedure to excrete the contrast dye through urine. Nevertheless, the patient will be suggested to drink more fluids to expel the contrast dye through urine.
- In case of pain at the insertion site, the interventional cardiologist might prescribe pain medication.
- The patient will be provided with an "after angioplasty diet chart” that includes foods to avoid after angioplasty, such as processed meat and a diet rich in saturated and trans-fat. In addition, the patient might receive information about when to resume the halted medications (if any).
- The patient will be advised to avoid lifting heavy objects and strenuous exercises, and be adherent to further follow-ups.
Angioplasty Risks
The angioplasty risks and angioplasty stent risks depend on the patient's age, as angioplasty risks for the elderly are more when compared to adults, general health, and the existence of any associated diseases.
Angioplasty complications - Side effects of angioplasty procedure
Post-angioplasty complications might include a risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast agent (dye), anaesthesia or other materials used during the angioplasty procedure. However, angioplasty risks of death are minimal. In addition, the complications after angioplasty procedure are as follows:
Local Complications
- Blood clots or Thrombosis
- Bleeding at the site of catheter insertion (access site)
Systemic Complications
- Atheroembolism
- Infection
- Radiation Exposure
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythms)
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Coronary perforation
- Abrupt vessel closure
Angioplasty Vs Bypass Surgery - Angioplasty vs CABG (Coronary artery bypass grafting)
Both are the treatment procedures used to restore the flow of blood; however, the following are the differences:
| Angioplasty surgery | Heart Bypass Surgery (CABG) |
|---|---|
| It is a minimally invasive method | It is a open heart surgery |
| It takes much quicker than bypass surgery whereas it might take a week (for planned angioplasty) | It takes nearly three months to recover |
| It require shorter hospitalisation stay | It require longer hospitalisation stay |
| In Angioplasty procedure, a ballon catheter widens the blocked vessel and restores normal blood flow. | In Heart Bypass Surgery, creates a new path for the blood flow by taking a healthy blood vessel from the patient's leg. |
| Indicated for patients with coronary artery disease and peripheral arterial disease, however, it is not advisable for everyone with Congenital heart defects (CHDs). | Indicated for patients with diabetes or with, triple-vessel disease or a severe form of coronary artery disease. |
Factors affecting Angioplasty Surgery Cost
Factors Affecting Angioplasty Surgery Cost:
- Type of Procedure: Balloon angioplasty without stent is more affordable, while angioplasty with drug-eluting stents (DES) or bare-metal stents (BMS) adds to cost. Advanced procedures like rotablation or complex PCI for calcified or multiple vessel blockages are priced higher. Emergency angioplasty involves additional ICU care and urgency-related expenses.
- Number and Type of Stents Used: Single stent procedures are cheaper than multi-stent cases. Indian stents cost less compared to imported options. Drug-eluting stents (DES) are more expensive but reduce the risk of re-blockage compared to bare-metal stents (BMS).
- Complexity of Disease: Cost increases with the number of blocked arteries-single, double, or triple vessel disease. Chronic total occlusions (CTO), bifurcation lesions, or calcified arteries require longer time, specialized tools, and more expertise, leading to higher charges.
- Hospital Stay & Room Category: Daycare angioplasty is cost-effective but longer stays increase the bill. Choice of room can be shared ward, private room, or deluxe suite-affects cost. ICU care may be needed in high-risk or emergency cases.
- Surgeon’s Expertise: Senior interventional cardiologists or specialists in complex angioplasties may charge higher fees. Use of advanced guidance systems like IVUS (Intravascular Ultrasound) or OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) adds to the cost.
- Stent / Device / Equipment Cost: Stent prices vary based on brand and type. Additional tools like rotablation drills, cutting balloons, or guide extension catheters used in complex cases increase equipment costs.
- Diagnostic & Perioperative Care: Includes angiography, ECG, 2D Echo, blood tests, OT charges, anesthesia, and post-operative cardiac monitoring. All of these influence the total treatment expense.
- Rehabilitation & Cardiac Aftercare: Cardiac rehab, diet and lifestyle guidance, and follow-ups contribute to ongoing costs. Long-term medications like blood thinners, statins, and blood pressure drugs are also part of the post-angioplasty care.
- Insurance & Payment Mode: Costs vary based on insurance coverage-cashless via TPA, reimbursement, or out-of-pocket. Some health schemes like ECHS (Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme), Arogya Bhadratha TS Police, CGHS (Central Government Health Scheme) and ESI (Employees' State Insurance Scheme of India) reduce costs for eligible patients. EMI and self-pay options are available in private hospitals.
Angioplasty Cost in Hyderabad, Telangana, India
The cost of Angioplasty in Hyderabad generally ranges from ₹90,000 to ₹3,50,000 (approximately US $1,080 – US $4,210). The exact angioplasty price varies depending on several factors such as the number of blockages, whether a single or multiple stents are required, the type of stent used (bare-metal or drug-eluting), the complexity of the coronary artery disease, cardiologist expertise, and the hospital facilities chosen - including cashless treatment options, TPA corporate tie-ups, and assistance with medical insurance approvals wherever applicable.
Cost breakdown according to type of angioplasty / procedure:
- Single Stent Angioplasty (Drug-Eluting Stent) – ₹1,40,000 – ₹2,20,000 (US $1,690 – US $2,650)
- Double Stent Angioplasty – ₹2,10,000 – ₹3,20,000 (US $2,530 – US $3,850)
- Triple Vessel Angioplasty – ₹2,60,000 – ₹3,50,000 (US $3,120 – US $4,210)
- Balloon Angioplasty (Without Stent) – ₹90,000 – ₹1,40,000 (US $1,080 – US $1,690)
- Complex / High-Risk Angioplasty (Bifurcation, Chronic Total Occlusion, etc.) – ₹2,40,000 – ₹3,50,000 (US $2,890 – US $4,210)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Angioplasty Procedure
What is the difference between atherectomy and angioplasty?
Atherectomy is a special procedure used to remove the stenosis or blocked plaque with the help of specialised devices such as mechanical, rotational, laser, or orbital devices, through which the plaque will be disrupted or ablated. Whereas in Angioplasty, a balloon catheter is used to widen the blood vessels and restore blood flow. In some patients, a wire mesh tube known as a stent will be placed to prevent the recurrence of atherosclerotic plaque.
How is angioplasty done?
Angioplasty procedure is performed by the insertion of a thin, flexible tube catheter, where a balloon with or without stent is attached to the catheter’s tip into the patient's blood vessel (arm, groin, or legs) through the access site. X-rays are then used to guide the catheter to the narrowed or blocked area of the artery by administering contrast dye. Once the catheter reaches the blocked location, the balloon present at the tip of the catheter will be inflated, widening the blocked or narrowed artery and restoring blood flow. In some cases, a stent, will be placed into an artery to keep it open and prevent further blocking.
How to sleep after angioplasty surgery?
It is clinically evident patients with angioplasty surgery do have trouble sleeping. Though there is no specific sleep pattern for patients with angioplasty, sleeping in an upright position with a neck pillow help to reduce pressure on the heart.
How much rest is required after angioplasty procedure?
The bed rest required for the patient after an angioplasty procedure depends on their condition. However, a patient generally needs two to six hours of bed rest post-angioplasty. In some patients, the sheath used to insert the catheter will be left in place due to clinical need. In such instances, the patient might have a long bed rest.
What is the difference between angioplasty and stent?
Angioplasty vs stent
Angioplasty or balloon angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure where an interventional cardiologist treats the blockage or atherosclerotic plaque by widening the blocked artery through a balloon inflammation process and restoring normal blood flow. Whereas Stent is a wire mesh tube that can be placed in the blood vessel to prevent the recurrence of atherosclerotic plaque, post widening of blood vessels through the balloon technique.
What is the difference between angiogram and angioplasty procedures?
Angiogram is a diagnostic test used to identify the block's location in the blood vessels, whereas an angioplasty is a minimally invasive therapeutic procedure used to widen the block with the help of inflating /deflating balloon catheter or placement of a stent.
Is angioplasty painful?
No, the angioplasty procedure is not painful, as it is a minimal invasive where a small cut will be placed to create an access site.
However, interventional cardiologists might give a local anaesthetic to numb the area while inserting the catheter. The patient might feel some pressure while the catheter is loading and experience discomfort while inflating the balloon during the angioplasty procedure.